We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]

How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]
Written by: Krystle Wong Jul 20, 2023

A top-notch presentation possesses the power to drive action. From winning stakeholders over and conveying a powerful message to securing funding — your secret weapon lies within the realm of creating an effective presentation .
Being an excellent presenter isn’t confined to the boardroom. Whether you’re delivering a presentation at work, pursuing an academic career, involved in a non-profit organization or even a student, nailing the presentation game is a game-changer.
In this article, I’ll cover the top qualities of compelling presentations and walk you through a step-by-step guide on how to give a good presentation. Here’s a little tip to kick things off: for a headstart, check out Venngage’s collection of free presentation templates . They are fully customizable, and the best part is you don’t need professional design skills to make them shine!
These valuable presentation tips cater to individuals from diverse professional backgrounds, encompassing business professionals, sales and marketing teams, educators, trainers, students, researchers, non-profit organizations, public speakers and presenters.
No matter your field or role, these tips for presenting will equip you with the skills to deliver effective presentations that leave a lasting impression on any audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What are the 10 qualities of a good presentation?
Step-by-step guide on how to prepare an effective presentation, 9 effective techniques to deliver a memorable presentation, faqs on making a good presentation, how to create a presentation with venngage in 5 steps.
When it comes to giving an engaging presentation that leaves a lasting impression, it’s not just about the content — it’s also about how you deliver it. Wondering what makes a good presentation? Well, the best presentations I’ve seen consistently exhibit these 10 qualities:
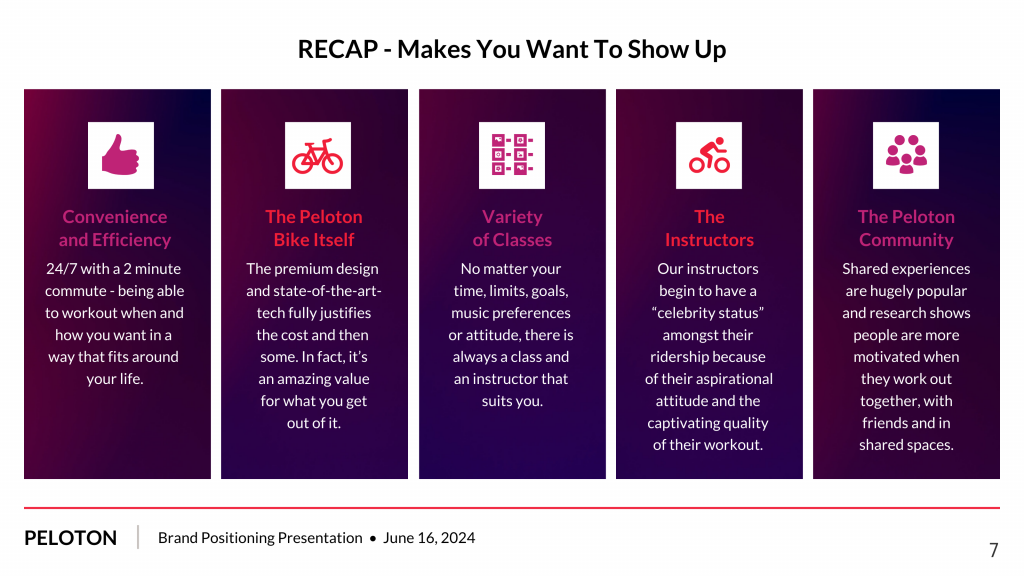
1. Clear structure
No one likes to get lost in a maze of information. Organize your thoughts into a logical flow, complete with an introduction, main points and a solid conclusion. A structured presentation helps your audience follow along effortlessly, leaving them with a sense of satisfaction at the end.
Regardless of your presentation style , a quality presentation starts with a clear roadmap. Browse through Venngage’s template library and select a presentation template that aligns with your content and presentation goals. Here’s a good presentation example template with a logical layout that includes sections for the introduction, main points, supporting information and a conclusion:

2. Engaging opening
Hook your audience right from the start with an attention-grabbing statement, a fascinating question or maybe even a captivating anecdote. Set the stage for a killer presentation!
The opening moments of your presentation hold immense power – check out these 15 ways to start a presentation to set the stage and captivate your audience.
3. Relevant content
Make sure your content aligns with their interests and needs. Your audience is there for a reason, and that’s to get valuable insights. Avoid fluff and get straight to the point, your audience will be genuinely excited.
4. Effective visual aids
Picture this: a slide with walls of text and tiny charts, yawn! Visual aids should be just that—aiding your presentation. Opt for clear and visually appealing slides, engaging images and informative charts that add value and help reinforce your message.
With Venngage, visualizing data takes no effort at all. You can import data from CSV or Google Sheets seamlessly and create stunning charts, graphs and icon stories effortlessly to showcase your data in a captivating and impactful way.

5. Clear and concise communication
Keep your language simple, and avoid jargon or complicated terms. Communicate your ideas clearly, so your audience can easily grasp and retain the information being conveyed. This can prevent confusion and enhance the overall effectiveness of the message.
6. Engaging delivery
Spice up your presentation with a sprinkle of enthusiasm! Maintain eye contact, use expressive gestures and vary your tone of voice to keep your audience glued to the edge of their seats. A touch of charisma goes a long way!
7. Interaction and audience engagement
Turn your presentation into an interactive experience — encourage questions, foster discussions and maybe even throw in a fun activity. Engaged audiences are more likely to remember and embrace your message.
Transform your slides into an interactive presentation with Venngage’s dynamic features like pop-ups, clickable icons and animated elements. Engage your audience with interactive content that lets them explore and interact with your presentation for a truly immersive experience.

8. Effective storytelling
Who doesn’t love a good story? Weaving relevant anecdotes, case studies or even a personal story into your presentation can captivate your audience and create a lasting impact. Stories build connections and make your message memorable.
A great presentation background is also essential as it sets the tone, creates visual interest and reinforces your message. Enhance the overall aesthetics of your presentation with these 15 presentation background examples and captivate your audience’s attention.
9. Well-timed pacing
Pace your presentation thoughtfully with well-designed presentation slides, neither rushing through nor dragging it out. Respect your audience’s time and ensure you cover all the essential points without losing their interest.
10. Strong conclusion
Last impressions linger! Summarize your main points and leave your audience with a clear takeaway. End your presentation with a bang , a call to action or an inspiring thought that resonates long after the conclusion.
In-person presentations aside, acing a virtual presentation is of paramount importance in today’s digital world. Check out this guide to learn how you can adapt your in-person presentations into virtual presentations .
Preparing an effective presentation starts with laying a strong foundation that goes beyond just creating slides and notes. One of the quickest and best ways to make a presentation would be with the help of a good presentation software .
Otherwise, let me walk you to how to prepare for a presentation step by step and unlock the secrets of crafting a professional presentation that sets you apart.
1. Understand the audience and their needs
Before you dive into preparing your masterpiece, take a moment to get to know your target audience. Tailor your presentation to meet their needs and expectations , and you’ll have them hooked from the start!
2. Conduct thorough research on the topic
Time to hit the books (or the internet)! Don’t skimp on the research with your presentation materials — dive deep into the subject matter and gather valuable insights . The more you know, the more confident you’ll feel in delivering your presentation.
3. Organize the content with a clear structure
No one wants to stumble through a chaotic mess of information. Outline your presentation with a clear and logical flow. Start with a captivating introduction, follow up with main points that build on each other and wrap it up with a powerful conclusion that leaves a lasting impression.
Delivering an effective business presentation hinges on captivating your audience, and Venngage’s professionally designed business presentation templates are tailor-made for this purpose. With thoughtfully structured layouts, these templates enhance your message’s clarity and coherence, ensuring a memorable and engaging experience for your audience members.
Don’t want to build your presentation layout from scratch? pick from these 5 foolproof presentation layout ideas that won’t go wrong.

4. Develop visually appealing and supportive visual aids
Spice up your presentation with eye-catching visuals! Create slides that complement your message, not overshadow it. Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words, but that doesn’t mean you need to overload your slides with text.
Well-chosen designs create a cohesive and professional look, capturing your audience’s attention and enhancing the overall effectiveness of your message. Here’s a list of carefully curated PowerPoint presentation templates and great background graphics that will significantly influence the visual appeal and engagement of your presentation.
5. Practice, practice and practice
Practice makes perfect — rehearse your presentation and arrive early to your presentation to help overcome stage fright. Familiarity with your material will boost your presentation skills and help you handle curveballs with ease.
6. Seek feedback and make necessary adjustments
Don’t be afraid to ask for help and seek feedback from friends and colleagues. Constructive criticism can help you identify blind spots and fine-tune your presentation to perfection.
With Venngage’s real-time collaboration feature , receiving feedback and editing your presentation is a seamless process. Group members can access and work on the presentation simultaneously and edit content side by side in real-time. Changes will be reflected immediately to the entire team, promoting seamless teamwork.
7. Prepare for potential technical or logistical issues
Prepare for the unexpected by checking your equipment, internet connection and any other potential hiccups. If you’re worried that you’ll miss out on any important points, you could always have note cards prepared. Remember to remain focused and rehearse potential answers to anticipated questions.
8. Fine-tune and polish your presentation
As the big day approaches, give your presentation one last shine. Review your talking points, practice how to present a presentation and make any final tweaks. Deep breaths — you’re on the brink of delivering a successful presentation!
In competitive environments, persuasive presentations set individuals and organizations apart. To brush up on your presentation skills, read these guides on how to make a persuasive presentation and tips to presenting effectively .

Whether you’re an experienced presenter or a novice, the right techniques will let your presentation skills soar to new heights!
From public speaking hacks to interactive elements and storytelling prowess, these 9 effective presentation techniques will empower you to leave a lasting impression on your audience and make your presentations unforgettable.
1. Confidence and positive body language
Positive body language instantly captivates your audience, making them believe in your message as much as you do. Strengthen your stage presence and own that stage like it’s your second home! Stand tall, shoulders back and exude confidence.
2. Eye contact with the audience
Break down that invisible barrier and connect with your audience through their eyes. Maintaining eye contact when giving a presentation builds trust and shows that you’re present and engaged with them.
3. Effective use of hand gestures and movement
A little movement goes a long way! Emphasize key points with purposeful gestures and don’t be afraid to walk around the stage. Your energy will be contagious!
4. Utilize storytelling techniques
Weave the magic of storytelling into your presentation. Share relatable anecdotes, inspiring success stories or even personal experiences that tug at the heartstrings of your audience. Adjust your pitch, pace and volume to match the emotions and intensity of the story. Varying your speaking voice adds depth and enhances your stage presence.

5. Incorporate multimedia elements
Spice up your presentation with a dash of visual pizzazz! Use slides, images and video clips to add depth and clarity to your message. Just remember, less is more—don’t overwhelm them with information overload.
Turn your presentations into an interactive party! Involve your audience with questions, polls or group activities. When they actively participate, they become invested in your presentation’s success. Bring your design to life with animated elements. Venngage allows you to apply animations to icons, images and text to create dynamic and engaging visual content.
6. Utilize humor strategically
Laughter is the best medicine—and a fantastic presentation enhancer! A well-placed joke or lighthearted moment can break the ice and create a warm atmosphere , making your audience more receptive to your message.
7. Practice active listening and respond to feedback
Be attentive to your audience’s reactions and feedback. If they have questions or concerns, address them with genuine interest and respect. Your responsiveness builds rapport and shows that you genuinely care about their experience.

8. Apply the 10-20-30 rule
Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it!
9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule
Simplicity is key. Limit each slide to five bullet points, with only five words per bullet point and allow each slide to remain visible for about five seconds. This rule keeps your presentation concise and prevents information overload.
Simple presentations are more engaging because they are easier to follow. Summarize your presentations and keep them simple with Venngage’s gallery of simple presentation templates and ensure that your message is delivered effectively across your audience.

1. How to start a presentation?
To kick off your presentation effectively, begin with an attention-grabbing statement or a powerful quote. Introduce yourself, establish credibility and clearly state the purpose and relevance of your presentation.
2. How to end a presentation?
For a strong conclusion, summarize your talking points and key takeaways. End with a compelling call to action or a thought-provoking question and remember to thank your audience and invite any final questions or interactions.
3. How to make a presentation interactive?
To make your presentation interactive, encourage questions and discussion throughout your talk. Utilize multimedia elements like videos or images and consider including polls, quizzes or group activities to actively involve your audience.
In need of inspiration for your next presentation? I’ve got your back! Pick from these 120+ presentation ideas, topics and examples to get started.
Creating a stunning presentation with Venngage is a breeze with our user-friendly drag-and-drop editor and professionally designed templates for all your communication needs.
Here’s how to make a presentation in just 5 simple steps with the help of Venngage:
Step 1: Sign up for Venngage for free using your email, Gmail or Facebook account or simply log in to access your account.
Step 2: Pick a design from our selection of free presentation templates (they’re all created by our expert in-house designers).
Step 3: Make the template your own by customizing it to fit your content and branding. With Venngage’s intuitive drag-and-drop editor, you can easily modify text, change colors and adjust the layout to create a unique and eye-catching design.
Step 4: Elevate your presentation by incorporating captivating visuals. You can upload your images or choose from Venngage’s vast library of high-quality photos, icons and illustrations.
Step 5: Upgrade to a premium or business account to export your presentation in PDF and print it for in-person presentations or share it digitally for free!
By following these five simple steps, you’ll have a professionally designed and visually engaging presentation ready in no time. With Venngage’s user-friendly platform, your presentation is sure to make a lasting impression. So, let your creativity flow and get ready to shine in your next presentation!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- Interactive Presentation
How To Write A Presentation 101 | Step-by-Step Guides with Best Examples | 2024 Reveals
Jane Ng • 05 April, 2024 • 9 min read
Is it difficult to start of presentation? You're standing before a room full of eager listeners, ready to share your knowledge and captivate their attention. But where do you begin? How do you structure your ideas and convey them effectively?
Take a deep breath, and fear not! In this article, we'll provide a road map on how to write a presentation covering everything from crafting a script to creating an engaging introduction.
So, let's dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a presentation , what should be in a powerful presentation.
- How To Write A Presentation Script
- How to Write A Presentation Introduction
Key Takeaways
Tips for better presentation.
- How to start a presentation
- How to introduce yourself

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
Presentations are all about connecting with your audience.
Presenting is a fantastic way to share information, ideas, or arguments with your audience. Think of it as a structured approach to effectively convey your message. And you've got options such as slideshows, speeches, demos, videos, and even multimedia presentations!
The purpose of a presentation can vary depending on the situation and what the presenter wants to achieve.
- In the business world, presentations are commonly used to pitch proposals, share reports, or make sales pitches.
- In educational settings, presentations are a go-to for teaching or delivering engaging lectures.
- For conferences, seminars, and public events—presentations are perfect for dishing out information, inspiring folks, or even persuading the audience.
That sounds brilliant. But, how to write a presentation?

- Clear and Engaging Introduction: Start your presentation with a bang! Hook your audience's attention right from the beginning by using a captivating story, a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, or a powerful quote. Clearly state the purpose of your presentation and establish a connection with your listeners.
- Well-Structured Content: Organize your content logically and coherently. Divide your presentation into sections or main points and provide smooth transitions between them. Each section should flow seamlessly into the next, creating a cohesive narrative. Use clear headings and subheadings to guide your audience through the presentation.
- Compelling Visuals: Incorporate visual aids, such as images, graphs, or videos, to enhance your presentation. Make sure your visuals are visually appealing, relevant, and easy to understand. Use a clean and uncluttered design with legible fonts and appropriate color schemes.
- Engaging Delivery: Pay attention to your delivery style and body language. You should maintain eye contact with your audience, use gestures to emphasize key points, and vary your tone of voice to keep the presentation dynamic.
- Clear and Memorable Conclusion: Leave your audience with a lasting impression by providing a strong closing statement, a call to action, or a thought-provoking question. Make sure your conclusion ties back to your introduction and reinforces the core message of your presentation.

How To Write A Presentation Script (With Examples)
To successfully convey your message to your audience, you must carefully craft and organize your presentation script. Here are steps on how to write a presentation script:
1/ Understand Your Purpose and Audience
- Clarify the purpose of your presentation. Are you informing, persuading, or entertaining?
- Identify your target audience and their knowledge level, interests, and expectations.
- Define what presentation format you want to use
2/ Outline the Structure of Your Presentation
Strong opening.
Start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience's attention and introduces your topic. Some types of openings you can use are:
- Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: "Have you ever...?"
- Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: "Did you know that....?"
- Use a Powerful Quote: "As Maya Angelou once said,...."
- Tell a Compelling Story : "Picture this: You're standing at...."
- Start with a Bold Statement: "In the fast-paced digital age...."
Main Points
Clearly state your main points or key ideas that you will discuss throughout the presentation.
- Clearly State the Purpose and Main Points: Example: "In this presentation, we will delve into three key areas. First,... Next,... Finally,.... we'll discuss...."
- Provide Background and Context: Example: "Before we dive into the details, let's understand the basics of....."
- Present Supporting Information and Examples: Example: "To illustrate...., let's look at an example. In,....."
- Address Counterarguments or Potential Concerns: Example: "While..., we must also consider... ."
- Recap Key Points and Transition to the Next Section: Example: "To summarize, we've... Now, let's shift our focus to..."
Remember to organize your content logically and coherently, ensuring smooth transitions between sections.
You can conclude with a strong closing statement summarizing your main points and leaving a lasting impression. Example: "As we conclude our presentation, it's clear that... By...., we can...."
3/ Craft Clear and Concise Sentences
Once you've outlined your presentation, you need to edit your sentences. Use clear and straightforward language to ensure your message is easily understood.
Alternatively, you can break down complex ideas into simpler concepts and provide clear explanations or examples to aid comprehension.
4/ Use Visual Aids and Supporting Materials
Use supporting materials such as statistics, research findings, or real-life examples to back up your points and make them more compelling.
- Example: "As you can see from this graph,... This demonstrates...."
5/ Include Engagement Techniques
Incorporate interactive elements to engage your audience, such as Q&A sessions , conducting live polls, or encouraging participation. You can also spin more funs into group, by randomly dividing people into different groups to get more diverse feedbacks!
6/ Rehearse and Revise
- Practice delivering your presentation script to familiarize yourself with the content and improve your delivery.
- Revise and edit your script as needed, removing any unnecessary information or repetitions.
7/ Seek Feedback
You can share your script or deliver a practice presentation to a trusted friend, colleague, or mentor to gather feedback on your script and make adjustments accordingly.
More on Script Presentation

How to Write A Presentation Introduction with Examples
How to write presentations that are engaging and visually appealing? Looking for introduction ideas for the presentation? As mentioned earlier, once you have completed your script, it's crucial to focus on editing and refining the most critical element—the opening of your presentation - the section that determines whether you can captivate and retain your audience's attention right from the start.
Here is a guide on how to craft an opening that grabs your audience's attention from the very first minute:
1/ Start with a Hook
To begin, you can choose from five different openings mentioned in the script based on your desired purpose and content. Alternatively, you can opt for the approach that resonates with you the most, and instills your confidence. Remember, the key is to choose a starting point that aligns with your objectives and allows you to deliver your message effectively.
2/ Establish Relevance and Context
Then you should establish the topic of your presentation and explain why it is important or relevant to your audience. Connect the topic to their interests, challenges, or aspirations to create a sense of relevance.
3/ State the Purpose
Clearly articulate the purpose or goal of your presentation. Let the audience know what they can expect to gain or achieve by listening to your presentation.
4/ Preview Your Main Points
Give a brief overview of the main points or sections you will cover in your presentation. It helps the audience understand the structure and flow of your presentation and creates anticipation.
5/ Establish Credibility
Share your expertise or credentials related to the topic to build trust with the audience, such as a brief personal story, relevant experience, or mentioning your professional background.
6/ Engage Emotionally
Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning.
Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations. Aim for clarity and brevity to maintain the audience's attention.
For example, Topic: Work-life balance
"Good morning, everyone! Can you imagine waking up each day feeling energized and ready to conquer both your personal and professional pursuits? Well, that's exactly what we'll explore today – the wonderful world of work-life balance. In a fast-paced society where work seems to consume every waking hour, it's vital to find that spot where our careers and personal lives harmoniously coexist. Throughout this presentation, we'll dive into practical strategies that help us achieve that coveted balance, boost productivity, and nurture our overall well-being.
But before we dive in, let me share a bit about my journey. As a working professional and a passionate advocate for work-life balance, I have spent years researching and implementing strategies that have transformed my own life. I am excited to share my knowledge and experiences with all of you today, with the hope of inspiring positive change and creating a more fulfilling work-life balance for everyone in this room. So, let's get started!"
🎉 Check out: How to Start a Presentation?

Whether you're a seasoned speaker or new to the stage, understanding how to write a presentation that conveys your message effectively is a valuable skill. By following the steps in this guide, you can become a captivating presenter and make your mark in every presentation you deliver.
Additionally, AhaSlides can significantly enhance your presentation's impact. With AhaSlides, you can use live polls , quizzes , and word cloud to turn your presentation into an engaging and interactive experience. Let's take a moment to explore our vast template library !
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a presentation step by step .
You can refer to our step-by-step guide on How To Write A Presentation Script: Understand Your Purpose and Audience Outline the Structure of Your Presentation Craft Clear and Concise Sentences Use Visual Aids and Supporting Material Include Engagement Techniques Rehearse and Revise Seek Feedback
How do you start a presentation?
You can start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience's attention and introduces your topic. Consider using one of the following approaches: Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: "Have you ever...?" Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: "Did you know that....?" Use a Powerful Quote: "As Maya Angelou once said,...." Tell a Compelling Story : "Picture this: You're standing at...." Start with a Bold Statement: "In the fast-paced digital age...."
What are the five parts of a presentation?
When it comes to presentation writing, a typical presentation consists of the following five parts: Introduction: Capturing the audience's attention, introducing yourself, stating the purpose, and providing an overview. Main Body: Presenting main points, evidence, examples, and arguments. Visual Aids: Using visuals to enhance understanding and engage the audience. Conclusion: Summarizing main points, restating key message, and leaving a memorable takeaway or call to action. Q&A or Discussion: Optional part for addressing questions and encouraging audience participation.

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides


- High-impact business writing
- Effective email writing
- Bid, tender and sales-proposal writing
- Technical writing
- Writing for customer service

- Customer-service writing
- Effective report writing

Business writing essentials
How to write a presentation (and deliver it, even via Zoom)
Jack elliott.
31 minute read

You’ve been asked to give a presentation. Chances are, your response will be roughly one of the following:
1. It’s a subject you’re passionate about and you’re a confident speaker. You’re pleased to have the opportunity.
2. You secretly worry that your style is flat and unengaging. You’re not looking forward to it.
3. At best, the prospect makes you nervous; at worst, terrified. You’d rather have root canal surgery.
If you belong in one of the last two categories, you probably know you’re not alone. You may have heard the statistic that public speaking is more widely feared even than death .

However you feel about the prospect of presenting, this comprehensive guide will take you step by step through the process of planning, writing and delivering a presentation you can be proud of (even via Zoom).
Use the contents links below to jump to the section you need most, make your way through methodically from start to finish, or bookmark this page for next time you need it.
What is a presentation?
Essentially, it’s a story. And its origins go back thousands of years – to when our ancestors gathered around the campfire to listen to the wise elders of the tribe. Without PowerPoint!
These days, presentations encompass the glitz and scale of the Oscars or the new iPhone launch through to business briefings to smaller audiences, in person or – increasingly – online. We’re focusing on the business side.
Whatever the occasion, there’s always an element of drama involved. A presentation is not a report you can read at your leisure, it’s an event – speakers are putting themselves on the spot to explain, persuade or inspire you. Good presentations use this dynamic to support their story.
Always remember: everyone wants you to do well
If you are nervous, always remember: no one sets out to write a poor presentation and no one wants to go to one either. There may be private agendas in the room, but for the most part audiences approach presentations positively. They want to be engaged and to learn. They want you to do well.
First things first: the date’s in the diary and you need to prepare. Let’s break it down.

1. Preparing your presentation
Imagine you’re a designer in the automotive industry and your boss has asked you to give a presentation. The subject: the future of the car and how it will fit with all the other modes of transport.
Where to start? How to approach it? First you need an angle, a key idea.
We talk about ‘giving’ a presentation – and of course it’s the audience who will be receiving it. So, instead of beginning with cars (in this case), let’s think about people. That way we can root the talk in the everyday experience we all share.
Maybe you remember a time you were stuck in traffic on a motorway. Morning rush hour. No one moving. Up ahead children were crossing a footbridge on their way to school, laughing at the cars going nowhere. And you thought, ‘Enjoy it while you can! This will be you one day.’ But maybe not. Surely we can do better for future generations!
There’s your opening – the whole issue captured in a single image, and you’ve immediately engaged your audience with a simple story.
The who, the why and the what
Always begin with the people you’ll be addressing in mind. Before you start writing, answer three fundamental questions: who is your audience, why are you talking to them and what do you want to say?
The answers will provide the strong foundations you need and start the ideas flowing. Ignore them and you risk being vague and unfocused. Clear writing is the result of clear thinking and thinking takes time, but it’s time well spent.
Got a presentation to write? Before you do anything else, answer three fundamental questions: who is your audience, why are you talking to them and what do you want to say? @EmphasisWriting Share on X
Start with the audience
Are you a senior car designer talking to your team? If the answer’s yes, you can assume high-level, shared knowledge.
But if you’re talking to the sales or marketing departments, you can’t make the same assumptions – there are issues you might have to explain and justify. And if it’s a press briefing, it’s about getting the message out to the general public – a different story again.
Knowing your audience will also dictate your tone. Your presentation to the board is likely to be quite formal, whereas a talk for your team can be more relaxed.
And what’s the audience’s mood? On another occasion you might have bad news to deliver – perhaps the national economy and the company’s finances are threatening people’s jobs. Then you must empathise – put yourself in their position and adapt your tone accordingly.
I want to …
You also need a clear objective (the why ). For our car designer, the overriding objective should be to plant a key idea in the audience’s mind. Starting with that image of the schoolchildren, it’s to convince the audience that the company has a radical and distinctive design future.
That’s the takeaway. How should they do that? Should they explain, persuade or inspire – the three key strategies for any presentation? You may need to use several of them to achieve your goal.
Objectives should always complete the statement ‘I want to …’. What do you want to do ?
It’s about …
The what is the substance of your presentation – the building blocks, all the facts and figures that tell the audience ‘It’s about …’.
Back to our designer. The move away from petrol and diesel will allow a complete rethink of car design. The electric power unit and battery can lie under the car’s floor, freeing up all the space taken up by the conventional engine. And then there are all the issues around emission-free, autonomous vehicles in the ‘smart’ cities of the future.
When you’re planning, it can be helpful to get all the information out of your head and onto the page, using a mind map , like the example below (for a talk on UK transport policy).
This is an effective way of unlocking everything you know (or still need to do more research on). Start with your main topic, then keep asking yourself questions (like who, what, when, where, how and why) to dig into all the aspects.
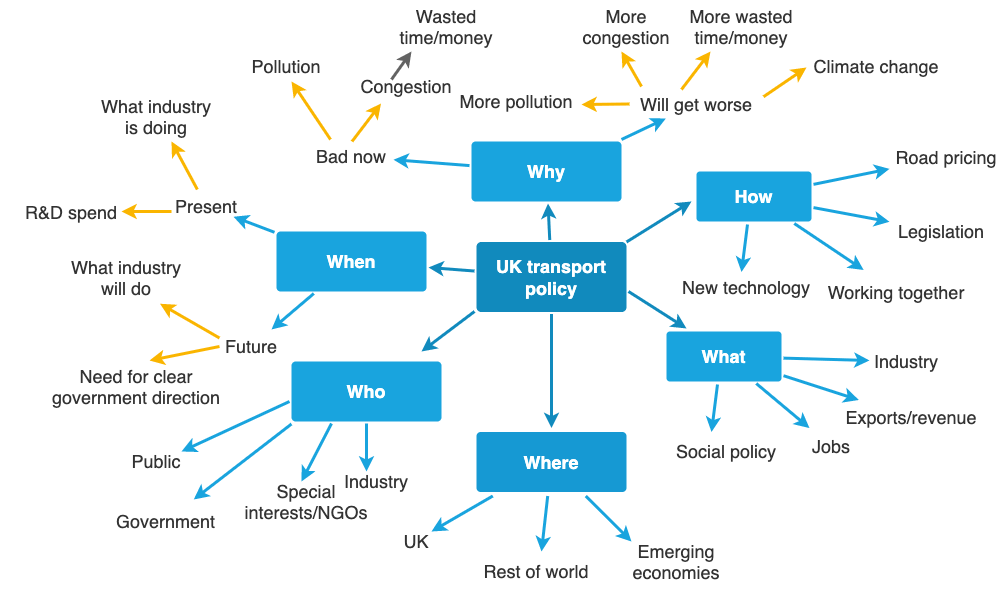
Mind map with the topic of ‘UK transport policy at the centre. Arrows point out to six bubbles with the labels ‘Who’, ‘When’, ‘Why’, ‘How’, ‘What’ and ‘Where’. More arrows point out from each of these bubbles to explore related points in each area, and still more arrows from some of those points to expand further. The information reads:
- Special interests / NGOs
- Need for clear government direction
- What industry will do
- R&D spend
- What industry is doing
- Congestion [this leads to the sub-point ‘Wasted time and money’]
- More pollution
- More congestion
- More wasted time and money
- Climate change
- Road pricing
- Legislation
- Working together
- New technology
- Exports/revenue
- Social policy
- Rest of world
- Emerging economies
Once you’ve got it all out on the page, you can identify which parts actually belong in your presentation. Don’t try to include every last detail: audiences don’t want to process piles of information. They are more interested in your ideas and conclusions.
Now let’s put all this research and planning into a structure.
2. How to structure your presentation
On 28 August 1963, Dr Martin Luther King Jr stood on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial in Washington DC and delivered one of the most powerful speeches in history: ‘I have a dream’.
He was the leader of the civil rights movement in the US and his audience that day numbered in the hundreds of thousands. His goal was to inspire them to continue the struggle.
Presentations usually aim to either explain, persuade or inspire – sometimes with elements of all three. Your aim will determine your structure. This will be the backbone of your presentation, giving it strength and direction.
Explain in a logical sequence
When you explain, you add to people’s knowledge to build the key idea. But ask yourself, what does this audience already know?
If you’re an astrophysicist talking to an audience of your peers, you can use terms and concepts you know they’ll be familiar with. If you’re explaining black holes to Joe Public, you can’t do that. Typically, you’ll have to use simple analogies to keep the audience with you (‘Imagine you’re in a huge dark room …’).
Whether it’s black holes or new software, good explanations start with what we know and then build on that understanding, step by step, layer by layer. The audience will stay with you if they can follow your logic and you can help this with linking comments – ‘Building on that … ‘, ‘This means …’, ‘To illustrate that, I’ve always found …’.
Presentations usually aim to either explain, persuade or inspire – sometimes with elements of all three. Your aim will determine your presentation's structure. @EmphasisWriting Share on X
We need to change
If you’re writing a persuasive presentation, you also need to follow a particular sequence.
Whether you’re writing a pitch for a prospective customer or making research-based recommendations to a client, you follow the same structure. That structure is the Four Ps . It’s a powerful way of leading your audience’s thinking.
Start with the current situation – where you are now ( position ). Explain why you can’t stay there, so the audience agrees things have to change ( problem ). Suggest up to three credible ways you can address the issue ( possibilities ). Then decide which one is the optimum solution ( proposal ).
Three is a magic number for writers – not too many, not too few. But there may be one standout possibility, in which case you go straight to it ( position, problem, proposal ).
Think about how the pandemic has profoundly changed our working lives. Towns and cities are full of offices that people used to commute to. But to maintain social distancing, we’ve been encouraged to work from home where possible and to stay away from public transport.
At some point, decision-makers within organisations will have to make a call – or share a recommendation – about what to do long term. Should we go back to the office, stay at home or combine the two?
If we had to present on this choice using the Four Ps structure, we could outline the pros and cons of each possibility and then make a push for the one we recommend above the others. Or we could join the likes of Google and Twitter and simply propose purely remote working well into the future.
I have a dream
A presentation that inspires is about the future – about what could be. Scientists inspire children to follow careers in astronomy or physics with their passion and stunning visuals. Designers re-energise companies with their radical, exciting visions. Business leaders convince their staff that they really can turn things around.

An audience watching an inspirational presentation is not going to take away lots of facts and figures. What’s important is their emotional and intellectual engagement with the speaker, their shared sense of purpose. One way to build that engagement is with your structure.
From dark to light
The most inspiring presentations are so often born of shared struggle. On 13 May 1940, Winston Churchill addressed the British parliament – and the British people listening on their radios – in the darkest days of the Second World War.
He was brutally realistic in his assessment of the current position: ‘We have before us many, many long months of struggle and of suffering.’ He then set out his policy: ‘To wage war by sea, land and air, with all our might … against a monstrous tyranny’, and the prize: ‘Victory, however long and hard the road may be.’
In difficult situations, audiences immediately see through false hope and empty rhetoric. They want honest acknowledgement, and the determination and clear strategy to lead them to the future.
We can imagine how the same structure could show up in a more business-related context:
‘I’m not going to sugar-coat the figures. We have to change to save jobs and secure our future. There will be dark days and sacrifices along the way, but what’s the hardest part of any turnaround? It’s getting started. To do that, we all need to keep asking two fundamental questions: where can we improve, how can we improve? And if we push hard enough and if we’re utterly relentless, change will come and our momentum will build.’

Are you going to appeal to your audience’s
- habits of thought (current beliefs)?
If your recommendations run counter to their current beliefs, try appealing to their emotions.
3. Writing your presentation script
You don’t have to write a script. Some people put a few PowerPoint slides together and wing it; others make do with bullets on a smartphone, laptop or cue cards. It depends on the event and the presenter.
Writing a full script takes time, but if it’s a very important presentation and you might use it again – perhaps to appeal for investment – it will be worth it.
Some people will write a full script because the company or organisation that’s commissioned a presentation will want to see a copy well ahead of the event (often for legal reasons). Others will write the script, edit it down to the required time and then edit it down again to bullets or notes.
If the presentation is to a small audience, your notes or bullets will suit a more conversational approach. There are no rules here – see what works best for you. But what you must do is know your subject inside out.
To write clearly, you must think clearly and a full script will expose the areas that aren’t clear – where an explanation needs strengthening, for example, or where you should work on a transition.
Timing is everything
A full script also helps with working out timing, and timing is crucial. TED talks, for example, have a strict 18-minute limit, whether in front of an audience or online. That’s short enough to hold attention, but long enough to communicate a key idea. (The ‘I have a dream’ speech lasted 17 minutes 40 seconds and it changed the world.)
It takes a very skilled presenter to go much over 30 minutes. If you are taking questions during or after your presentation , however, it’s fine to build in extra time.
Imagine you’re writing your presentation in full and your slot is 20 minutes. On an A4 page with a 14-point Calibri font and 1.5 line spacing, that will equate to about 10 pages.
You can also divide the page in two, with slides on the left and text on the right (or vice versa). Then you can plan your words and visuals in parallel – and that will be roughly 20 pages.
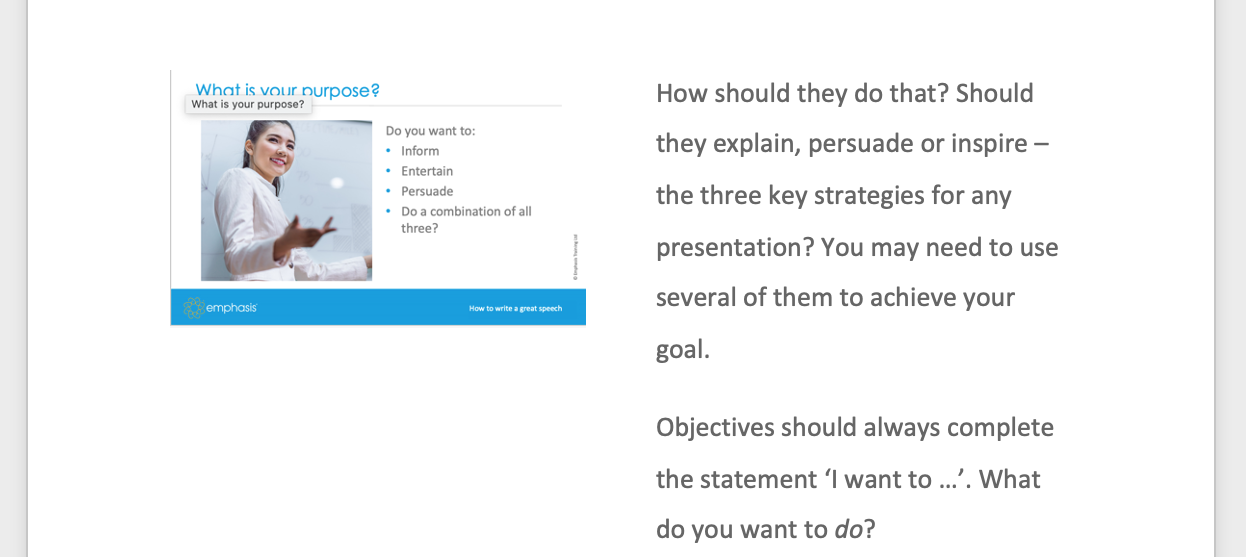
Script page with a slide on the left-hand side and text on the right. The slide has the heading ‘What is your purpose?’ and has a photo of a smiling person at a whiteboard mid-presentation. The text on the slide reads:
Do you want to:
- do a combination of all three?
The notes next to the slide read:
How should they do that? Should they explain, persuade or inspire – the three key strategies for any presentation? You may need to use several of them to achieve your goal.
The most powerful key on your keyboard – Delete
Use these numbers as your goal, but your first draft will probably be longer. That’s when you start deleting.
Be ruthless. Anything not adding to the story must go, including those anecdotes you’ve been telling for years ( especially those anecdotes). It’s not about what you want to tell the audience, it’s about what they need to hear.
Don’t feel you have to include every single issue either. Dealing with two or three examples in some detail is far better than saying a little bit about many more.
And interpret visual material you’re displaying rather than describing it, just as you wouldn’t repeat the text that’s on the screen. The audience can see it already.
It’s a conversation
Be yourself – don’t write a script that’s not in your style. We want the real you, not a supercharged version.
Some people are naturals when it comes to presenting – which can mean they’ve learned how to draw on their authentic strengths.
Sir David Attenborough is a great example. He has a wide-ranging knowledge of the natural world. He has an infectious passion and enthusiasm for his subject. And most importantly, he doesn’t lecture the camera: he talks naturally to his audience (and he’s now using Instagram to inspire new generations).
You can take a cue from Sir David and make your presentation style your own. Knowing your own strengths and really understanding your why will help you speak with purpose and passion.
And aim to speak naturally. Use conversational, inclusive language. That means lots of personal pronouns ( I believe, we can) and contractions ( Don’t you wonder …, you’re probably thinking …).
Sir David Attenborough introduces his new series, Our Planet at its premiere. He builds up our awareness by layering information alongside arresting statistics. These are framed simply, in relatable terms (‘96% of mass on the planet is us …’), so we easily grasp their shocking significance. He also uses ‘we’ and ‘us’ a lot to underline how this environmental emergency affects us all on ‘the planet we all call home’.
Finding the right words
Imagine you’re talking to someone as you write. And try saying the words out loud – it’s a good way to catch those complex, overlong sentences or particular words that will be difficult to say.
Presentations are not reports that can be reread – the audience has to understand what you are saying in the moment . Don’t leave them wondering what on earth you’re talking about, as they will only fall behind.
So avoid using long or complex words, or words you wouldn’t hear in everyday conversation (if your everyday conversation includes ‘quarks’ and ‘vectors’, that’s fine). And beware of jargon – it can exclude the audience and it quickly becomes clichéd and outdated.
Here are some more hints and tips on how to write effectively for speaking:
Syntax (word order): Disentangle your thoughts and arrange the words in your sentences to be simple and logical. Often, complex syntax shows up when the main point is getting lost inside excess information (or that the speaker is unsure what their main point is).
Pace, rhythm and tone: Varying the pace, rhythm and tone of sentences makes both the speaking and listening experience far more enjoyable.
Make sure the stress falls on the most important words. For example, ‘To be or not to be ‘ (where the stress rises and falls on alternate words) or ‘I have a dream ‘ (where the stress falls on the final word).
Vary the length of sentences and experiment with using very short sentences to emphasise a point.
Play with rhythm by arranging words in pairs and trios. Saying things in threes gives a sense of movement, progression and resolution: Going, going … gone . Saying words in pairs gives a more balanced tone (‘courage and commitment’, ‘energy and effort’) or a sense of tension between the words (‘war and peace’, ‘imports and exports’).
Analogies: Good analogies can work well in presentations because they paint vivid pictures for the audience. The best way to do it is to use either a simile (‘It wasn’t so much a dinner party, more like feeding time at the zoo’) or a metaphor (‘He was the fox and the company was the henhouse’).
Alliteration: This means using two or more words that start with the same sound, like ‘big and bold’, ‘sleek and shiny’ or ‘key components’. On the page alliteration may look contrived, but it can effectively highlight important phrases in a presentation.
Words to avoid: Be careful about using clichés like ‘pushing the envelope’, ‘playing hardball’ and ‘thinking outside the box’. And think carefully about using any word that ends with -ism, -ise, -based, -gate, -focused and -driven.
Be careful with humour too: don’t write jokes unless you can naturally tell them well. Keep the tone light if it fits the occasion, but a badly told joke can be excruciating.
4. How to start your presentation
People tend to remember beginnings and endings the most, so make sure your opening and conclusion are both strong.
You have about a minute to engage an audience. You want them to be intrigued, to want to know more, to come slightly forward in their seats. If you only learn one part of your presentation by heart, make it that minute.
A quick ‘thank you’ is fine if someone has introduced you. A quick ‘good morning’ to the audience is fine too. But don’t start thanking them for coming and hoping they’ll enjoy what you have to say – you’re not accepting an Oscar, and they can tell you what they thought when it’s over. Get straight down to business.
There are four basic types of introduction which will draw your audience in:
- News – ‘Positive Covid-19 tests worldwide have now reached …’
- Anecdotal – ‘About ten years ago, I was walking to work and I saw …’
- Surprise – ‘Every five minutes, an American will die because of the food they eat.’
- Historical – ‘In 1800, the world’s population was one billion. It’s now 7.8 billion.’
You can interpret these beginnings in any number of ways. If you were to say, ‘I have an admission to make …’, we will expect a personal anecdote relating to your main theme. And because you’re alone in front of us, it’s playing on your vulnerability. We’re intrigued straight away, and you’ve established a good platform for the rest of the presentation.
You can also combine these techniques. The historical beginning creates a sense of movement – that was then and this is now – as well as a surprising fact. It may prompt a thought like, ‘Wow, where’s this going?’ And you can trade on this with your own rhetorical question: ‘What does this mean for everyone in this room? It’s not what you think …’.
As well as setting up your story, you need to quickly reassure the audience they’re in safe hands. One way to do that is to give them a map – to tell them where you’re going to take them and what they’re going to see along the way.
Then you’re starting the journey together.
5. How to end your presentation
Your ending is what you want the audience to take away: your call to action, your vision of the future and how they can contribute.
If your presentation is online or to a small group in a small room, your ending is not going to be a battle cry, a call to man the barricades – that would be totally inappropriate. But equally don’t waste it with something flat and uninspiring.
Here are four effective ways to end your talk (like the intros, you can combine them or come up with your own):
- Predict the future – ‘So what can we expect in the next ten years? …’
- Quotation – ‘As our chief exec said at the meeting yesterday, …’
- Repeat a major issue – ‘We can’t carry on with the same old same old.’
- Summarise – ‘Continuous improvement isn’t our goal. It’s our culture.’
Predicting the future fits well with a historical beginning – it completes the arc of your presentation.
If you end with a quotation, make sure it’s relevant and credible – it has to be an authoritative stamp.
Repeating a major issue means pulling out and highlighting a major strand of your presentation, while summarising is about encapsulating your argument in a couple of sentences.
Your ending can also be a change of tone, perhaps signalled by the single word ‘Finally …’. It’s the audience’s cue to come slightly forward again and pay close attention.
As with your opening, it will have more impact if you’ve learned your ending – put down your notes, take a couple of steps towards the audience and address them directly, before a simple ‘Thank you.’
6. Creating your PowerPoint slides
We’ve all been there – watching a seemingly endless, poorly designed slide deck that’s simply restating what the presenter is saying. So common is this tortuous experience that there’s a name for it: Death by PowerPoint. But it doesn’t have to be like this.
Do you need slides at all?
As with your script, the first thing you should ask is ‘Do I actually need this?’ In 2019, Sir Tim Berners-Lee gave the Richard Dimbleby lecture for the BBC. He spoke for about 40 minutes with no autocue (he’d memorised his script) – and no speaker support.
This is a uniquely powerful form of presentation because the audience’s attention is totally focused on that one person. The call to action at the end of a presentation and delivering bad news are also best done without visuals.
Visual support
But if they’re well-judged and relevant, slides or other visuals can add enormously to a presentation – whether it’s photography, video or the ubiquitous PowerPoint. There are, however, two things everyone should know about PowerPoint in particular:
- It’s incredibly versatile and convenient.
- In the wrong hands, it can be unbearably tedious.
Your PowerPoint slides should not essentially be your cue cards projected onto a screen. They shouldn’t be packed margin to margin with text or full of complex diagrams.
If the presentation is live, the audience has come to watch you, not your slide deck. Online, the deck may have to work harder to sustain visual interest.
As with the script, keep your finger poised over that Delete key when you’re putting the deck together.
How many slides?
There’s no hard-and-fast rule about how many slides you should use, but think in terms of no more than one or two a minute on average. And don’t use more than a couple of short video inserts in a 20-minute presentation.
You might have a section where you show a few slides in a sequence or hold a single slide for a couple of minutes, which is fine. Varying the pacing helps to keep a presentation moving.
Optimise for psychology
As self-professed presentation aficionado David JP Phillips notes in his TEDx talk , people – and that includes your audience – have terrible working memories. If you don’t account for this fact in your slides, your talk will not have a lasting impact. In fact, most of it will be forgotten within around 30 seconds.
To counter this effect, David identifies five key strategies to use when designing your PowerPoint:
- Only have one message per slide: more than that and you’re splitting your audience’s attention.
- Don’t use full sentences on slides, and certainly don’t imagine you can talk over them if you do. People trying to read and listen at the same time will fail at both and absorb nothing. Move your running text into the documentation section instead, and keep the slide content short and sweet.
- People’s focus will be drawn to the biggest thing on the slide. If your headline is less important than the content below it, make the headline text the smaller of the two.
- You can also direct people’s attention using contrast. This can be as simple as guiding their point of focus by using white text (on a dark background) for the words you want to highlight, while the surrounding text is greyed out.
- Including too many objects per slide will sap your audience’s cognitive resources. (Your headline, every bullet, any references, even a page number each count as an object.) Include a maximum of six objects per slide and viewers will give a mental sigh of relief. This will probably mean creating more slides overall – and that’s fine.
More Powerpoint and visual aid tips
Here are a few more guidelines for creating your visual aids:
- Never dive into PowerPoint as job one in creating your presentation. Work out your talk’s structure (at least) before designing your slide deck. Making a genuinely effective PowerPoint requires that you know your subject inside out.
- List any visuals you’ll need as you prepare your script. That terrific photo you saw recently could be difficult to track down, and you might need permission and to pay to use it.
- It bears repeating: keep each slide to one key idea.
- Use the build effect of adding one bullet at a time (or use the contrast trick above) and try not to use more than three bullets per frame (or six objects overall).
- Strip each bullet to the bare minimum – no articles (‘a’, ‘an’ and ‘the’), no prepositions (‘in’, ‘at’, ‘to’ etc) and cut right back on punctuation.
- Every word that’s not there for a reason has to go. Delete, delete, delete.
‘Extra’ slides
- Use a ‘walk-in’ slide. Rather than have the audience arrive to a blank screen, this tells them who you are and your presentation’s title.
- Use occasional holding slides in between those with more content – perhaps an image but no text. They give the audience a visual rest and put the focus back on you.
- A plain white background might look fine on a computer monitor, but it will be glaring on a big screen. Invert the norm with a dark background, or use shading or ‘ghosted’ images to break up backgrounds and add visual interest.
- Some colours work better than others on-screen. Blues and greys are soft and easy on the eye. Red is a no-no, whether for backgrounds or text. And if you stick with a light background, favour a more subtle dark grey over black for the text.
- Use sans serif fonts (like Arial, Helvetica or Calibri) and think about point size – make sure it’s easily legible.
- Only use upper case where absolutely necessary.
Images and data
- Photos work well full screen, but they also really stand out well on a black background.
- Make sure your charts and graphics aren’t too complex. The dense information that’s fine on the page will not work on-screen – it’s too much to take in. Graphs behind a TV newsreader are often reduced to a single line going dramatically up or down.
- Don’t present data or graphs and expect them to speak for themselves. You need to find the story and significance in the data and present that .
And finally
- Proofread, proofread, proofread – or risk standing in front of an embarrassing spelling mistake.
Technical check
- Check what laptop they’re using at your venue. If you’ve written your deck on a PC, run it on a PC (and, of course, the same rule applies if you’ve used a Mac).
- If you’ve emailed your presentation to the venue, take a USB copy along as back-up.
- If you’re presenting online, check which platform you’ll be using and get comfortable with it. If someone else will be hosting the event, make sure you arrange a time for a rehearsal, especially if there will be a producer.
7. Delivering your presentation
You’ve put a lot of time and effort into preparing your presentation and now you’ve come to the sharp end – it’s time to stand and deliver.
Run it through
You don’t have to rehearse, but most presenters do and for good reason – it catches weak points and awkward transitions. And, crucially, it bolsters confidence.
Read your script or go through your bullets aloud – it will help to settle your nerves. If you use colleagues as a dummy audience, you can do a sense check too: ‘Does that bit work?’ ‘Have I explained it clearly?’ ‘Do you get the big picture?’ And rehearsing out loud will catch those words and sentences you thought you could say but can’t.
The more you rehearse, the more familiar and natural the presentation will become. Rehearse the technical side too – where the video is going to come in, how you’re going to vary your pace and tone to maintain interest.
Try speaking slightly more slowly than you would normally so the audience catches every word, and don’t be afraid to pause now and again. It gives a breathing space for you and the audience.

Connect with your audience
When you deliver your presentation for real, establish eye contact with the audience, just as you would in a conversation. In a small room with a small audience, talk to individuals. In a larger space, don’t talk to the first couple of rows and ignore the rest – include everyone.
And if you stumble over your words here or there, carry on and don’t dwell on it – you’ll lose your concentration. Audiences are generally forgiving and they might not even notice.
Each audience is unique: they react differently in different places. And although tomorrow might be the tenth time you’ve done the same presentation, it will be the first time this audience sees it. Your duty is to keep it fresh for them.
A final point
This is your presentation – you’re in control and the audience needs to feel they’re in safe hands.
It’s perfectly natural to feel nervous , but it’s the thought of doing it that’s the worst bit. Once you get going – and especially when you sense the audience is with you – the nerves will start to disappear. Try to enjoy it. If you enjoy it, it’s far more likely the audience will too.
And remember: everyone wants you to do well.

8. How to present online
Taking to Zoom or another online platform to present was once the exception. These days, online presenting is as essential a skill as presenting in person.
The switch to online can be nerve-wracking and cause even usually skilled presenters to falter. But there’s no need for that to happen.
Indeed, all of the advice we’ve talked about on preparing, structuring and writing for in-person presenting is equally relevant for your online delivery. You just need to be ready for the unique challenges that remote presentations pose.
An obvious one is that while you still have an audience, it will probably be muted and possibly even unseen (if webcams are switched off). This makes it far more difficult to gauge audience reaction, and if the event is pre-recorded, there might not be any at all – at least not immediately. Clapping and laughing emojis are not quite like the real thing.
Keep eye contact
But although your audience may be many miles away, there are still ways you can – and should – create a sense of connection with them. Your presentation will have much more impact if you do.
Whether the event is live or recorded, at least start with your webcam on (unless you really can only use slides). If it’s an option and feels appropriate, consider keeping your camera on throughout – remember, you are the presentation as much as any visuals.
If you will be on display, make sure you know where your webcam’s lens is and at key moments of your talk look directly into it – and out at your audience – to punctuate those points.
And don’t look at a second screen to cue up your PowerPoint – viewers will think your attention is wandering.
Engage your online audience
Being an engaging speaker is always important, but remember that the online world is already a place we associate with distraction. It’s also easier for a viewer behind their laptop to disguise their wandering attention than it would be for one in an auditorium or boardroom.
This isn’t to say your audience don’t want to give you their attention. But it is more important than ever to keep your presentation sharp and concise. Revisit your structure, your script or cue cards and your slides. Take a really critical eye to it and (as always) delete, delete, delete anything that’s not directly relevant.
If it works for your format, you can look at making your presentation interactive. You can then break the content into short segments, interspersed with comment, polls, questions and discussion. The variety will be a welcome change for your viewers.
Your visuals are part of what will keep people with you – along with the interplay you create between you and them. This means following the best-practice guidance we covered earlier is even more important.
Using Zoom for your presentation? Master the art of online delivery through this simple mix of set-up, delivery and technical tricks @EmphasisWriting Share on X
Modulate your voice
Your tone of voice is extremely important here because presenting online is like radio with pictures. When people say ‘You have a great voice for radio’ what they mean is that it’s easy to listen to, often because you’re using quite a low-pitched, warm and relaxed register.
Listen to voices on the radio and voiceovers and identify the ones you particularly enjoy. What do you like about them? Why do you enjoy some voices and not others?
A flat, unmodulated voice, for instance, is difficult to listen to for long periods (and isn’t likely to inspire anyone).
Experiment with intentionally adding energy to your voice, as internet audio can have a dulling effect. As our trainer Gary Woodward puts it: ‘Turn up the enthusiasm dial even higher than you think, to make sure it comes through.’ And always vary your pace and tone as you would in a normal conversation.
And if it suits the tone of your talk, smile now and again. Smiling is contagious, and people will hear it in your voice even if they can’t see you.
Perfect your transitions
One of the other key challenges of remote presentations is that you have another layer of technology to wrestle with: sharing your PowerPoint online.
This means that many presentations begin with the popular catchphrase ‘Can you see my screen?’
This can also cause many presenters to stumble through their transitions, making the links between their slides clunky. And while remote audiences may be forgiving, for a slick presentation it’s best to prevent these sort of fumbles.
Naturally, practice plays a part here. But you can also give yourself the advantage with your set-up.
Dave Paradi from Think Outside the Slide explains one great way of setting up Zoom so you can smoothly cue up and run your slide deck – and be certain what’s being displayed.
You’ll even be able to see the rest of your screen (but the audience won’t). As you’ll be able to see what’s coming up, your transitions can also be seamless.
The trick is to use one of Zoom’s advanced settings after you hit ‘Share screen’, to share only a portion of your screen:
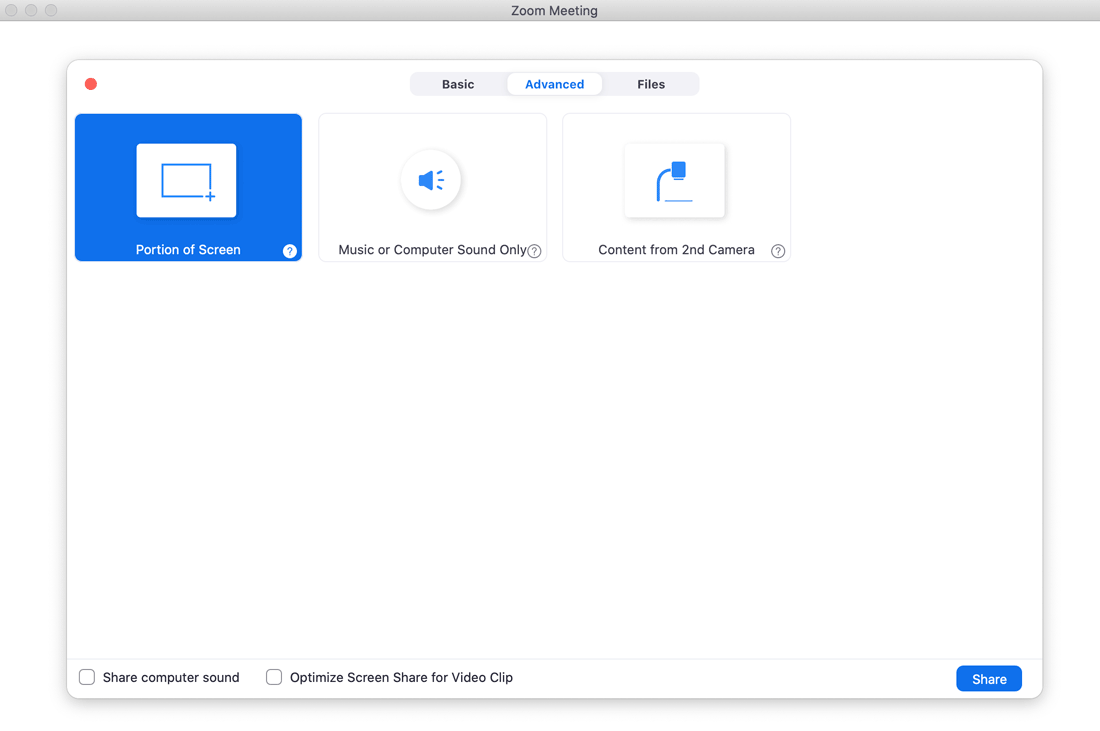
Advanced screensharing options pop-up box in Zoom, with the options ‘Portion of Screen’, ‘Music or Computer Sound Only’ and ‘Content from 2nd Camera’. The ‘Portion of Screen’ option is highlighted in blue.
This will give you a frame you can move to the part of the screen you want the audience to see.
Put your PowerPoint slides into ‘presenter view’ before launching the screenshare. Then you’ll be able to see the upcoming slides and your notes throughout, and your animations (like build slides) will work as normal.
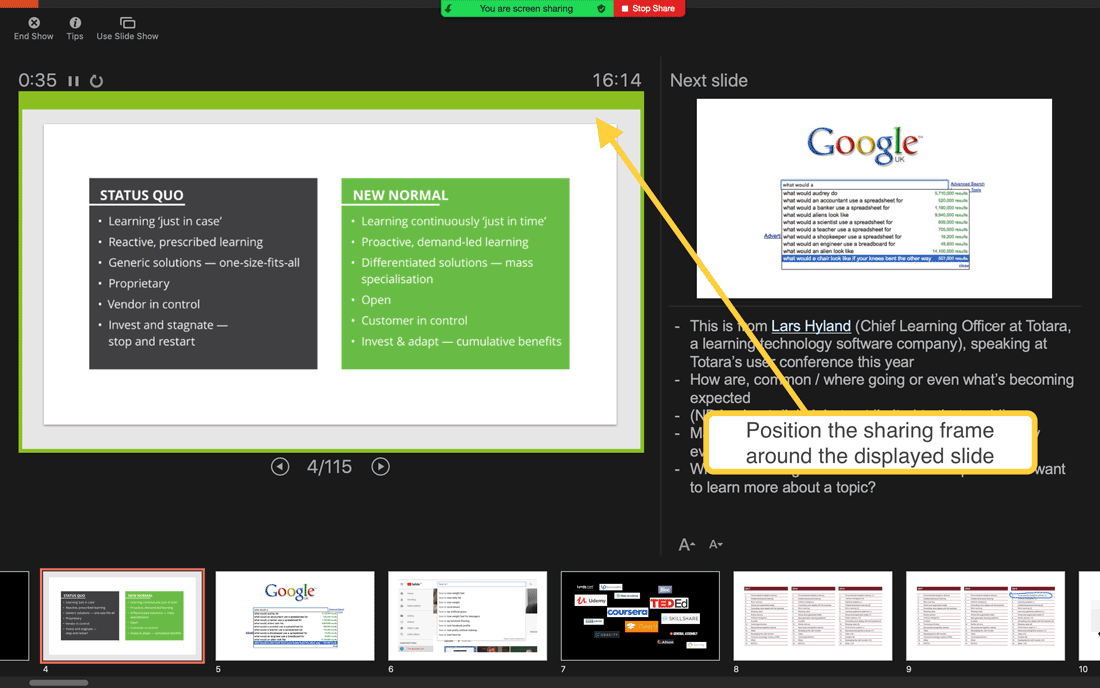
Zoom’s ‘portion of screen’ setting in action
Presenter view in PowerPoint, with the current displayed slide on the left and the upcoming slide displaying smaller on the right, with notes below it. There is a notification saying ‘You are screen sharing’ at the top and a sharing frame positioned around the current slide.
The other part of the trick? Set it up in advance shortly before you’re due to speak. Once you’re happy with the set up, you can stop sharing until it’s time to kick off your talk. When you return to ‘Share screen’ again, it will reopen the frame in the same place.
Dave shows you the process in this video:
Five practical tips for a truly professional online presentation
You’re happy with the content of your talk, you’ve ruthlessly streamlined your slides and mastered your radio voice. Now just make sure you cover these crucial practicalities for a polished presentation:
1. Create a good space Make sure you have your environment well set up:
- Keep the background on display as tidy and minimalist as possible – a plain wall or backdrop is great, if you can.
- Manage and minimise background noise (shut the window, ensure your phone’s on silent, put the cat out, make sure someone’s watching the kids in another room – whatever it takes).
- Check your lighting: have your light source in front of you, not behind you (or you’ll be in shadow).
- Set up your computer or device at eye level so that you are well-framed and facing it straight on – avoid looming above it while providing a lovely view into your nostrils.
2. Think about your appearance Dress in the same way you would if the presentation were in person, and judge your choice of attire based on the formality of the event and your audience.
3. Practise! Run through the presentation and rehearse the technical side. Practise your transitions, including the initial cueing up of your slides (perhaps using the Zoom tip above), so that you can be confident in doing it all smoothly.
4. Be primed and ready Log in early on the day of your talk. Check all your tech is working, get your headset on and ensure everything is set up well ahead of time. This will save any last-minute issues (and stress) and means you can hit the ground running.
5. Stand and deliver Even online, consider giving your presentation standing up, if you can do so comfortably (adjusting your device or webcam accordingly). This may put you more into a presenting frame of mind and will differentiate you from most remote presenters.
Are you still there?
Live audiences have a group dynamic – as soon as a few people start laughing it becomes infectious and the others join in. It’s naturally different online. But that doesn’t have to throw you.
You might not get that immediate feedback, but don’t overcompensate and feel you have to win them back.
Yes, it’s often more difficult to gauge an audience’s reaction online – especially if their audio is muted and their webcams off. Yes, this can be daunting. But they are still out there listening. You may or may not hear (or see) laughter, but they could still be smiling and very interested in what you have to say. Have faith in your own content. Whatever form your delivery will take, keep coming back to your purpose and message for giving this talk – and keep considering the people you’ll be talking to. Whether the address will be online or in person, it is keeping this focus which is the key to every powerful presentation.
Ready to learn even more? Work one-to-one on your presentation-writing skills with one of our expert trainers or join our scheduled presentation-writing courses . If your team are looking to upskill, we also offer tailored in-house training . And if fear of presenting is holding your team back, check out our in-house course The reluctant presenter .
Image credit: lightpoet / Shutterstock

Your go-to guide to better writing
Get your own PDF copy of The Write Stuff , the definitive guide for everyone who writes at work.

These days he's one of Emphasis' top business-writing trainers, but in previous career lives Jack has written for many public and private sector organisations. He has an in-depth knowledge of the engineering and manufacturing sectors, particularly the UK automotive industry. As the lead scriptwriter for chairmen and CEOs, he has been responsible for proposals, pitches and reports as well as high-profile speeches and global product launches.
Was this article helpful?
This helps us make better content for you

You might also like

The readability techniques you need for clear business writing

Writing to the board
Writing a report for the board? Here’s what you need to know
![How to write a winning marketing proposal [with presentation template] 5 A business woman sits at a desk, presenting a proposal (on a laptop screen) to the man sitting across from her.](https://www.writing-skills.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/business-woman-presents-proposal-300x161.jpg)
Writing for marketing
How to write a winning marketing proposal [with presentation template]

Bids and proposals
Is your bid presentation pushing prospects into the cold?
Get expert advice, how-tos and resources for good writing (and great work).

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
August 3, 2018 - Dom Barnard
For many people the thought of delivering a presentation is a daunting task and brings about a great deal of nerves . However, if you take some time to understand how effective presentations are structured and then apply this structure to your own presentation, you’ll appear much more confident and relaxed.
Here is our complete guide for structuring your presentation, with examples at the end of the article to demonstrate these points.
Why is structuring a presentation so important?
If you’ve ever sat through a great presentation, you’ll have left feeling either inspired or informed on a given topic. This isn’t because the speaker was the most knowledgeable or motivating person in the world. Instead, it’s because they know how to structure presentations – they have crafted their message in a logical and simple way that has allowed the audience can keep up with them and take away key messages.
Research has supported this, with studies showing that audiences retain structured information 40% more accurately than unstructured information.
In fact, not only is structuring a presentation important for the benefit of the audience’s understanding, it’s also important for you as the speaker. A good structure helps you remain calm, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences.
What will affect your presentation structure?
Generally speaking, there is a natural flow that any decent presentation will follow which we will go into shortly. However, you should be aware that all presentation structures will be different in their own unique way and this will be due to a number of factors, including:
- Whether you need to deliver any demonstrations
- How knowledgeable the audience already is on the given subject
- How much interaction you want from the audience
- Any time constraints there are for your talk
- What setting you are in
- Your ability to use any kinds of visual assistance
Before choosing the presentation’s structure answer these questions first:
- What is your presentation’s aim?
- Who are the audience?
- What are the main points your audience should remember afterwards?
When reading the points below, think critically about what things may cause your presentation structure to be slightly different. You can add in certain elements and add more focus to certain moments if that works better for your speech.

What is the typical presentation structure?
This is the usual flow of a presentation, which covers all the vital sections and is a good starting point for yours. It allows your audience to easily follow along and sets out a solid structure you can add your content to.
1. Greet the audience and introduce yourself
Before you start delivering your talk, introduce yourself to the audience and clarify who you are and your relevant expertise. This does not need to be long or incredibly detailed, but will help build an immediate relationship between you and the audience. It gives you the chance to briefly clarify your expertise and why you are worth listening to. This will help establish your ethos so the audience will trust you more and think you’re credible.
Read our tips on How to Start a Presentation Effectively
2. Introduction
In the introduction you need to explain the subject and purpose of your presentation whilst gaining the audience’s interest and confidence. It’s sometimes helpful to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped to help filter down your topic:
- Introduce your general topic
- Explain your topic area
- State the issues/challenges in this area you will be exploring
- State your presentation’s purpose – this is the basis of your presentation so ensure that you provide a statement explaining how the topic will be treated, for example, “I will argue that…” or maybe you will “compare”, “analyse”, “evaluate”, “describe” etc.
- Provide a statement of what you’re hoping the outcome of the presentation will be, for example, “I’m hoping this will be provide you with…”
- Show a preview of the organisation of your presentation
In this section also explain:
- The length of the talk.
- Signal whether you want audience interaction – some presenters prefer the audience to ask questions throughout whereas others allocate a specific section for this.
- If it applies, inform the audience whether to take notes or whether you will be providing handouts.
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and then conclude what this means for the audience.
Keep in mind that the main aim of the introduction is to grab the audience’s attention and connect with them.
3. The main body of your talk
The main body of your talk needs to meet the promises you made in the introduction. Depending on the nature of your presentation, clearly segment the different topics you will be discussing, and then work your way through them one at a time – it’s important for everything to be organised logically for the audience to fully understand. There are many different ways to organise your main points, such as, by priority, theme, chronologically etc.
- Main points should be addressed one by one with supporting evidence and examples.
- Before moving on to the next point you should provide a mini-summary.
- Links should be clearly stated between ideas and you must make it clear when you’re moving onto the next point.
- Allow time for people to take relevant notes and stick to the topics you have prepared beforehand rather than straying too far off topic.
When planning your presentation write a list of main points you want to make and ask yourself “What I am telling the audience? What should they understand from this?” refining your answers this way will help you produce clear messages.
4. Conclusion
In presentations the conclusion is frequently underdeveloped and lacks purpose which is a shame as it’s the best place to reinforce your messages. Typically, your presentation has a specific goal – that could be to convert a number of the audience members into customers, lead to a certain number of enquiries to make people knowledgeable on specific key points, or to motivate them towards a shared goal.
Regardless of what that goal is, be sure to summarise your main points and their implications. This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there.
Follow these steps:
- Signal that it’s nearly the end of your presentation, for example, “As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…”
- Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation – “In this speech I wanted to compare…”
- Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions
- Indicate what is next/a call to action/a thought-provoking takeaway
- Move on to the last section
5. Thank the audience and invite questions
Conclude your talk by thanking the audience for their time and invite them to ask any questions they may have. As mentioned earlier, personal circumstances will affect the structure of your presentation.
Many presenters prefer to make the Q&A session the key part of their talk and try to speed through the main body of the presentation. This is totally fine, but it is still best to focus on delivering some sort of initial presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.

Other common presentation structures
The above was a description of a basic presentation, here are some more specific presentation layouts:
Demonstration
Use the demonstration structure when you have something useful to show. This is usually used when you want to show how a product works. Steve Jobs frequently used this technique in his presentations.
- Explain why the product is valuable.
- Describe why the product is necessary.
- Explain what problems it can solve for the audience.
- Demonstrate the product to support what you’ve been saying.
- Make suggestions of other things it can do to make the audience curious.
Problem-solution
This structure is particularly useful in persuading the audience.
- Briefly frame the issue.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it ‘s such a problem. Use logos and pathos for this – the logical and emotional appeals.
- Provide the solution and explain why this would also help the audience.
- Call to action – something you want the audience to do which is straightforward and pertinent to the solution.
Storytelling
As well as incorporating stories in your presentation , you can organise your whole presentation as a story. There are lots of different type of story structures you can use – a popular choice is the monomyth – the hero’s journey. In a monomyth, a hero goes on a difficult journey or takes on a challenge – they move from the familiar into the unknown. After facing obstacles and ultimately succeeding the hero returns home, transformed and with newfound wisdom.
Storytelling for Business Success webinar , where well-know storyteller Javier Bernad shares strategies for crafting compelling narratives.
Another popular choice for using a story to structure your presentation is in media ras (in the middle of thing). In this type of story you launch right into the action by providing a snippet/teaser of what’s happening and then you start explaining the events that led to that event. This is engaging because you’re starting your story at the most exciting part which will make the audience curious – they’ll want to know how you got there.
- Great storytelling: Examples from Alibaba Founder, Jack Ma
Remaining method
The remaining method structure is good for situations where you’re presenting your perspective on a controversial topic which has split people’s opinions.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it’s such a problem – use logos and pathos.
- Rebut your opponents’ solutions – explain why their solutions could be useful because the audience will see this as fair and will therefore think you’re trustworthy, and then explain why you think these solutions are not valid.
- After you’ve presented all the alternatives provide your solution, the remaining solution. This is very persuasive because it looks like the winning idea, especially with the audience believing that you’re fair and trustworthy.
Transitions
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions which are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different forms, here are some examples:
Moving from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shifting between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Key slides for your presentation
Slides are a useful tool for most presentations: they can greatly assist in the delivery of your message and help the audience follow along with what you are saying. Key slides include:
- An intro slide outlining your ideas
- A summary slide with core points to remember
- High quality image slides to supplement what you are saying
There are some presenters who choose not to use slides at all, though this is more of a rarity. Slides can be a powerful tool if used properly, but the problem is that many fail to do just that. Here are some golden rules to follow when using slides in a presentation:
- Don’t over fill them – your slides are there to assist your speech, rather than be the focal point. They should have as little information as possible, to avoid distracting people from your talk.
- A picture says a thousand words – instead of filling a slide with text, instead, focus on one or two images or diagrams to help support and explain the point you are discussing at that time.
- Make them readable – depending on the size of your audience, some may not be able to see small text or images, so make everything large enough to fill the space.
- Don’t rush through slides – give the audience enough time to digest each slide.
Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
Here are some additional resources for slide design:
- 7 design tips for effective, beautiful PowerPoint presentations
- 11 design tips for beautiful presentations
- 10 tips on how to make slides that communicate your idea
Group Presentations
Group presentations are structured in the same way as presentations with one speaker but usually require more rehearsal and practices. Clean transitioning between speakers is very important in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this consists of:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Elnaz will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Elnaz”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Joe.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Example of great presentation structure and delivery
Having examples of great presentations will help inspire your own structures, here are a few such examples, each unique and inspiring in their own way.
How Google Works – by Eric Schmidt
This presentation by ex-Google CEO Eric Schmidt demonstrates some of the most important lessons he and his team have learnt with regards to working with some of the most talented individuals they hired. The simplistic yet cohesive style of all of the slides is something to be appreciated. They are relatively straightforward, yet add power and clarity to the narrative of the presentation.
Start with why – by Simon Sinek
Since being released in 2009, this presentation has been viewed almost four million times all around the world. The message itself is very powerful, however, it’s not an idea that hasn’t been heard before. What makes this presentation so powerful is the simple message he is getting across, and the straightforward and understandable manner in which he delivers it. Also note that he doesn’t use any slides, just a whiteboard where he creates a simple diagram of his opinion.
The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout – by Rick Rigsby
Here’s an example of a presentation given by a relatively unknown individual looking to inspire the next generation of graduates. Rick’s presentation is unique in many ways compared to the two above. Notably, he uses no visual prompts and includes a great deal of humour.
However, what is similar is the structure he uses. He first introduces his message that the wisest man he knew was a third-grade dropout. He then proceeds to deliver his main body of argument, and in the end, concludes with his message. This powerful speech keeps the viewer engaged throughout, through a mixture of heart-warming sentiment, powerful life advice and engaging humour.
As you can see from the examples above, and as it has been expressed throughout, a great presentation structure means analysing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart the audience with, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
By preparing a solid structure, and practising your talk beforehand, you can walk into the presentation with confidence and deliver a meaningful message to an interested audience.
It’s important for a presentation to be well-structured so it can have the most impact on your audience. An unstructured presentation can be difficult to follow and even frustrating to listen to. The heart of your speech are your main points supported by evidence and your transitions should assist the movement between points and clarify how everything is linked.
Research suggests that the audience remember the first and last things you say so your introduction and conclusion are vital for reinforcing your points. Essentially, ensure you spend the time structuring your presentation and addressing all of the sections.

- PRESENTATION SKILLS
Writing Your Presentation
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- What is a Presentation?
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Few of us feel entirely comfortable writing a presentation. There is something very daunting for many people about the process of moving your thoughts from your head to paper (or a series of slides on the computer).
However, there are things that you can do to help yourself. These include knowing your material well and taking time to consider what you want to say.
This page provides advice on how to write a presentation. It discusses the initial writing, and then also explains how to review and edit your work. This will help to ensure that your presentation is as effective as possible.
Before you start...
Before you start to write your presentation, you need certain information: the objective, the subject, and details of the audience, for example. For more about this, see our page on Preparing Your Presentation .
Based on the information you have gathered, you should also have started to develop your ideas and select the main points to include. For more about this, see our page on Organising Your Material .
Some basic starting points
There are two really important things to remember when starting to write a presentation:
1. Give your presentation an introduction, a main message, and a conclusion.
Some people summarise this as ‘say what you’re going to say, say it, then say what you’ve said’ .
However, that is not the whole story. Your introduction needs to ‘set the scene’ a bit and give a broad outline of what you are going to cover in your presentation. If you are using presentation software such as PowerPoint, this should be a single slide. Your conclusion needs to sum up and present your main message to your audience, probably again in a single slide.
If you are taking questions after your presentation, and you are using PowerPoint, you will probably have a slide up on the screen during questions. You could, of course, have a final slide that says something like “Thank you for listening, any questions?”, or gives your contact details.
However, you could also leave up a final slide that highlights your conclusions.
This will help to ensure that your key messages remain in the minds of your audience.
2. Think about using stories to get your message across
We are hard-wired by thousands of years of evolution to listen to stories. Stories helped us survive by reminding us about important behaviours. We therefore tend to remember them much better than dry lists of facts or bullet points.
It is much easier to work with this than ignore it.
There are two aspects of this.
First, you should try to think about your presentation as telling a story to your audience. What is the point that you are trying to make, and how can you best get it across?
Second, it is helpful to use stories as part of your presentation . For example, if you start by telling a story or anecdote, it will act as a ‘hook’ to draw in your audience. You can also use stories to illustrate each point you want to make. Of course, your story has to link to your main message, because you can pretty much guarantee that your audience will remember the story much longer than the conclusion!
Structuring Your Presentation
The structure and content of your presentation will of course be unique to you.
Only you can decide on the best way to present your messages. However, you might like to consider some standard presentation structures for inspiration:
1. Harnessing the Power of Three
In public speaking and rhetorical debate, as well as in much communication, three is a magic number. The brain finds it relatively easy to grasp three points at a time.
People find three points, ideas or numbers, easier to understand and remember than four or more.
You could therefore structure your presentation using the magic number of three.
For example, your presentation should have three main elements: the introduction, middle and conclusions. Within the main body of your presentation, divide your key message into three elements and then expand each of these points into three sub-points. If you are using a visual aid such as PowerPoint, limit the number of bullet points to three on each slide and expand on each of these as you go along.
What should you do if you have more than three points to make?
Reduce them until you don’t have more than three points!
Your audience will probably only remember three of your five or six points anyway—but which three? Do the work for them, and identify the three most important points, and leave the others out.
2. What, Why, How?
An alternative structure uses the questions “What?”, “Why?” and “How?” to communicate your message to the audience. In a way, this also harnesses the power of three, but is a special case for driving action.
“What?” identifies the key message you wish to communicate. Think about the benefit of your message for your audience. What will they gain, what can they do with the information, and what will the benefit be?
“Why?” addresses the next obvious question that arises for the audience . Having been told “what”, the audience will naturally then start to think “why should I do that?”, “why should I think that?” or “why should that be the case?”. Directly addressing the “why?” question in the next stage of your presentation means that you are answering these questions and your talk is following a natural route through the material. This will ensure that you have the audience on your side immediately.
“How?” is the final question that naturally arises in the audience’s mind . They want to know how they are going to achieve what you have just suggested. Try not to be too prescriptive here. Instead of telling people exactly how they should act on your message, offer suggestions as to how they can act, perhaps using examples.
You should try to back up what you say with evidence. You can use case studies, personal examples or statistics here, but try to ensure that you use them in the form of stories.
There is more about this on our page Presenting Data .
Editing Your Content
Once you have a first draft of your presentation, it is important to review and edit this.
This will help to ensure that it really does get your message across in the most effective way.
When editing presentation content, you should consider:
The language . Make sure that what you are saying will be clear to your audience. Remove any jargon and try to use plain English instead. If necessary, explain terms when you first use them.
Sentence structure . Use short sentences and keep the structure simple. Remember that you will be talking through your ideas and that the audience will be listening rather than reading.
The flow . Make sure that your presentation structure leads your audience through your ideas and helps them to draw your conclusion for themselves.
Use metaphors and stories to aid understanding and retention.
‘Hooks’ to get and hold the audience’s attention . Ensure that you have included several ‘hooks’ at various points in the presentation. This will help you to get and then keep the audience’s attention. These might be stories, or audience participation, or some alternative visual aids , such as a short video.
Check, and double check, for spelling and grammar . Make sure that any presentation slides or illustrations, titles, captions, handouts or similar are free from spelling mistakes.
Ideally, you should take a break from the presentation before editing so that you can look at your writing with a fresh pair of eyes.
You might also want to ask a friend or colleague to have a look, particularly at the flow and the language. If possible, ask someone who is not familiar with the material .
A final thought
The actual writing of your presentation is really the final stage of your preparation.
If you have done your homework, you will already be clear about the reason why you are presenting, the subject matter, and the main points you want to make. Actually putting it down on paper should therefore be relatively straightforward.
Continue to: Deciding the Presentation Method Preparing for a Presentation
See also: Organising the Presentation Material Working with Visual Aids Coping with Presentation Nerves Dealing with Questions
How to Write a Presentation Speech: A Step-by-Step Guide
Learn to craft an engaging presentation speech with our step-by-step guide on audience engagement, content structure, and effective delivery.
Step 1: Understand Your Audience
Step 2: define your purpose, step 3: research thoroughly, step 4: create an outline.
- Introduction : Introduce yourself, your topic, and your main thesis or the purpose of your speech.
- Body : Divide the body into several sections, each dedicated to a specific main point. Use bullet points to list out supporting details, such as data, anecdotes, and references.
- Conclusion : Summarize the main points and restate the importance of your topic. End with a strong call to action or a memorable closing thought.
Step 5: Write and Revise
Step 6: practice makes perfect, step 7: use visual aids wisely, step 8: prepare for q&a, create ppt using ai.
Just Enter Topic, Youtube URL, PDF, or Text to get a beautiful PPT in seconds. Use the bulb for AI suggestions.
character count: 0 / 6000 (we can fetch data from google)
upload pdf, docx, .png, .mp4
less than 2 min
How to Title a PowerPoint Presentation: For the Perfect First Impression
23 August 2024
How to Generate Presentation Ideas for School: A Complete Guide
What Is a Presentation Outline? A Complete Guide
How to Memorize a Presentation in One Night?
What is a Sales Presentation? Unpacking Its Role and Impact in Business
Real Estate Listing Presentation: Essential Points to Address for Success
When Giving a Presentation, What Is a Good Tactic for Engaging the Audience?
What to Include in an "All About Me" Presentation
22 August 2024
Stunning presentations in seconds with AI
Install MagicSlides app now and start creating beautiful presentations. It's free!

Get AI-Generated Presentations Ready in Seconds
Free AI PPT Tools

How To Write A Presentation: An Ultimate Guide
Table of Contents
Preparing a presentation can be a daunting experience. Standing in front of an audience to give a speech can be an even more overwhelming prospect. However, you are unlikely to get through university without having to create a presentation. Depending on your subject, instructors may require you to provide feedback from a group task or deliver the findings of a scientific experiment. Whatever the topic, you’ll be presenting to your tutor and fellow students. While preparing a presentation and making your case in front of them is not easy, especially if you’re not used to doing it, it is a good practice since many employers use presentations as part of the recruitment process.
How to Write a PowerPoint Presentation Successfully
Creating an excellent PowerPoint presentation is a skill that any professional must have, especially in the corporate and business world. The problem? It is very easy to get it wrong. From poor color choices to confusing slides, a bad PowerPoint slideshow can distract the audience from the awesome content. A PowerPoint presentation is like a poster presentation; only that the information is on computer slides rather than actual posters. It often accompanies and enhances oral presentations instead of serving as speaking notes. Well-designed slides used sparingly and with good timing can be brilliant. Heck, they can even make an otherwise good presentation awesome. Here are some tips to help you illustrate why your creative talents are the perfect ingredients for a killer presentation.
Use the 10-20-30 Rule
A PowerPoint slide should only have the main points. Guy Kawaski suggested the 10-20-30 rule to make presentations engaging and captivating. He says that a good presentation should not contain more than ten slides, shouldn’t last for more than 20 minutes, and the content should not be more than 30 points. But how do you make your texts lean on the slides? Draw relevant information from your narrative and feature only core ideas and points on slides. You can use the “6×6 technique” to avoid getting too wordy. This guideline suggests using no more than six bullet points or lines per slide with no more than six words per line.
Write an abstract for a Presentation
The purpose of an abstract is to highlight the most critical information in a piece of writing. However, a presentation abstract is different. Try to think of it as an invitation to a party. You want to create as much excitement and curiosity for your presentation as possible. Writing an abstract for a presentation requires the presented information to be more succinct. Unlike a typical abstract or executive summary, the presentation abstract should have less than 250 words and have a simplified and condensed breakdown. The abstract should come after your short bio.
Write A Presentation Outline
When preparing a presentation, there are various ways you can use it to share relevant ideas. One tool that helps presenters is a presentation outline – a synopsis of a talk or pitch. Presentation outlines help you organize your agenda and create a logical flow of thoughts in your script. They give you a clear path to transition your audience from your current status to where you want them to be. Follow these steps to create an outline for your presentation:
- Consider the purpose of your presentation
- Create a structure – introduction, main body, and conclusion
- Use an attention grabber
- Consider visual content
- Include a call to action
Use a Paper Writing Service
Writing presentations can be a stressful process. Students often struggle to get it right and need a guiding hand to help them create engaging and captivating slides. Luckily, CustomWritings presentation writing services that can take care of your PowerPoint presentations. Their team of writers can break down any topic to create slides precisely according to your custom instructions. Besides, the company offers presentation examples and other academic writing services, such as research papers, term papers, assignments, admission essays, and dissertations, at affordable prices across the board for all sorts of projects. No matter your academic level. Whether a Ph.D. or Master’s, you will always get personalized, original, quality, and professional papers at accommodating rates.
Stick to One Idea Per Slide
Like keeping slides virtually uncluttered, focusing on one key idea per slide can help your audience quickly follow along. Too many ideas on one slide can detract the audience from the significance of each idea. By featuring only one point per slide, you also give the idea room for visual impact. For instance, you can experiment with fonts and image sizes to deliver the desired effect.
Include Powerful Visuals
Adding visual elements to your presentation makes your deck more engaging and dynamic. However, the caveat is that visuals used as an afterthought can counter your ideas rather than complement them. Such visuals as nostalgic photos can appeal to the audience’s emotions in a way that a generic stock picture might not. Likewise, using eye-catching charts and graphs to simplify complex information instead of writing out a slew of statistics as text can keep your audience from getting overwhelmed with data. Remember that visual aids should complement your oral presentations, not repeat them or deliver the presentation for you.
Be Savvy with Design Details
A good design can make or break a presentation. If you haven’t got a budget for a designer, presentation tools, such as Canva and Visme, can help you make great slides. Firstly, use color consistently. Bright colors can dazzle, but too many can be off-putting. Use the colors most relevant to your message. Secondly, be consistent with the font. Consistent designs make your presentation look professional. Don’t switch from caps and lower case, Cosmic Sans to Times New Roman, or 10-to-18-point text size. Keep your on-screen text uniform for a more cohesive message. Lastly, format to precision. A wonky line on a slide or a badly pixelated graphic can put some people off, as it looks like you haven’t tried very hard, or worse, you just aren’t good enough. In a snapshot;
- Use color sparingly
- Use font consistently
- Format to perfection
Polish Several Times
Like your favorite shoes, a good presentation needs a few rounds of dusting before it’s all shiny and sparkly. Don’t be afraid to get messy. Arrange your ideas side-by-side and discover new connections that you didn’t see before. You should edit the slides ruthlessly. At first, you may have a considerable amount of information and struggle to get down six bullet points per slide. Edit thoroughly until you pair your message down to the bare essentials. You can also get a fresh pair of eyes to refine your presentation.
Final Thought about Presentation Writing
Written presentations are a powerful way to share ideas – if you create a deck that communicates your points clearly and effectively. Other communication dynamics, such as your oratory skills and body language, can influence your presentation’s success. Nonetheless, a well-written presentation is a resource that your audience can revisit long after you’ve shared it. By applying these PowerPoint presentation tips, you’ll be in a stronger position to inform, entertain, inspire, and activate your audience through a clear message.
Join the thousands who have sharpened their business writing skills with our award winning courses.
Copyright © 2024 Businesswritingblog.com.
Ready to get started?
- Inspiration
23 presentation examples that really work (plus templates!)

- 30 Mar 2023
To help you in your quest for presentation greatness, we’ve gathered 23 of the best business presentation examples out there. These hand-picked ideas range from business PowerPoint presentations, to recruitment presentations, and everything in between.
As a bonus, several of our examples include editable video presentation templates from Biteable .
Biteable allows anyone to create great video presentations — no previous video-making skills required. The easy-to-use platform has hundreds of brandable templates and video scenes designed with a business audience in mind. A video made with Biteable is just what you need to add that wow factor and make an impact on your audience.
Create videos that drive action
Activate your audience with impactful, on-brand videos. Create them simply and collaboratively with Biteable.
Video presentation examples
Video presentations are our specialty at Biteable. We love them because they’re the most visually appealing and memorable way to communicate.
1. Animated characters
Our first presentation example is a business explainer video from Biteable that uses animated characters. The friendly and modern style makes this the perfect presentation for engaging your audience.
Bonus template: Need a business video presentation that reflects the beautiful diversity of your customers or team? Use Biteable’s workplace scenes . You can change the skin tone and hair color for any of the animated characters.
2. Conference video
Videos are also ideal solutions for events (e.g. trade shows) where they can be looped to play constantly while you attend to more important things like talking to people and handing out free cheese samples.
For this event presentation sample below, we used bright colours, stock footage, and messaging that reflects the brand and values of the company. All these elements work together to draw the attention of passers-by.
For a huge selection of video presentation templates, take a look at our template gallery .

Business PowerPoint presentation examples
Striking fear into the hearts of the workplace since 1987, PowerPoint is synonymous with bland, boring presentations that feel more like an endurance test than a learning opportunity. But it doesn’t have to be that way. Check out these anything-but-boring business PowerPoint presentation examples.
3. Design pointers
This PowerPoint presentation takes a tongue-in-cheek look at how the speakers and users of PowerPoint are the problem, not the software itself.
Even at a hefty 61 slides, the vintage theme, appealing colors, and engaging content keep the viewer interested. It delivers useful and actionable tips on creating a better experience for your audience.
Pixar, as you’d expect, redefines the meaning of PowerPoint in their “22 Rules for Phenomenal Storytelling”. The character silhouettes are instantly recognizable and tie firmly to the Pixar brand. The bright colour palettes are carefully chosen to highlight the content of each slide.
This presentation is a good length, delivering one message per slide, making it easy for an audience to take notes and retain the information.
Google slides examples
If you’re in business, chances are you’ll have come across slide decks . Much like a deck of cards, each slide plays a key part in the overall ‘deck’, creating a well-rounded presentation.
If you need to inform your team, present findings, or outline a new strategy, slides are one of the most effective ways to do this.
Google Slides is one of the best ways to create a slide deck right now. It’s easy to use and has built-in design tools that integrate with Adobe, Lucidchart, and more. The best part — it’s free!
5. Teacher education
Here’s a slide deck that was created to educate teachers on how to use Google Slides effectively in a classroom. At first glance it seems stuffy and businessy, but if you look closer it’s apparent the creator knows his audience well, throwing in some teacher-friendly content that’s bound to get a smile.
The slides give walkthrough screenshots and practical advice on the different ways teachers can use the software to make their lives that little bit easier and educate their students at the same time.
6. Charity awareness raiser
This next Google slide deck is designed to raise awareness for an animal shelter. It has simple, clear messaging, and makes use of the furry friends it rescues to tug on heartstrings and encourage donations and adoptions from its audience.
Pro tip: Creating a presentation is exciting but also a little daunting. It’s easy to feel overwhelmed — especially if the success of your business or nonprofit depends on it.
Prezi presentation examples
If you haven’t come across Prezi , it’s a great alternative to using static slides. Sitting somewhere between slides and a video presentation, it allows you to import other content and add motion to create a more engaging viewer experience.
7. Red Bull event recap
This Prezi was created to document the Red Bull stratosphere freefall stunt a few years ago. It neatly captures all the things that Prezi is capable of, including video inserts and the zoom effect, which gives an animated, almost 3D effect to what would otherwise be still images.
Prezi has annual awards for the best examples of presentations over the year. This next example is one of the 2018 winners. It was made to highlight a new Logitech tool.
8. Logitech Spotlight launch
What stands out here are the juicy colors, bold imagery, and the way the designer has used Prezi to its full extent, including rotations, panning, fades, and a full zoom out to finish the presentation.

Sales presentation examples
If you’re stuck for ideas for your sales presentation, step right this way and check out this video template we made for you.
9. Sales enablement video presentation
In today’s fast-paced sales environment, you need a way to make your sales enablement presentations memorable and engaging for busy reps. Sales enablement videos are just the ticket. Use this video presentation template the next time you need to present on your metrics.
10. Zuroa sales deck
If you’re after a sales deck, you can’t go past this example from Zuora. What makes it great? It begins by introducing the worldwide shift in the way consumers are shopping. It’s a global phenomenon, and something we can all relate to.
It then weaves a compelling story about how the subscription model is changing the face of daily life for everyone. Metrics and testimonials from well-known CEOs and executives are included for some slamming social proof to boost the sales message.
Pitch presentation examples
Pitch decks are used to give an overview of business plans, and are usually presented during meetings with customers, investors, or potential partners.
11. Uber pitch deck
This is Uber’s original pitch deck, which (apart from looking a teensy bit dated) gives an excellent overview of their business model and clearly shows how they intended to disrupt a traditional industry and provide a better service to people. Right now, you’re probably very grateful that this pitch presentation was a winner.
You can make your own pitch deck with Biteable, or start with one of our video templates to make something a little more memorable.
12. Video pitch template
This video pitch presentation clearly speaks to the pains of everyone who needs to commute and find parking. It then provides the solution with its app that makes parking a breeze.
The video also introduces the key team members, their business strategy, and what they’re hoping to raise in funding. It’s a simple, clear pitch that positions the company as a key solution to a growing, worldwide problem. It’s compelling and convincing, as a good presentation should be.
13. Fyre Festival pitch deck
The most epic example of a recent pitch deck is this one for Fyre Festival – the greatest event that never happened. Marvel at its persuasion, gasp at the opportunity of being part of the cultural experience of the decade, cringe as everything goes from bad to worse.
Despite the very public outcome, this is a masterclass in how to create hype and get funding with your pitch deck using beautiful imagery, beautiful people, and beautiful promises of riches and fame.
Business presentation examples
Need to get the right message out to the right people? Business presentations can do a lot of the heavy lifting for you.
Simply press play and let your video do the talking. No fumbling your words and sweating buckets in front of those potential clients, just you being cool as a cucumber while your presentation does the talking.
Check out two of our popular templates that you can use as a starting point for your own presentations. While they’re business-minded, they’re definitely not boring.
14. Business intro template
Modern graphics, animations, and upbeat soundtracks keep your prospects engaged as they learn about your business, your team, your values, and how you can help them.
15. Business explainer template
Research presentation examples.
When you’re giving a more technical presentation such as research findings, you need to strike the perfect balance between informing your audience and making sure they stay awake.
As a rule, slides are more effective for research presentations, as they are used to support the speaker’s knowledge rather can capture every small detail on screen.
With often dry, complex, and technical subject matter, there can be a temptation for presentations to follow suit. Use images instead of walls of text, and keep things as easy to follow as possible.
16. TrackMaven research deck
TrackMaven uses their endearing mascot to lighten up this data-heavy slide deck. The graphs help to bring life to their findings, and they ensure to only have one bite-size takeaway per slide so that viewers can easily take notes.
17. Wearable tech research report
Obviously, research can get very researchy and there’s not a lot to be done about it. This slide deck below lays out a ton of in-depth information but breaks it up well with quotes, diagrams, and interesting facts to keep viewers engaged while it delivers its findings on wearable technology.
Team presentation examples
Motivating your team can be a challenge at the best of times, especially when you need to gather them together for….another presentation!
18. Team update template
We created this presentation template as an example of how to engage your team. In this case, it’s for an internal product launch. Using colorful animation and engaging pacing, this video presentation is much better than a static PowerPoint, right?
19. Officevibe collaboration explainer
This short slide deck is a presentation designed to increase awareness of the problems of a disengaged team. Bright colors and relevant images combine with facts and figures that compel viewers to click through to a download to learn more about helping their teams succeed.
Recruitment presentation examples
Recruiting the right people can be a challenge. Presentations can help display your team and your business by painting a dynamic picture of what it’s like to work with you.
Videos and animated slides let you capture the essence of your brand and workplace so the right employees can find you.
20. Company culture explainer
If you’re a recruitment agency, your challenge is to stand out from the hundreds of other agencies in the marketplace.
21. Kaizen culture
Showcasing your agency using a slide deck can give employers and employees a feel for doing business with you. Kaizen clearly displays its credentials and highlights its brand values and personality here (and also its appreciation of the coffee bean).
Explainer presentation examples
Got some explaining to do? Using an explainer video is the ideal way to showcase products that are technical, digital, or otherwise too difficult to explain with still images and text.
Explainer videos help you present the features and values of your product in an engaging way that speaks to your ideal audience and promotes your brand at the same time.
22. Product explainer template
23. lucidchart explainer.
Lucidchart does a stellar job of using explainer videos for their software. Their series of explainers-within-explainers entertains the viewer with cute imagery and an endearing brand voice. At the same time, the video is educating its audience on how to use the actual product. We (almost) guarantee you’ll have more love for spiders after watching this one.
Make a winning video presentation with Biteable
Creating a winning presentation doesn’t need to be difficult or expensive. Modern slide decks and video software make it easy for you to give compelling presentations that sell, explain, and educate without sending your audience to snooze town.
For the best online video presentation software around, check out Biteable. The intuitive platform does all the heavy lifting for you, so making a video presentation is as easy as making a PowerPoint.
Use Biteable’s brand builder to automatically fetch your company colors and logo from your website and apply them to your entire video with the click of a button. Even add a clickable call-to-action button to your video.
Share your business presentation anywhere with a single, trackable URL and watch your message turn into gold.
Make stunning videos with ease.
Take the struggle out of team communication.
Try Biteable now.
- No credit card required
- No complicated design decisions
- No experience necessary
Home Blog Presentation Ideas How to Write a Presentation Script
How to Write a Presentation Script

Delivering a successful presentation is a combination of a confident speech and professional-quality graphics. The first element is sometimes neglected, as presenters rely mostly on the slides and add an improvisation element to the speech. Truth is, if you aim to hone your presentation skills, you need to work on the speech. And for that to be a powerful asset, the answer is to learn how to write an effective presentation script.
This article will detail how to create a presentation script, which elements it should contain, how to relate the script to the presenter’s notes, and much more.
Table of Contents
What is a Presentation Script
How do you start a presentation script, how do you write a presentation script, how to connect a presentation script with presenter notes, recommended ppt templates to write a presentation script, final words.
A presentation script is a written guide that outlines what a speaker will say during a presentation. It includes the key points, transitions, and supporting details needed to communicate the message clearly and effectively. The script helps the speaker stay on track, ensuring the presentation is organized, concise, and delivered within the allotted time. It often integrates cues for visual aids and other presentation elements.

Defining the Purpose and Objective
Every effective presentation script starts with clearly understanding its purpose and objectives. Defining these elements early ensures your script remains focused, relevant, and aligned with your desired outcomes.
Your core message is the central idea you want your audience to take away from your presentation. It should be clear, concise, and memorable. To define your core message, ask yourself:
- What is the one thing I want my audience to remember?
- Why is this message important?
- How does this message benefit my audience?
Once you have a clear core message, everything in your script for a speech should support and reinforce it. This focus will help you avoid straying into irrelevant topics and ensure your presentation remains cohesive.
Next, the presenter should establish clear objectives for the talk. Objectives must be specific, measurable outcomes you want to achieve with your presentation. They give you a clear direction and help you measure the success of your presentation. Objectives can be:
- Informational: Educate the audience on a particular topic.
- Persuasive: Convince the audience to adopt a viewpoint or take a specific action.
- Motivational: Inspire the audience to feel or act in a certain way.
- Instructional: Teach the audience how to do something.
For example, suppose your core message is about the importance of cybersecurity. In that case, your objectives might include informing the audience about common threats, persuading them to adopt better security practices, and instructing them on implementing them.
Check our article on SMART goal setting for a practical approach to defining measurable goals.
Aligning the Script with Desired Outcomes
Once you’ve defined your core message and objectives, your script should be structured to achieve these outcomes. This involves:
- Prioritizing content: Focus on the information and arguments directly contributing to your objectives.
- Building logical flow: Ensure that each section of your presentation leads naturally to the next, creating a narrative that reinforces your core message.
- Incorporating calls to action: If your objective is to persuade or motivate, include clear, actionable steps your audience can take after the presentation.
By defining the purpose and objectives of your presentation script, you set the stage for a focused, effective, and impactful delivery.
In this section, we’ll explore section by section how to write a presentation script. The following image is a guideline of presentation script examples on how to create icebreakers for each section

Crafting a Compelling Introduction
The introduction is your opportunity to capture the audience’s attention and set the tone for the rest of the presentation. It should be engaging and clearly overview what the audience can expect.
If you are wondering how to start a presentation , key elements of a strong introduction include:
- Opening hook: Start with a statement, question, or anecdote that grabs the audience’s attention. This could be a surprising statistic, a relevant quote, or a provocative question.
- Purpose statement: Clearly state the purpose of your presentation and what you hope to achieve. This helps the audience understand why they should care about your words.
- Agenda overview: Briefly outline the main points you will cover. This will give the audience a roadmap of what to expect and help them follow along.
Let’s say your presentation is about digital marketing trends. In that case, you might start with a surprising statistic about the growth of AI technology usage, followed by a statement about the importance of staying ahead of digital trends, and then outline the specific trends you will discuss in an upcoming slide.

Organizing the Body of the Script
The body of your script is where you present your main content. It should be organized logically, with each section building on the previous one to reinforce your core message.
Break down your content into clear, manageable sections. Each section should cover a specific point or idea. Smooth transitions between sections help maintain the flow of your presentation and keep the audience engaged . Phrases like “building on that idea,” “another important factor,” or “let’s now shift our focus to” can help guide the audience through your presentation.
Use data, examples, case studies , and visuals to support your points. This will strengthen your argument and make your presentation more engaging.
For instance, in a presentation about social media’s impact on consumer behavior, you might organize the body into sections on social media usage trends, the psychology of social media influence, and case studies of successful social media campaigns.

Engaging the Audience with Stories and Examples
One of the most effective ways to make your presentation engaging and relatable is by incorporating stories and examples. These elements help illustrate your points, making them more memorable and impactful.
Consider the following strategies:
- Use personal anecdotes: Sharing personal experiences related to your topic can help establish a connection with the audience and make your presentation more relatable.
- Include case studies: Real-world examples or case studies can help illustrate how the concepts you’re discussing apply in practice. This is especially effective when presenting to a business or professional audience.
- Tell a story: Structure part of your presentation as a narrative, with a clear beginning, middle, and end. Stories are inherently engaging and can make complex information more digestible.
You can learn more about this technique with our article on storytelling for presentations .
Developing a Memorable Conclusion
The conclusion is your final opportunity to reinforce your core message and leave a lasting impression on your audience.
A strong conclusion should:
- Summarize key points: Recap the main points of your presentation to reinforce them in the audience’s mind.
- Reiterate the core message: Restate your core message in a way that resonates with the audience and underscores its importance.
- End with impact: Conclude with a powerful statement, call to action, or thought-provoking question that leaves the audience with something to think about or do.
If your presentation was about the importance of innovation in business, you might conclude by summarizing its key benefits, restating that innovation is crucial for long-term success, and ending with a call to action for the audience to start thinking about how they can innovate in their roles.

Get more insights on how to end a presentation with our article.
Although the presentation script is a fantastic resource for preparing your presentation and also for rehearsal, presenters cannot bring lengthy text pages with them and start reading if they feel lost. This is where presenter notes come in handy, and in this section, we’ll learn how to turn the presentation script into presenter notes.
The first step in this process is to go through the detailed script a couple of times, highlighting the main ideas, data, and messages to convey to the audience. You can follow the process as with meeting notes and apply the strategies explained in that article.
Now, we need to condense the information into simpler sentences, direct phrases, or keywords that trigger memory recall. These phrases will be added to the slides in the format of speaker notes linked to each slide. It’s crucial to mark the transitions from one topic to another in the presentation so we can articulate the speech or remember to emphasize a point.
Remember, if we suddenly need to include last-minute details, we can use visual cues or a printed version of our slides with extra handwritten notes.
Before we conclude this article, we want to recommend some PowerPoint templates that can help the presentation script creation process, especially for team collaboration, where the presentation goes through multiple iterations. Remember these designs also serve as Google Slides templates .
1. 6 Step Creative Timeline Diagram for Presentation Scripts

Say you need to create a sample script for a presentation or work with your team for a department presentation: this is where this best PPT template is beneficial. We can summarize processes or points that we intend the presentation to cover into six actionable steps that can be discussed within the team. The icons included help us to connect concepts with the steps we’re describing.
Use This Template
2. Product Timeline Script of Speech PPT Template

In sales and product presentations, we need to contextualize the dates on which we expect things to happen. By using this timeline PPT template as a visual aid, presenters can carry a printed version or digital version on another device to remind themselves of the milestones that a product or service is due in the near future.
3. The Presentation Experience Script PowerPoint Template

Although this template is tailored to sales presentations, this slide deck is ideal for writing a recap of the presentation script. You can add facts, questions, numeric data, and more.
4. Steps & Stairs Diagram Presentation Script Google Slides Template

This diagram template for PowerPoint and Google Slides is a highly visual 3D aid intended for defining the steps to write the script or to present processes. Use this staircase design template to summarize key information about your presentation speech.
Creating a detailed, professional presentation script doesn’t have to be a daunting process. As long as we understand the basis of how to structure what we intend to say, questions and answers about which content to include shall arise.
Follow the steps shown in this article and you will master the process to create your own presentation scripts in no time.
Like this article? Please share
Presentation Skills, Speech Filed under Presentation Ideas
Related Articles

Filed under Presentation Ideas • October 23rd, 2024
Formal vs Informal Presentation: Understanding the Differences
Learn the differences between formal and informal presentations and how to transition smoothly. PPT templates and tips here!

Filed under Presentation Ideas • October 3rd, 2024
Icebreaker Questions for Presentations: Engaging Your Audience from the Start
Presentations are not just about conveying information; they are about connecting with your audience, sparking interest, and fostering an environment conducive to learning and collaboration. One of the most effective tools to achieve this is using icebreaker questions. These questions serve to “break the ice” by easing tension, encouraging participation, and building rapport among participants, […]
Filed under Business • October 1st, 2024
How to Set Presentation Skills on a Resume
Discover the best ways to highlight your presentation skills on a resume, helping you stand out as a strong communicator and leader during job applications.
Leave a Reply
27 Presentation Examples That Engage, Motivate & Stick
Browse effective professional business presentation samples & templates. Get great simple presentation examples with perfect design & content beyond PowerPoint.
7 minute read

helped business professionals at:

Short answer
What makes a good presentation.
A good presentation deck excels with a clear, engaging narrative, weaving information into a compelling story. It combines concise, relevant content with visually appealing design to ensure simplicity and impact.
Personalizing the story to resonate with the audience's interests also enhances engagement and understanding.
Let’s face it - most slides are not interesting - are yours?
We've all been there—trapped in a never-ending session of mind-numbing slides, with no hope in sight. It's called "Death by PowerPoint," and it's the silent killer of enthusiasm and engagement. But fear not! You're a short way from escaping this bleak fate.
We've curated perfect presentation examples, crafted to captivate and inspire., They will transform your slides from yawn-inducing to jaw-dropping. And they’re all instantly usable as templates.
Prepare to wow your audience, command the room, and leave them begging for more!
What makes a bad presentation?
We've all sat through them, the cringe-worthy presentations that make us want to reach for our phones or run for the hills. But what exactly pushes a presentation from mediocre to downright unbearable? Let's break it down:
Lack of clarity: When the presenter's message is buried in a heap of confusing jargon or irrelevant details, it's hard to stay focused.
Poor visuals: Low-quality or irrelevant images can be distracting and fail to support the main points.
Overloaded slides: Too much text or clutter on a slide is overwhelming and makes it difficult to grasp the key ideas.
Monotonous delivery: A presenter who drones on without variation in tone or pace can quickly put their audience to sleep.
No connection: Failing to engage with the audience or tailor the presentation to their needs creates a disconnect that stifles interest.
What makes an exceptional presentation?
A clear structure set within a story or narrative: Humans think in stories. We relate to stories and we remember stories, it’s in our genes. A message without a story is like a cart full of goods with no wheels.
Priority and hierarchy of information: Attention is limited, you won’t have your audience forever, 32% of readers bounce in the first 15 seconds and most don’t make it past the 3rd slide. Make your first words count. They will determine whether your audience sticks around to hear the rest.
Interactive content: Like 99% of us, you’ve learned that presentation = PowerPoint. But that’s the past, my friend. PowerPoint is inherently static, and while static slides can be really beautiful, they are all too often really boring. Interactive slides get the readers involved in the presentation which makes it much more enjoyable.
Wanna see the actual difference between static and interactive slides? Here’s an example. Which one would you lean into?

Get started with business presentation templates
We have quite a few presentation examples to show you further down the page (all of them creative and inspiring), but if you’re itching to start creating your first interactive presentation I don’t blame you.
You can grab a presentation template that you like right here, right now and get started on your best presentation yet, or you can check out our perfect presentation examples and get back to your template later…
Business presentations by type and use
The arena of business presentations is deep and wide. You can easily get lost in it. But let us be your guide in the business document jungle.
Below is a quick bird’s eye view of the main presentation types, what each type is used for, where it’s situated in the marketing and sales funnel, and how you should measure it.
Let's dive right in.
Perfect presentation examples to inspire you
Feeling ready to unleash your presentation skills? Hold on to your socks, because we've got a lineup of battle-tasted business presentation samples that'll knock ’em right off!
From cutting-edge design to irresistible storytelling, these effective business presentations exemplify best practices and are primed to drive results.
See exceptional presentations by type:
Report presentations
Effective report presentations distil complex data into clear insights, essential for informed decision-making in business or research. The key lies in making data approachable and actionable for your audience.
Meta interactive corporate report
SNC DeserTech long-form report
Business report
Pitch deck presentations
Pitch deck presentations are your storytelling canvas to captivate investors, blending inspiring ideas with solid data. It's essential to create a narrative that showcases potential and practicality in equal measure.
Cannasoft investment pitch deck
Y Combinator pitch deck
Investor pitch deck
One-pager presentations are a masterclass in brevity, offering a snapshot of your product or idea. This concise format is designed to spark interest and invite deeper engagement.
Yotpo SaaS product one-pager
Octopai outbound sales one-pager
Startup one-pager
Sales deck presentations
Serving as a persuasive tool to convert prospects into customers, sales deck presentations emphasize product benefits and solutions. The goal is to connect with your audience's needs and present a compelling solution.
ScaleHub sales deck
Deliveright logistics sales deck
AI sales deck
Product marketing presentations
Product marketing presentations are a strategic showcase, introducing a new product or feature to the market with a focus on its unique value proposition. It's not just about listing features; it's about weaving a narrative that connects these features to real customer needs and desires.
Mayku physical product deck
Matics digital product brochure
Modern product launch
Business proposal presentations
At the heart of closing deals, business proposal presentations combine persuasive argumentation with clear data. Articulating the unique value proposition and the mutual benefits of the proposal is key.
WiseStamp personalized proposal deck
RFKeeper retail proposal deck
General business proposal
White papers
White paper presentations are an authoritative deep dive into a specific problem and its solution. Providing well-researched, informative content educates and influences your audience, showcasing your expertise.
Drive automotive research white paper
Executive white paper
Business white paper
Case studies
Case study presentations use real-world success stories as a storytelling tool. Building trust by showcasing how your product or service effectively solved a client's problem is their primary function.
Boom25 interactive case study deck
Light mode case study
Business case study
Business plan presentations
Business plan presentations lay out your strategic roadmap, crucial for securing funding or internal buy-in. Clearly articulating your vision, strategy, and the practical steps for success is vital for a successful deck.
Start-up business plan
Business plan one-pager
Light mode business plan
Best presentation content examples
The secret sauce for a business presentation that leaves a lasting impression lies in delivering your content within a story framework.
3 presentation content examples that captivate and inspire the audience:
1. Inspirational story:
An emotional, relatable story can move hearts and change minds. Share a personal anecdote, a customer success story, or an account of overcoming adversity to create a deep connection with your audience.
Remember, vulnerability and authenticity can be your greatest assets.
2. Mystery - Gap theory:
Keep your audience on the edge of their seats by building suspense through the gap theory. Start by presenting a problem, a puzzle, or a question that leaves them craving the answer. Gradually reveal the solution, creating anticipation and excitement as you guide them through the resolution.
3. The Hero's Journey:
Transform your presentation into an epic adventure by incorporating the classic hero's journey narrative.
Introduce a "hero" (your audience), and introduce yourself or your company as a “guide” that will take them on a transformative journey filled with challenges, lessons, and triumphs.
This powerful storytelling structure helps your audience relate to your message and stay engaged from start to finish.
Here’s a great video on how to structure an effective sales story:

Best presentation document formats
Selecting the right format for your business presentation plays a huge part in getting or losing engagement. Let's explore popular presentation document formats, each with its own unique advantages and disadvantages.
PowerPoint : Microsoft's PowerPoint is a tried-and-true classic, offering a wide array of design options and features for crafting visually appealing static presentations.
Google Slides : For seamless collaboration and real-time editing, Google Slides is the go-to choice. This cloud-based platform allows you to create static presentations that are accessible from anywhere.
Keynote : Apple's Keynote offers a sleek, user-friendly interface and stunning design templates, making it a popular choice for crafting polished static presentations on Mac devices .
PDF: PDF is ideal for sharing static presentations that preserve their original layout, design, and fonts across different devices and operating systems.
Prezi : Break free from traditional slide-based presentations with Prezi's dynamic, zoomable canvas. Prezi allows you to create interactive decks, but it follows a non-chronological presentation format, so it may take some time to get the hang of it.
Storydoc : Elevate your presentations with Storydoc's interactive, web-based format. Transform your static content into immersive, visually rich experiences that captivate and inspire your audience.
Best tool to create a perfect presentation
There are countless presentation software options. From legacy tools like PowerPoint or Google Slides to more modern design tools such as Pitch or Canva.
If you want to create pretty presentations any of these tools would do just fine. But if you want to create unforgettable, interactive experiences , you may want to consider using the Storydoc interactive presentation maker instead.
Storydoc specializes in storytelling. You get special storytelling slides built to help you weave your content into a compelling narrative.
You can do better than “pretty” - you can make a presentation that engages, motivates and sticks.

Hi, I'm Dominika, Content Specialist at Storydoc. As a creative professional with experience in fashion, I'm here to show you how to amplify your brand message through the power of storytelling and eye-catching visuals.
Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live.
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.

Create your best presentation to date.
Stop losing opportunities to ineffective presentations. Your new amazing deck is one click away!
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
by Carmine Gallo

Summary .
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
Partner Center
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Sonja Stetzler
Effective Connecting
October 25, 2011 By Sonja Stetzler
Oral Presentations Vs Written Presentation

Communication – the way you speak, the way you write, even the way you carry yourself each carry a great deal of power. They each allow you to reach an audience and deliver a message. When you are called upon to deliver a presentation you will find yourself faced with a decision. Will you deliver a written or oral presentation? While both can be powerful, there are quite a few differences in the way that they are affected through communication.
A written presentation tends to be rather direct and to the point. It is typically very objective in nature, highly organized, and yet may seem to be rather impersonal. When you plan a written presentation it will often require careful planning and may rely on rote listing of information in order to achieve its message.
You will find that an oral presentation may be altogether different. Oral communication is by nature a very dynamic method for transferring information between individuals and/or groups. Rather than relying on the more rigid rules of language, oral presentations can allow you to connect with your audience using everyday language.
Holding an oral presentation either live or through video allows you to incorporate non-verbal communication to help engage your audience on a deeper level. Rather than simply relying on the written word to feed out information, you can achieve a much more conversational feel with a softer tone. Oral presentations can be subjective in nature and may allow you to truly share your personal feelings on the subject matter.
Another bonus that oral presentations offer is that you may clarify points that don’t quite come across properly the first time through. You can also correct mistakes at the time you make them unlike those made in written presentations which may tend to be intractable.
You should always keep in mind that there may always be occasions when written presentations could be required; however, oral presentations offer you a level of power and control over the message and your connection with the audience that is second to none. In the end that is what effective connecting is all about!
Share the post "Oral Presentations Vs Written Presentation"
Transform your Presentations
20 Great Examples of PowerPoint Presentation Design [+ Templates]
Updated: August 06, 2024
Published: May 24, 2010
When it comes to PowerPoint presentation design, there's no shortage of avenues you can take.

While all that choice — colors, formats, visuals, fonts — can feel liberating, it‘s important that you’re careful in your selection as not all design combinations add up to success.
In this blog post, I’m sharing some of my favorite PowerPoint tips and templates to help you nail your next presentation.
Table of Contents
What makes a good PowerPoint presentation?
Powerpoint design ideas, best powerpoint presentation slides, good examples of powerpoint presentation design.

10 Free PowerPoint Templates
Download ten free PowerPoint templates for a better presentation.
- Creative templates.
- Data-driven templates.
- Professional templates.
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
In my opinion, a great PowerPoint presentation gets the point across succinctly while using a design that doesn't detract from it.
Here are some of the elements I like to keep in mind when I’m building my own.
1. Minimal Animations and Transitions
Believe it or not, animations and transitions can take away from your PowerPoint presentation. Why? Well, they distract from the content you worked so hard on.
A good PowerPoint presentation keeps the focus on your argument by keeping animations and transitions to a minimum. I suggest using them tastefully and sparingly to emphasize a point or bring attention to a certain part of an image.
2. Cohesive Color Palette
I like to refresh my memory on color theory when creating a new PowerPoint presentation.
A cohesive color palette uses complementary and analogous colors to draw the audience’s attention and help emphasize certain aspects at the right time.

Image source
Mesmerize your audience by adding some neon colors and effects to your PowerPoint slides. Adding pops of color to your presentation will create visual interest and keep your audience engaged.
What I like: Neon will add personality and depth to your presentation and will help the information you're providing stand out and be more memorable.
2. Use an interesting background image.

Do you have some interesting nature photos from a recent road trip? Or maybe a holiday passed, and you have gorgeous photos to share? If so, consider incorporating them into your PowerPoint.
What I like: PowerPoints don't have to be stuffy and boring. They can be fun and a unique or interesting background will enhance the experience of your presentation.
3. Or be minimal.

Have you ever heard of K.I.S.S.? Not the band! I mean, Keep It Simple, Sweetheart. If you're worried too many colors or visuals could take attention away from the message of your presentation, consider going minimal.
Pro tip: Stick to no more than three colors if you're going for a minimalist design in your slides.
4. Incorporate illustrations.

Illustrations are a great way to highlight or break down a point in your presentation. They can also add a bit of whimsy and fun to keep viewers engaged.
5. Use all caps.

Using all capital letters can draw your audience's eyes to where you need them, helping cement your message in their minds. It can also just be aesthetically pleasing.
Pro tip: If you choose to use all capital letters, use varying fonts so readers can tell which information is important and which are supporting details.
6. Alternate slide layouts
You don't want readers to grow bored with your presentation. So, to retain visual interest, use alternating slide layouts. The example above shows PowerPoint slides alternating between vertical and horizontal layouts.
This keeps things interesting and ensures your presentation isn't monotonous.
7. Inject a little humor.
Humor is a great way to drive a point home and help people remember the information you're presenting. People remember a good joke, so if you have a funny pun to connect to a concept in a presentation, why not use it in a slide?
Pro tip: Remember you're in a professional setting, so keep your jokes appropriate. If you're worried a joke can get you a meeting with HR, then keep it to yourself.
8. Use duotones.

Duotones (or gradience) can take the aesthetic of your PowerPoint to new levels. They can provide a calming energy to your presentation and make viewers feel relaxed and eager to stay focused.
9. Include printed materials.
Let's say you have a PowerPoint you're proud of, but you want to go that extra mile to ensure your audience understands the material. A great way to do this would be to supplement your presentation with printed materials, as such as:
- Pamphlets
- Printed slides
- Short quizzes on the material
10. Keep it to one chart or graph per slide.
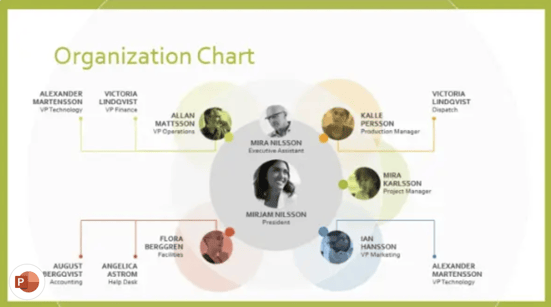
This is both a design example and a warning. Graphs and charts are an excellent way of displaying quantitative data in a digestible format.
However, you should have no more than one graph or chart per slide so your presentation doesn't get too confusing or muddled.
11. Use a large font.

Just like capital letters, a large font will help your shift your audience's focus to key points in your presentation.
Pro tip: You can combine large fonts and capital letters to boost its effectiveness.
12. Include videos.
Embedding a video into your PowerPoint can help you expand on a point or effectively break down a complex topic. You can either embed a video from a platform like YouTube or TikTok or use HubSpot's Clip Creator to make your own.
Pro tip: Try to keep videos short, like, under a minute, and don't use more than one or two.
13. Use GIFs.
GIFs add more visual interest, and they can be a great way to add humor or personal touch to your PowerPoint presentation.
14. Use contrasting colors when comparing two ideas or arguments.

Contrasting colors can convey the difference between two opposing thoughts or arguments in a way that is visually appealing.
15. Add a touch of nature.

If you want your presentation to exude a calming energy to your audience, including images of trees, flowers, and natural landscapes can do the trick.
PowerPoint Theme Ideas
Atlas (theme).
Covering a more creative subject for a younger or more energetic audience? I’d recommend using the cover slide design below. Its vibrant red color blocks and fun lines will appeal to your audience.

This simplistic presentation example employs several different colors and font weights, but instead of coming off as disconnected, the varied colors work with one another to create contrast and call out specific concepts.
What I like: The big, bold numbers help set the reader's expectations, as they clearly signify how far along the viewer is in the list of tips.
10. “Pixar's 22 Rules to Phenomenal Storytelling,” Gavin McMahon
This presentation by Gavin McMahon features color in all the right places. While each of the background images boasts a bright, spotlight-like design, all the characters are intentionally blacked out.
What I like: This helps keep the focus on the tips, while still incorporating visuals. Not to mention, it's still easy for me to identify each character without the details. (I found you on slide eight, Nemo.)
11. “Facebook Engagement and Activity Report,” We Are Social
Here's another great example of data visualization in the wild.
What I like: Rather than displaying numbers and statistics straight up, this presentation calls upon interesting, colorful graphs, and charts to present the information in a way that just makes sense.
12. “The GaryVee Content Model,” Gary Vaynerchuk
This wouldn‘t be a true Gary Vaynerchuk presentation if it wasn’t a little loud, am I right?
What I like: Aside from the fact that I love the eye-catching, bright yellow background, Vaynerchuk does a great job of incorporating screenshots on each slide to create a visual tutorial that coincides with the tips. He also does a great job including a visual table of contents that shows your progress as you go .
13. “20 Tweetable Quotes to Inspire Marketing & Design Creative Genius,” IMPACT Branding & Design
We‘ve all seen our fair share of quote-chronicling presentations but that isn’t to say they were all done well. Often the background images are poor quality, the text is too small, or there isn't enough contrast.
Well, this professional presentation from IMPACT Branding & Design suffers from none of said challenges.
What I like: The colorful filters over each background image create just enough contrast for the quotes to stand out.
14. “The Great State of Design,” Stacy Kvernmo
This presentation offers up a lot of information in a way that doesn't feel overwhelming.
What I like: The contrasting colors create visual interest and “pop,” and the comic images (slides 6 through 12) are used to make the information seem less buttoned-up and overwhelming.
15. “Clickbait: A Guide To Writing Un-Ignorable Headlines,” Ethos3
Not going to lie, it was the title that convinced me to click through to this presentation but the awesome design kept me there once I arrived.
What I like: This simple design adheres to a consistent color pattern and leverages bullet points and varied fonts to break up the text nicely.
16. “Digital Transformation in 50 Soundbites,” Julie Dodd
This design highlights a great alternative to the “text-over-image” display we've grown used to seeing.
What I like: By leveraging a split-screen approach to each presentation slide, Julie Dodd was able to serve up a clean, legible quote without sacrificing the power of a strong visual.
17. “Fix Your Really Bad PowerPoint,” Slide Comet
When you‘re creating a PowerPoint about how everyone’s PowerPoints stink, yours had better be terrific. The one above, based on the ebook by Seth Godin, keeps it simple without boring its audience.
What I like: Its clever combinations of fonts, together with consistent color across each slide, ensure you're neither overwhelmed nor unengaged.
18. “How Google Works,” Eric Schmidt
Simple, clever doodles tell the story of Google in a fun and creative way. This presentation reads almost like a storybook, making it easy to move from one slide to the next.
What I like: This uncluttered approach provides viewers with an easy-to-understand explanation of a complicated topic.
19. “What Really Differentiates the Best Content Marketers From The Rest,” Ross Simmonds
Let‘s be honest: These graphics are hard not to love. I especially appreciate the author’s cartoonified self-portrait that closes out the presentation. Well played, Ross Simmonds.
What I like: Rather than employing the same old stock photos, this unique design serves as a refreshing way to present information that's both valuable and fun.
20. “Be A Great Product Leader,” Adam Nash
This presentation by Adam Nash immediately draws attention by putting the company's logo first — a great move if your company is well known.
What I like: He uses popular images, such as ones of Megatron and Pinocchio, to drive his points home. In the same way, you can take advantage of popular images and media to keep your audience engaged.
And if you want more templates and examples, you can download them here .
PowerPoint Presentation Examples for the Best Slide Presentation
Mastering a PowerPoint presentation begins with the design itself.
Get inspired by my ideas above to create a presentation that engages your audience, builds upon your point, and helps you generate leads for your brand.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in March 2013 and has been updated for comprehensiveness. This article was written by a human, but our team uses AI in our editorial process. Check out our full disclosure to learn more about how we use AI.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![a written presentation How to Create an Infographic in Under an Hour — the 2024 Guide [+ Free Templates]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/Make-infographic-hero%20%28598%20%C3%97%20398%20px%29.jpg)
How to Create an Infographic in Under an Hour — the 2024 Guide [+ Free Templates]
![a written presentation How to Create the Best PowerPoint Presentations [Examples & Templates]](https://knowledge.hubspot.com/hubfs/powerpoint.webp)
How to Create the Best PowerPoint Presentations [Examples & Templates]
![a written presentation 17 PowerPoint Presentation Tips From Pro Presenters [+ Templates]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/powerpoint-design-tricks_7.webp)
17 PowerPoint Presentation Tips From Pro Presenters [+ Templates]
![a written presentation How to Write an Ecommerce Business Plan [Examples & Template]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/ecommerce%20business%20plan.png)
How to Write an Ecommerce Business Plan [Examples & Template]

Get Buyers to Do What You Want: The Power of Temptation Bundling in Sales

How to Create an Engaging 5-Minute Presentation
![a written presentation How to Start a Presentation [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-to-start-presenting.webp)
How to Start a Presentation [+ Examples]

120 Presentation Topic Ideas Help You Hook Your Audience

The Presenter's Guide to Nailing Your Next PowerPoint
![a written presentation How to Create a Stunning Presentation Cover Page [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/presentation-cover-page_3.webp)
How to Create a Stunning Presentation Cover Page [+ Examples]
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
How to write a good abstract for a scientific paper or conference presentation
Chittaranjan andrade.
- Author information
- Copyright and License information
Address for correspondence: Dr. Chittaranjan Andrade, Department of Psychopharmacology, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bangalore – 560 029, Karnataka, India. E-mail: [email protected]
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstracts of scientific papers are sometimes poorly written, often lack important information, and occasionally convey a biased picture. This paper provides detailed suggestions, with examples, for writing the background, methods, results, and conclusions sections of a good abstract. The primary target of this paper is the young researcher; however, authors with all levels of experience may find useful ideas in the paper.
Keywords: Abstract, preparing a manuscript, writing skills
INTRODUCTION
This paper is the third in a series on manuscript writing skills, published in the Indian Journal of Psychiatry . Earlier articles offered suggestions on how to write a good case report,[ 1 ] and how to read, write, or review a paper on randomized controlled trials.[ 2 , 3 ] The present paper examines how authors may write a good abstract when preparing their manuscript for a scientific journal or conference presentation. Although the primary target of this paper is the young researcher, it is likely that authors with all levels of experience will find at least a few ideas that may be useful in their future efforts.
The abstract of a paper is the only part of the paper that is published in conference proceedings. The abstract is the only part of the paper that a potential referee sees when he is invited by an editor to review a manuscript. The abstract is the only part of the paper that readers see when they search through electronic databases such as PubMed. Finally, most readers will acknowledge, with a chuckle, that when they leaf through the hard copy of a journal, they look at only the titles of the contained papers. If a title interests them, they glance through the abstract of that paper. Only a dedicated reader will peruse the contents of the paper, and then, most often only the introduction and discussion sections. Only a reader with a very specific interest in the subject of the paper, and a need to understand it thoroughly, will read the entire paper.
Thus, for the vast majority of readers, the paper does not exist beyond its abstract. For the referees, and the few readers who wish to read beyond the abstract, the abstract sets the tone for the rest of the paper. It is therefore the duty of the author to ensure that the abstract is properly representative of the entire paper. For this, the abstract must have some general qualities. These are listed in Table 1 .
General qualities of a good abstract

SECTIONS OF AN ABSTRACT
Although some journals still publish abstracts that are written as free-flowing paragraphs, most journals require abstracts to conform to a formal structure within a word count of, usually, 200–250 words. The usual sections defined in a structured abstract are the Background, Methods, Results, and Conclusions; other headings with similar meanings may be used (eg, Introduction in place of Background or Findings in place of Results). Some journals include additional sections, such as Objectives (between Background and Methods) and Limitations (at the end of the abstract). In the rest of this paper, issues related to the contents of each section will be examined in turn.
This section should be the shortest part of the abstract and should very briefly outline the following information:
What is already known about the subject, related to the paper in question
What is not known about the subject and hence what the study intended to examine (or what the paper seeks to present)
In most cases, the background can be framed in just 2–3 sentences, with each sentence describing a different aspect of the information referred to above; sometimes, even a single sentence may suffice. The purpose of the background, as the word itself indicates, is to provide the reader with a background to the study, and hence to smoothly lead into a description of the methods employed in the investigation.
Some authors publish papers the abstracts of which contain a lengthy background section. There are some situations, perhaps, where this may be justified. In most cases, however, a longer background section means that less space remains for the presentation of the results. This is unfortunate because the reader is interested in the paper because of its findings, and not because of its background.
A wide variety of acceptably composed backgrounds is provided in Table 2 ; most of these have been adapted from actual papers.[ 4 – 9 ] Readers may wish to compare the content in Table 2 with the original abstracts to see how the adaptations possibly improve on the originals. Note that, in the interest of brevity, unnecessary content is avoided. For instance, in Example 1 there is no need to state “The antidepressant efficacy of desvenlafaxine (DV), a dual-acting antidepressant drug , has been established…” (the unnecessary content is italicized).
Examples of the background section of an abstract
The methods section is usually the second-longest section in the abstract. It should contain enough information to enable the reader to understand what was done, and how. Table 3 lists important questions to which the methods section should provide brief answers.
Questions regarding which information should ideally be available in the methods section of an abstract

Carelessly written methods sections lack information about important issues such as sample size, numbers of patients in different groups, doses of medications, and duration of the study. Readers have only to flip through the pages of a randomly selected journal to realize how common such carelessness is.
Table 4 presents examples of the contents of accept-ably written methods sections, modified from actual publications.[ 10 , 11 ] Readers are invited to take special note of the first sentence of each example in Table 4 ; each is packed with detail, illustrating how to convey the maximum quantity of information with maximum economy of word count.
Examples of the methods section of an abstract
The results section is the most important part of the abstract and nothing should compromise its range and quality. This is because readers who peruse an abstract do so to learn about the findings of the study. The results section should therefore be the longest part of the abstract and should contain as much detail about the findings as the journal word count permits. For example, it is bad writing to state “Response rates differed significantly between diabetic and nondiabetic patients.” A better sentence is “The response rate was higher in nondiabetic than in diabetic patients (49% vs 30%, respectively; P <0.01).”
Important information that the results should present is indicated in Table 5 . Examples of acceptably written abstracts are presented in Table 6 ; one of these has been modified from an actual publication.[ 11 ] Note that the first example is rather narrative in style, whereas the second example is packed with data.
Information that the results section of the abstract should ideally present

Examples of the results section of an abstract
CONCLUSIONS
This section should contain the most important take-home message of the study, expressed in a few precisely worded sentences. Usually, the finding highlighted here relates to the primary outcome measure; however, other important or unexpected findings should also be mentioned. It is also customary, but not essential, for the authors to express an opinion about the theoretical or practical implications of the findings, or the importance of their findings for the field. Thus, the conclusions may contain three elements:
The primary take-home message
The additional findings of importance
The perspective
Despite its necessary brevity, this section has the most impact on the average reader because readers generally trust authors and take their assertions at face value. For this reason, the conclusions should also be scrupulously honest; and authors should not claim more than their data demonstrate. Hypothetical examples of the conclusions section of an abstract are presented in Table 7 .
Examples of the conclusions section of an abstract
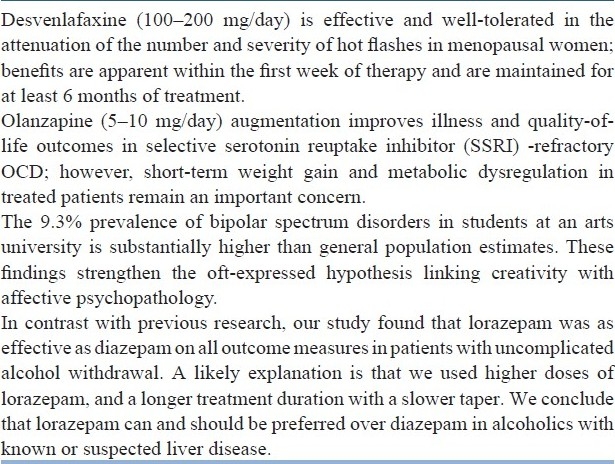
MISCELLANEOUS OBSERVATIONS
Citation of references anywhere within an abstract is almost invariably inappropriate. Other examples of unnecessary content in an abstract are listed in Table 8 .
Examples of unnecessary content in a abstract
It goes without saying that whatever is present in the abstract must also be present in the text. Likewise, whatever errors should not be made in the text should not appear in the abstract (eg, mistaking association for causality).
As already mentioned, the abstract is the only part of the paper that the vast majority of readers see. Therefore, it is critically important for authors to ensure that their enthusiasm or bias does not deceive the reader; unjustified speculations could be even more harmful. Misleading readers could harm the cause of science and have an adverse impact on patient care.[ 12 ] A recent study,[ 13 ] for example, concluded that venlafaxine use during the second trimester of pregnancy may increase the risk of neonates born small for gestational age. However, nowhere in the abstract did the authors mention that these conclusions were based on just 5 cases and 12 controls out of the total sample of 126 cases and 806 controls. There were several other serious limitations that rendered the authors’ conclusions tentative, at best; yet, nowhere in the abstract were these other limitations expressed.
As a parting note: Most journals provide clear instructions to authors on the formatting and contents of different parts of the manuscript. These instructions often include details on what the sections of an abstract should contain. Authors should tailor their abstracts to the specific requirements of the journal to which they plan to submit their manuscript. It could also be an excellent idea to model the abstract of the paper, sentence for sentence, on the abstract of an important paper on a similar subject and with similar methodology, published in the same journal for which the manuscript is slated.
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
- 1. Andrade C, Mendhekar DN. Lithium, trifluperazine, and idiopathic leucopenia: Author and reviewer perspectives on how to write a good case report. Indian J Psychiatry. 2010;52:187–90. doi: 10.4103/0019-5545.64594. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Andrade C. A 6-week, multicentre, randomized controlled clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of placeboxetine hydrochloride in the treatment of major depressive disorder in an Indian setting. Indian J Psychiatry. 2011;53:69–72. doi: 10.4103/0019-5545.75555. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Andrade C. Placeboxetine for major depressive disorder: Researcher, author, reader, and reviewer perspectives on randomized controlled trials. Indian J Psychiatry. 2011;53:73–7. doi: 10.4103/0019-5545.75553. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Andrade C, Radhakrishnan R. Prayer and healing: A medical and scientific perspective on randomized controlled trials. Indian J Psychiatry. 2009;51:247–53. doi: 10.4103/0019-5545.58288. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. Shah N, Mahadeshwar S, Bhakta S, Bhirud M, Fernandes P, Andrade C. The safety and efficacy of benzodiazepine-modified treatments as a special form of unmodified ECT. J ECT. 2010;26:23–9. doi: 10.1097/YCT.0b013e3181d2711f. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 6. Andrade C, Srihari BS, Reddy KP, Chandramma L. Melatonin in medically ill patients with insomnia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62:41–5. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v62n0109. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 7. Andrade C, Madhavan AP, Kishore ML. Testing logical memory using a complex passage: Development and standardization of a new test. Indian J Psychiatry. 2001;43:252–6. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 8. Andrade AC, Pai S, Cardoza S, Andrade C. Personality profile of urban, female college students. Indian J Psychol Med. 1994;17:41–6. [ Google Scholar ]
- 9. Andrade C, Postma K, Abraham K. Influence of women's work status on the well-being of Indian couples. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 1999;45:65–75. doi: 10.1177/002076409904500108. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 10. Kumar CN, Andrade C, Murthy P. A randomized, double-blind comparison of lorazepam and chlordiazepoxide in patients with uncomplicated alcohol withdrawal. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2009;70:457–74. doi: 10.15288/jsad.2009.70.467. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 11. Margoob MA, Ali Z, Andrade C. Efficacy of ECT in chronic, severe, antidepressant- and CBT-refractory PTSD: An open, prospective study. Brain Stimul. 2010;3:28–35. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2009.04.005. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 12. Rao TS, Andrade C. The MMR vaccine and autism: Sensation, refutation, retraction, and fraud. Editorial. Indian J Psychiatry. 2011;53:95–6. doi: 10.4103/0019-5545.82529. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 13. Ramos I, St-Andri M, Birard A. Association between antidepressant use during pregnancy and infants born small for gestational age. Can J Psychiatry. 2010;55:643–52. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Data and Statistics on ADHD
- Free Materials on ADHD
- Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder Articles
- Clinical Care and Treatment
- Facts About ADHD in Adults
- View All Home
Symptoms of ADHD
- ADHD symptoms can present as mostly inattentive, mostly hyperactive-impulsive, or a combination of both types of symptoms.
- If you think you or someone you know might have ADHD, the first step is to talk with a healthcare provider.

Signs and symptoms
It is normal for children to have trouble focusing and behaving at one time or another. However, children with ADHD do not just grow out of these behaviors. The symptoms continue, can be severe, and can cause difficulty at school, at home, or with friends.
A child with ADHD might
- daydream a lot
- forget or lose things a lot
- squirm or fidget
- talk too much
- make careless mistakes or take unnecessary risks
- have a hard time resisting temptation
- have trouble taking turns
- have difficulty getting along with others
Based on the types of symptoms, three kinds (presentations) of ADHD can occur:
- Predominantly Inattentive Presentation
- Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Presentation
- Combined Presentation (a combination of inattentive and hyper-impulsive symptoms)
Because symptoms can change over time, the presentation may change over time as well.
When to talk to your doctor
If you are concerned about whether a child might have ADHD, the first step is to talk with a healthcare provider to find out if the symptoms fit an ADHD diagnosis. The diagnosis can be made by a mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, or by a primary care provider, like a pediatrician.
Is there a test for ADHD?
Deciding if a person has ADHD is a process with several steps. There is no single test to diagnose ADHD, and many other problems, such as sleep disorders, anxiety, depression, and certain types of learning disabilities, can also have symptoms similar to ADHD.
Read more about diagnosing ADHD.
- Treatment of ADHD
- Other Concerns and Conditions with ADHD
Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
CDC's Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) site includes information on symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, data, research, and free resources.
For Everyone
Health care providers, public health.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn the 10 qualities of a good presentation and follow a step-by-step guide to create an effective one. Venngage offers free presentation templates, interactive features and data visualization tools to help you impress your audience.
Summary. A strong presentation is so much more than information pasted onto a series of slides with fancy backgrounds. Whether you're pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing ...
Learn how to write a presentation with a clear structure, engaging introduction, compelling visuals, and engaging delivery. Follow the step-by-step guide with examples and tips from AhaSlides, a tool for interactive presentations.
Learn the difference between a presentation and a PowerPoint presentation, and how to plan, design, and deliver an effective presentation. This article covers topics such as choosing a topic, preparing content, using visual tools, and rehearsing your speech.
Learn how to plan, write and deliver a presentation that engages your audience and achieves your goal. This comprehensive guide covers everything from preparing your presentation to creating your PowerPoint slides and presenting online.
Learn how to structure your presentation effectively with a logical and simple flow that engages your audience. Follow the typical presentation structure or explore other options such as demonstration, problem-solution, or storytelling.
Learn how to write a presentation with clear structure, language and flow. Find tips on using stories, the power of three, and what, why, how questions to communicate your message.
Learn to craft an engaging presentation speech with our guide on audience engagement, content structure, and effective delivery. Follow the eight steps from understanding your audience to preparing for Q&A, and use visual aids wisely to enhance your message.
Learn how to write an effective PowerPoint presentation with a clear thesis, outline, and script. Find tips on research, design, and delivery, and download a free eBook on making presentations.
Learn how to create a PowerPoint presentation that is engaging, concise, and visually appealing. Follow the 10-20-30 rule, write an abstract, use an outline, and polish your slides with tips and examples.
Written presentations are a powerful way to share ideas—if you create a deck that communicates your points clearly and effectively. Other communication factors might influence your presentation's success, like your oratory techniques and body language. However, a well-written presentation is a resource that your audience can revisit long ...
Learn from 23 business presentation examples that range from video, PowerPoint, Google Slides, and Prezi. Find out how to create engaging and effective presentations with tips, templates, and inspiration.
Learn how to create a presentation script that outlines what you will say and how to deliver it effectively. Find out the key elements, structure, and tips for writing a script that supports your core message and objectives.
Learn how to practice, prepare and deliver killer presentations with these tips from Visme, a presentation design platform. Find out how to use slides, props, stories, templates and more to impress your audience.
Learn how to create engaging and effective presentations with these 27 examples for different purposes and formats. Discover the best practices, tips, and templates for storytelling, design, and interactivity.
Learn from a Silicon Valley CEO and a Harvard instructor how to deliver effective and memorable business presentations. Find out the secrets of concise, visual, vocal, and rehearsed communication.
A written presentation tends to be rather direct and to the point. It is typically very objective in nature, highly organized, and yet may seem to be rather impersonal. When you plan a written presentation it will often require careful planning and may rely on rote listing of information in order to achieve its message.
Learn how to create engaging presentations with colorful slides, embedded videos, interactivity, animation, and more. See 25 awesome presentation examples from various use cases and get ready-to-use templates from Visme.
Learn how to create engaging and effective PowerPoint presentations with tips, ideas, and templates. See examples of different design styles, colors, visuals, and layouts for various purposes and audiences.
Earlier articles offered suggestions on how to write a good case report, and how to read, write, or review a paper on randomized controlled trials.[2,3] The present paper examines how authors may write a good abstract when preparing their manuscript for a scientific journal or conference presentation. Although the primary target of this paper ...
Guest post written by John Thompson, IFLS Libary System In response to a recommendation from the Wisconsin Public Library Facilities Assessment, two presentation slide decks and instructions were created to educate and inform key stakeholders about the importance of libraries and advocate for funding to build or renovate.The two templates contain similar background information, but the Need an ...
Learn how to recognize the signs and symptoms of ADHD in children and adults, and how to get a diagnosis from a healthcare provider. Find out the types of ADHD presentations, the differences between normal and abnormal behaviors, and the resources for treatment and support.