- Privacy Policy

Home » 500+ Quantitative Research Titles and Topics

500+ Quantitative Research Titles and Topics
Table of Contents

Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships among variables. This method is widely used in social sciences, psychology , economics , and other fields where researchers aim to understand human behavior and phenomena through statistical analysis. If you are looking for a quantitative research topic, there are numerous areas to explore, from analyzing data on a specific population to studying the effects of a particular intervention or treatment. In this post, we will provide some ideas for quantitative research topics that may inspire you and help you narrow down your interests.
Quantitative Research Titles
Quantitative Research Titles are as follows:
Business and Economics
- “Statistical Analysis of Supply Chain Disruptions on Retail Sales”
- “Quantitative Examination of Consumer Loyalty Programs in the Fast Food Industry”
- “Predicting Stock Market Trends Using Machine Learning Algorithms”
- “Influence of Workplace Environment on Employee Productivity: A Quantitative Study”
- “Impact of Economic Policies on Small Businesses: A Regression Analysis”
- “Customer Satisfaction and Profit Margins: A Quantitative Correlation Study”
- “Analyzing the Role of Marketing in Brand Recognition: A Statistical Overview”
- “Quantitative Effects of Corporate Social Responsibility on Consumer Trust”
- “Price Elasticity of Demand for Luxury Goods: A Case Study”
- “The Relationship Between Fiscal Policy and Inflation Rates: A Time-Series Analysis”
- “Factors Influencing E-commerce Conversion Rates: A Quantitative Exploration”
- “Examining the Correlation Between Interest Rates and Consumer Spending”
- “Standardized Testing and Academic Performance: A Quantitative Evaluation”
- “Teaching Strategies and Student Learning Outcomes in Secondary Schools: A Quantitative Study”
- “The Relationship Between Extracurricular Activities and Academic Success”
- “Influence of Parental Involvement on Children’s Educational Achievements”
- “Digital Literacy in Primary Schools: A Quantitative Assessment”
- “Learning Outcomes in Blended vs. Traditional Classrooms: A Comparative Analysis”
- “Correlation Between Teacher Experience and Student Success Rates”
- “Analyzing the Impact of Classroom Technology on Reading Comprehension”
- “Gender Differences in STEM Fields: A Quantitative Analysis of Enrollment Data”
- “The Relationship Between Homework Load and Academic Burnout”
- “Assessment of Special Education Programs in Public Schools”
- “Role of Peer Tutoring in Improving Academic Performance: A Quantitative Study”
Medicine and Health Sciences
- “The Impact of Sleep Duration on Cardiovascular Health: A Cross-sectional Study”
- “Analyzing the Efficacy of Various Antidepressants: A Meta-Analysis”
- “Patient Satisfaction in Telehealth Services: A Quantitative Assessment”
- “Dietary Habits and Incidence of Heart Disease: A Quantitative Review”
- “Correlations Between Stress Levels and Immune System Functioning”
- “Smoking and Lung Function: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Influence of Physical Activity on Mental Health in Older Adults”
- “Antibiotic Resistance Patterns in Community Hospitals: A Quantitative Study”
- “The Efficacy of Vaccination Programs in Controlling Disease Spread: A Time-Series Analysis”
- “Role of Social Determinants in Health Outcomes: A Quantitative Exploration”
- “Impact of Hospital Design on Patient Recovery Rates”
- “Quantitative Analysis of Dietary Choices and Obesity Rates in Children”
Social Sciences
- “Examining Social Inequality through Wage Distribution: A Quantitative Study”
- “Impact of Parental Divorce on Child Development: A Longitudinal Study”
- “Social Media and its Effect on Political Polarization: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “The Relationship Between Religion and Social Attitudes: A Statistical Overview”
- “Influence of Socioeconomic Status on Educational Achievement”
- “Quantifying the Effects of Community Programs on Crime Reduction”
- “Public Opinion and Immigration Policies: A Quantitative Exploration”
- “Analyzing the Gender Representation in Political Offices: A Quantitative Study”
- “Impact of Mass Media on Public Opinion: A Regression Analysis”
- “Influence of Urban Design on Social Interactions in Communities”
- “The Role of Social Support in Mental Health Outcomes: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Examining the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Employment Status”
Engineering and Technology
- “Performance Evaluation of Different Machine Learning Algorithms in Autonomous Vehicles”
- “Material Science: A Quantitative Analysis of Stress-Strain Properties in Various Alloys”
- “Impacts of Data Center Cooling Solutions on Energy Consumption”
- “Analyzing the Reliability of Renewable Energy Sources in Grid Management”
- “Optimization of 5G Network Performance: A Quantitative Assessment”
- “Quantifying the Effects of Aerodynamics on Fuel Efficiency in Commercial Airplanes”
- “The Relationship Between Software Complexity and Bug Frequency”
- “Machine Learning in Predictive Maintenance: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Wearable Technologies and their Impact on Healthcare Monitoring”
- “Quantitative Assessment of Cybersecurity Measures in Financial Institutions”
- “Analysis of Noise Pollution from Urban Transportation Systems”
- “The Influence of Architectural Design on Energy Efficiency in Buildings”
Quantitative Research Topics
Quantitative Research Topics are as follows:
- The effects of social media on self-esteem among teenagers.
- A comparative study of academic achievement among students of single-sex and co-educational schools.
- The impact of gender on leadership styles in the workplace.
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic performance of students.
- The effect of mindfulness meditation on stress levels in college students.
- The relationship between employee motivation and job satisfaction.
- The effectiveness of online learning compared to traditional classroom learning.
- The correlation between sleep duration and academic performance among college students.
- The impact of exercise on mental health among adults.
- The relationship between social support and psychological well-being among cancer patients.
- The effect of caffeine consumption on sleep quality.
- A comparative study of the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy in treating depression.
- The relationship between physical attractiveness and job opportunities.
- The correlation between smartphone addiction and academic performance among high school students.
- The impact of music on memory recall among adults.
- The effectiveness of parental control software in limiting children’s online activity.
- The relationship between social media use and body image dissatisfaction among young adults.
- The correlation between academic achievement and parental involvement among minority students.
- The impact of early childhood education on academic performance in later years.
- The effectiveness of employee training and development programs in improving organizational performance.
- The relationship between socioeconomic status and access to healthcare services.
- The correlation between social support and academic achievement among college students.
- The impact of technology on communication skills among children.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction programs in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- The relationship between employee turnover and organizational culture.
- The correlation between job satisfaction and employee engagement.
- The impact of video game violence on aggressive behavior among children.
- The effectiveness of nutritional education in promoting healthy eating habits among adolescents.
- The relationship between bullying and academic performance among middle school students.
- The correlation between teacher expectations and student achievement.
- The impact of gender stereotypes on career choices among high school students.
- The effectiveness of anger management programs in reducing violent behavior.
- The relationship between social support and recovery from substance abuse.
- The correlation between parent-child communication and adolescent drug use.
- The impact of technology on family relationships.
- The effectiveness of smoking cessation programs in promoting long-term abstinence.
- The relationship between personality traits and academic achievement.
- The correlation between stress and job performance among healthcare professionals.
- The impact of online privacy concerns on social media use.
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating anxiety disorders.
- The relationship between teacher feedback and student motivation.
- The correlation between physical activity and academic performance among elementary school students.
- The impact of parental divorce on academic achievement among children.
- The effectiveness of diversity training in improving workplace relationships.
- The relationship between childhood trauma and adult mental health.
- The correlation between parental involvement and substance abuse among adolescents.
- The impact of social media use on romantic relationships among young adults.
- The effectiveness of assertiveness training in improving communication skills.
- The relationship between parental expectations and academic achievement among high school students.
- The correlation between sleep quality and mood among adults.
- The impact of video game addiction on academic performance among college students.
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating eating disorders.
- The relationship between job stress and job performance among teachers.
- The correlation between mindfulness and emotional regulation.
- The impact of social media use on self-esteem among college students.
- The effectiveness of parent-teacher communication in promoting academic achievement among elementary school students.
- The impact of renewable energy policies on carbon emissions
- The relationship between employee motivation and job performance
- The effectiveness of psychotherapy in treating eating disorders
- The correlation between physical activity and cognitive function in older adults
- The effect of childhood poverty on adult health outcomes
- The impact of urbanization on biodiversity conservation
- The relationship between work-life balance and employee job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) in treating trauma
- The correlation between parenting styles and child behavior
- The effect of social media on political polarization
- The impact of foreign aid on economic development
- The relationship between workplace diversity and organizational performance
- The effectiveness of dialectical behavior therapy in treating borderline personality disorder
- The correlation between childhood abuse and adult mental health outcomes
- The effect of sleep deprivation on cognitive function
- The impact of trade policies on international trade and economic growth
- The relationship between employee engagement and organizational commitment
- The effectiveness of cognitive therapy in treating postpartum depression
- The correlation between family meals and child obesity rates
- The effect of parental involvement in sports on child athletic performance
- The impact of social entrepreneurship on sustainable development
- The relationship between emotional labor and job burnout
- The effectiveness of art therapy in treating dementia
- The correlation between social media use and academic procrastination
- The effect of poverty on childhood educational attainment
- The impact of urban green spaces on mental health
- The relationship between job insecurity and employee well-being
- The effectiveness of virtual reality exposure therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between childhood trauma and substance abuse
- The effect of screen time on children’s social skills
- The impact of trade unions on employee job satisfaction
- The relationship between cultural intelligence and cross-cultural communication
- The effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy in treating chronic pain
- The correlation between childhood obesity and adult health outcomes
- The effect of gender diversity on corporate performance
- The impact of environmental regulations on industry competitiveness.
- The impact of renewable energy policies on greenhouse gas emissions
- The relationship between workplace diversity and team performance
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating substance abuse
- The correlation between parental involvement and social skills in early childhood
- The effect of technology use on sleep patterns
- The impact of government regulations on small business growth
- The relationship between job satisfaction and employee turnover
- The effectiveness of virtual reality therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic motivation in adolescents
- The effect of social media on political engagement
- The impact of urbanization on mental health
- The relationship between corporate social responsibility and consumer trust
- The correlation between early childhood education and social-emotional development
- The effect of screen time on cognitive development in young children
- The impact of trade policies on global economic growth
- The relationship between workplace diversity and innovation
- The effectiveness of family therapy in treating eating disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and college persistence
- The effect of social media on body image and self-esteem
- The impact of environmental regulations on business competitiveness
- The relationship between job autonomy and job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of virtual reality therapy in treating phobias
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic achievement in college
- The effect of social media on sleep quality
- The impact of immigration policies on social integration
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee well-being
- The effectiveness of psychodynamic therapy in treating personality disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and executive function skills
- The effect of parental involvement on STEM education outcomes
- The impact of trade policies on domestic employment rates
- The relationship between job insecurity and mental health
- The effectiveness of exposure therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and social mobility
- The effect of social media on intergroup relations
- The impact of urbanization on air pollution and respiratory health.
- The relationship between emotional intelligence and leadership effectiveness
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between early childhood education and language development
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in STEM fields
- The impact of trade policies on income inequality
- The relationship between workplace diversity and customer satisfaction
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and civic engagement in adolescents
- The effect of social media on mental health among teenagers
- The impact of public transportation policies on traffic congestion
- The relationship between job stress and job performance
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between early childhood education and cognitive development
- The effect of parental involvement on academic motivation in college
- The impact of environmental regulations on energy consumption
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee engagement
- The effectiveness of art therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in vocational education
- The effect of social media on academic achievement in college
- The impact of tax policies on economic growth
- The relationship between job flexibility and work-life balance
- The effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and social competence
- The effect of parental involvement on career readiness in high school
- The impact of immigration policies on crime rates
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee retention
- The effectiveness of play therapy in treating trauma
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in online learning
- The effect of social media on body dissatisfaction among women
- The impact of urbanization on public health infrastructure
- The relationship between job satisfaction and job performance
- The effectiveness of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between early childhood education and social skills in adolescence
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in the arts
- The impact of trade policies on foreign investment
- The relationship between workplace diversity and decision-making
- The effectiveness of exposure and response prevention therapy in treating OCD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in special education
- The impact of zoning laws on affordable housing
- The relationship between job design and employee motivation
- The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation therapy in treating traumatic brain injury
- The correlation between early childhood education and social-emotional learning
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in foreign language learning
- The impact of trade policies on the environment
- The relationship between workplace diversity and creativity
- The effectiveness of emotion-focused therapy in treating relationship problems
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in music education
- The effect of social media on interpersonal communication skills
- The impact of public health campaigns on health behaviors
- The relationship between job resources and job stress
- The effectiveness of equine therapy in treating substance abuse
- The correlation between early childhood education and self-regulation
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in physical education
- The impact of immigration policies on cultural assimilation
- The relationship between workplace diversity and conflict resolution
- The effectiveness of schema therapy in treating personality disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in career and technical education
- The effect of social media on trust in government institutions
- The impact of urbanization on public transportation systems
- The relationship between job demands and job stress
- The correlation between early childhood education and executive functioning
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in computer science
- The effectiveness of cognitive processing therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in homeschooling
- The effect of social media on cyberbullying behavior
- The impact of urbanization on air quality
- The effectiveness of dance therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and math achievement
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in health education
- The impact of global warming on agriculture
- The effectiveness of narrative therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in character education
- The effect of social media on political participation
- The impact of technology on job displacement
- The relationship between job resources and job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of art therapy in treating addiction
- The correlation between early childhood education and reading comprehension
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in environmental education
- The impact of income inequality on social mobility
- The relationship between workplace diversity and organizational culture
- The effectiveness of solution-focused brief therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in physical therapy education
- The effect of social media on misinformation
- The impact of green energy policies on economic growth
- The relationship between job demands and employee well-being
- The correlation between early childhood education and science achievement
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in religious education
- The impact of gender diversity on corporate governance
- The relationship between workplace diversity and ethical decision-making
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in dental hygiene education
- The effect of social media on self-esteem among adolescents
- The impact of renewable energy policies on energy security
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in social studies
- The impact of trade policies on job growth
- The relationship between workplace diversity and leadership styles
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in online vocational training
- The effect of social media on self-esteem among men
- The impact of urbanization on air pollution levels
- The effectiveness of music therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between early childhood education and math skills
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in language arts
- The impact of immigration policies on labor market outcomes
- The effectiveness of hypnotherapy in treating phobias
- The effect of social media on political engagement among young adults
- The impact of urbanization on access to green spaces
- The relationship between job crafting and job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of exposure therapy in treating specific phobias
- The correlation between early childhood education and spatial reasoning
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in business education
- The impact of trade policies on economic inequality
- The effectiveness of narrative therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in nursing education
- The effect of social media on sleep quality among adolescents
- The impact of urbanization on crime rates
- The relationship between job insecurity and turnover intentions
- The effectiveness of pet therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and STEM skills
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in culinary education
- The impact of immigration policies on housing affordability
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee satisfaction
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction in treating chronic pain
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in art education
- The effect of social media on academic procrastination among college students
- The impact of urbanization on public safety services.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

500+ Psychology Research Topic Ideas

500+ Climate Change Research Topics

500+ Music Research Topics

500+ Business Research Topics

500+ Cyber Security Research Topics

500+ Economics Research Topics
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
100+ Quantitative Research Topics For Students

Quantitative research is a research strategy focusing on quantified data collection and analysis processes. This research strategy emphasizes testing theories on various subjects. It also includes collecting and analyzing non-numerical data.
Quantitative research is a common approach in the natural and social sciences , like marketing, business, sociology, chemistry, biology, economics, and psychology. So, if you are fond of statistics and figures, a quantitative research title would be an excellent option for your research proposal or project.
How to Get a Title of Quantitative Research
How to make quantitative research title, what is the best title for quantitative research, amazing quantitative research topics for students, creative quantitative research topics, perfect quantitative research title examples, unique quantitative research titles, outstanding quantitative research title examples for students, creative example title of quantitative research samples, outstanding quantitative research problems examples, fantastic quantitative research topic examples, the best quantitative research topics, grade 12 quantitative research title for students, list of quantitative research titles for high school, easy quantitative research topics for students, trending topics for quantitative research, quantitative research proposal topics, samples of quantitative research titles, research title about business quantitative.
Finding a great title is the key to writing a great quantitative research proposal or paper. A title for quantitative research prepares you for success, failure, or mediocre grades. This post features examples of quantitative research titles for all students.
Putting together a research title and quantitative research design is not as easy as some students assume. So, an example topic of quantitative research can help you craft your own. However, even with the examples, you may need some guidelines for personalizing your research project or proposal topics.
So, here are some tips for getting a title for quantitative research:
- Consider your area of studies
- Look out for relevant subjects in the area
- Expert advice may come in handy
- Check out some sample quantitative research titles
Making a quantitative research title is easy if you know the qualities of a good title in quantitative research. Reading about how to make a quantitative research title may not help as much as looking at some samples. Looking at a quantitative research example title will give you an idea of where to start.
However, let’s look at some tips for how to make a quantitative research title:
- The title should seem interesting to readers
- Ensure that the title represents the content of the research paper
- Reflect on the tone of the writing in the title
- The title should contain important keywords in your chosen subject to help readers find your paper
- The title should not be too lengthy
- It should be grammatically correct and creative
- It must generate curiosity
An excellent quantitative title should be clear, which implies that it should effectively explain the paper and what readers can expect. A research title for quantitative research is the gateway to your article or proposal. So, it should be well thought out. Additionally, it should give you room for extensive topic research.
A sample of quantitative research titles will give you an idea of what a good title for quantitative research looks like. Here are some examples:
- What is the correlation between inflation rates and unemployment rates?
- Has climate adaptation influenced the mitigation of funds allocation?
- Job satisfaction and employee turnover: What is the link?
- A look at the relationship between poor households and the development of entrepreneurship skills
- Urbanization and economic growth: What is the link between these elements?
- Does education achievement influence people’s economic status?
- What is the impact of solar electricity on the wholesale energy market?
- Debt accumulation and retirement: What is the relationship between these concepts?
- Can people with psychiatric disorders develop independent living skills?
- Children’s nutrition and its impact on cognitive development
Quantitative research applies to various subjects in the natural and social sciences. Therefore, depending on your intended subject, you have numerous options. Below are some good quantitative research topics for students:
- The difference between the colorific intake of men and women in your country
- Top strategies used to measure customer satisfaction and how they work
- Black Friday sales: are they profitable?
- The correlation between estimated target market and practical competitive risk assignment
- Are smartphones making us brighter or dumber?
- Nuclear families Vs. Joint families: Is there a difference?
- What will society look like in the absence of organized religion?
- A comparison between carbohydrate weight loss benefits and high carbohydrate diets?
- How does emotional stability influence your overall well-being?
- The extent of the impact of technology in the communications sector
Creativity is the key to creating a good research topic in quantitative research. Find a good quantitative research topic below:
- How much exercise is good for lasting physical well-being?
- A comparison of the nutritional therapy uses and contemporary medical approaches
- Does sugar intake have a direct impact on diabetes diagnosis?
- Education attainment: Does it influence crime rates in society?
- Is there an actual link between obesity and cancer rates?
- Do kids with siblings have better social skills than those without?
- Computer games and their impact on the young generation
- Has social media marketing taken over conventional marketing strategies?
- The impact of technology development on human relationships and communication
- What is the link between drug addiction and age?
Need more quantitative research title examples to inspire you? Here are some quantitative research title examples to look at:
- Habitation fragmentation and biodiversity loss: What is the link?
- Radiation has affected biodiversity: Assessing its effects
- An assessment of the impact of the CORONA virus on global population growth
- Is the pandemic truly over, or have human bodies built resistance against the virus?
- The ozone hole and its impact on the environment
- The greenhouse gas effect: What is it and how has it impacted the atmosphere
- GMO crops: are they good or bad for your health?
- Is there a direct link between education quality and job attainment?
- How have education systems changed from traditional to modern times?
- The good and bad impacts of technology on education qualities
Your examiner will give you excellent grades if you come up with a unique title and outstanding content. Here are some quantitative research examples titles.
- Online classes: are they helpful or not?
- What changes has the global CORONA pandemic had on the population growth curve?
- Daily habits influenced by the global pandemic
- An analysis of the impact of culture on people’s personalities
- How has feminism influenced the education system’s approach to the girl child’s education?
- Academic competition: what are its benefits and downsides for students?
- Is there a link between education and student integrity?
- An analysis of how the education sector can influence a country’s economy
- An overview of the link between crime rates and concern for crime
- Is there a link between education and obesity?
Research title example quantitative topics when well-thought guarantees a paper that is a good read. Look at the examples below to get started.
- What are the impacts of online games on students?
- Sex education in schools: how important is it?
- Should schools be teaching about safe sex in their sex education classes?
- The correlation between extreme parent interference on student academic performance
- Is there a real link between academic marks and intelligence?
- Teacher feedback: How necessary is it, and how does it help students?
- An analysis of modern education systems and their impact on student performance
- An overview of the link between academic performance/marks and intelligence
- Are grading systems helpful or harmful to students?
- What was the impact of the pandemic on students?
Irrespective of the course you take, here are some titles that can fit diverse subjects pretty well. Here are some creative quantitative research title ideas:
- A look at the pre-corona and post-corona economy
- How are conventional retail businesses fairing against eCommerce sites like Amazon and Shopify?
- An evaluation of mortality rates of heart attacks
- Effective treatments for cardiovascular issues and their prevention
- A comparison of the effectiveness of home care and nursing home care
- Strategies for managing effective dissemination of information to modern students
- How does educational discrimination influence students’ futures?
- The impacts of unfavorable classroom environment and bullying on students and teachers
- An overview of the implementation of STEM education to K-12 students
- How effective is digital learning?
If your paper addresses a problem, you must present facts that solve the question or tell more about the question. Here are examples of quantitative research titles that will inspire you.
- An elaborate study of the influence of telemedicine in healthcare practices
- How has scientific innovation influenced the defense or military system?
- The link between technology and people’s mental health
- Has social media helped create awareness or worsened people’s mental health?
- How do engineers promote green technology?
- How can engineers raise sustainability in building and structural infrastructures?
- An analysis of how decision-making is dependent on someone’s sub-conscious
- A comprehensive study of ADHD and its impact on students’ capabilities
- The impact of racism on people’s mental health and overall wellbeing
- How has the current surge in social activism helped shape people’s relationships?
Are you looking for an example of a quantitative research title? These ten examples below will get you started.
- The prevalence of nonverbal communication in social control and people’s interactions
- The impacts of stress on people’s behavior in society
- A study of the connection between capital structures and corporate strategies
- How do changes in credit ratings impact equality returns?
- A quantitative analysis of the effect of bond rating changes on stock prices
- The impact of semantics on web technology
- An analysis of persuasion, propaganda, and marketing impact on individuals
- The dominant-firm model: what is it, and how does it apply to your country’s retail sector?
- The role of income inequality in economy growth
- An examination of juvenile delinquents’ treatment in your country
Excellent Topics For Quantitative Research
Here are some titles for quantitative research you should consider:
- Does studying mathematics help implement data safety for businesses
- How are art-related subjects interdependent with mathematics?
- How do eco-friendly practices in the hospitality industry influence tourism rates?
- A deep insight into how people view eco-tourisms
- Religion vs. hospitality: Details on their correlation
- Has your country’s tourist sector revived after the pandemic?
- How effective is non-verbal communication in conveying emotions?
- Are there similarities between the English and French vocabulary?
- How do politicians use persuasive language in political speeches?
- The correlation between popular culture and translation
Here are some quantitative research titles examples for your consideration:
- How do world leaders use language to change the emotional climate in their nations?
- Extensive research on how linguistics cultivate political buzzwords
- The impact of globalization on the global tourism sector
- An analysis of the effects of the pandemic on the worldwide hospitality sector
- The influence of social media platforms on people’s choice of tourism destinations
- Educational tourism: What is it and what you should know about it
- Why do college students experience math anxiety?
- Is math anxiety a phenomenon?
- A guide on effective ways to fight cultural bias in modern society
- Creative ways to solve the overpopulation issue
An example of quantitative research topics for 12 th -grade students will come in handy if you want to score a good grade. Here are some of the best ones:
- The link between global warming and climate change
- What is the greenhouse gas impact on biodiversity and the atmosphere
- Has the internet successfully influenced literacy rates in society
- The value and downsides of competition for students
- A comparison of the education system in first-world and third-world countries
- The impact of alcohol addiction on the younger generation
- How has social media influenced human relationships?
- Has education helped boost feminism among men and women?
- Are computers in classrooms beneficial or detrimental to students?
- How has social media improved bullying rates among teenagers?
High school students can apply research titles on social issues or other elements, depending on the subject. Let’s look at some quantitative topics for students:
- What is the right age to introduce sex education for students
- Can extreme punishment help reduce alcohol consumption among teenagers?
- Should the government increase the age of sexual consent?
- The link between globalization and the local economy collapses
- How are global companies influencing local economies?
There are numerous possible quantitative research topics you can write about. Here are some great quantitative research topics examples:
- The correlation between video games and crime rates
- Do college studies impact future job satisfaction?
- What can the education sector do to encourage more college enrollment?
- The impact of education on self-esteem
- The relationship between income and occupation
You can find inspiration for your research topic from trending affairs on social media or in the news. Such topics will make your research enticing. Find a trending topic for quantitative research example from the list below:
- How the country’s economy is fairing after the pandemic
- An analysis of the riots by women in Iran and what the women gain to achieve
- Is the current US government living up to the voter’s expectations?
- How is the war in Ukraine affecting the global economy?
- Can social media riots affect political decisions?
A proposal is a paper you write proposing the subject you would like to cover for your research and the research techniques you will apply. If the proposal is approved, it turns to your research topic. Here are some quantitative titles you should consider for your research proposal:
- Military support and economic development: What is the impact in developing nations?
- How does gun ownership influence crime rates in developed countries?
- How can the US government reduce gun violence without influencing people’s rights?
- What is the link between school prestige and academic standards?
- Is there a scientific link between abortion and the definition of viability?
You can never have too many sample titles. The samples allow you to find a unique title you’re your research or proposal. Find a sample quantitative research title here:
- Does weight loss indicate good or poor health?
- Should schools do away with grading systems?
- The impact of culture on student interactions and personalities
- How can parents successfully protect their kids from the dangers of the internet?
- Is the US education system better or worse than Europe’s?
If you’re a business major, then you must choose a research title quantitative about business. Let’s look at some research title examples quantitative in business:
- Creating shareholder value in business: How important is it?
- The changes in credit ratings and their impact on equity returns
- The importance of data privacy laws in business operations
- How do businesses benefit from e-waste and carbon footprint reduction?
- Organizational culture in business: what is its importance?
We Are A Call Away
Interesting, creative, unique, and easy quantitative research topics allow you to explain your paper and make research easy. Therefore, you should not take choosing a research paper or proposal topic lightly. With your topic ready, reach out to us today for excellent research paper writing services .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is Quantitative Research? Definition, Methods, Types, and Examples

If you’re wondering what is quantitative research and whether this methodology works for your research study, you’re not alone. If you want a simple quantitative research definition , then it’s enough to say that this is a method undertaken by researchers based on their study requirements. However, to select the most appropriate research for their study type, researchers should know all the methods available.
Selecting the right research method depends on a few important criteria, such as the research question, study type, time, costs, data availability, and availability of respondents. There are two main types of research methods— quantitative research and qualitative research. The purpose of quantitative research is to validate or test a theory or hypothesis and that of qualitative research is to understand a subject or event or identify reasons for observed patterns.
Quantitative research methods are used to observe events that affect a particular group of individuals, which is the sample population. In this type of research, diverse numerical data are collected through various methods and then statistically analyzed to aggregate the data, compare them, or show relationships among the data. Quantitative research methods broadly include questionnaires, structured observations, and experiments.
Here are two quantitative research examples:
- Satisfaction surveys sent out by a company regarding their revamped customer service initiatives. Customers are asked to rate their experience on a rating scale of 1 (poor) to 5 (excellent).
- A school has introduced a new after-school program for children, and a few months after commencement, the school sends out feedback questionnaires to the parents of the enrolled children. Such questionnaires usually include close-ended questions that require either definite answers or a Yes/No option. This helps in a quick, overall assessment of the program’s outreach and success.

Table of Contents
What is quantitative research ? 1,2
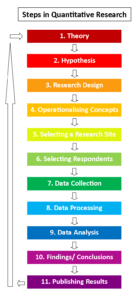
The steps shown in the figure can be grouped into the following broad steps:
- Theory : Define the problem area or area of interest and create a research question.
- Hypothesis : Develop a hypothesis based on the research question. This hypothesis will be tested in the remaining steps.
- Research design : In this step, the most appropriate quantitative research design will be selected, including deciding on the sample size, selecting respondents, identifying research sites, if any, etc.
- Data collection : This process could be extensive based on your research objective and sample size.
- Data analysis : Statistical analysis is used to analyze the data collected. The results from the analysis help in either supporting or rejecting your hypothesis.
- Present results : Based on the data analysis, conclusions are drawn, and results are presented as accurately as possible.
Quantitative research characteristics 4
- Large sample size : This ensures reliability because this sample represents the target population or market. Due to the large sample size, the outcomes can be generalized to the entire population as well, making this one of the important characteristics of quantitative research .
- Structured data and measurable variables: The data are numeric and can be analyzed easily. Quantitative research involves the use of measurable variables such as age, salary range, highest education, etc.
- Easy-to-use data collection methods : The methods include experiments, controlled observations, and questionnaires and surveys with a rating scale or close-ended questions, which require simple and to-the-point answers; are not bound by geographical regions; and are easy to administer.
- Data analysis : Structured and accurate statistical analysis methods using software applications such as Excel, SPSS, R. The analysis is fast, accurate, and less effort intensive.
- Reliable : The respondents answer close-ended questions, their responses are direct without ambiguity and yield numeric outcomes, which are therefore highly reliable.
- Reusable outcomes : This is one of the key characteristics – outcomes of one research can be used and replicated in other research as well and is not exclusive to only one study.
Quantitative research methods 5
Quantitative research methods are classified into two types—primary and secondary.
Primary quantitative research method:
In this type of quantitative research , data are directly collected by the researchers using the following methods.
– Survey research : Surveys are the easiest and most commonly used quantitative research method . They are of two types— cross-sectional and longitudinal.
->Cross-sectional surveys are specifically conducted on a target population for a specified period, that is, these surveys have a specific starting and ending time and researchers study the events during this period to arrive at conclusions. The main purpose of these surveys is to describe and assess the characteristics of a population. There is one independent variable in this study, which is a common factor applicable to all participants in the population, for example, living in a specific city, diagnosed with a specific disease, of a certain age group, etc. An example of a cross-sectional survey is a study to understand why individuals residing in houses built before 1979 in the US are more susceptible to lead contamination.
->Longitudinal surveys are conducted at different time durations. These surveys involve observing the interactions among different variables in the target population, exposing them to various causal factors, and understanding their effects across a longer period. These studies are helpful to analyze a problem in the long term. An example of a longitudinal study is the study of the relationship between smoking and lung cancer over a long period.
– Descriptive research : Explains the current status of an identified and measurable variable. Unlike other types of quantitative research , a hypothesis is not needed at the beginning of the study and can be developed even after data collection. This type of quantitative research describes the characteristics of a problem and answers the what, when, where of a problem. However, it doesn’t answer the why of the problem and doesn’t explore cause-and-effect relationships between variables. Data from this research could be used as preliminary data for another study. Example: A researcher undertakes a study to examine the growth strategy of a company. This sample data can be used by other companies to determine their own growth strategy.

– Correlational research : This quantitative research method is used to establish a relationship between two variables using statistical analysis and analyze how one affects the other. The research is non-experimental because the researcher doesn’t control or manipulate any of the variables. At least two separate sample groups are needed for this research. Example: Researchers studying a correlation between regular exercise and diabetes.
– Causal-comparative research : This type of quantitative research examines the cause-effect relationships in retrospect between a dependent and independent variable and determines the causes of the already existing differences between groups of people. This is not a true experiment because it doesn’t assign participants to groups randomly. Example: To study the wage differences between men and women in the same role. For this, already existing wage information is analyzed to understand the relationship.
– Experimental research : This quantitative research method uses true experiments or scientific methods for determining a cause-effect relation between variables. It involves testing a hypothesis through experiments, in which one or more independent variables are manipulated and then their effect on dependent variables are studied. Example: A researcher studies the importance of a drug in treating a disease by administering the drug in few patients and not administering in a few.
The following data collection methods are commonly used in primary quantitative research :
- Sampling : The most common type is probability sampling, in which a sample is chosen from a larger population using some form of random selection, that is, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. The different types of probability sampling are—simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling.
- Interviews : These are commonly telephonic or face-to-face.
- Observations : Structured observations are most commonly used in quantitative research . In this method, researchers make observations about specific behaviors of individuals in a structured setting.
- Document review : Reviewing existing research or documents to collect evidence for supporting the quantitative research .
- Surveys and questionnaires : Surveys can be administered both online and offline depending on the requirement and sample size.
The data collected can be analyzed in several ways in quantitative research , as listed below:
- Cross-tabulation —Uses a tabular format to draw inferences among collected data
- MaxDiff analysis —Gauges the preferences of the respondents
- TURF analysis —Total Unduplicated Reach and Frequency Analysis; helps in determining the market strategy for a business
- Gap analysis —Identify gaps in attaining the desired results
- SWOT analysis —Helps identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a product, service, or organization
- Text analysis —Used for interpreting unstructured data
Secondary quantitative research methods :
This method involves conducting research using already existing or secondary data. This method is less effort intensive and requires lesser time. However, researchers should verify the authenticity and recency of the sources being used and ensure their accuracy.
The main sources of secondary data are:
- The Internet
- Government and non-government sources
- Public libraries
- Educational institutions
- Commercial information sources such as newspapers, journals, radio, TV

When to use quantitative research 6
Here are some simple ways to decide when to use quantitative research . Use quantitative research to:
- recommend a final course of action
- find whether a consensus exists regarding a particular subject
- generalize results to a larger population
- determine a cause-and-effect relationship between variables
- describe characteristics of specific groups of people
- test hypotheses and examine specific relationships
- identify and establish size of market segments
A research case study to understand when to use quantitative research 7
Context: A study was undertaken to evaluate a major innovation in a hospital’s design, in terms of workforce implications and impact on patient and staff experiences of all single-room hospital accommodations. The researchers undertook a mixed methods approach to answer their research questions. Here, we focus on the quantitative research aspect.
Research questions : What are the advantages and disadvantages for the staff as a result of the hospital’s move to the new design with all single-room accommodations? Did the move affect staff experience and well-being and improve their ability to deliver high-quality care?
Method: The researchers obtained quantitative data from three sources:
- Staff activity (task time distribution): Each staff member was shadowed by a researcher who observed each task undertaken by the staff, and logged the time spent on each activity.
- Staff travel distances : The staff were requested to wear pedometers, which recorded the distances covered.
- Staff experience surveys : Staff were surveyed before and after the move to the new hospital design.
Results of quantitative research : The following observations were made based on quantitative data analysis:
- The move to the new design did not result in a significant change in the proportion of time spent on different activities.
- Staff activity events observed per session were higher after the move, and direct care and professional communication events per hour decreased significantly, suggesting fewer interruptions and less fragmented care.
- A significant increase in medication tasks among the recorded events suggests that medication administration was integrated into patient care activities.
- Travel distances increased for all staff, with highest increases for staff in the older people’s ward and surgical wards.
- Ratings for staff toilet facilities, locker facilities, and space at staff bases were higher but those for social interaction and natural light were lower.
Advantages of quantitative research 1,2
When choosing the right research methodology, also consider the advantages of quantitative research and how it can impact your study.
- Quantitative research methods are more scientific and rational. They use quantifiable data leading to objectivity in the results and avoid any chances of ambiguity.
- This type of research uses numeric data so analysis is relatively easier .
- In most cases, a hypothesis is already developed and quantitative research helps in testing and validatin g these constructed theories based on which researchers can make an informed decision about accepting or rejecting their theory.
- The use of statistical analysis software ensures quick analysis of large volumes of data and is less effort intensive.
- Higher levels of control can be applied to the research so the chances of bias can be reduced.
- Quantitative research is based on measured value s, facts, and verifiable information so it can be easily checked or replicated by other researchers leading to continuity in scientific research.
Disadvantages of quantitative research 1,2
Quantitative research may also be limiting; take a look at the disadvantages of quantitative research.
- Experiments are conducted in controlled settings instead of natural settings and it is possible for researchers to either intentionally or unintentionally manipulate the experiment settings to suit the results they desire.
- Participants must necessarily give objective answers (either one- or two-word, or yes or no answers) and the reasons for their selection or the context are not considered.
- Inadequate knowledge of statistical analysis methods may affect the results and their interpretation.
- Although statistical analysis indicates the trends or patterns among variables, the reasons for these observed patterns cannot be interpreted and the research may not give a complete picture.
- Large sample sizes are needed for more accurate and generalizable analysis .
- Quantitative research cannot be used to address complex issues.

Frequently asked questions on quantitative research
Q: What is the difference between quantitative research and qualitative research? 1
A: The following table lists the key differences between quantitative research and qualitative research, some of which may have been mentioned earlier in the article.
Q: What is the difference between reliability and validity? 8,9
A: The term reliability refers to the consistency of a research study. For instance, if a food-measuring weighing scale gives different readings every time the same quantity of food is measured then that weighing scale is not reliable. If the findings in a research study are consistent every time a measurement is made, then the study is considered reliable. However, it is usually unlikely to obtain the exact same results every time because some contributing variables may change. In such cases, a correlation coefficient is used to assess the degree of reliability. A strong positive correlation between the results indicates reliability.
Validity can be defined as the degree to which a tool actually measures what it claims to measure. It helps confirm the credibility of your research and suggests that the results may be generalizable. In other words, it measures the accuracy of the research.
The following table gives the key differences between reliability and validity.
Q: What is mixed methods research? 10
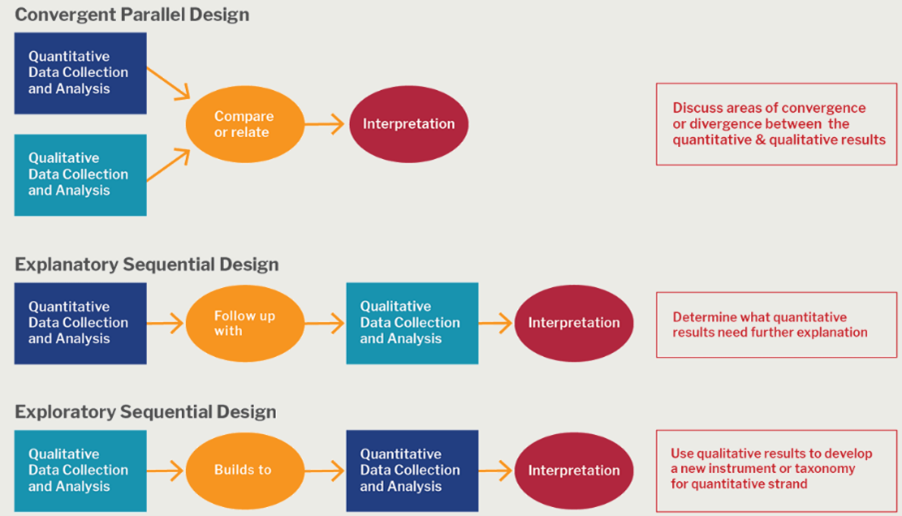
A: A mixed methods approach combines the characteristics of both quantitative research and qualitative research in the same study. This method allows researchers to validate their findings, verify if the results observed using both methods are complementary, and explain any unexpected results obtained from one method by using the other method. A mixed methods research design is useful in case of research questions that cannot be answered by either quantitative research or qualitative research alone. However, this method could be more effort- and cost-intensive because of the requirement of more resources. The figure 3 shows some basic mixed methods research designs that could be used.
Thus, quantitative research is the appropriate method for testing your hypotheses and can be used either alone or in combination with qualitative research per your study requirements. We hope this article has provided an insight into the various facets of quantitative research , including its different characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, and a few tips to quickly understand when to use this research method.
References
- Qualitative vs quantitative research: Differences, examples, & methods. Simply Psychology. Accessed Feb 28, 2023. https://simplypsychology.org/qualitative-quantitative.html#Quantitative-Research
- Your ultimate guide to quantitative research. Qualtrics. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://www.qualtrics.com/uk/experience-management/research/quantitative-research/
- The steps of quantitative research. Revise Sociology. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://revisesociology.com/2017/11/26/the-steps-of-quantitative-research/
- What are the characteristics of quantitative research? Marketing91. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://www.marketing91.com/characteristics-of-quantitative-research/
- Quantitative research: Types, characteristics, methods, & examples. ProProfs Survey Maker. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://www.proprofssurvey.com/blog/quantitative-research/#Characteristics_of_Quantitative_Research
- Qualitative research isn’t as scientific as quantitative methods. Kmusial blog. Accessed March 5, 2023. https://kmusial.wordpress.com/2011/11/25/qualitative-research-isnt-as-scientific-as-quantitative-methods/
- Maben J, Griffiths P, Penfold C, et al. Evaluating a major innovation in hospital design: workforce implications and impact on patient and staff experiences of all single room hospital accommodation. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2015 Feb. (Health Services and Delivery Research, No. 3.3.) Chapter 5, Case study quantitative data findings. Accessed March 6, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK274429/
- McLeod, S. A. (2007). What is reliability? Simply Psychology. www.simplypsychology.org/reliability.html
- Reliability vs validity: Differences & examples. Accessed March 5, 2023. https://statisticsbyjim.com/basics/reliability-vs-validity/
- Mixed methods research. Community Engagement Program. Harvard Catalyst. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://catalyst.harvard.edu/community-engagement/mmr
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

What is Correlational Research: Definition, Types, and Examples

What is Research Protocol? How to Write It (with Examples)
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods
What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analysing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalise results to wider populations.
Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research , which involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g. text, video, or audio).
Quantitative research is widely used in the natural and social sciences: biology, chemistry, psychology, economics, sociology, marketing, etc.
- What is the demographic makeup of Singapore in 2020?
- How has the average temperature changed globally over the last century?
- Does environmental pollution affect the prevalence of honey bees?
- Does working from home increase productivity for people with long commutes?
Table of contents
Quantitative research methods, quantitative data analysis, advantages of quantitative research, disadvantages of quantitative research, frequently asked questions about quantitative research.
You can use quantitative research methods for descriptive, correlational or experimental research.
- In descriptive research , you simply seek an overall summary of your study variables.
- In correlational research , you investigate relationships between your study variables.
- In experimental research , you systematically examine whether there is a cause-and-effect relationship between variables.
Correlational and experimental research can both be used to formally test hypotheses , or predictions, using statistics. The results may be generalised to broader populations based on the sampling method used.
To collect quantitative data, you will often need to use operational definitions that translate abstract concepts (e.g., mood) into observable and quantifiable measures (e.g., self-ratings of feelings and energy levels).
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once data is collected, you may need to process it before it can be analysed. For example, survey and test data may need to be transformed from words to numbers. Then, you can use statistical analysis to answer your research questions .
Descriptive statistics will give you a summary of your data and include measures of averages and variability. You can also use graphs, scatter plots and frequency tables to visualise your data and check for any trends or outliers.
Using inferential statistics , you can make predictions or generalisations based on your data. You can test your hypothesis or use your sample data to estimate the population parameter .
You can also assess the reliability and validity of your data collection methods to indicate how consistently and accurately your methods actually measured what you wanted them to.
Quantitative research is often used to standardise data collection and generalise findings . Strengths of this approach include:
- Replication
Repeating the study is possible because of standardised data collection protocols and tangible definitions of abstract concepts.
- Direct comparisons of results
The study can be reproduced in other cultural settings, times or with different groups of participants. Results can be compared statistically.
- Large samples
Data from large samples can be processed and analysed using reliable and consistent procedures through quantitative data analysis.
- Hypothesis testing
Using formalised and established hypothesis testing procedures means that you have to carefully consider and report your research variables, predictions, data collection and testing methods before coming to a conclusion.
Despite the benefits of quantitative research, it is sometimes inadequate in explaining complex research topics. Its limitations include:
- Superficiality
Using precise and restrictive operational definitions may inadequately represent complex concepts. For example, the concept of mood may be represented with just a number in quantitative research, but explained with elaboration in qualitative research.
- Narrow focus
Predetermined variables and measurement procedures can mean that you ignore other relevant observations.
- Structural bias
Despite standardised procedures, structural biases can still affect quantitative research. Missing data , imprecise measurements or inappropriate sampling methods are biases that can lead to the wrong conclusions.
- Lack of context
Quantitative research often uses unnatural settings like laboratories or fails to consider historical and cultural contexts that may affect data collection and results.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioural avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure.
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something:
- Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions).
- Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure).
If you are doing experimental research , you also have to consider the internal and external validity of your experiment.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, October 10). What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 October 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-quantitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research

Quantitative Research: What It Is, Types & Methods
Quantitative research involves analyzing and gathering numerical data to uncover trends, calculate averages, evaluate relationships, and derive overarching insights. It’s used in various fields, including the natural and social sciences. Quantitative data analysis employs statistical techniques for processing and interpreting numeric data.
Research designs in the quantitative realm outline how data will be collected and analyzed with methods like experiments and surveys. Qualitative methods complement quantitative research by focusing on non-numerical data, adding depth to understanding. Data collection methods can be qualitative or quantitative, depending on research goals. Researchers often use a combination of both approaches to gain a comprehensive understanding of phenomena.
What is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is a systematic investigation of phenomena by gathering quantifiable data and performing statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques.
Quantitative research collects statistically significant information from existing and potential customers. It uses sampling methods and sending out online surveys , online polls , and questionnaires , for example.
One of the main characteristics of this type of research is that the results can be depicted in numerical form . After carefully collecting structured observations and understanding these numbers, it’s possible to predict the future of a product or service, establish causal relationships or Causal Research , and make changes accordingly.
Quantitative research primarily centers on the analysis of numerical data and utilizes inferential statistics to derive conclusions that can be extrapolated to the broader population.
An example of a quantitative research study is the survey conducted to understand how long a doctor takes to tend to a patient when the patient walks into the hospital. A patient satisfaction survey can be administered to ask questions like how long a doctor takes to see a patient, how often a patient walks into a hospital, and other such questions, which are dependent variables in the research. This kind of research method is often employed in the social sciences, and it involves using mathematical frameworks and theories to effectively present data, ensuring that the results are logical, statistically sound, and unbiased.
Data collection in quantitative research uses a structured method and is typically conducted on larger samples representing the entire population. Researchers use quantitative methods to collect numerical data, which is then subjected to statistical analysis to determine statistically significant findings. This approach is valuable in both experimental research and social research. It helps in making informed decisions and drawing reliable conclusions based on quantitative data.
Quantitative Research Characteristics
Quantitative research has several unique characteristics that make it well-suited for specific projects. Let’s explore the most crucial of these characteristics so that you can consider them when planning your next research project:

- Structured tools: Quantitative research relies on structured tools such as surveys, polls, or questionnaires to gather quantitative data . Using such structured methods helps collect in-depth and actionable numerical data from the survey respondents, making it easier to perform data analysis.
- Sample size: Quantitative research is conducted on a significant sample size representing the target market . Appropriate Survey Sampling methods, a fundamental aspect of quantitative research methods, must be employed when deriving the sample to fortify the research objective and ensure the reliability of the results.
- Close-ended questions: Closed-ended questions , specifically designed to align with the research objectives, are a cornerstone of quantitative research. These questions facilitate the collection of quantitative data and are extensively used in data collection processes.
- Prior studies: Before collecting feedback from respondents, researchers often delve into previous studies related to the research topic. This preliminary research helps frame the study effectively and ensures the data collection process is well-informed.
- Quantitative data: Typically, quantitative data is represented using tables, charts, graphs, or other numerical forms. This visual representation aids in understanding the collected data and is essential for rigorous data analysis, a key component of quantitative research methods.
- Generalization of results: One of the strengths of quantitative research is its ability to generalize results to the entire population. It means that the findings derived from a sample can be extrapolated to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions for improvement based on numerical data analysis.
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods are systematic approaches used to gather and analyze numerical data to understand and draw conclusions about a phenomenon or population. They are usually divided into two large groups to understand and organize them easily.:
- Primary quantitative research methods
- Secondary quantitative research methods
Primary Quantitative Research Methods
Primary quantitative research is the most widely used method of conducting market research. The distinct feature of primary research is that the researcher focuses on collecting data directly rather than depending on data collected from previously done research. Primary quantitative research design can be broken down into three further distinctive tracks and the process flow. They are:
A. Techniques and Types of Primary Studies
There are multiple types of primary quantitative research. They can be distinguished into the four following distinctive methods, which are:
01. Survey Research
Survey Research is fundamental for all quantitative outcome research methodologies and studies. Surveys are used to ask questions to a sample of respondents, using various types such as online polls, online surveys, paper questionnaires, web-intercept surveys , etc. Every small and big organization intends to understand what their customers think about their products and services, how well new features are faring in the market, and other such details.
By conducting survey research, an organization can ask multiple survey questions , collect data from a pool of customers, and analyze this collected data to produce numerical results. It is the first step towards collecting data for any research. You can use single ease questions . A single-ease question is a straightforward query that elicits a concise and uncomplicated response.
This type of research can be conducted with a specific target audience group and also can be conducted across multiple groups along with comparative analysis . A prerequisite for this type of research is that the sample of respondents must have randomly selected members. This way, a researcher can easily maintain the accuracy of the obtained results as a huge variety of respondents will be addressed using random selection.
Traditionally, survey research was conducted face-to-face or via phone calls. Still, with the progress made by online mediums such as email or social media, survey research has also spread to online mediums.There are two types of surveys , either of which can be chosen based on the time in hand and the kind of data required:
Cross-sectional surveys
Cross-sectional surveys are observational surveys conducted in situations where the researcher intends to collect data from a sample of the target population at a given point in time. Researchers can evaluate various variables at a particular time. Data gathered using this type of survey is from people who depict similarity in all variables except the variables which are considered for research . Throughout the survey, this one variable will stay constant.
- Cross-sectional surveys are popular with retail, SMEs, and healthcare industries. Information is garnered without modifying any parameters in the variable ecosystem.
- Multiple samples can be analyzed and compared using a cross-sectional survey research method.
- Multiple variables can be evaluated using this type of survey research.
- The only disadvantage of cross-sectional surveys is that the cause-effect relationship of variables cannot be established as it usually evaluates variables at a particular time and not across a continuous time frame.
Longitudinal surveys
Longitudinal surveys are also observational surveys , but unlike cross-sectional surveys, longitudinal surveys are conducted across various time durations to observe a change in respondent behavior and thought processes. This time can be days, months, years, or even decades. For instance, a researcher planning to analyze the change in buying habits of teenagers over 5 years will conduct longitudinal surveys.
- In cross-sectional surveys, the same variables were evaluated at a given time, and in longitudinal surveys, different variables can be analyzed at different intervals.
- Longitudinal surveys are extensively used in the field of medicine and applied sciences. Apart from these two fields, they are also used to observe a change in the market trend analysis , analyze customer satisfaction, or gain feedback on products/services.
- In situations where the sequence of events is highly essential, longitudinal surveys are used.
- Researchers say that when research subjects need to be thoroughly inspected before concluding, they rely on longitudinal surveys.
02. Correlational Research
A comparison between two entities is invariable. Correlation research is conducted to establish a relationship between two closely-knit entities and how one impacts the other, and what changes are eventually observed. This research method is carried out to give value to naturally occurring relationships, and a minimum of two different groups are required to conduct this quantitative research method successfully. Without assuming various aspects, a relationship between two groups or entities must be established.
Researchers use this quantitative research design to correlate two or more variables using mathematical analysis methods. Patterns, relationships, and trends between variables are concluded as they exist in their original setup. The impact of one of these variables on the other is observed, along with how it changes the relationship between the two variables. Researchers tend to manipulate one of the variables to attain the desired results.
Ideally, it is advised not to make conclusions merely based on correlational research. This is because it is not mandatory that if two variables are in sync that they are interrelated.
Example of Correlational Research Questions :
- The relationship between stress and depression: Is there a significant correlation between levels of stress and symptoms of depression among adults?
- The equation between fame and money: What is the relationship between an individual’s level of fame and their financial earnings?
- The relation between activities in a third-grade class and its students: How do classroom activities influence the academic performance and social development of third-grade students?
03. Causal-comparative Research
This research method mainly depends on the factor of comparison. Also called quasi-experimental research , this quantitative research method is used by researchers to conclude the cause-effect equation between two or more variables, where one variable is dependent on the other independent variable. The independent variable is established but not manipulated, and its impact on the dependent variable is observed. These variables or groups must be formed as they exist in the natural setup. As the dependent and independent variables will always exist in a group, it is advised that the conclusions are carefully established by keeping all the factors in mind.
Causal-comparative research is not restricted to the statistical analysis of two variables but extends to analyzing how various variables or groups change under the influence of the same changes. This research is conducted irrespective of the type of relationship that exists between two or more variables. Statistical analysis plan is used to present the outcome using this quantitative research method.
Example of Causal-Comparative Research Questions:
- The impact of drugs on a teenager: How do different types of drug use affect the academic performance and social behavior of teenagers?
- The effect of good education on a freshman: What is the effect of receiving a quality education in high school on the academic success of college freshmen?
- The effect of substantial food provision in the villages of Africa: How does substantial food provision impact the health and economic productivity of villagers in rural African communities?
04. Experimental Research
Also known as true experimentation, this research method relies on a theory. As the name suggests, experimental research is usually based on one or more theories. This theory has yet to be proven before and is merely a supposition. In experimental research, an analysis is done around proving or disproving the statement. This research method is used in natural sciences. Traditional research methods are more effective than modern techniques.
There can be multiple theories in experimental research. A theory is a statement that can be verified or refuted.
After establishing the statement, efforts are made to understand whether it is valid or invalid. This quantitative research method is mainly used in natural or social sciences as various statements must be proved right or wrong.
- Traditional research methods are more effective than modern techniques.
- Systematic teaching schedules help children who struggle to cope with the course.
- It is a boon to have responsible nursing staff for ailing parents.
B. Data Collection Methodologies
The second major step in primary quantitative research is data collection. Data collection can be divided into sampling methods and data collection using surveys and polls.
01. Data Collection Methodologies: Sampling Methods
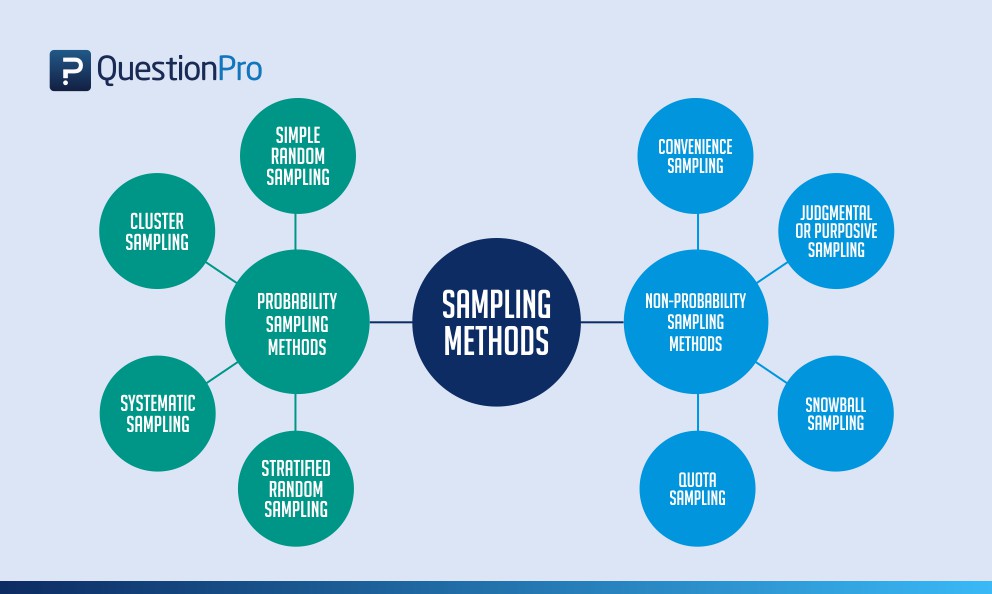
There are two main sampling methods for quantitative research: Probability and Non-probability sampling .
Probability sampling
A theory of probability is used to filter individuals from a population and create samples in probability sampling . Participants of a sample are chosen by random selection processes. Each target audience member has an equal opportunity to be selected in the sample.
There are four main types of probability sampling:
- Simple random sampling: As the name indicates, simple random sampling is nothing but a random selection of elements for a sample. This sampling technique is implemented where the target population is considerably large.
- Stratified random sampling: In the stratified random sampling method , a large population is divided into groups (strata), and members of a sample are chosen randomly from these strata. The various segregated strata should ideally not overlap one another.
- Cluster sampling: Cluster sampling is a probability sampling method using which the main segment is divided into clusters, usually using geographic segmentation and demographic segmentation parameters.
- Systematic sampling: Systematic sampling is a technique where the starting point of the sample is chosen randomly, and all the other elements are chosen using a fixed interval. This interval is calculated by dividing the population size by the target sample size.
Non-probability sampling
Non-probability sampling is where the researcher’s knowledge and experience are used to create samples. Because of the researcher’s involvement, not all the target population members have an equal probability of being selected to be a part of a sample.
There are five non-probability sampling models:
- Convenience sampling: In convenience sampling , elements of a sample are chosen only due to one prime reason: their proximity to the researcher. These samples are quick and easy to implement as there is no other parameter of selection involved.
- Consecutive sampling: Consecutive sampling is quite similar to convenience sampling, except for the fact that researchers can choose a single element or a group of samples and conduct research consecutively over a significant period and then perform the same process with other samples.
- Quota sampling: Using quota sampling , researchers can select elements using their knowledge of target traits and personalities to form strata. Members of various strata can then be chosen to be a part of the sample as per the researcher’s understanding.
- Snowball sampling: Snowball sampling is conducted with target audiences who are difficult to contact and get information. It is popular in cases where the target audience for analysis research is rare to put together.
- Judgmental sampling: Judgmental sampling is a non-probability sampling method where samples are created only based on the researcher’s experience and research skill .
02. Data collection methodologies: Using surveys & polls
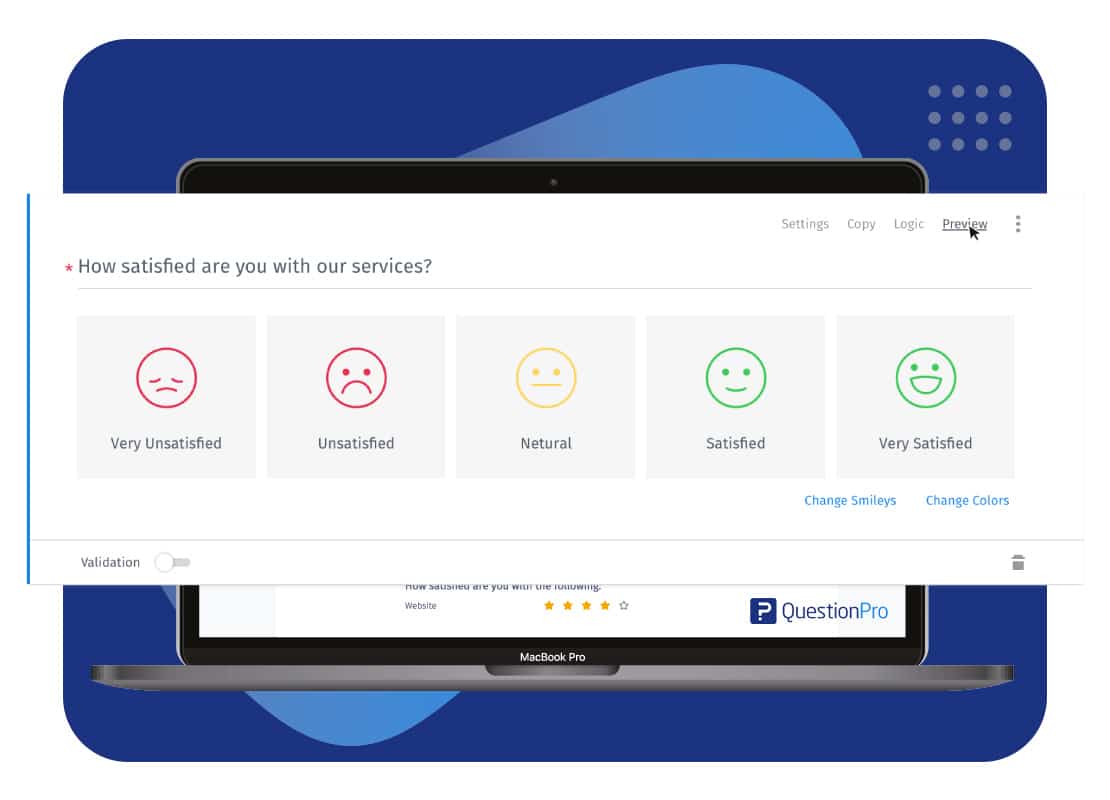
Once the sample is determined, then either surveys or polls can be distributed to collect the data for quantitative research.
Using surveys for primary quantitative research
A survey is defined as a research method used for collecting data from a pre-defined group of respondents to gain information and insights on various topics of interest. The ease of survey distribution and the wide number of people it can reach depending on the research time and objective makes it one of the most important aspects of conducting quantitative research.
Fundamental levels of measurement – nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales
Four measurement scales are fundamental to creating a multiple-choice question in a survey. They are nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio measurement scales without the fundamentals of which no multiple-choice questions can be created. Hence, it is crucial to understand these measurement levels to develop a robust survey.
Use of different question types
To conduct quantitative research, close-ended questions must be used in a survey. They can be a mix of multiple question types, including multiple-choice questions like semantic differential scale questions , rating scale questions , etc.
Survey Distribution and Survey Data Collection
In the above, we have seen the process of building a survey along with the research design to conduct primary quantitative research. Survey distribution to collect data is the other important aspect of the survey process. There are different ways of survey distribution. Some of the most commonly used methods are:
- Email: Sending a survey via email is the most widely used and effective survey distribution method. This method’s response rate is high because the respondents know your brand. You can use the QuestionPro email management feature to send out and collect survey responses.
- Buy respondents: Another effective way to distribute a survey and conduct primary quantitative research is to use a sample. Since the respondents are knowledgeable and are on the panel by their own will, responses are much higher.
- Embed survey on a website: Embedding a survey on a website increases a high number of responses as the respondent is already in close proximity to the brand when the survey pops up.
- Social distribution: Using social media to distribute the survey aids in collecting a higher number of responses from the people that are aware of the brand.
- QR code: QuestionPro QR codes store the URL for the survey. You can print/publish this code in magazines, signs, business cards, or on just about any object/medium.
- SMS survey: The SMS survey is a quick and time-effective way to collect a high number of responses.
- Offline Survey App: The QuestionPro App allows users to circulate surveys quickly, and the responses can be collected both online and offline.
Survey example
An example of a survey is a short customer satisfaction (CSAT) survey that can quickly be built and deployed to collect feedback about what the customer thinks about a brand and how satisfied and referenceable the brand is.
Using polls for primary quantitative research
Polls are a method to collect feedback using close-ended questions from a sample. The most commonly used types of polls are election polls and exit polls . Both of these are used to collect data from a large sample size but using basic question types like multiple-choice questions.
C. Data Analysis Techniques
The third aspect of primary quantitative research design is data analysis . After collecting raw data, there must be an analysis of this data to derive statistical inferences from this research. It is important to relate the results to the research objective and establish the statistical relevance of the results.
Remember to consider aspects of research that were not considered for the data collection process and report the difference between what was planned vs. what was actually executed.
It is then required to select precise Statistical Analysis Methods , such as SWOT, Conjoint, Cross-tabulation, etc., to analyze the quantitative data.
- SWOT analysis: SWOT Analysis stands for the acronym of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threat analysis. Organizations use this statistical analysis technique to evaluate their performance internally and externally to develop effective strategies for improvement.
- Conjoint Analysis: Conjoint Analysis is a market analysis method to learn how individuals make complicated purchasing decisions. Trade-offs are involved in an individual’s daily activities, and these reflect their ability to decide from a complex list of product/service options.
- Cross-tabulation: Cross-tabulation is one of the preliminary statistical market analysis methods which establishes relationships, patterns, and trends within the various parameters of the research study.
- TURF Analysis: TURF Analysis , an acronym for Totally Unduplicated Reach and Frequency Analysis, is executed in situations where the reach of a favorable communication source is to be analyzed along with the frequency of this communication. It is used for understanding the potential of a target market.
Inferential statistics methods such as confidence interval, the margin of error, etc., can then be used to provide results.
Secondary Quantitative Research Methods
Secondary quantitative research or desk research is a research method that involves using already existing data or secondary data. Existing data is summarized and collated to increase the overall effectiveness of the research.
This research method involves collecting quantitative data from existing data sources like the internet, government resources, libraries, research reports, etc. Secondary quantitative research helps to validate the data collected from primary quantitative research and aid in strengthening or proving, or disproving previously collected data.
The following are five popularly used secondary quantitative research methods:
- Data available on the internet: With the high penetration of the internet and mobile devices, it has become increasingly easy to conduct quantitative research using the internet. Information about most research topics is available online, and this aids in boosting the validity of primary quantitative data.
- Government and non-government sources: Secondary quantitative research can also be conducted with the help of government and non-government sources that deal with market research reports. This data is highly reliable and in-depth and hence, can be used to increase the validity of quantitative research design.
- Public libraries: Now a sparingly used method of conducting quantitative research, it is still a reliable source of information, though. Public libraries have copies of important research that was conducted earlier. They are a storehouse of valuable information and documents from which information can be extracted.
- Educational institutions: Educational institutions conduct in-depth research on multiple topics. And hence, the reports that they publish are an important source of validation in quantitative research.
- Commercial information sources: Local newspapers, journals, magazines, radio, and TV stations are great sources to obtain data for secondary quantitative research. These commercial information sources have in-depth, first-hand information on market research, demographic segmentation, and similar subjects.
Quantitative Research Examples
Some examples of quantitative research are:
- A customer satisfaction template can be used if any organization would like to conduct a customer satisfaction (CSAT) survey . Through this kind of survey, an organization can collect quantitative data and metrics on the goodwill of the brand or organization in the customer’s mind based on multiple parameters such as product quality, pricing, customer experience, etc. This data can be collected by asking a net promoter score (NPS) question , matrix table questions, etc. that provide data in the form of numbers that can be analyzed and worked upon.
- Another example of quantitative research is an organization that conducts an event, collecting feedback from attendees about the value they see from the event. By using an event survey , the organization can collect actionable feedback about the satisfaction levels of customers during various phases of the event such as the sales, pre and post-event, the likelihood of recommending the organization to their friends and colleagues, hotel preferences for the future events and other such questions.
Quantitative Research vs Qualitative Research
Quantitative research and qualitative research are two distinct approaches to conducting research, each with its own set of methods and objectives. Here’s a comparison of the two:

Quantitative Research
- Objective: The primary goal of quantitative research is to quantify and measure phenomena by collecting numerical data. It aims to test hypotheses, establish patterns, and generalize findings to a larger population.
- Data Collection: Quantitative research employs systematic and standardized approaches for data collection, including techniques like surveys, experiments, and observations that involve predefined variables. It is often collected from a large and representative sample.
- Data Analysis: Data is analyzed using statistical techniques, such as descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and mathematical modeling. Researchers use statistical tests to draw conclusions and make generalizations based on numerical data.
- Sample Size: Quantitative research often involves larger sample sizes to ensure statistical significance and generalizability.
- Results: The results are typically presented in tables, charts, and statistical summaries, making them highly structured and objective.
- Generalizability: Researchers intentionally structure quantitative research to generate outcomes that can be helpful to a larger population, and they frequently seek to establish causative connections.
- Emphasis on Objectivity: Researchers aim to minimize bias and subjectivity, focusing on replicable and objective findings.
Qualitative Research
- Objective: Qualitative research seeks to gain a deeper understanding of the underlying motivations, behaviors, and experiences of individuals or groups. It explores the context and meaning of phenomena.
- Data Collection: Qualitative research employs adaptable and open-ended techniques for data collection, including methods like interviews, focus groups, observations, and content analysis. It allows participants to express their perspectives in their own words.
- Data Analysis: Data is analyzed through thematic analysis , content analysis, or grounded theory. Researchers focus on identifying patterns, themes, and insights in the data.
- Sample Size: Qualitative research typically involves smaller sample sizes due to the in-depth nature of data collection and analysis.
- Results: Findings are presented in narrative form, often in the participants’ own words. Results are subjective, context-dependent, and provide rich, detailed descriptions.
- Generalizability: Qualitative research does not aim for broad generalizability but focuses on in-depth exploration within a specific context. It provides a detailed understanding of a particular group or situation.
- Emphasis on Subjectivity: Researchers acknowledge the role of subjectivity and the researcher’s influence on the Research Process . Participant perspectives and experiences are central to the findings.
Researchers choose between quantitative and qualitative research methods based on their research objectives and the nature of the research question. Each approach has its advantages and drawbacks, and the decision between them hinges on the particular research objectives and the data needed to address research inquiries effectively.
What are the Advantages of Quantitative Research?
There are many advantages to quantitative research. Some of the major advantages of why researchers use this method in market research are:
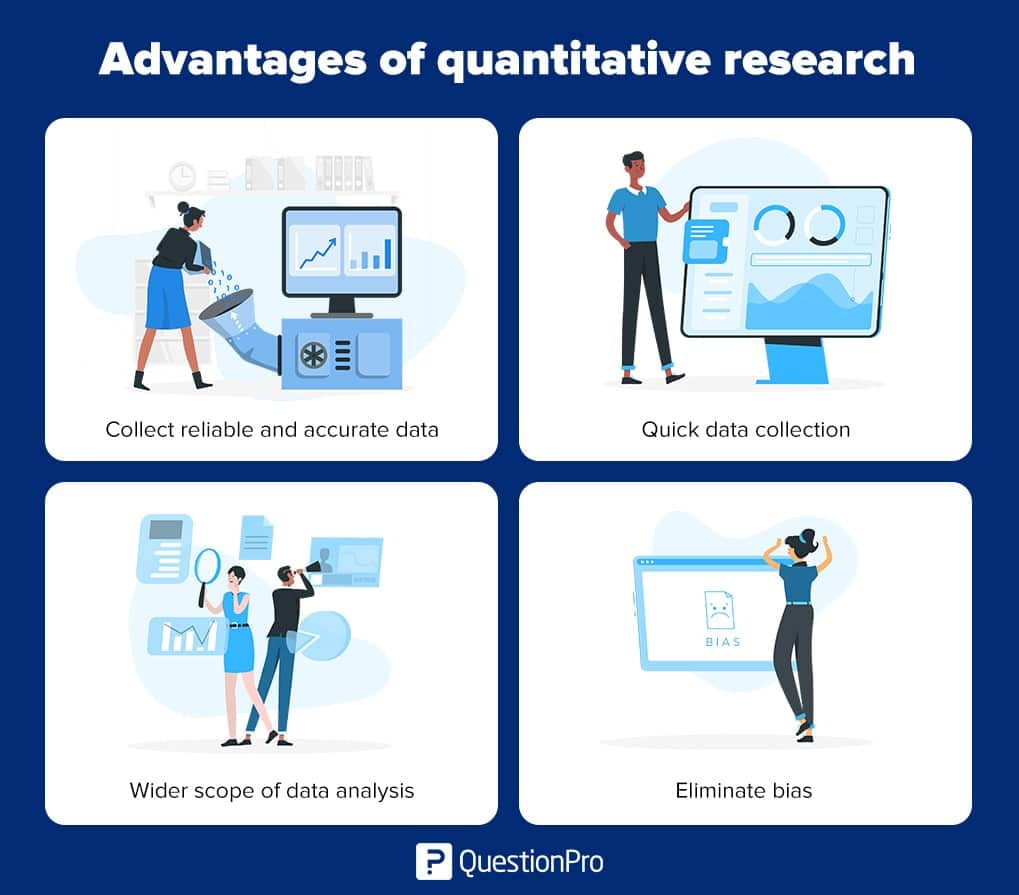
Collect Reliable and Accurate Data:
Quantitative research is a powerful method for collecting reliable and accurate quantitative data. Since data is collected, analyzed, and presented in numbers, the results obtained are incredibly reliable and objective. Numbers do not lie and offer an honest and precise picture of the conducted research without discrepancies. In situations where a researcher aims to eliminate bias and predict potential conflicts, quantitative research is the method of choice.
Quick Data Collection:
Quantitative research involves studying a group of people representing a larger population. Researchers use a survey or another quantitative research method to efficiently gather information from these participants. It makes the process of analyzing the data and identifying patterns faster and more manageable through the use of statistical analysis. This advantage makes quantitative research an attractive option for projects with time constraints.
Wider Scope of Data Analysis:
Quantitative research, thanks to its utilization of statistical methods, offers an extensive range of data collection and analysis. Researchers can explore a broader spectrum of variables and relationships within the data. It can enable a more thorough comprehension of the subject under investigation. This expanded scope is precious when dealing with complex research questions that require in-depth numerical analysis.
Eliminate Bias:
One of the significant advantages of quantitative research is its ability to eliminate bias. This research method leaves no room for personal comments or the biasing of results, as the findings are presented in numerical form. This objectivity makes the results fair and reliable in most cases, reducing the potential for researcher bias or subjectivity.
In summary, quantitative research involves collecting, analyzing, and presenting quantitative data using statistical analysis. It offers numerous advantages, including:
- The collection of reliable and accurate data
- Quick data collection
- A broader scope of data analysis
- The elimination of bias
These advantages makes it a valuable approach in the field of research. When considering the benefits of quantitative research, it’s essential to recognize its strengths in contrast to qualitative methods and its role in collecting and analyzing numerical data for a more comprehensive understanding of research topics.
Best Practices to Conduct Quantitative Research
Here are some best practices for conducting quantitative research:

- Differentiate between quantitative and qualitative: Understand the difference between the two methodologies and apply the one that suits your needs best.
- Choose a suitable sample size: Ensure that you have a sample representative of your population and large enough to be statistically weighty.
- Keep your research goals clear and concise: Know your research goals before you begin data collection to ensure you collect the right amount and the right quantity of data.
- Keep the questions simple: Remember that you will be reaching out to a demographically wide audience. Pose simple questions for your respondents to understand easily.
Quantitative research is a structured way of collecting and analyzing data from various sources. Its purpose is to quantify the problem and understand its extent, seeking results that someone can project to a larger population.
Companies that use quantitative rather than qualitative research typically aim to measure magnitudes and seek objectively interpreted statistical results. So if you want to obtain quantitative data that helps you define the structured cause-and-effect relationship between the research problem and the factors, you should opt for this type of research.
At QuestionPro, we have various Best Data Collection Tools and features to conduct investigations of this type. You can create questionnaires and distribute them through our various methods. We also have sample services or various questions to guarantee the success of your study and the quality of the collected data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Quantitative research is a systematic and structured approach to studying phenomena that involves the collection of measurable data and the application of statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques for analysis.
Quantitative research is characterized by structured tools like surveys, substantial sample sizes, closed-ended questions, reliance on prior studies, data presented numerically, and the ability to generalize findings to the broader population.
The two main methods of quantitative research are Primary quantitative research methods, involving data collection directly from sources, and Secondary quantitative research methods, which utilize existing data for analysis.
1.Surveying to measure employee engagement with numerical rating scales. 2.Analyzing sales data to identify trends in product demand and market share. 4.Examining test scores to assess the impact of a new teaching method on student performance. 4.Using website analytics to track user behavior and conversion rates for an online store.
1.Differentiate between quantitative and qualitative approaches. 2.Choose a representative sample size. 3.Define clear research goals before data collection. 4.Use simple and easily understandable survey questions.
MORE LIKE THIS

Total Experience in Trinidad & Tobago — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Oct 29, 2024

You Can’t Please Everyone — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Oct 22, 2024
Edit survey: A new way of survey building and collaboration
Oct 10, 2024

Pulse Surveys vs Annual Employee Surveys: Which to Use
Oct 4, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships among variables. This method is widely used in social sciences, psychology, economics, and other fields where researchers aim to understand human behavior and phenomena through statistical analysis.
Finding a great title is the key to writing a great quantitative research proposal or paper. A title for quantitative research prepares you for success, failure, or mediocre grades. This post features examples of quantitative research titles for all students.
Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to wider populations.
In summary, quantitative research offers a structured, objective framework geared for hypothesis testing and generalizable insights, while non-quantitative research provides a finer-grained, context-sensitive exploration of phenomena.
Quantitative research stands as a powerful research methodology dedicated to the systematic collection and analysis of measurable data. Learn more about quantitative research Examples, key advantages, methods and best practices.
Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest. This type of research helps in testing the causal relationships between variables, making predictions, and generalizing results to wider populations.
Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analysing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalise results to wider populations.
The necessity, importance, relevance, and urgency of quantitative research are articulated, establishing a strong foundation for the subsequent discussion, which delineates the scope,...
What is quantitative research? Research methods in education (and the other social sciences) are often divided into two main types: quantitative and qualitative methods. This book will discuss one of these two main strands: ‘quantitative methods’, and what distinguishes quantitative from qualitative methods.
Quantitative research is a systematic investigation of phenomena by gathering quantifiable data and performing statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. Quantitative research collects statistically significant information from existing and potential customers.