College of Liberal Arts & Sciences

Department of History
- Why Study History
- Student Financial Aid
- Visit Illinois
- Graduate Admissions
- Graduate Studies and Admissions
- Undergraduate Studies
- Convocation
- Proficiency Exams
- Course Listings
- Fields of Study
- Undergraduate Research
- Faculty Publications
- Women and Gender History Symposium
- Administration & Staff
- Affiliated Faculty
- Graduate Students
- Faculty Resources
- Undergraduate Student Resources
- Public Resources
- News Stories
- Newsletters
- Career Paths in History
- Alumni Spotlights
- Give to History
- Stay Connected
PhD Pre-Defense and Final Defense
Pre-Defense
The pre-defense is an occasion for the dissertator and their committee to come together over a draft of the dissertation to discuss the main arguments, evidence, structure, and organization. This is a good juncture at which each of the committee members can advise the student about major revisions and additions to the tasks of research and thinking that need to be accomplished before the final defense.
The pre-defense generally takes place three to six months before the final defense.
The student is responsible for setting up the meeting: arranging the time and place as well as distributing the draft of the dissertation in time for all the readers to engage with it in a substantive way. The department should also be notified about the event with an e-mail message to the Graduate Secretary.
The pre-defense usually lasts two hours. During the pre-defense each of the committee members has a chance to ask the student questions and usually an organic conversation emerges. If one of the committee members is off campus, they should be asked to participate by sharing comments in advance with the committee chair and the student or might participate via internet. It is not imperative that the entire committee be assembled for the pre-defense.
There is no formal or Graduate College paperwork involved. When the conversation is complete and the student has the instructions from the committee, the advisor should notify the DGS with a short e-mail summary of the pre-defense (about one paragraph). This will be placed in the student's file. A notation will also be added to the Graduate Secretary's records that the pre-defense has taken place.
Final Defense
Instructions for Preparations of Thesis, and a history department thesis checklist, are distributed to each student who becomes ABD. Questions should be directed the Thesis office of the Graduate College and/or the Graduate Secretary. For Graduate College policies about doctoral committees and the final defense, see pages 36-45 in the Graduate College Handbook .
All members of the Doctoral Examination Committee should receive a copy of the dissertation well in advance of the final defense, and in any case not less than one month prior. Some faculty are willing to read electronic copies, but this should not be assumed--please ask your committee members. The Chair of the Committee is responsible for the scheduling, but may delegate the task to the student.
During the final defense, the student is normally asked to leave the room at the beginning of the meeting so committee members can confer about the dissertation and decide on the order in which they will question the student and willingness to have others chime in during their “time” with related questions. The student is then usually invited to return and initiates discussion by briefly describing the dissertation, its main arguments, significance, their own assessments of its strengths and weaknesses, and questions they may have for the committee. Committee members ask questions in sequence, usually ending with the advisor/chair of the dissertation committee. At the end of the two hours the student is asked to leave the room again so the committee members can confer on the result. The result is conveyed orally to the student immediately, and in writing on the forms provided by the graduate secretary.
Time Limitations
Graduate College rules:
- A student who enters the graduate program with a BA must complete the PhD within seven years after first registration in the Graduate College.
- A student who has received an MA elsewhere must complete the PhD within six years after first registering in the Graduate College.
- A student who has an MA from Illinois, then terminates his/her enrollment only to return to the PhD program a year or more later, must complete the PhD no more than six years after the date of return.
Graduate students who have reached these official Graduate College time limits--which differ slightly from norms in history-- must petition for approval from the Graduate College to continue. To receive this approval, the student will present evidence of substantial progress toward the degree (supported by the thesis advisor) and set a date for completion. A petition must be submitted to the Graduate Secretary, who will obtain the necessary signatures and forward to the Graduate College.
Students who have completed 96 hours and all other requirements, save the dissertation, may cease to enroll at the University while they continue to work on the thesis. Students should remember that unless registered they will not have access to services for which they do not pay fees. Upon completion or near completion, a PhD student may re-apply to register for the semester during which the final defense will be taken. Procedures for this vary according to how long the student has been unregistered; and students are advised to contact the Graduate Secretary several months in advance of when they intend to register.
If more than five years elapse between advancement to candidacy (ABD) and the final defense, students are required to demonstrate the currency of their knowledge by retaking the prelim exam, usually in the form of an oral exam with the dissertation committee prior to defense of the thesis--this could be additional time allotted at the start of the final defense. Evidence such as scholarly publications and college-level teaching may be taken as partial evidence of currency, but a prelim exam committee must be appointed, the exam given, and the results reported to the Graduate College.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to prepare an excellent thesis defense
What is a thesis defense?
How long is a thesis defense, what happens at a thesis defense, your presentation, questions from the committee, 6 tips to help you prepare for your thesis defense, 1. anticipate questions and prepare for them, 2. dress for success, 3. ask for help, as needed, 4. have a backup plan, 5. prepare for the possibility that you might not know an answer, 6. de-stress before, during, and after, frequently asked questions about preparing an excellent thesis defense, related articles.
If you're about to complete, or have ever completed a graduate degree, you have most likely come across the term "thesis defense." In many countries, to finish a graduate degree, you have to write a thesis .
A thesis is a large paper, or multi-chapter work, based on a topic relating to your field of study.
Once you hand in your thesis, you will be assigned a date to defend your work. Your thesis defense meeting usually consists of you and a committee of two or more professors working in your program. It may also include other people, like professionals from other colleges or those who are working in your field.
During your thesis defense, you will be asked questions about your work. The main purpose of your thesis defense is for the committee to make sure that you actually understand your field and focus area.
The questions are usually open-ended and require the student to think critically about their work. By the time of your thesis defense, your paper has already been evaluated. The questions asked are not designed so that you actually have to aggressively "defend" your work; often, your thesis defense is more of a formality required so that you can get your degree.
- Check with your department about requirements and timing.
- Re-read your thesis.
- Anticipate questions and prepare for them.
- Create a back-up plan to deal with technology hiccups.
- Plan de-stressing activities both before, and after, your defense.
How long your oral thesis defense is depends largely on the institution and requirements of your degree. It is best to consult your department or institution about this. In general, a thesis defense may take only 20 minutes, but it may also take two hours or more. The length also depends on how much time is allocated to the presentation and questioning part.
Tip: Check with your department or institution as soon as possible to determine the approved length for a thesis defense.
First of all, be aware that a thesis defense varies from country to country. This is just a general overview, but a thesis defense can take many different formats. Some are closed, others are public defenses. Some take place with two committee members, some with more examiners.
The same goes for the length of your thesis defense, as mentioned above. The most important first step for you is to clarify with your department what the structure of your thesis defense will look like. In general, your thesis defense will include:
- your presentation of around 20-30 minutes
- questions from the committee
- questions from the audience (if the defense is public and the department allows it)
You might have to give a presentation, often with Powerpoint, Google slides, or Keynote slides. Make sure to prepare an appropriate amount of slides. A general rule is to use about 10 slides for a 20-minute presentation.
But that also depends on your specific topic and the way you present. The good news is that there will be plenty of time ahead of your thesis defense to prepare your slides and practice your presentation alone and in front of friends or family.
Tip: Practice delivering your thesis presentation in front of family, friends, or colleagues.
You can prepare your slides by using information from your thesis' first chapter (the overview of your thesis) as a framework or outline. Substantive information in your thesis should correspond with your slides.
Make sure your slides are of good quality— both in terms of the integrity of the information and the appearance. If you need more help with how to prepare your presentation slides, both the ASQ Higher Education Brief and James Hayton have good guidelines on the topic.
The committee will ask questions about your work after you finish your presentation. The questions will most likely be about the core content of your thesis, such as what you learned from the study you conducted. They may also ask you to summarize certain findings and to discuss how your work will contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
Tip: Read your entire thesis in preparation of the questions, so you have a refreshed perspective on your work.
While you are preparing, you can create a list of possible questions and try to answer them. You can foresee many of the questions you will get by simply spending some time rereading your thesis.
Here are a few tips on how to prepare for your thesis defense:
You can absolutely prepare for most of the questions you will be asked. Read through your thesis and while you're reading it, create a list of possible questions. In addition, since you will know who will be on the committee, look at the academic expertise of the committee members. In what areas would they most likely be focused?
If possible, sit at other thesis defenses with these committee members to get a feel for how they ask and what they ask. As a graduate student, you should generally be adept at anticipating test questions, so use this advantage to gather as much information as possible before your thesis defense meeting.
Your thesis defense is a formal event, often the entire department or university is invited to participate. It signals a critical rite of passage for graduate students and faculty who have supported them throughout a long and challenging process.
While most universities don't have specific rules on how to dress for that event, do regard it with dignity and respect. This one might be a no-brainer, but know that you should dress as if you were on a job interview or delivering a paper at a conference.
It might help you deal with your stress before your thesis defense to entrust someone with the smaller but important responsibilities of your defense well ahead of schedule. This trusted person could be responsible for:
- preparing the room of the day of defense
- setting up equipment for the presentation
- preparing and distributing handouts
Technology is unpredictable. Life is too. There are no guarantees that your Powerpoint presentation will work at all or look the way it is supposed to on the big screen. We've all been there. Make sure to have a plan B for these situations. Handouts can help when technology fails, and an additional clean shirt can save the day if you have a spill.
One of the scariest aspects of the defense is the possibility of being asked a question you can't answer. While you can prepare for some questions, you can never know exactly what the committee will ask.
There will always be gaps in your knowledge. But your thesis defense is not about being perfect and knowing everything, it's about how you deal with challenging situations. You are not expected to know everything.
James Hayton writes on his blog that examiners will sometimes even ask questions they don't know the answer to, out of curiosity, or because they want to see how you think. While it is ok sometimes to just say "I don't know", he advises to try something like "I don't know, but I would think [...] because of x and y, but you would need to do [...] in order to find out.” This shows that you have the ability to think as an academic.
You will be nervous. But your examiners will expect you to be nervous. Being well prepared can help minimize your stress, but do know that your examiners have seen this many times before and are willing to help, by repeating questions, for example. Dora Farkas at finishyourthesis.com notes that it’s a myth that thesis committees are out to get you.
Two common symptoms of being nervous are talking really fast and nervous laughs. Try to slow yourself down and take a deep breath. Remember what feels like hours to you are just a few seconds in real life.
- Try meditational breathing right before your defense.
- Get plenty of exercise and sleep in the weeks prior to your defense.
- Have your clothes or other items you need ready to go the night before.
- During your defense, allow yourself to process each question before answering.
- Go to dinner with friends and family, or to a fun activity like mini-golf, after your defense.
Allow yourself to process each question, respond to it, and stop talking once you have responded. While a smile can often help dissolve a difficult situation, remember that nervous laughs can be irritating for your audience.
We all make mistakes and your thesis defense will not be perfect. However, careful preparation, mindfulness, and confidence can help you feel less stressful both before, and during, your defense.
Finally, consider planning something fun that you can look forward to after your defense.
It is completely normal to be nervous. Being well prepared can help minimize your stress, but do know that your examiners have seen this many times before and are willing to help, by repeating questions for example if needed. Slow yourself down, and take a deep breath.
Your thesis defense is not about being perfect and knowing everything, it's about how you deal with challenging situations. James Hayton writes on his blog that it is ok sometimes to just say "I don't know", but he advises to try something like "I don't know, but I would think [...] because of x and y, you would need to do [...] in order to find out".
Your Powerpoint presentation can get stuck or not look the way it is supposed to do on the big screen. It can happen and your supervisors know it. In general, handouts can always save the day when technology fails.
- Dress for success.
- Ask for help setting up.
- Have a backup plan (in case technology fails you).
- Deal with your nerves.

- Campus Life
- ...a student.
- ...a veteran.
- ...an alum.
- ...a parent.
- ...faculty or staff.
- UTC Learn (Canvas)
- Class Schedule
- Crisis Resources
- People Finder
- Change Password
UTC RAVE Alert
Pre-defense process, the pre-defense.
The Pre-Defense meeting serves as a “dress rehearsal” for the Final Defense presentation and is the opportune time to address any final edits, questions, or concerns leading up to the Final Defense. Prior to scheduling the Pre-Defense, the candidate will provide the complete manuscript to the Chair. When the Chair is satisfied with the quality of the complete written manuscript (solid in terms of content, clean in terms of overall formatting standards/EndNote references, and free from any major issues/errors/omissions), s/he will contact the candidate and Committee to schedule a final “Pre-Defense” meeting of the candidate and Committee (allotting 60 minutes). The Chair will request the Pre-Defense date and time with the Program Office ( [email protected] ) and must provide the Committee with the manuscript draft at least 14 days prior to the Pre-Defense.
The Chair will guide the candidate in preparing for the Pre-Defense. The candidate will provide the Chair with a draft of the PowerPoint presentation at least 14 days prior to the Pre-Defense. The PowerPoint presentation is typically limited to no more than 30 slides (not including references). Please note it is recommended to rebuild data/results tables using PowerPoint (rather than copying/pasting SPSS tables).
The Pre-Defense (and Final Defense) PowerPoint should be built from the Proposal presentation and should follow the following recommended organization:
- Introduction to the Topic (1-2 slides)
- Summary of the Background/Literature (2-4 slides)
- Research Questions and Research Design (3-5 slides)
- Limitations (1 slide)
- Descriptive Statistics (2-4 slides)
- Findings by Research Question (5-8 slides)
- Implications for Practice (1-2 slides)
- Recommendations for Future Research (1-2 slides)
- Conclusions (1-2 slides)
- References (as needed)
The candidate is responsible to being able to access an electronic copy of research and presentation materials for the defense (a backup plan is strongly recommended). The candidate will present a 25-30 minute oral defense of the study with an emphasis on the findings and the conclusions. The oral defense may not exceed 35 minutes. Candidates are expected to dress in professional business attire for the defense presentation.
- If upon completion of the Pre-Defense the manuscript is not ready for approval, the Chair will notify the Program Office ( [email protected] ) to hold the Examination Results Form. The candidate will work with the Chair to complete the manuscript based upon the Committee’s feedback, and another defense meeting will be convened within a time frame agreed upon by the Dissertation Committee.
- If there are revisions needed for the Pre-Defense manuscript, the Chair will notify the Program Office ( [email protected] ) to hold the Examination Results Form. Once the requested revisions have been made and approved, the Chair will request that the Program Office circulate the Examination Results Form for digital signatures from each Committee member and the Program Director/Advisor.
- If the Pre-Defense manuscript is approved (with only minor revisions), the Chair will request that the Program Office circulate the Examination Results Form for digital signatures from each Committee members and the Program Director/Advisor.
Once the Pre-Defense manuscript has been approved by the Committee and the Program Director/Advisor and the Examination Results Form has been signed by the Committee and the Program Director/Advisor, the Final Defense may be scheduled. The Pre-Defense manuscript and Examination Results Form must be fully approved at least 14 days prior to the Final Dissertation Defense.
Applying for Graduation
For doctoral candidates, the graduation application process should not be completed until the Pre-Defense stage of the dissertation process is approved. Once the candidate has successfully completed the Pre-Defense stage of the dissertation, the Program Office will notify the candidate to apply for graduation, as well as the appropriate steps to complete. Commencement ceremonies are held each year in May and December with a degree conferral option in August. Refer to the Registrar Graduation website for graduation ceremony participation guidelines (link: Registrar - scroll down to access the Graduation section).
Confirming Graduation Eligibility
The Graduate School will audit the candidate’s file in preparation for graduation. Candidates must earn a minimum of 66 total graduate credit hours (Ed.D.) / 75 total graduate credit hours (Ph.D.) toward the doctoral program of study and meet all other academic requirements as listed in the Graduate Catalog in order to be eligible for the graduation ceremony and degree conferral/release of the diploma and transcript. For questions regarding graduation eligibility, contact Mr. Mark Fairchild at [email protected] .
Learning and Leadership Doctorate's Program
Lead programs.
- Hunter Hall #412
- Dept 4141
- 651 McCallie Avenue
- 423-425-5445
- [email protected]
Unsupported browser
This site was designed for modern browsers and tested with Internet Explorer version 10 and later.
It may not look or work correctly on your browser.
- Presentations
How to Start and Give a Great Thesis Defense Presentation
To complete a graduate degree, you'll likely need to create a thesis defense presentation. You must complete a thesis to finish many graduate degree programs.

A thesis is a paper where you explore a topic in depth that's related to what you’ve studied. After completing your thesis paper, you will be asked to defend it through a presentation.
You give this thesis defense in a meeting with a panel of two or more professors in your program. The panel could include other professionals related to your field.
In your thesis defense presentation, you will be asked questions about your topic. The purpose of the questions is to get you to think deeply about your work, so the questions could be open-ended.
To create a thesis defense presentation, you need to know how to make a thesis presentation and how to start your thesis defense. Keep reading to find out more about thesis defense presentations.
How to Structure Your PPT for Thesis Defense

Thesis defense presentations can vary in length. They can be 20 minutes long or two hours long. It depends on how much time is allowed for your presentation and questions.
Talk to your professor to find out how much time is set aside for your presentation. Your thesis defense presentation will be unique to your thesis. But a good presentation includes the following structure:
- Title . You need a title just as your research paper needed a title. The title slide will include the information that you’d include on your paper title. This information can include the title, your name, your school, and course name.
- Introduction . Just like most presentations, your thesis defense presentation should include an introduction slide. This slide should have the topic of your thesis and the question that your presentation answers. It should also include any objections to your research and the answer you’ll be defending in your thesis presentation.
- Literature Review . Next, create two or more slides with a review of the literature used in your research. It doesn’t need to be a complete bibliography. Although you do need to cite your sources, these slides should include your most relevant sources.
- Methodology . These slides in your thesis presentation are where you describe what method you used and an explanation of why you chose that method. If you've got some original research, include the details of that research and how you analyzed the data that you got from that research.
- Results . Some of the most important slides of your PPT for thesis defense contain the results of your research. This should include a description of the data you collected by researching and the results of your data analysis. You also should highlight what your most noteworthy finding was.
- Discussion . These slides of your PPT for thesis defense need to include your research results. Also, show how the results support your argument and how it relates to your original question.
- Conclusion . The conclusion thesis presentation slides should restate your original research questions, show the results of your research, and suggest future research and any final recommendations.
- Ending Slide . The ending slides of your thesis defense presentation are where you add an interesting fact, quote, gif, or hypothetical question. The point is to get your audience to continue to think about your topic while also grabbing their attention. You want your presentation to be memorable.
How to Make a Thesis Presentation
After you’ve seen what the structure of a thesis defense presentation is, there are some more tips that you can follow. Here are tips on how to create a thesis defense presentation:
1. Define Your Concept

After choosing which template to use, the next step is to choose the concept of your thesis defense presentation. Your concept should be relevant to your thesis. To have a fully rounded concept, try to make your presentation templates design relevant to your thesis topic.
Before working on your defense, think about the message you want to convey. This will help you choose elements such as font images and a theme that'll be cohesive.
2. Know Your Audience
Most people give their thesis defense presentation to an academic panel. This panel will look to see if you've developed a thorough understanding of your topic and thesis. They’ll also be looking to see if you've got a solid foundation for your argument.
This is why your presentation is important. You don’t want a sloppy presentation because it can give the impression of laziness and that you don’t care about your presentation. So, choose all aspects of your presentation carefully.
3. Keep Your Slides Focused

Part of giving a good thesis presentation is to have focused slides. This means that you don’t want to have too much information on a slide. It’s best to follow the rule of one point per slide. If you've got too much on a single slide, it can be hard for the audience to follow you.
4. Structure Your Presentation
After you’ve chosen your concept, it's time to structure the content of your thesis. When structuring your information, you want to show that you understand the subject matter and that you're organized.
5. Less Is More

Each slide should have enough information that you can make your point. It’s important that your audience listens more than they read. By speaking, you show your audience that you know the topic you’re presenting on. So, when creating your slides, remember that less is more.
6. Consider Your Typography
After choosing your thesis presentation subject, consider what typography to use. Your typography should create an impact without distracting from your topic.
When considering your typography, consider your text's colors. Your text's colors should contrast with your slide's background. If the text doesn’t contrast well, it can distract the audience, causing them not to pay attention as you speak.
7. Stick to Important Data

Include data that'll strengthen your argument. Your data should also show that you’ve researched your thesis. If you can, add visuals that are relevant to your data. Visuals stimulate your brain and can increase how fast you process information. So, including relevant visuals can make your data easier to process and remember.
8. Consistency Is Key
When thinking about how to make a thesis presentation, think about consistency. For an impressive presentation, your presentation should flow well. It’s easier to have consistency when using a template because it’s already designed by a professional.
Check your finished presentation for consistency. This means making sure all your titles on slides are the same font and font size. Also, make sure that your body text is consistent throughout.
9. Explain Your Thesis

The next step in how to make a thesis presentation is to explain your thesis in great detail. The first part of this is your methodology slide . This is where you explain what method you used for your research, why you chose the topic, and how you conducted your research.
For this part of your thesis, chart and tables in your presentation are helpful in explaining data. In this section, keep your text minimal to let the chart, graphs, and data stand out.
Next, tell the audience what the data means. Infographics are a great option to use in this section. Infographics and icons can quickly and simply show your message.
10. End Your Thesis
The last section of your thesis presentation is where you end it. Make your ending memorable to keep your audience thinking.
In your conclusion, overview your thesis topic and remind the audience of the answer that your research proved. Next, cover the important research points you want your audience to remember. A slide with icons is a great way to do this. Also, address your shortcomings in your research and how there can be improvements in future research.
Finally, use some more presentation tips by reading this helpful article:

A Top Source for Presentation Templates
Envato Elements is the best place for presentation templates. Plus, they also have more than just premium templates. They've icons, photos, fonts, and more. To gain access to these digital elements, you must pay a low monthly fee and sign up to become a member. Once you sign up , you get unlimited access and downloads to digital elements.
Explore Presentation Templates

A premium template saves you time because you're starting with a great base. Just add your information when using a template. This is a lot quicker than trying to design a presentation from scratch. If you like to customize your presentation, you still can find a good premium template that's easily customizable.
Every template is designed by a professional to look stylish and impressive. This means that your presentation will stand out among all the made-from-scratch presentations.
Use a Premium Template for Your Thesis Defense Presentation Today!
Now that you’ve been given tips on how to start a thesis presentation and what it should contain, put this information to use when creating your thesis presentation. Save time from having to create a presentation from scratch by downloading a premium template today!

- Slidesgo School
- Presentation Tips
How to Start a Thesis Defense Presentation

After months and years of hard work, the moment to wrap things all up is finally here—your thesis defense presentation.
Whether you’re pursuing a master’s degree or doctorate, it’s the final step to that much-deserved achievement.
A thesis defense requires a lot of prior research and preparation. And as important as its content is, so is how you present it because a stunning design with clear data and text hierarchy plays an immense role in comprehension.
In this article, we’ll explore how you make your thesis defense .
The organization is the key to success. Establishing some previous steps before any project or work is essential for the result to be very positive. And the defense of a thesis could not be less.
Below, we will develop all the necessary steps to make a thesis defense presentation and we will give you some tips on how to carry them out.
How to Make an Amazing Presentation
Defining the concept of your thesis presentation, structuring your thesis defense presentation, how do you welcome the audience, tell them why you did this thesis, go into the content by explaining your thesis part by part, how to end the defense of the thesis.
After a long time of research and study, the content of your thesis is ready. Now, you have to find the best way to reflect all that effort behind your work. The information comes across more clearly if you use a visual format, as it attracts the attention of the audience. To present your thesis information in a clear, concise, and ultimately amazing way, you can use one of our unique thesis defense templates , available at Slidesgo.
As an example, in this article, we are going to use the Ecology Thesis template . With it, we will show you what to include in your presentation and how to make an attractive design.
After choosing the Google Slides and PowerPoint template that best suits the needs and subject matter of your thesis, it is time to define an overarching concept.
This is the main theme on which your designs are based. It must be relevant to your thesis as its purpose is to guide your selection of colors, typography, images, style, etc.
These must be portrayed in a way that supports the main message of your slides and should be aligned with your concept both visually and sociologically.
Once you have defined the concept, you will have to move on to the next step: structuring the content of your thesis. A good structure will show that there is a good organization behind the work, but most importantly: it will highlight your content.
In this article, we are going to show you a structure that could be a good example of how to structure a thesis, but you can adapt it to what your specific content requires.
Before you begin your thesis defense, you should welcome your audience. A good presentation will make you connect with your audience, which will result in more general interest in your work.
Use an appropriate language register (avoid informal language), but be approachable and natural.
"Welcome to the thesis defense on [the title of your thesis]". Next, introduce yourself with your name and give a short description of your background and occupation.
Don't forget to say “thank you for attending!”
To continue establishing that connection with your audience, explain the reasons that led you to do this thesis. Tell the professional reasons, and you can even say some personal ones, which will denote closeness, and your audience will appreciate it.
Now it's time to go into the content of the thesis ! After these preliminary steps, which are just as important as the thesis itself, it is time to explain part by part the structure (which you had previously established). We are going to propose a structure for your project, but the final decision is always yours!

First impressions are very important. Because your title page is the very first thing viewers see, it must be striking and impactful. It also sets the stage for the rest of your slides.
In one glance, the following should be established:
- Thesis defense topic
- Design style
For instance, the ecology thesis’s title page uses illustrations of a natural landscape to represent the topic of nature and a striking shade of blue to set the tone.
The sans serif font used depicts clean-cut typography and style and the thesis topic is written in large and bold typography, which draws attention to it immediately.
.jpg)
Right after your title page, include an introduction slide to provide more details about your topic.
This means explaining what you hope to answer with your research, its importance to your field, and why you chose it.
Continue to incorporate design elements relevant to your concept. This example has done just that by using a different natural landscape and including animals. For coherence, stick to the same typography and style throughout your presentation.
.jpg)
The aim of the literature review slide is to illustrate your knowledge of your thesis topic and any relevant theories.
Walls of text kill a design. For clarity, we recommend presenting this with bullet points. Each one should be short and sweet and only touch on the basics; you can elaborate on them in your speech.
Don’t forget to be consistent with your design. In our example, we’ve maintained the tone of blue chosen and added illustrations of leaves in the far corners of the slide.
Also, address similar research that has been done. This is to showcase your topic’s originality and, if relevant, how it’s different and/or an improvement from previously done research.
.jpg)
This is one of the most important parts of a thesis defense presentation.
It allows your viewers to assess the rationality and validity of your approach and consequently, the accuracy of your results.
A great methodology slide explains the what , how, and why :
- What method did you use for your research
- Why did you choose it
- How did you conduct it
Because this part of your thesis will be rather technical, the most effective way to aid understanding is by using graphics like charts and tables.
.jpg)
Keep text to a minimum to avoid drawing attention away from the graphics. If there is a text that must absolutely be included, consider using bullet points and keep them short.
Don’t forget to maintain color, style, and typography coherence.
.jpg)
The results slides are easily the most quantitative part of a thesis defense.
Here, your aim is to simply introduce your findings. Select the most impactful data and highlight them here.
Just as with methodology, use graphics like charts, tables, and graphs to portray the data in a clear way. And, once again, try not to write too much text. Let the visual content do the talking .
.jpg)
After you’ve introduced your data, the next step would be to help your audience make sense of it. That means understanding what it means in the context of your thesis research topic and your discipline.
Simply put, you should answer the question: What do the numbers mean?
The best way to approach this would be to do it as if you were creating an infographic .
Illustrations like icons are a quick and simple way to represent your message. It also reduces the amount of text on your slide, which makes the information much more digestible.
For a balanced thesis presentation, you should also address any outliers and anomalies.
To quote bestselling author Robin Sharma, “Starting strong is good. Finishing strong is epic.”
That’s exactly what to aim for in your conclusion.
Provide an overview of your thesis topic and remind your audience what you set out to answer with your research. In our example, we’ve used three icons accompanied by a short title and text.
.jpg)
Following that, reiterate the important points of your research results you want your audience to take away from your thesis defense presentation.
You can do so by expanding the next slide to have more icons and points, for example.
.jpg)
Don’t forget to address any shortcomings and limitations in your approach and extra points for suggesting possible improvements for future research.
We are going to give you a little tip to make your thesis defense a success. You can combine your defense with good public speaking techniques. Take a look at our article "How to become a great speaker" .
We hope this article has been of great help, have you already seen our templates to make the presentation of your thesis ? Choose the one that best suits your needs, we are sure that one of them will go perfectly with your thesis presentation!
Good luck from Slidesgo.

Do you find this article useful?
Related tutorials.

How to present a business plan (with tips and templates)
The aim of a good business plan is to get an external party interested in a particular business project. Whether it’s an investor or a potential partner, business plans have to be powerful enough to paint a picture and motivate action.For a long time, business projects exist only in the minds of those involved in them. Putting those ideas in a way an external party can fully understand and value them can be a challenging task. However, there are some key aspects that, when considered, will set your business plan apart from the get-go.We’ll review in this article five tips to build...

Slidesgo for Education: How to use it being a school district
Education is always on the move, and the integration of technology into classrooms is revolutionizing the way we teach and learn. In this way, Slidesgo has come in handy for teachers worldwide, but… did you know we have more than just slides? Now is your chance to redefine the educational scene in your school district. However, to do so, a flashy presentation alone won’t cut it—you need the right approach and the proper set of tools to truly change the way educators and students connect. By streamlining teaching and ramping up engagement, you can make a real, tangible difference. Let’s explore how Slidesgo for Education can inspire and...

Lesson plan generator: AI-mazing classes that empower minds
Teaching is an art, but even the most creative educators need a little help streamlining their planning. With just 24 hours in a day, it often feels like we need days with 37 hours to get everything done. That’s where we at Slidesgo come in, tackling this issue head-on and developing a practical, simple, and—most importantly—fast solution for educators.Our brand-new AI lesson plan generator is not just another digital tool; it’s your new teaching assistant that will transform your lesson planning process. With just a few details—your lesson topic, classroom level, and setting—you’ll get within seconds a fully formed lesson plan tailored to engage...

Why do you need Slidesgo if you are a student?
Being a student can be a bit tough— juggling deadlines to absorbing heaps of new information, students face many challenges on a daily basis.Fortunately, technology has tackled some of the most time-consuming aspects of learning, giving students room to develop complex skills. Even if traditional education is still catching up with some of these advancements, students are finding and using helpful educational tools to streamline their study routines.Slidesgo is one of these tools, making the learning experience more rewarding. Let’s find out why!

PhD Dissertation Defense Slides Design: Start
- Tips for designing the slides
- Presentation checklist
- Example slides
- Additional Resources
Purpose of the Guide
This guide was created to help ph.d. students in engineering fields to design dissertation defense presentations. the guide provides 1) tips on how to effectively communicate research, and 2) full presentation examples from ph.d. graduates. the tips on designing effective slides are not restricted to dissertation defense presentations; they can be used in designing other types of presentations such as conference talks, qualification and proposal exams, and technical seminars., the tips and examples are used to help students to design effective presentation. the technical contents in all examples are subject to copyright, please do not replicate. , if you need help in designing your presentation, please contact julie chen ([email protected]) for individual consultation. .
- Example Slides Repository
- Defense slides examples Link to examples dissertation defense slides.
Useful Links
- CIT Thesis and dissertation standards
- Dissertations and Theses @ Carnegie Mellon This link opens in a new window Covers 1920-present. Full text of some dissertations may be available 1997-present. Citations and abstracts of dissertations and theses CMU graduate students have published through UMI Dissertation Publishing. In addition to citations and abstracts, the service provides free access to 24 page previews and the full text in PDF format, when available. In most cases, this will be works published in 1997 forward.
- Communicate your research data Data visualization is very important in communicating your data effectively. Check out these do's and don'ts for designing figures.
Power Point Template and other Resources
- CEE Powerpoint Slide Presentation Template 1
- CEE Powerpoint Slide Presentation Template 2
Source: CEE Department Resources https://www.cmu.edu/cee/resources/index.html
- CMU Powerpoint Slide Template
Source: CMU Marketing and Communications
https://www.cmu.edu/marcom/brand-standards/downloads/index.html
- Use of CMU logos, marks, and Unitmarks
Email me for questions and schedule an appointment

Top 7 tips for your defense presentation
1. show why your study is important, remember, your audience is your committee members, researchers in other fields, and even the general public. you want to convince all of them why you deserve a ph.d. degree. you need to talk about why your study is important to the world. in the engineering field, you also need to talk about how your study is useful. try to discuss why current practice is problematic or not good enough, what needs to be solved, and what the potential benefits will be. , see how dr. posen and dr. malings explained the importance of their studies..
- Carl Malings Defense Slides with Notes
- I. Daniel Posen Defense Slides with Notes
2. Emphasize YOUR contribution
Having a ph.d. means that you have made some novel contributions to the grand field. this is about you and your research. you need to keep emphasizing your contributions throughout your presentation. after talking about what needs to be solved, try to focus on emphasizing the novelty of your work. what problems can be solved using your research outcomes what breakthroughs have you made to the field why are your methods and outcomes outstanding you need to incorporate answers to these questions in your presentation. , be clear what your contributions are in the introduction section; separate what was done by others and what was done by you. , 3. connect your projects into a whole piece of work, you might have been doing multiple projects that are not strongly connected. to figure out how to connect them into a whole piece, use visualizations such as flow charts to convince your audience. the two slides below are two examples. in the first slide, which was presented in the introduction section, the presenter used a flow diagram to show the connection between the three projects. in the second slide, the presenter used key figures and a unique color for each project to show the connection..

- Xiaoju Chen Defense Slides with Notes
4. Tell a good story
The committee members do not necessarily have the same background knowledge as you. plus, there could be researchers from other fields and even the general public in the room. you want to make sure all of your audience can understand as much as possible. focus on the big picture rather than technical details; make sure you use simple language to explain your methods and results. your committee has read your dissertation before your defense, but others have not. , dr. cook and dr. velibeyoglu did a good job explaining their research to everyone. the introduction sessions in their presentations are well designed for this purpose. .
- Laren M. Cook Defense Slides with Notes
- Irem Velibeyoglu Defense with Notes
5. Transition, transition, transition
Use transition slides to connect projects , it's a long presentation with different research projects. you want to use some sort of transition to remind your audience what you have been talking about and what is next. you may use a slide that is designed for this purpose throughout your presentation. , below are two examples. these slides were presented after the introduction section. the presenters used the same slides and highlighted the items for project one to indicate that they were moving on to the first project. throughout the presentation, they used these slides and highlighted different sections to indicate how these projects fit into the whole dissertation. .

You can also use some other indications on your slides, but remember not to make your slides too busy. Below are two examples. In the first example, the presenter used chapter numbers to indicate what he was talking about. In the second example, the presenter used a progress bar with keywords for each chapter as the indicator.

Use transition sentences to connect slides
Remember transition sentences are also important; use them to summarize what you have said and tell your audience what they will expect next. if you keep forgetting the transition sentence, write a note on your presentation. you can either write down a full sentence of what you want to say or some keywords., 6. be brief, put details in backup slides , you won't have time to explain all of the details. if your defense presentation is scheduled for 45 minutes, you can only spend around 10 minutes for each project - that's shorter than a normal research conference presentation focus on the big picture and leave details behind. you can put the details in your backup slides, so you might find them useful when your committee (and other members of the audience) ask questions regarding these details., 7. show your presentation to your advisor and colleagues, make sure to ask your advisor(s) for their comments. they might have a different view on what should be emphasized and what should be elaborated. , you also want to practice at least once in front of your colleagues. they can be your lab mates, people who work in your research group, and/or your friends. they do not have to be experts in your field. ask them to give you some feedback - their comments can be extremely helpful to improve your presentation. , below are some other tips and resources to design your defense presentation. .
- Tips for designing your defense presentation
How important is your presentation, and cookies?

- Next: Tips for designing the slides >>
- Last Updated: Jan 9, 2024 11:18 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.cmu.edu/c.php?g=883178
How Do I Prepare for a Successful Defence?
Vivas and Presentations
- First Online: 19 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Sue Reeves ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3017-0559 3 &
- Bartek Buczkowski ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4146-3664 4
420 Accesses
Once you have submitted your dissertation, you may be asked to do a defence of your dissertation. This could be in the form of an oral presentation, a poster presentation of your findings, or you could be invited to a viva voce. Vivas, as they are usually known, are particularly common for research degrees such as MPhils or PhDs and are essentially a verbal defence of your thesis that is conducted in an interview style format. At a minimum, the viva is a way of checking you authored the thesis yourself and understand the detail, but it is also an opportunity to discuss your research findings and interpretations in depth with experts. Preparation is key for defending your thesis in a viva or a presentation format. With a bit of groundwork, you could even enjoy the discussion, after all the thesis is the culmination of all your hard work, and no one knows it better than you.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or Ebook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Ratcliffe R (2015) How to survive a PhD viva: 17 top tips. https://www.theguardian.com/higher-education-network/2015/jan/08/how-to-survive-a-phd-viva-17-top-tips. Accessed 3 Mar 2023
Further Reading
Levin P, Topping G (2006) Perfect presentations. Open University Press
Google Scholar
Smith P (2014) The PhD viva: how to prepare for your oral examination. Macmillan, New York
Book Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Roehampton, London, UK
Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
Bartek Buczkowski
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Reeves, S., Buczkowski, B. (2023). How Do I Prepare for a Successful Defence?. In: Mastering Your Dissertation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_14
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_14
Published : 19 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-41910-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-41911-9
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Prepare for Your Dissertation Defense

4-minute read
- 1st August 2023
After years of research and study, you’ve finally reached the grand finale of your PhD years: your dissertation defense. Since defending your dissertation is the culmination of all your hard work, it’s essential to do everything you can to prepare for it.
In this post, we’ll take you through how to ready yourself for your dissertation defense so you can focus on your accomplishments and excel during this crucial professional moment.
What is a Dissertation Defense?
The dissertation defense is the crowning moment of years of research – the final examination before a PhD student is awarded their doctoral degree.
During a dissertation defense, the student presents their research, methodology, findings, and conclusions to a committee of faculty members and experts in their field. The committee then engages in a question-and-answer session to assess the student’s understanding of the subject matter, the quality of their research, and their ability to defend their work under scrutiny.
Many PhD students consider it to be the defining moment of their academic career and their chance to prove their expertise in their chosen research field.
If all this sounds overwhelming – don’t worry. If you’re a PhD student, you’ll have plenty of time and opportunity to adequately prepare for your dissertation defense. Below are some strategies to help you get ready for this significant occasion in your career.
1. Know the Requirements
Familiarize yourself with your institution’s guidelines and requirements for the defense process. Understanding the format, time limit, and expectations for the presentation will help you to prepare your material and anticipate any issues.
2. Review Your Dissertation
Even if you think you know it inside and out, review your dissertation from beginning to end. It may have been some time since you’ve last read and considered certain portions of your research and findings. Consider what your committee might ask about your research questions , data analysis, and conclusions.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
3. Work on Starting Strong
To begin your defense on a strong note, work on creating a clear and engaging introduction. You can start by briefly outlining the purpose of your study, research questions, and methodology . Try to stay on topic and don’t veer off track by discussing unrelated or unnecessary information.
4. Practice Presenting
Practice your presentation skills by rehearsing your defense multiple times. Focus on clarity and pacing and try to stay within the allotted time limit. It also helps to record yourself so that you can see yourself from your audience’s point of view.
5. Practice Q&A Sessions
To build your confidence, enlist friends and colleagues to conduct mock question-and-answer sessions. When practicing, remember to pause before answering questions you’re unsure of. It’s better to take your time delivering a response than it is to give an inaccurate or incorrect answer.
6. Seek Feedback
Find out if your institution offers mock defense sessions where peers or mentors play the role of the committee, ask you questions, and give feedback . You can also have colleagues, mentors, or advisors review your presentation and offer practical feedback.
7. Create Visual Aids
Think about any visual aids , such as slides, you may want to use to illustrate your defense and prepare them in advance. Be sure to check that your university allows visuals or images and that they enhance, rather than overwhelm, your presentation.
8. Stay Calm and Confident
It’s natural to feel nervous but try to stay calm and composed during your defense. Take deep breaths and remind yourself of the expertise you’ve gained through the experience of writing your dissertation.
Expert Proofreading Services
The best way to prepare for your dissertation defense is to have your dissertation professionally proofread. Our editing experts have extensive experience with a wide variety of academic subjects and topics and can help ensure your dissertation is ready for presentation. Send in a free sample of 500 words or less and get started today.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
17 Thesis Defense Questions and How to Answer Them

A thesis defense gives you the chance to show off your thesis work and demonstrate your expertise in your field of study. During this one- to two-hour discussion with the members of your thesis committee, you'll have some control over how you present your research, but your committee will ask you some prodding questions to test your knowledge and preparedness. They will all have read your thesis beforehand, so their questions will relate to your study, topic, methods, data sample, and other aspects.
A good defense requires mastery of the thesis itself, so before you consider the questions you might face,
1. What is your topic, and why did you choose it?
Give a quick summary in just a few sentences on what you've researched. You could certainly go on for hours about your work, but make sure you prepare a way to give a very brief overview of your thesis. Then, give a quick background on your process for choosing this topic.
2. How does your topic contribute to the existing literature? How is it important?
Many researchers identify a need in the field and choose a topic to bridge the gaps that previous literature has failed to cover. For example, previous studies might not have included a certain population, region, or circumstance. Talk about how your thesis enhances the general understanding of the topic to extend the reach beyond what others have found, and then give examples of why the world needs that increased understanding. For instance, a thesis on romaine lettuce crops in desert climates might bring much-needed knowledge to a region that might not have been represented in previous work.
3. What are the key findings of your study?
When reporting your main results, make sure you have a handle on how detailed your committee wants you to be. Give yourself several options by preparing 1) a very general, quick summary of your findings that takes a minute or less, 2) a more detailed rundown of what your study revealed that is 3-5 minutes long, and 3) a 10- to 15-minute synopsis that delves into your results in detail. With each of these responses prepared, you can gauge which one is most appropriate in the moment, based on what your committee asks you and what has already been requested.
4. What type of background research did you do for your study?
Here you'll describe what you did while you were deciding what to study. This usually includes a literary review to determine what previous researchers have already introduced to the field. You also likely had to look into whether your study was going to be possible and what you would need in order to collect the needed data. Did you need info from databases that require permissions or fees?

5. What was your hypothesis, and how did you form it?
Describe the expected results you had for your study and whether your hypothesis came from previous research experience, long-held expectations, or cultural myths.
6. What limitations did you face when writing your text?
It's inevitable — researchers will face roadblocks or limiting factors during their work. This could be a limited population you had access to, like if you had a great method of surveying university students, but you didn't have a way to reach out to other people who weren't attending that school.
7. Why did you choose your particular method for your study?
Different research methods are more fitting to specific studies than others (e.g., qualitative vs. quantitative ), and knowing this, you applied a method that would present your findings most effectively. What factors led you to choose your method?
8. Who formed the sample group of your study, and why did you choose this population?
Many factors go into the selection of a participant group. Perhaps you were motivated to survey women over 50 who experience burnout in the workplace. Did you take extra measures to target this population? Or perhaps you found a sample group that responded more readily to your request for participation, and after hitting dead ends for months, convenience is what shaped your study population. Make sure to present your reasoning in an honest but favorable way.
9. What obstacles or limitations did you encounter while working with your sample?
Outline the process of pursuing respondents for your study and the difficulties you faced in collecting enough quality data for your thesis. Perhaps the decisions you made took shape based on the participants you ended up interviewing.
10. Was there something specific you were expecting to find during your analysis?
Expectations are natural when you set out to explore a topic, especially one you've been dancing around throughout your academic career. This question can refer to your hypotheses , but it can also touch on your personal feelings and expectations about this topic. What did you believe you would find when you dove deeper into the subject? Was that what you actually found, or were you surprised by your results?
11. What did you learn from your study?
Your response to this question can include not only the basic findings of your work (if you haven't covered this already) but also some personal surprises you might have found that veered away from your expectations. Sometimes these details are not included in the thesis, so these details can add some spice to your defense.
12. What are the recommendations from your study?
With connection to the reasons you chose the topic, your results can address the problems your work is solving. Give specifics on how policymakers, professionals in the field, etc., can improve their service with the knowledge your thesis provides.
13. If given the chance, what would you do differently?
Your response to this one can include the limitations you encountered or dead ends you hit that wasted time and funding. Try not to dwell too long on the annoyances of your study, and consider an area of curiosity; for example, discuss an area that piqued your interest during your exploration that would have been exciting to pursue but didn't directly benefit your outlined study.
14. How did you relate your study to the existing theories in the literature?
Your paper likely ties your ideas into those of other researchers, so this could be an easy one to answer. Point out how similar your work is to some and how it contrasts other works of research; both contribute greatly to the overall body of research.
15. What is the future scope of this study?
This one is pretty easy, since most theses include recommendations for future research within the text. That means you already have this one covered, and since you read over your thesis before your defense, it's already fresh in your mind.
16. What do you plan to do professionally after you complete your study?
This is a question directed more to you and your future professional plans. This might align with the research you performed, and if so, you can direct your question back to your research, maybe mentioning the personal motivations you have for pursuing study of that subject.
17. Do you have any questions?
Although your thesis defense feels like an interrogation, and you're the one in the spotlight, it provides an ideal opportunity to gather input from your committee, if you want it. Possible questions you could ask are: What were your impressions when reading my thesis? Do you believe I missed any important steps or details when conducting my work? Where do you see this work going in the future?
Bonus tip: What if you get asked a question to which you don't know the answer? You can spend weeks preparing to defend your thesis, but you might still be caught off guard when you don't know exactly what's coming. You can be ready for this situation by preparing a general strategy. It's okay to admit that your thesis doesn't offer the answers to everything – your committee won't reasonably expect it to do so. What you can do to sound (and feel!) confident and knowledgeable is to refer to a work of literature you have encountered in your research and draw on that work to give an answer. For example, you could respond, "My thesis doesn't directly address your question, but my study of Dr. Leifsen's work provided some interesting insights on that subject…." By preparing a way to address curveball questions, you can maintain your cool and create the impression that you truly are an expert in your field.
After you're done answering the questions your committee presents to you, they will either approve your thesis or suggest changes you should make to your paper. Regardless of the outcome, your confidence in addressing the questions presented to you will communicate to your thesis committee members that you know your stuff. Preparation can ease a lot of anxiety surrounding this event, so use these possible questions to make sure you can present your thesis feeling relaxed, prepared, and confident.
Header image by Kasto .
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Take your thesis to new heights with our expert editing
The top 10 thesis defense questions (+ how to prepare strong answers)

Crafting a thesis is significant, but defending it often feels like the ultimate test. While nerve-wracking, proper preparation can make it manageable. Prepare for your thesis defense with insights on the top questions you can expect, including strategies for answering convincingly.
Mastering the thesis defense: cultivate a success mindset
Confidence enables you to present your research with conviction, while composure allows you to navigate any challenges with grace and clarity.
Remember, you know your thesis best, so trust in your expertise.
Stay composed and focused, relying on your thorough preparation. If you encounter a question you can’t answer, gracefully guide the conversation back to familiar topics.
By embracing these principles and staying confident and adaptable, you’ll navigate your thesis defense with ease.
Question 1: Why did you choose this particular topic for your research?
Moreover, discuss the gaps you identified in the existing literature that motivated you to contribute to your field. What deficiencies or unanswered questions did you observe? How did these gaps inspire you to embark on your research journey with the aim of filling these voids? By articulating the specific shortcomings in the current body of knowledge, you demonstrate a nuanced understanding of your research area and underscore the significance of your work.
Question 2: How does your research contribute to the existing body of knowledge?
This question delves into the vital role your research plays within the existing body of knowledge, urging you to articulate its significance and impact. It’s not merely about the subject matter you’ve studied, but also about the unique contributions and advancements your research brings to your field. To effectively respond, delve into the intricacies of your work and its implications for the broader academic landscape.
Illuminate how your findings could influence future research trajectories. Explore potential avenues for further inquiry that emerge from your research findings. Consider how your work opens up new questions or areas of exploration for future researchers. By identifying these potential research directions, you demonstrate the forward-looking nature of your work and its potential to shape the future trajectory of your field.
Question 3: What are the key findings of your research?
Furthermore, relate these findings to the broader implications they hold for your field. Articulate how your research contributes to advancing knowledge or addressing pressing issues within your academic discipline. Consider the potential impact of your findings on theory, practice, or policy, highlighting their relevance and significance within the larger scholarly community.
Question 4: Can you defend your research methodology?
Defending your research methodology entails a comprehensive understanding of its rationale, alignment with research objectives, and acknowledgment of potential limitations. It’s not merely about explaining the methods employed but also justifying why they were chosen over alternative approaches. To effectively respond, delve into the intricacies of your methodology and its implications for the study.
Be prepared to discuss the limitations inherent in your chosen methodology and how you mitigated them. Acknowledge any constraints or shortcomings associated with the selected approach, such as potential biases, sample size limitations, or data collection challenges. Demonstrate your awareness of these limitations and discuss the strategies implemented to address or minimize their impact on the validity and reliability of your findings.
Question 5: How did you analyze the data and what challenges did you encounter?
Begin by outlining the techniques used for data analysis. Describe the specific methods, tools, and software employed to process and interpret the data collected. Whether it involved quantitative statistical analysis, qualitative coding techniques, or a combination of both, provide insights into the analytical framework guiding your study. Additionally, discuss the rationale behind the chosen analytical approach and how it aligns with the research objectives and questions.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about data analysis, consider the following key points:
Question 6: What theoretical frameworks or references underpin your research?
Begin by naming the key theories and seminal works that guided your research. Identify the theoretical frameworks that provided the conceptual scaffolding for your study, as well as the seminal works that shaped your understanding of the research area. Discuss how these theories and references informed your research design, methodology, and analytical approach, providing a theoretical lens through which to interpret your findings.
Elucidate on how these frameworks shaped your hypothesis and analysis. Describe how the theoretical perspectives and insights gleaned from seminal works informed the development of your research questions, hypotheses, and analytical framework. Discuss the ways in which these theoretical frameworks guided your data collection and interpretation, influencing the selection of variables, measures, and analytical techniques employed in your study.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about theoretical frameworks, consider the following key points:
Question 7: How did you address ethical considerations in your research?
When addressing ethical considerations in your research, it’s essential to demonstrate a commitment to upholding ethical standards and protecting the rights and well-being of participants. Responding to inquiries about ethical protocols involves explaining the steps taken to ensure ethical conduct throughout the research process, describing the consent process and data protection measures implemented, and mentioning any institutional review board (IRB) approvals obtained.
Mention any institutional ethics review board approvals you obtained. Highlight any formal ethical review processes or approvals obtained from relevant regulatory bodies, such as IRBs or ethics committees. Discuss how the research protocol was reviewed for compliance with ethical guidelines and standards, including considerations of participant welfare, informed consent procedures, and data protection measures. By acknowledging the oversight and approval of institutional review bodies, you demonstrate your commitment to ethical integrity and accountability in conducting research involving human subjects.
Question 8: In what ways does your research contribute to the field?
Begin by detailing the novel insights your thesis provides. Articulate the key findings, discoveries, or perspectives that distinguish your research from existing literature and contribute to advancing knowledge within your field. Discuss how your study fills gaps in current understanding, challenges established assumptions, or offers innovative approaches to addressing pressing issues, highlighting its potential to generate new avenues of inquiry and broaden the scope of scholarly discourse.
In summary, when addressing inquiries about the contributions of your research to the field, consider the following key points:
Question 9: How did you ensure your research was free from bias?
Describe any blind or double-blind procedures employed in the study. Explain how blinding techniques were used to prevent bias in data collection, analysis, or interpretation. This may involve withholding certain information from researchers or participants to minimize the potential for conscious or unconscious bias to influence the results. Discuss how these procedures were implemented and their impact on enhancing the credibility and impartiality of the research outcomes.
Question 10: Where can future research go from here?
When considering the potential trajectory of your research topic, it’s essential to identify areas where further investigation could yield valuable insights, discuss unexplored questions that emerged from your research, and reflect on the limitations of your study as starting points for future research endeavors. Responding to inquiries about the future direction of research involves suggesting fruitful areas for further investigation, highlighting unresolved questions, and leveraging the limitations of your study as opportunities for future exploration.
Reflect on the limitations of your study as starting points for future research. Acknowledge any constraints, biases, or methodological shortcomings that may have influenced the outcomes or interpretations of your study. Discuss how these limitations provide opportunities for future research to refine methodologies, address confounding variables, or explore alternative theoretical frameworks. Consider how addressing these limitations could enhance the validity, reliability, and generalizability of future research findings within your field.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox, how to harness theoretical and conceptual frameworks for groundbreaking research, 25 short graduation quotes: inspiration in four words or less, related articles, how to deal with procrastination productively during thesis writing, 75 linking words for academic writing (+examples), how to write a unique thesis acknowledgement (+ faqs), theoretical vs. conceptual frameworks: simple definitions and an overview of key differences.
Swath and Dive: A pattern for PhD defense presentations
In recent times I’m having the fortune of seeing several of my own doctoral students approach the end of the doctoral journey (yes, it does end!). As they submit the dissertation and prepare for their defense, there is one piece of advice I find myself giving again and again, about how to tackle the impossible task of presenting multiple years of research work in less than one hour. In this post, I describe a “presentation design pattern” for thesis defenses, which builds upon classic conceptualization exercises advocated in the blog. I also illustrate it with an example from my own thesis defense presentation, more than ten years ago (gasp!).
I still vividly remember when I had to prepare my defense presentation, how I tried to shoehorn tons of concepts into an impossibly small number of slides… which still were too many for the 45-minute talk I was supposed to give at the defense. After several rehearsals (with an audience!) and lots of feedback from my colleagues and advisors, I finally stumbled upon a solution. Later on, I have found that a similar structure was also helpful to other doctoral students preparing their defenses.
The rest of the post takes the form of a presentation design pattern , i.e., a description of “a problem that occurs over and over again in our environment, and […] the core of the solution to that problem, in such a way that you can use this solution a million times over, without ever doing it the same way twice." 1 (a concept originally proposed in architecture, and later used in software engineering, pedagogy and many other fields). I have called this pattern Swath and Dive (for reasons that will become obvious in a minute).
The context: when is this pattern applicable?
When you have to prepare an oral presentation for a doctoral dissertation defense. This pattern is especially helpful if the research is a bit complicated (e.g., composed of multiple contributions , multiple studies, or using multiple research methods) and it is not obvious what contents to include/exclude from the presentation.
What is the problem? What forces are at play?
The main problem this pattern tries to solve is the seeming impossibility of showing 3+ years of research work in less than one hour. While time restrictions and structure for the defense are different in different countries, typically 25-60 minutes are allocated for the presentation. This limited time is a key force at play, but there are others as well:
- The sheer volume of a thesis dissertation’s contents (typically, a 100-500 pages document), which itself is a condensation of years of hard research work.
- Defending PhD students need to prove to the jury that they are now competent, independent researchers (i.e., they master the literature of their topic, are able to apply a research methodology and think critically about the results ).
- The varying levels of expertise and familiarity of the jury members with the concrete thesis topic.
- The varying levels of knowledge that jury members have of the dissertation materials (i.e., did they read the dissertation document in full? with what level of attention?). While all members are supposed to have read the document, in practice there is a lot of heterogeneity in compliance.
The typical end product of these forces is what I call the “skimming” approach to the defense presentation (see picture below): The presentation provides only a very high level overview of the main elements of the dissertation document (sort of like a table of contents). More often than not, too much time is spent in the introductory and related literature parts of the presentation (which are somehow “safe”, less likely to be criticized – another instance of avoidance at work in the PhD ), and time runs out when the student is getting to the really interesting part for the jury (the student’s own work). This approach of course has the critical flaw of not showcasing enough of the student’s own abilities and research outcomes.
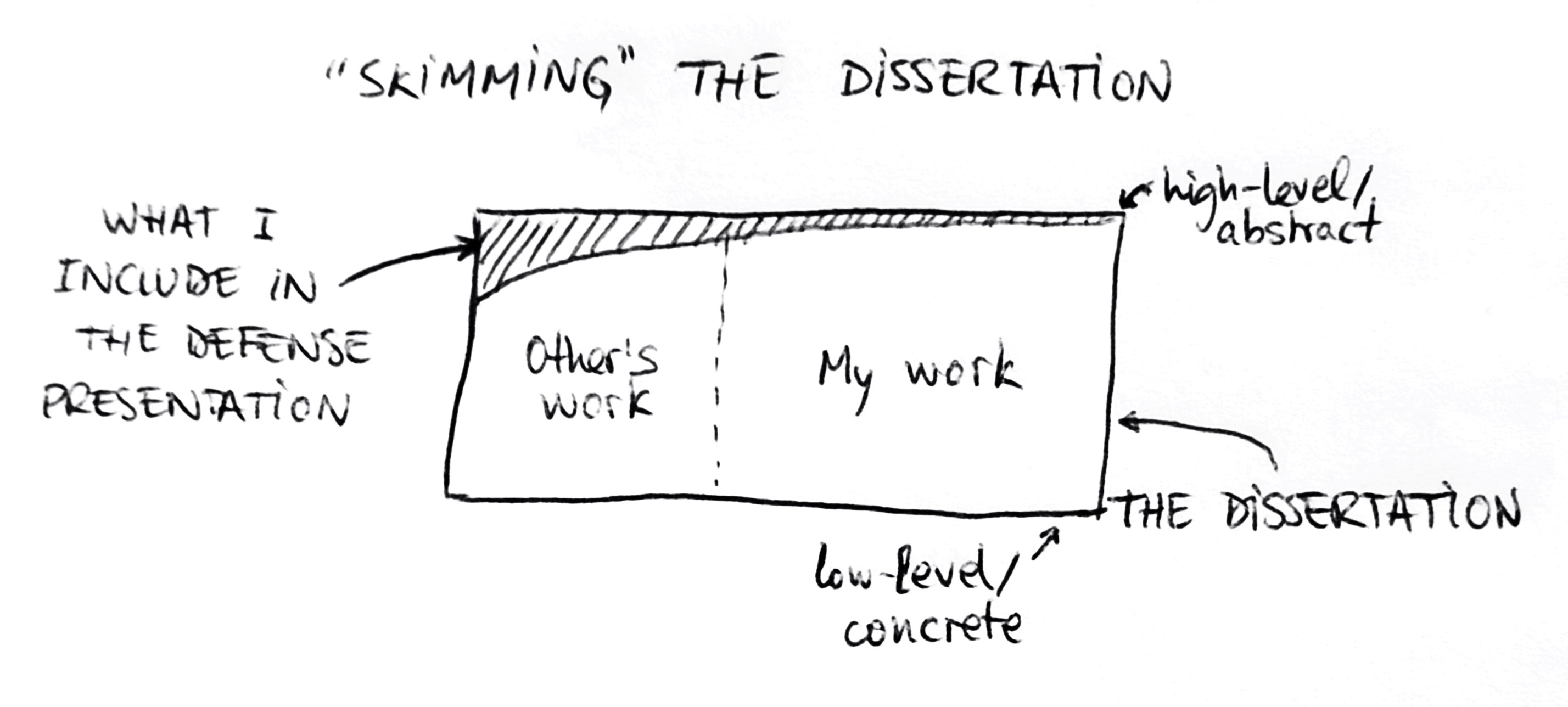
Skimming: A typical approach to selecting thesis defense content
How to avoid “skimming” your dissertation? Enter Swath and Dive .
The solution: Swath and Dive
What I propose in this pattern is to structure the presentation in a different way, a way that tries to balance the need for an overview of the dissertation and (at least some of) the richness of the investigation and the hard work the student has put behind it. The proposed structure goes like this:
A swath is “a long broad strip or belt” of grass, often left by a scythe or a lawnmower. In the context of a dissertation defense presentation, this is where the student gives the overview of the main elements of the thesis: key related scientific literature , main research questions , contributions to knowledge the dissertation makes, etc. Long-time readers of the blog will recognize these key elements as the components of the CQOCE diagram , one of the key reflection exercises in the “Happy PhD Toolkit” to (iteratively) understand and discuss with supervisors the overall view of the thesis. Aside from those key elements, probably some notes about the research methodology followed (which are not part of the canonical CQOCE diagram exercise) will also be needed.
In a sense, the Swath is not so different from the typical “skimming” mentioned above. There are several crucial differences, however: 1) when developing the Swath , we need to keep in mind that this is only a part (say, 50%) of the presentation time/length/slides; 2) the Swath should give equal importance to all its key elements (e.g., avoiding too much time on the literature context of the thesis, and making the necessary time for the student’s own research questions, contributions and studies); and 3) the Swath does not need to follow the chapter structure of the dissertation manuscript, rather focusing on the aforementioned key elements (although scattering pointers to the relevant chapters will help orient the jury members who read the dissertation).
Then, within this high-level Swath describing the dissertation, when we mention a particular contribution or study, it is time to do…
This part of the presentation is where the student selects one study or finding of the thesis and zooms in to describe the nitty-gritty details of the evidence the student gathered and analyzed (if it is empirical research), how that was done, and what findings came out of such analysis. The goal here is to help the audience trace at least one of those high-level, abstract elements, all the way down to (some) particular pieces of the raw data, the evidence used to form them.
How to select which part to Dive into? That is a bit up to the student and the particular dissertation. The student can select the main contribution of the dissertation, the most surprising finding, the largest or most impressive study within the work, or the coolest, most novel, or most difficult research method that was used during the dissertation process (e.g., to showcase how skillfully and systematically it was used). The student should give all the steps of the logic leading from low-level evidence to high-level elements – or as much as possible within the time constraints of the presentation (say, 30% of the total length/time/slides).
An essential coda: Limitations and Future Work
Although this didn’t make it to the title of the pattern, I believe it is crucially important to keep in mind another element in any good defense presentation: the limitations of the student’s research work, and the new avenues for research that the dissertation opens. These two areas are often neglected in crafting the defense presentation, maybe with a single slide just copy-pasting a few ideas from the dissertation manuscript (which were themselves hastily written when the student was exhausted and rushing to finish the whole thing). Yet, if the student convinced the jury of her basic research competence and knowledge during the Swath and Dive part, a big part of the jury questions and discussion will focus on these apparently trivial sections.
When doing the limitations, the student should gloss over the obvious (e.g., sample could have been bigger, there are questions about the generalizability of results) and think a bit deeper about alternative explanations that cannot be entirely ruled out, debatable aspects of the methodology followed… squeeze your brain (and ask your supervisors/colleagues) to brainstorm as many ideas as possible, and select the most juicy ones. For future work, also go beyond the obvious and think big : if someone gave you one million dollars (or 10 million!), what cool new studies could continue the path you opened? what new methods could be applied? what experts would you bring from other disciplines to understand the phenomenon from a different perspective? what other phenomena could be studied in the same way as you did this one? Try to close the presentation with a vision of the brighter future that this research might unleash upon the world.
Swath and Dive: a different way of structuring your defense presentation
To understand how this pattern could look like, I can point you to my own thesis defense presentation, which is still available online . This is not because the presentation is perfect in any way, or even a good example (viewing it today I find it overcomplicated, and people complained of motion sickness due to its fast pace and Prezi’s presentation metaphor of moving along an infinite canvas)… but at least it will give you a concrete idea of what I described in abstract terms above.
If you play the presentation , you will notice that the first few slides (frames 1-6) just lay out the main construct the dissertation focuses on (“orchestration”), the structure of the presentation and its mapping to dissertation chapters. Then, the bulk of the presentation (frames 7-117) goes over the main elements of the dissertation according to the CQOCE diagram , i.e., the Swath part of the pattern. Within this high-level view of the dissertation, I inserted a short detour on the research methodology followed (frames 25-28) and, more importantly, several Dives into specific findings and the evidence behind them (frames 43-48, 66-72, and 99-112). Then, frames 118-136 provide the conclusive coda that includes the future work (but not the limitations, which were peppered through the Swath part of the presentation – a dubious choice, if you ask me today).
Variations and related patterns
As you can see from the example above, one does not need to follow the canonical version of Swath and Dive (mine is rather Swath and Three Dives ). Yet, paraphrasing Alexander, that is the point of the pattern: to have the core of the idea, which you can use to produce a million different solutions, tailored to your particular context and subject matter.
It is also important to realize that this structuring pattern for thesis defense presentations does not invalidate (rather, complements) other advice on preparing scientific presentations 2 , 3 , 4 and thesis defenses more specifically 5 . It is all very sound advice! For instance, once you have the structure of your Swath and Dive defense presentation, you could use the NABC technique to ensure that the Need, Approach, Benefits and Competition of each of your knowledge contributions are adequately emphasized. And you can rehearse intensively, and with an audience able to come up with nasty questions. And so on…
May you defend your thesis broadly and deeply!
Do you know other defense presentation structures that work really well in your discipline? Have you used Swath and Dive in your own defense successfully? Let us know (and share your examples) in the comments area below! (or leave a voice message)
Header image by DALL-E
Alexander, C., Ishikawa, S., & Silverstein, M. (1977). A Pattern Language: Towns, Buildings, Construction (Vol. 2). Oxford University Press. ↩︎
Carter, M. (2013). Designing science presentations: A visual guide to figures, papers, slides, posters, and more (First edition). Elsevier/Academic Press. ↩︎
Anholt, R. R. H. (2009). Dazzle ’Em with Style: The Art of Oral Scientific Presentation (2nd ed). Elsevier, Ebsco Publishing [distributor]. ↩︎
Alley, M. (2013). The craft of scientific presentations: Critical steps to succeed and critical errors to avoid (Second edition). Springer. ↩︎
Davis, M., Davis, K. J., & Dunagan, M. M. (2012). Scientific papers and presentations (Third edition). Elsevier/Academic Press. ↩︎
- Dissertation
- Communication

Luis P. Prieto
Luis P. is a Ramón y Cajal research fellow at the University of Valladolid (Spain), investigating learning technologies, especially learning analytics. He is also an avid learner about doctoral education and supervision, and he's the main author at the A Happy PhD blog.
Google Scholar profile
- Graduate School
How to Prepare for a Thesis Defense

You’ve spent years on your studies to acquire your advanced degree, and whether a master’s thesis or doctorate, you need to know how to prepare for a thesis defense. Treat this as more of a siege than a defense, and be prepared to outlast any foe, any siege engine, any army at your gates.
You have already built up a great thesis, with instruction from professors, and maybe even the help of a great thesis writing service , and you are finally ready for your defense. What does that phase of your academic career look like?
In this article, we will give you the tools and tips to make it through. We will start with a preparation section, focusing on various aspects of how to study and what to study, then talk about the lead-up to the big day: preparing materials and handling anxiety. We’ll also touch on what to do on the day and how a thesis defense will, or could, go. At the end of it all, you will have a clear idea of how to approach the preparation for, and the defense of, your thesis.
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 12 min read
Know your thesis.
We put this first knowing that it is the most important element of your entire presentation. The crux of your defense hinges on this. You must know your thesis, backwards and forwards. There must be nothing about it that you have forgotten. However miniscule the detail, and however insubstantial to your thesis that detail ultimately is, you must nevertheless know it.
When it comes time to question you, after presentation of your work, questions you cannot answer will strike you down. Knowledge is your shield.
Know the Big Picture: What Are You Trying to Prove?
While you will already be intimately familiar with your research, readings, and revisions of your opus, you should still allot yourself time prior to your defense in which to know crucial elements of your thesis front to back. This is your primary concern.
What are you trying to prove? This is your number one concern, and being able to state this clearly, and back up your efforts with sources and arguments, is the main point of your thesis defense.
So, start with the big picture. Know your main points and the crux of your arguments. You have one, main thrust with this thesis, and you have one, primary tentpole holding it up. No doubt you have more evidence than one primary source, but inevitably one will have more weight and potency than the others. Start there and work your way out.
Don’t memorize words to say, but memorize the web of arguments you have woven together to support your work. Your research was about X, and you have Y as a result, and now you share that and defend your assertions.
You can’t memorize the whole thesis – it will be large – but you can memorize a few, important points that support your main argument, and give credibility to your assertions. Again, you aren’t memorizing a speech to give, but you should know some of your more crucial statistics and datapoints so you can reference them easily.
Know Your Secondary Sources
It’s not just enough to know what your own thesis says, but you must be knowledgeable about its foundations. Your thesis is built on sources and materials that you have cited and referenced throughout. These deserve your attention as well.
If you are being questioned and, without a beat, you can cite chapter and verse on the proofs for your claims, this gives your own arguments depth and clarity. A successful thesis will add to the knowledge base of your field, but it must be built on the knowledge that came before. Knowing your secondary sources demonstrates your knowledge, shows how your thesis connects to that knowledge, and solidifies your arguments through the foundational assertions of prior experts.
Are you looking for grad school tips that will help you succeed in your application and once you get in? Watch this:
Sun Tzu Was Right
“Know your enemy,” wrote the philosopher and military commander Sun Tzu, “as you know yourself, and you will have victory in many battles.”
Your thesis makes a claim, adds to the body of knowledge in your field, and does so with evidence, research – not to mention panache – and is given its gravitas by the myriad of sources and proofs that you have to offer. Great, but don’t forget about those who disagree.
In most fields – certainly all the ones worth studying – anybody who makes a claim will have that claim challenged.
This is, perhaps, the most important step to preparing your defense: know why your detractors will say your thesis is wrong. If you can “steel man” – the opposite of “straw man” – their arguments, and phrase counter-arguments to your own statements – as well as anybody who holds those ideas would – then you have already, essentially, anticipated many, if not all, of the questions the examining board will put to you.
With that knowledge, you will also know to prepare defenses, explanations, and counter-arguments to each of these perceived complaints. Make sure that your counter-arguments would satisfy the majority of reasonable, educated persons in your field – if not any potential naysayers themselves.
Of course, having the main points, secondary points, data, references, detractions, and answers to those detractions all at your mind’s immediate beck and call would be wonderful; but, if you can manage to memorize all of that reliably within your head, don’t count on nothing but pure, rote learning to bring up all of this information. We recommend you keep quick reference notes to help you.
When you’re asked a question, having quick access to well-kept notes will serve you well. Notes themselves are nice, but you also need to be able to access them quickly. Any paradigm that works for you will do, but here is a sample schema for you to consider:
From a dollar store or office supply store \u2013 with reference numbers to bookmark key passages. These reference numbers will correspond to your table of contents. "}]">
Again, use any rubric you want, but pick a system and make sure it works for you. How do you know it works? By testing it.
A Baptism of Fire, and How to Avoid It
That term - “baptism of fire” – refers to being trained via a quick shove onto a battlefield. You might also think of mother and father bird shoving their younglings out of the nest, peeping encouragement at them to fly.
Don’t let this happen to you. Check your wings first.
Mock interviews are extremely useful for interview preparation. Arrange a mock thesis defense. Get professionals who know what they are doing to grill you on your thesis. A professional mock panel will simulate the time, let you run through your presentation, and put you through your paces by asking insightful, challenging questions; they might even ask questions you didn’t anticipate – in which case, lucky for you it was caught beforehand.
Or, not so lucky. Lucky is what happens to a soldier in a baptism of fire, but you’re not doing that. You’re preparing, training, and refining your methods to be bulletproof before anybody fires upon you at all.
A mock defense will simulate the real thing as close as possible, likely even giving you a taste of the nerves and letting you learn how to cope with anxiety. Plus, you can test your filing system for quick recall.
Before the Day - What to Get Ready
The most crucial elements to get ready are anything that you will directly need. That is to say that you should have access to your presentation itself, as well as your notes, and anything else that you’ll require for the defense. Everything else is secondary, and while it’s not a great idea to show up without combing your hair, at least you can still mount a defense with bedhead; you can’t defend your thesis without your critical notes.
With that said, definitely comb your hair. Presenting your thesis is about presenting yourself, as well, so put on some professional-casual clothes so you are comfortable and presentable.
Bring along anything else you need to be comfortable in the room, such as a water bottle or pencils and a notepad – anything you might want to help you succeed.
The exception: don’t overload so much that you are carrying multiple bags around with you.
Want to learn how to prepare for thesis defense questions? Check this infographic:
On the Day - Mental and Anxiety Control
The very nature of the activity of thesis defense means that you will be spending your presentation and your day on the defensive. This is, inherently, a stressful position to take, but a strong aggravating factor is the stakes of the event. This is a momentous occasion. You are at the proverbial moment of truth where you will either advance to the next, major phase of your career, or you will be forced to reconcile yourself to returning and revising – another revision and exploration and another defense.
Naturally, it follows that stress management is going to be one of the most important aspects of your day.
Prevention is the Best Cure
Give yourself an on-the-day boost by planning your studying and preparation well in advance. This will enable you to take a break before the actual day. If the day before your thesis defense can be one spent in contemplation, meditation, or relaxation, you’ll have a much better mental state for the defense itself.
Also of utmost importance: sleep. Maintaining a decent sleep schedule can be nigh-impossible, let alone sporadically getting in the actual recommended hours of sleep that your doctor really wants you to get. Nevertheless, make an extra effort to get a lot of rest, ideally within a sleep schedule, so that you are bright-eyed come defense time.
Long-term Stress Management
The rise of app culture is seen by some as the fall of civilization – particularly those spiritual or personal aspects of life. Tech is really just a tool, however, and finding a good meditation app can give you the right tech-based buddy system to keep you in good mental health. Meditation can be a great stress-management technique, and trying out some basic techniques will help you to stay alert, focused, and calm on your big day.
Physical Health IS Mental Health
How are you eating? Do you get out to exercise?
These are things that can easily fall by the wayside while pursuing higher academics. There is a reason that there is a cliched stereotype of undernourished, sleepless academics: it’s hard to absorb, retain, and study knowledge at this demanding level while maintaining a good balance with the more physical aspects of your life. Nonetheless, good physical health is strongly linked with good mental health, and you should pursue both.
Remember Step One...
Preventing panic is often a case of focus being unable to override insecurity. You’ve already taken care of your knowledge base: know your thesis. With that, you can keep insecurity at bay. Now for focus. What is the first thing you have to do when you get in the room? You’ll have some opening remarks, but even before that, you’ll likely want to quickly introduce yourself and welcome and thank your thesis screening panel. Forget everything else. Stop worrying about it, because you just have to do that first thing.
Concentrate on the Next Thing
After that, keeping yourself from getting distracted by insecurity is a question of focusing on whatever you must do next. You’ve made it through your introduction: great. What’s next? Since you’ve composed a careful set of notes, and carefully arranged those notes on your desk, table, or podium – or computing device – you can glance down and look to “point two” to carry you forward. Focus on doing your best job on that point. Once it’s over, focus on point three. Keep on in this way, and you have exorcised the twin demons of distraction and insecurity.
Fix Mistakes with No Fanfare
What if you misspeak? Just go back over it and fix the error quickly. “I’m sorry, I meant to say that 33% of the population favors blue above other colors, not 30 %. ”
Once you’ve fixed the error, move on. Dwelling on it does nothing at best, and exacerbates your problems at worst.
What if your PowerPoint presentation gums up? What if your computer freezes? What if the projector won’t project?
Remember that everybody in the room deals with glitches and tech errors, just like you, and do your best.
Don’t hide it – it's not hidden – but just briefly acknowledge the problem, “It seems the computer has frozen. Pardon me,” and see if you can fix it. If you can’t, rely on your notes to keep going. If you have infographics or charts and data that you wanted to highlight, offer to show those elements to the thesis screening panel, or to describe the data they need.
You’re being judged based on your logic, reasoning, rationales, recommendations, findings, data, and the effectiveness of your thesis. Nobody’s going to dock points from your presentation if there was a power failure.
Plus, if you’ve followed our advice thus far, you have redundant note systems with you, and you’ll be fine.
How to Stay Calm, Generally
Keep your breath under control. This ties in with meditation, to some extent, but controlled breath will keep your heart-rate down and your anxiety levels far more controlled than they would otherwise be. That is not to say that you won’t feel any anxiety, per se, just that – statistically speaking – you are far more likely to have far less anxiety.
Many people like to imagine a humorous image, particularly of their audience, to calm themselves down. This might work for you, but what this technique is getting at is a way to take your mind off of your anxieties and force it to focus on something else.
To do this, you needn’t go to the cliché of imagining anybody in underwear. Rather, just have a calming image or idea in your head that you can focus on. Pick something that makes you calm, or brings out a smile, and something that you can concentrate on to stop any panic moments and take away the snowball effect that happens whenever you dwell on something negative or that makes you anxious.
A Final Tip on Courtesy
Remember to be courteous, gracious, and polite. It really helps if you remember the names of the people on your thesis panel, so write those down if you have to.
What Does a Thesis Defense Look Like?
A thesis defense consists of a short presentation – about twenty or thirty minutes – on your thesis, followed by a discussion. That discussion is the actual defense of your thesis, as the thesis panel will be asking you questions and challenging you on your research, your conclusions, and your ideas.
The questioning period might take another twenty minutes or an hour, or even longer. There is no guaranteed time duration, so be prepared for a lengthy discussion and debate after your presentation.
Standard format would probably include the use of a PowerPoint-type accompaniment to your summation of your thesis. It is recommended that you provide more than just a lecture. If you want your panel to have anything like infographics, charts, or statistics, you need to provide it, either as part of a visual slideshow presentation, handout sheets, or both.
Common Types of Questions and How to Respond
Knowing what kind of thesis defense questions can come your way will be very advantageous for you because it will help you understand the kinds of answers you need to give.
Probing Questions
These feel your argument out a bit, just to test and see if you know your stuff, or if you’ve just memorized a very specific subset of data. These will seem almost unbearably easy if you have studied extensively while researching your thesis. If you haven’t, they will be painfully difficult. If you cannot answer these basic questions, you will seem as though you have crafted a thesis with blinders on, and it is unlikely you will survive further, deeper rounds of questioning.
Data Clarification
Maybe a chart didn’t go deep enough. Maybe somebody is curious if that statistic you gave was per capita or not. These clarification questions will just seek to clear up any misconceptions or blind spots in your presentation. This is why it’s important to know both your material and the secondary sources and citations you have made. If you understand all of this information thoroughly, you’ll be able to go deeper than any one chart and explain everything. This is also why it’s necessary to keep quick reference cards and tables of contents. If you blank on that per capita question, your index card won’t.
Opposing Viewpoint and Supporting Data
These questions will seek to challenge your ideas and stress your thesis by digging deep. They will present opposing views and find out whether or not you have considered alternate points of view. These are the most crucial questions to have excellent answers to, because these are the questions that directly challenge your work and are what you are “defending” your thesis from. We have already warned you to know your “enemy” as you know yourself. We stress this again here: have top-grade answers to cutting questions, or fail in your attempt.
Arm yourself with knowledge of your own thesis and an anticipation of what your detractors might, or do, say, and then practice, practice, practice.
At the end of a long period of vigorous study, get some rest, keep calm, and fire up a meditation app – or go for a walk.
In short: follow our advice, your common sense, and trust to your knowledge base and the research and readings you’ve done over the past years, and you’ll have a solid thesis defense.
Ideally you will dedicate several weeks to thesis preparation. Start about three to five weeks ahead of the defense and put aside some time every day to work on some aspect of your defense.
There isn’t really such a thing as too much prep. You could take too many notes and wind up with a very large, unwieldy reference binder, but even that is mitigated by your “table of contents.”
Err on the side of “too much” rather than “not enough.”
They’re probably just testing your knowledge of the material versus whether or not you just memorized a speech. Treat this as a probing question and answer in reference to your work. If this is an accident, don’t draw attention to it, and don’t get exasperated.
Say it’s outside of your field or area of study, but explain why you didn’t go there. So, if they ask about something peripheral, acknowledge that this isn’t part of what you’ve learned, why you are aware of it, and why you didn’t pursue further research into that area. Above all else, don’t fake knowledge you don’t have.
Numbers may vary, but three to five is fairly typical.
If you need a short break, to use the restroom, for instance, you can ask for one.
Have talking points and a firm knowledge of your facts and ideas, but don’t memorize set speeches. You can come off sounding robotic and impersonal. Worse, if you are asked a question and you find yourself getting lost, you might not remember details of your speech without the “ramp up” into any given part. Better to know the data, rather than the exact words.
In the event that you are not awarded your master or doctorate, you will most likely be given the chance to revise your thesis and try again. The committee will give you feedback, and you will revise accordingly.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into grad school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Dissertation Defense: Steps To Follow To Succeed

A dissertation defense is arguably one of the most important milestones in every student’s career. While it signals that your tenure as a student is soon about to close, it validates all your efforts towards your thesis.
Being cautious about including all the necessary details is very important to successfully complete your dissertation proposal defense. This article tells you everything that you need to know about writing a defense that can add great credibility to you as a student.
What is A Dissertation Defense?
The first thing that you need to learn is what is a dissertation defense and what is its purpose. In simple terms, it is a presentation made by a student to defend all the ideas and views that are presented in a dissertation.
The presenter must include details like what is the reason for choosing specific research methods, the theory that has been selected for the paper, and other such points. This presentation is made before an audience that comprises of the university committee, professors and even fellow-students. It is met with questions and answers that gives the student an opportunity to provide more clarity on the dissertation in order to convince the committee to approve it.
Stages of a Dissertation Defense
One of the most important dissertation defense tips provided by several professors is to breakdown the process into three steps:
- Preparation : This stage involves collection of all the necessary information that must be included in the defense dissertation and making all the arrangements for the actual meeting.
- The defense meeting : This is where you decide how you will present the defense. The actual meeting is hugely reliant on the performance, body language and the confidence in your oral defense.
- After the defense meeting : This stage, also known as the follow up, requires you to make the necessary revisions suggested by the university committee. You can even provide bound copies of the whole dissertation to distribute among different members of your departments. In the follow up stage, one must also think about expense that are related to publishing the Ph.D. dissertation defense as well as printing additional copies of the manuscript, if required.
How Long is a Dissertation Defense?
The first thing that a student should know is how long does a dissertation defense last? The length has to be carefully calculated to make the impact that you want. One of the most important steps in the dissertation preparation is to understand how much time each department allocates to the closing oral defense. When you plan in the early stages of your dissertation itself, you can write it in a manner that allows you to defend it in the allocated time.
Usually these meetings including the presentation, the oral defense and the question and answer session last for about two hours. In most cases, these two hours also encompass the time needed by members of the committee to deliberate.
How to Prepare for the Dissertation Defense
Now that you know how long is a dissertation defense, the next step is to prepare well enough to make your presentation impressive.
Here are some tips on how to prepare for a dissertation defense:
- Watch other students in action to learn about different presentation styles. You can attend defenses of different colleagues in your department as well as other departments in your university.
- Get all the details about the deadlines and the rules of your college or university about scheduling your defense.
- Scheduling is also a very important part of your preparation. It is important to note that members of the committee and University chairs need to make time for these defences in a very packed schedule. Coordinate the date, venue and time of your defense as early as possible.
- Prepare a manuscript adhering to the necessary formatting rules. Review your manuscript thoroughly before you hand it in. During your PH.D, your faculty will also assist you with the defense. For this, they must have a crisp and polished copy of your manuscript.
- Most colleges have the facility for a pre-defense meeting. This is the best opportunity to sort out any concerns that you may have about the actual meeting. It is a good idea to ask the chairs what types of questions may be put forward and if there are any problems with the defense that need to be resolved. When you prepare for a pre-defense meeting, think of it as the final one and give it your all.
- Put together all the material that you need for the defense. A detailed, yet to-the-point presentation must be prepared.
- The final stage of preparation is practicing your presentation over and over again. It is not just the presentation but also the approach towards the questions that you must practice.
Tips To Nail Your Actual Meeting
With these tips you will be one step closer towards a successful defense that will help your dissertation pass and be approved:
- All meetings should begin by addressing the chair. Make sure you thank all the committee members and the advisors for the efforts that they have put it. This gives you a professional start to the presentation.
- The presentation should cover the following subjects in brief:
- The research topic
- Literature review
- The methods used for analysis
- The primary findings of the research
- Recommendations of additional research on the subject in the focus.
- Do not get rattled by any discussions among the chairs. They will deliberate on any disagreements or topics of interest. This is a part of the process and is not a reflection of the presentation itself.
- There are two questions that are commonly asked that you should be prepared for. This includes the weaknesses of the dissertation and the research plans that you have made post-dissertation.
- Use subtle gestures when you are talking. Do not overuse your hands when doing so. The whole meeting including the question and answer session should have a very formal appeal.
- The tone of your voice must be assertive without making it seem like you are trying to hard. Be clear and enunciate when you speak.
Once the questions have been answered, the committee will leave the room. Then, after the deliberation, you will be informed if your dissertation has passed or not.
For affordable thesis writing assistance , get in touch our team today. The pricing is cheap but students can be assured of top notch quality in all our final products.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates

Dissertation Advisory Committee and Thesis Defense
Keeping students on track towards excellence and completion of thesis research.
The semester after the successful completion of the Qualifying Exam, each student and their research mentor put together a dissertation advisory committee (DAC) that contains at least three members and eventually 5 members that are required to attend the dissertation defense. This committee is expected to meet with the student every semester. Not all members of the committee need to be present at each meeting (three members are sufficient for scheduling).
At least two DAC members must be from the group of GPN training faculty (ideally one from each campus). The final 5 member composition of the DAC at the defense includes a minimum of 2 readers of the dissertation. At least one thesis reader must not be a collaborator on the thesis project, although she/he can be a collaborator with the laboratory. The thesis mentor is the first reader. A completed Request for Special Service Appointment Form must be submitted for each non-BU committee member; students should submit these forms through the GMS registrar forms website . An electronic copy of the form should be emailed to the GPN Assistant Director . GMS will send the requesting student notice of the approval of the Special Service Appointment. The outside member can be a second or third reader, although this is not required. Members of a student’s Qualifying Exam Committee can also participate on their DAC; in fact, the three examining committee members may often end up being the readers of the dissertation, but this is not mandatory. The Chair of the committee cannot be a reader of the dissertation. The Chair’s chief responsibility is to make sure that the student works with the office to schedule the necessary meetings and serves as an interface between the committee’s recommendations to the student and any other concerns that the student or mentor may have during the training process. The Chair also formally introduces the student at the open defense presentation.
Composition of the DAC must be approved by the GPN Program Director in consultation with the GEC and when relevant, the Computational Neuroscience Curriculum Committee. Students should contact the GPN Program Director to obtain approval for the proposed DAC committee. During the DAC meeting (limited to 1 hour per semester) students make a short PowerPoint presentation to the group highlighting their research accomplishments over the past academic period (with review of research goals) and receive feedback from faculty regarding any issues in approach or interpretation. Scheduling of the DAC meetings is done by the student (with guidance from the GPN office if needed). At the conclusion of the DAC, the committee chair is responsible for completing the GPN Dissertation Advisory Committee Form and submitting it to the GPN office.
FORMAL PROGRESS REPORT
Usually one year before their pre-defense, with the approval of their Dissertation Advisory Committee (DAC), students make a formal oral presentation (50 min) to their committee and to the neuroscience community at large. This presentation is followed by a short formal meeting of their committee to discuss their progress and whether they are on target for the completion of their research and eventually the pre-defense (see below). Students are encouraged to schedule the Progress Report (third or fourth year in the program) once they have enough preliminary data to indicate that their Aims are sound and there is sufficient progress in their research direction for presentation and discussion. The outside member usually does not attend this exercise although they are definitely welcome. The seminar should take place at least one year before the defense date. It is expected that the student will provide a written progress report, not to exceed ten pages (double-spaced), that will be given to the members of the DAC one week before the seminar. It is encouraged that this report take the form of a research manuscript to motivate the student and mentor towards generating a draft of the student’s first author paper, a graduation requirement in GPN. At a minimum the written report should include:
- Statement of the problem and its significance. The hypothesis or hypotheses being tested.
- Literature review and background.
- Methods in use.
- Studies completed by the student.
- Proposal for future work and discussion of expected outcomes (include potential problems and alternative plans).
DISSERTATION OUTLINE/PROSPECTUS
Approximately 7-9 months prior to the defense date (Check Graduation Calendar ), the student must submit a dissertation outline (or prospectus for current PIN students), approved by the first and second reader (third reader is optional), to GMS using the GMS Dissertation Prospectus Outline Approval Page. All forms can be obtained from the GMS website and the submission is electronic. A copy of this document should be sent to the GPN Assistant Director for inclusion in the student’s files. This document will typically consist of an outline that provides proposed chapter and section headings for the dissertation document with headings that describe the key findings. Example outlines are on file in the GPN office.
DIPLOMA APPLICATION
A GMS PhD Diploma Application must be submitted to GMS approximately 4 months prior to the defense date (Check the Graduation Calendar ). Due date varies with graduation cycle.
DISSERTATION ABSTRACT
A dissertation abstract conforming to GMS format requirements must be approved by the first reader, and GPN Program Director, and submitted to GMS (using the PhD Dissertation Defense Abstract Form on the GMS Form website at least 3 weeks prior to the dissertation defense. Please note that prior to electronic submission of the defense abstract, students are required to meet with the GMS Registrar. The abstract must also be circulated to all DAC members prior to the Pre-Defense DAC Meeting.
PRE-DEFENSE AND DEFENSE
A pre-defense meeting of the DAC usually occurs two weeks prior to the defense to make sure that the quality of the dissertation document is close to being acceptable for the degree and to review necessary paperwork. At this time, the committee will review the abstract and title. Members of the DAC should have two weeks to review the thesis before the pre-defense. There is no oral presentation associated with this meeting. The outside member usually does not attend this exercise but does provide the student with feedback on the document, either by email or phone, before the meeting takes place. In most cases, the Chair of the committee makes sure that the views of the outside member are represented in the discussions.
SCHEDULING OF THESIS DEFENSE
After submission of the abstract and at least two weeks prior to the Thesis Defense, students must submit the Oral Defense Scheduling Form. At the time of their defense, students will give a 50-minute oral presentation, followed by 10 minutes of questions, that is open to all members of the University. We suggest GPN students have their defense in the Eichenbaum Colloquium Room (CILSE 101), 610 Commonwealth Avenue or in 5 Cummington Mall, Room 113. This public forum will be followed by a closed session of the DAC where the student is asked to respond to questions put forth by the committee to test her/his ability to defend the work presented in the dissertation document. It is expected that all members of the DAC will attend the entire formal defense, which should last a maximum of two hours.
DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO GMS
After the three dissertation readers have signed the dissertation signature sheets (TO BE PROVIDED BY THE STUDENT), the finalized dissertation is submitted to GMS to complete the PhD requirements. Note that GMS must approve the dissertation formatting before the final document can be submitted.
GMS DEADLINES
Deadlines for submission of forms: see the GMS Graduation Calendar
Specific forms can be obtained at the GMS Student Forms Page
All faculty on the DAC must have an appointment at BU. It is important to request a Special Service Appointment (due at time of Abstract Approval) for all non-BU members. Please notify the GPN office if you need any help in this matter.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Doctoral dissertation pre-defense in an online setting: lessons and challenges

PhD students of Translation Studies at ELTE University carry out a pre-defense before being awarded their doctorate degree at the final defense. The dissertation shall at this point conform to the rules regarding the format and content requirements of the final defense. Based on the opinions of the three pre-opponents and other members of the committee, the PhD candidate at this point can still modi- fy the dissertation in consultation with the supervisor. As certain measures had to be implemented due to the pandemic crisis, pre-defense was remarkably different from the normal procedure in having no oral examination after sharing the committee’s written comments in advance. Therefore, all members of the committee, the supervi- sor and the PhD candidate had to face new challenges. As a result, organizing the pre-defense in a written form required flexibility, empathy, and openness to online communication, while the stress associated with public performance has decreased significantly, in addition to the rather smooth organization of the event. The present study details the process, characteristics and lessons learned from the pre-defense organized in a distance-learning setting.
Related Papers
Science as Culture
Alexandra Supper
Adnan Salihbegovic
Organizing and completing the final oral defense of a Ph.D. thesis over the Internet as a videoconference session presented both a technical and legal challenge to participants in the process. In this paper we present the experience gained and some recommendations for future similar endeavors as a result of preparing and accomplishing the first Ph.D. defense held at the Universities of Bosnia Herzegovina, with the president of the defense committee guiding the event remotely from his office in the USA. The whole event took place at the Faculty of Electrical Engineering in Sarajevo.
UEF DSA Newspaper
Chloe Wells
Originally Published 2021 in UEF DSA Newspaper Vol. III No. 1 pp.4-6 As doctoral students at UEF we will have to defend our work in order to gain our doctorates. But what exactly does the doctoral defence involve? What are the steps and stages beforehand? And how can you best prepare for the occasion? As someone who has just successfully defended my PhD in Human Geography, I'm here to offer you some insights and advice.
Journal of Applied Linguistics and Professional Practice
Ahmad Izadi
Taking up the role of examiner in PhD dissertation defense (DD) sessions involves dealing with two contradictory desires: effective delivery of criticisms, and maintaining a positive interpersonal relationship with the recipients of those criticisms. This study explores the discourse strategies examiners use to express the speech act of criticism in the context of Iranian DD sessions in English for Academic Purposes. The data come from simplified transcriptions of 12 video-recorded sessions of PhD DD sessions, from between 63 to 123 minutes long. The examiners' criticisms, which are delivered in the Question and Answer part of the defense sessions, are selected for analysis. Consulting taxonomies of criticisms provided by previous studies as the point of departure, the study also formulates a specific taxonomy of criticisms which best fits its purpose. The identified 120 acts are classified into 10 strategy types. The analyses reveal a 'mixed message' in criticism acts, in that they ambivalently include elements of negativity and positivity. Most criticisms include a number of mitigating as well as aggravating strategies. In addition, they include strategies which ambivalently both mitigate and aggravate. It is therefore argued that examiners ambivalently establish relational connection with and separation from the candidates (and their supervisors) through criticisms.
Nicolas Barbier
This is the PDF document used during my PhD defense at the Université de Bourgogne. I defended my PhD dissertation in English. My PhD committee: Irène Bellier (EHESS, France), Yves Boquet (Univ. de Bourgogne, France), Christian Montès (Univ. Lyon 2, France), Gundars Rudzitis (Univ. of Idaho, USA)
Gonzalo Alvarez , Igor Campillo
Amin Karimnia
THE PRESENT WORK AIMED AT INVESTIGATING THE PROBLEMATIC ISSUES REPORTED BY TRANSLATION STUDIES (TS) PROFESSORS AND EXAMINERS DURING M.A. DEFENSE SESSIONS. TO DO THIS, THREE INSTRUMENTS WERE USED TO COLLECT THE DATA INCLUDING (A) AN AUTHOR-DESIGNED CHECKLIST CONTAINING THE REQUIRED PARTS IN A THESIS PROJECT; (B) SEMI-STRUCTURED INTERVIEWS WITH FIVE TS PROFESSORS MOSTLY ACTING AS TS EXAMINERS; AND (C) PERSONAL OBSERVATIONS MADE ON TRANSLATION STUDIES' M.A. DEFENSE SESSIONS. FIRST, THE RESEARCHERS SELECTED FOUR IAU BRANCHES THROUGH ACCIDENTAL SAMPLING. THESE INCLUDED FARS SCIENCE AND RESEARCH BRANCH, BANDAR ABBAS BRANCH, SHAHREZA BRANCH, AND SOUTH TEHRAN BRANCH. HAVING DEALT WITH THE AFORE-MENTIONED INSTRUMENTS, THE DATA WERE COLLECTED, ANALYZED AND FURTHER DISCUSSED. AS THE RESULTS OF THE RESEARCHER-MADE CHECKLIST REVEALED, “REFERENCES”, “DATA ANALYSIS”, AND “DISCUSSION” SECTIONS WERE AMONG THE MOST PROBLEMATIC CASES REPORTED BY THE PARTICIPANTS. IN ADDITION, THE RESULTS OF THE PERSONAL OBSERVATIONS REVEALED THAT “STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM” AND “REFERENCES” WERE AMONG THE MOST PROBLEMATIC ISSUES IN TS M.A. DEFENSE SESSIONS. LIKEWISE, “DATA ANALYSIS” AND “DISCUSSION” SECTIONS SHARED THE SAME FREQUENCIES. FINALLY, RESULTS OF THE SEMI-STRUCTURED INTERVIEWS WITH THE FIVE TS PROFESSORS REVEALED THAT M.A. THESES ON TS HAVE BEEN HIGHLY PROBLEMATIC. THE FINDINGS SHOWED THAT THESE CASES WERE MOSTLY RELATED TO THE STUDENTS’ WAY OF WRITING AND THEIR UNFAMILIARITY WITH THE OUTLINES OF AN ACADEMIC PIECE OF WRITING.
Problems of Information Technology
Ramiz M Aliguliyev
The article explores the international practice regarding the assessment of dissertation works. A method is proposed for automated assessment of dissertation works. In this regard, algorithms are developed for the automation of pre-examination. This method allows to determine the similarity of essential parts of the dissertation (the goal of dissertation, its tasks, chapters, obtained results, and published papers) automatically. For this porpose text mining technology that allows to define the semantic proximity of the texts is applied. An assesment is given to determine the accordance between proposed method and expert assessment.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Seyyed Morteza Alavi
Azlin Zainal
Research Papers in Language Teaching and Learning
Valentina Peroukidou
Jagiellonian University Institute of Public Affairs, Kraków.ISBN: 978 - 83 - 65688 - 35 - 4 (e-book)
Gülşah Taşçı
Michael Millerman
Kiyoung Kim
Jaime Alfredo Cabrera
Fr. Mark Slatter
Bello Aliyu M Wamakko
D. William Kay, EdD
doktori.btk.elte.hu
Márta Fischer
zuraidah Mohd Don , Ahmad Izadi
mounir dahmani
elvina Toek
instituteonteachingandmentoring.org
David Schuldberg
Yazid Basthomi
The New Birmingham Review, Dissertation Special Edition (2015)
Ioana Cerasella Chis , The New Birmingham Review , Eliza Garwood
Yazd University
ali hashemi
Annamaria Silvana de Rosa
Mendive. Revista de Educación
MARICELA MARIA GONZALEZ PEREZ
Anthony Masure
Sofia Papadimitriou
Ameen Olorunnimbe
Margaret Gopaul
gideon letaya
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- UNC Chapel Hill

Pre- and Post Defense Steps
Please review the Graduation Deadlines website for timelines of when you must apply for graduation vs when you must upload your thesis.
Pre-Defense
- Ensure you have met the requirement of publishing a first-author, peer-reviewed original research manuscript ( Dissertation Completion ), and talk with your committee to confirm with them that you are ready to defend.
- You must apply to graduate by the deadline ( additional information and application form can be found here ).
- Answer the question in the Graduation Publications form .
- Fill out the Graduation Notification form .
At your defense, we will have paperwork for your committee to sign off that will be sent to the Graduate School.
Post Defense
- You must submit your thesis by the deadline ( additional information can be found here ).
- We have been told the thesis approval process can be lengthy as they are incredibly picky about the formatting ( Thesis and Dissertation Resources )
- Please email [email protected] & cc [email protected] once you have uploaded your thesis so we can process the remaining paperwork.
- Please note the deadlines to apply for graduation and to submit your thesis here Graduation Deadlines .
- Fill out the PHCO exit survey found here https://unc.az1.qualtrics.com/jfe/form/SV_eQAzYpialf9HtT7
- Once your thesis is uploaded and approved, the Graduate School will email you an exit survey.
Post Graduating
- Update your UNC email out-of-office with a new email address.
- If you have dependents on your insurance, call BCBS to stop dependent payments.
Students can view the status of their degree milestones in their Student Center in ConnectCarolina (please note most of the milestones are completed after your upload your thesis, and this is why it’s important to let [email protected] know when you upload your thesis).

- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- GE Service Center
- International Affairs Office
- Academic Affairs Office
- Degree Affairs Office
- Administration Office
- Discipline Affairs Office
- Admission Office (for domestic students)
- Campus Life
- International Graduate Programs Admission
- Scholarships for Degree Programs
- Financial Support for International Conferences
- Courses Enrollment
- Students Login
Forms Download
Thesis Defense
Thesis Review
Degree-granting
Disciplines
China Credentials Verification
- Miscellaneous


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The pre-defense generally takes place three to six months before the final defense. The student is responsible for setting up the meeting: arranging the time and place as well as distributing the draft of the dissertation in time for all the readers to engage with it in a substantive way. The department should also be notified about the event ...
How to prepare for a thesis defense quick guide. Check with your department about requirements and timing. Re-read your thesis. Anticipate questions and prepare for them. Create a back-up plan to deal with technology hiccups. Plan de-stressing activities both before, and after, your defense.
The Pre-Defense manuscript and Examination Results Form must be fully approved at least 14 days prior to the Final Dissertation Defense. Applying for Graduation. For doctoral candidates, the graduation application process should not be completed until the Pre-Defense stage of the dissertation process is approved.
2. Know Your Audience. Most people give their thesis defense presentation to an academic panel. This panel will look to see if you've developed a thorough understanding of your topic and thesis. They'll also be looking to see if you've got a solid foundation for your argument.
This is to showcase your topic's originality and, if relevant, how it's different and/or an improvement from previously done research. Methodology. This is one of the most important parts of a thesis defense presentation. It allows your viewers to assess the rationality and validity of your approach and consequently, the accuracy of your ...
Purpose of the Guide. This Guide was created to help Ph.D. students in engineering fields to design dissertation defense presentations. The Guide provides 1) tips on how to effectively communicate research, and 2) full presentation examples from Ph.D. graduates. The tips on designing effective slides are not restricted to dissertation defense ...
thesis defense . You should also inform your Graduate Administrator that you have started the process to prepare for your defense . A master's thesis defense committee must include your advisor, a second faculty member from within your program, and a faculty member from outside of your department. Selecting a Defense Date . The
ram of study, there are several things that must be done before a thesis defense can occur. Most importantly, you must meet w. h your advisory committee to ensure that everyone agrees that the wo. is ready to defend. You will need to decide on a date by which the defense should occur. You should also infor.
If you are doing a PhD or an MPhil then you will definitely need to do a viva, and this will be conducted by at least two examiners, usually one from inside the university and one external to the university who is an expert in the field. At BSc or MSc level you may be asked to do a viva, however you may be expected to do an oral or a poster ...
3. Work on Starting Strong. To begin your defense on a strong note, work on creating a clear and engaging introduction. You can start by briefly outlining the purpose of your study, research questions, and methodology. Try to stay on topic and don't veer off track by discussing unrelated or unnecessary information. 4.
12 Free presentation templates for a Thesis Defense; Define your signature idea. Your thesis has a focus. A goal. A core concept. And this should be incorporated into your thesis defense presentation's design in every respect. A strong design will help to engage the committee and reinforce your expert understanding of your research area.
A thesis defense gives you the chance to show off your thesis work and demonstrate your expertise in your field of study. During this one- to two-hour discussion with the members of your thesis committee, you'll have some control over how you present your research, but your committee will ask you some prodding questions to test your knowledge and preparedness. They will all have read your ...
Pre-Defense to Publication A Checklist for Graduate Students Version 2.0, published 3.2022 for updates and questions email [email protected] BEFORE THE DEFENSE Map Out Your Schedule to Graduation ... NOTE As you plan your defense, be aware that University policy requires that
Crafting a thesis is significant, but defending it often feels like the ultimate test. While nerve-wracking, proper preparation can make it manageable. Prepare for your thesis defense with insights on the top questions you can expect, including strategies for answering convincingly. Contents Mastering the thesis defense: cultivate a success mindsetQuestion 1: Why did you choose
Common Questions, Preliminary Defense. In your defense, you will be showcasing the evidence that you used within the dissertation. To help you prepare for this, common questions you may be asked include: Ensure you can explain your research in one to two sentences (to be able to do this shows your level of clarity on the project).
POSTS Swath and Dive: A pattern for PhD defense presentations by Luis P. Prieto, November 11, 2022 - 10 minutes read - 2037 words In recent times I'm having the fortune of seeing several of my own doctoral students approach the end of the doctoral journey (yes, it does end!). As they submit the dissertation and prepare for their defense, there is one piece of advice I find myself giving ...
Give yourself an on-the-day boost by planning your studying and preparation well in advance. This will enable you to take a break before the actual day. If the day before your thesis defense can be one spent in contemplation, meditation, or relaxation, you'll have a much better mental state for the defense itself.
One of the most important dissertation defense tips provided by several professors is to breakdown the process into three steps: Preparation: This stage involves collection of all the necessary information that must be included in the defense dissertation and making all the arrangements for the actual meeting. The defense meeting: This is where ...
A pre-defense meeting of the DAC usually occurs two weeks prior to the defense to make sure that the quality of the dissertation document is close to being acceptable for the degree and to review necessary paperwork. At this time, the committee will review the abstract and title. Members of the DAC should have two weeks to review the thesis ...
The dissertation submitted for the pre-defense must comply with the formal and substantive requirements for the dissertation to be submitted for the final defense: the PhD candidate submits a paper that is considered to be completely ready for the defense, even if the possibility exists that the student will have to make major changes to the ...
Pre-Defense. Ensure you have met the requirement of publishing a first-author, peer-reviewed original research manuscript ( Dissertation Completion ), and talk with your committee to confirm with them that you are ready to defend. You must apply to graduate by the deadline ( additional information and application form can be found here ).
PhD students of Translation Studies at ELTE University carry out a pre-defense before being awarded their doctorate degree at the final defense. The dissertation shall at this point conform to the ...
Thesis Defense. Thesis Review. Degree-granting. Disciplines. China Credentials Verification. Forms Download. Flowchart for Pre-Defense of Doctoral Dissertation.