Essay Curve

Essay on Vegetables – Examples, 10 Lines to 1200 Words

Essay on Vegetables: Vegetables are an essential part of a healthy diet, providing us with vital nutrients and fiber that are crucial for our overall well-being. In this essay, we will explore the importance of vegetables in our diet, their health benefits, and the different ways we can incorporate them into our meals. From leafy greens to colorful bell peppers, vegetables offer a wide range of flavors and textures that can enhance any dish. Let’s delve into the world of vegetables and discover how they can contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
Table of Contents
Vegetables Essay Writing Tips
1. Start by introducing the topic of vegetables and their importance in a healthy diet. Explain that vegetables are essential for providing essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that our bodies need to function properly.
2. Discuss the various types of vegetables available, such as leafy greens, root vegetables, cruciferous vegetables, and more. Explain the benefits of each type of vegetable and how they contribute to overall health and well-being.
3. Highlight the nutritional value of vegetables, emphasizing their high fiber content, low calorie count, and abundance of antioxidants. Discuss how vegetables can help prevent chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
4. Explain the importance of incorporating a variety of vegetables into your diet to ensure you are getting a wide range of nutrients. Encourage readers to experiment with different types of vegetables and cooking methods to keep meals interesting and flavorful.
5. Discuss the environmental benefits of eating vegetables, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving water, and preserving natural habitats. Explain how choosing locally grown and organic vegetables can further reduce your carbon footprint.
6. Address common misconceptions about vegetables, such as the belief that they are boring or bland. Provide tips for making vegetables more appealing, such as adding herbs and spices, roasting or grilling them, or incorporating them into soups and stews.
7. Share practical tips for incorporating more vegetables into your diet, such as meal planning, batch cooking, and stocking up on frozen or canned vegetables for convenience. Encourage readers to get creative with their vegetable intake and try new recipes and cooking techniques.
8. Discuss the benefits of growing your own vegetables, either in a backyard garden or in containers on a balcony or windowsill. Explain how gardening can be a rewarding and therapeutic experience that allows you to connect with nature and enjoy the fruits of your labor.
9. Conclude your essay by reiterating the importance of vegetables in a healthy diet and encouraging readers to make them a priority in their daily meals. Emphasize the numerous benefits of eating vegetables for both personal health and the health of the planet.
Essay on Vegetables in 10 Lines – Examples
1. Vegetables are an essential part of a healthy diet, providing vitamins, minerals, and fiber. 2. They come in a variety of colors, shapes, and sizes, offering a wide range of nutrients. 3. Some popular vegetables include broccoli, carrots, spinach, and bell peppers. 4. Vegetables can be eaten raw, cooked, or juiced, making them versatile for different dishes. 5. They are low in calories and high in nutrients, making them ideal for weight management. 6. Eating a variety of vegetables can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer. 7. Farmers markets and grocery stores offer a wide selection of fresh, locally grown vegetables. 8. Some vegetables, like tomatoes and cucumbers, are technically fruits but are commonly classified as vegetables. 9. Vegetables can be grown in home gardens, providing a sustainable and cost-effective way to access fresh produce. 10. Overall, incorporating a variety of vegetables into your diet can lead to better health and well-being.
Sample Essay on Vegetables in 100-180 Words
Vegetables are an essential part of a healthy diet. They are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are crucial for maintaining good health. Eating a variety of vegetables can help prevent chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Vegetables are also low in calories and high in fiber, making them a great choice for weight management. They can help you feel full and satisfied while providing your body with the nutrients it needs.
There are countless types of vegetables to choose from, including leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, root vegetables, and more. Each type of vegetable offers its own unique set of nutrients and health benefits.
Incorporating a variety of vegetables into your diet can be easy and delicious. Try adding them to salads, stir-fries, soups, or simply enjoy them raw with hummus or a healthy dip. By making vegetables a staple in your diet, you can improve your overall health and well-being.
Short Essay on Vegetables in 200-500 Words
Vegetables are an essential part of a healthy diet. They are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are important for maintaining good health. Eating a variety of vegetables can help to reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
One of the key benefits of vegetables is their high nutrient content. They are rich in vitamins such as vitamin C, vitamin A, and vitamin K, as well as minerals like potassium, magnesium, and iron. These nutrients are important for supporting the immune system, promoting healthy skin and hair, and maintaining strong bones and teeth.
In addition to their nutrient content, vegetables are also a great source of antioxidants. Antioxidants help to protect the body from damage caused by free radicals, which are harmful molecules that can contribute to the development of chronic diseases. By including a variety of colorful vegetables in your diet, you can ensure that you are getting a wide range of antioxidants to help keep your body healthy.
Another benefit of vegetables is their high fiber content. Fiber is important for maintaining a healthy digestive system and can help to prevent constipation and other digestive issues. It also helps to keep you feeling full and satisfied, which can be helpful for weight management.
Eating a variety of vegetables can also help to reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Research has shown that people who eat a diet rich in vegetables have a lower risk of developing heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. This is likely due to the combination of nutrients, antioxidants, and fiber found in vegetables that work together to promote overall health.
There are many different types of vegetables to choose from, including leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, root vegetables, and nightshades. Each type of vegetable has its own unique nutritional profile, so it’s important to include a variety of vegetables in your diet to ensure that you are getting all of the nutrients your body needs.
In conclusion, vegetables are an important part of a healthy diet. They are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are important for maintaining good health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. By including a variety of colorful vegetables in your diet, you can ensure that you are getting all of the nutrients your body needs to thrive. So next time you’re planning a meal, be sure to include plenty of vegetables to support your overall health and well-being.
Essay on Vegetables in 1000-1500 Words
Vegetables are an essential part of a healthy diet, providing us with vital nutrients and vitamins that are necessary for our overall well-being. They come in a variety of shapes, sizes, colors, and flavors, making them a versatile and delicious addition to any meal. In this essay, we will explore the importance of vegetables in our diet, their health benefits, and the different ways in which we can incorporate them into our daily meals.
First and foremost, vegetables are packed with essential nutrients that are crucial for our health. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants that help protect our bodies from various diseases and illnesses. For example, leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale are high in vitamin K, which is important for bone health and blood clotting. Carrots are a great source of beta-carotene, which is converted into vitamin A in the body and is essential for good vision and a healthy immune system. Bell peppers are rich in vitamin C, which boosts our immune system and helps our bodies fight off infections. By incorporating a variety of vegetables into our diet, we can ensure that we are getting all the essential nutrients our bodies need to function properly.
In addition to their nutritional value, vegetables also offer a wide range of health benefits. They are low in calories and fat, making them an excellent choice for those looking to maintain a healthy weight or lose weight. The high fiber content in vegetables helps to keep us feeling full and satisfied, reducing the likelihood of overeating or snacking on unhealthy foods. Fiber also aids in digestion and helps to prevent constipation, keeping our digestive system healthy and functioning properly. Furthermore, the antioxidants found in vegetables help to protect our cells from damage caused by free radicals, reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. By including a variety of vegetables in our diet, we can improve our overall health and well-being.
There are countless ways to incorporate vegetables into our daily meals, making it easy to enjoy their health benefits and delicious flavors. One simple way to add more vegetables to your diet is to include them in your breakfast. You can add spinach, tomatoes, and mushrooms to your omelet or scramble, or blend them into a smoothie for a nutritious start to your day. For lunch, try adding a variety of vegetables to your salads, sandwiches, or wraps. You can also roast or grill vegetables like bell peppers, zucchini, and eggplant to add to your favorite dishes or enjoy as a side dish. In the evening, incorporate vegetables into your main dishes by stir-frying them with lean protein sources like chicken, tofu, or shrimp, or adding them to soups, stews, or pasta dishes. By getting creative with your vegetable choices and cooking methods, you can enjoy a wide variety of flavors and textures while reaping the health benefits of these nutritious foods.
In conclusion, vegetables are an essential part of a healthy diet, providing us with vital nutrients and health benefits that are necessary for our overall well-being. By including a variety of vegetables in our meals, we can ensure that we are getting all the essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants our bodies need to function properly. From leafy greens to colorful bell peppers, there are countless ways to enjoy the delicious flavors and health benefits of vegetables. So next time you sit down to eat, remember to fill your plate with a rainbow of vegetables to nourish your body and fuel your health.
Related Essays
Essay on A Visit To A Fair – 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words
Value of Games And Sports – Essay in 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words
Essay on Importance of Teacher – 100, 200, 500, 1000 Words
Essay on A Visit To A Museum – 100, 200, 500, 1000 Words
Essay on Effect of Social Media On Youth
Essay on Shri Guru Nanak Dev Ji – Short & Long Essay Examples
Essay on Nuclear Family – Short Essay & Long Essay upto 1500 Words
Essay on Anudeep Durishetty – 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words
Essay on Non Violence – Samples, 10 Lines to 1500 Words
Covid 19 Responsive School – Essay in 10 Lines, 100 to 1500 Words
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Study Today
Largest Compilation of Structured Essays and Exams
Essay on Vegetables for Children & Students
December 16, 2017 by Study Mentor Leave a Comment
Vegetables constitute a major part of our diet. There are some parts of the plant which are consumed by humans for their daily nutrition. The definition of vegetable is still unclear.
This is because it is defined by the culture and tradition which flows down the generations. When we talk about the vegetables we normally do not include the category of fruits, cereals, nuts, and pulses.
The origin of vegetable is still a matter of fascination. The primal man hunted animals and gathered fruits to sustain his hunger needs. But by some miracle a vegetable seed was sown due to the forces of nature. And when the humans noticed it they came to know that they could also cultivate the land for production of fruits and vegetables.
According to the evidences, the cultivation of vegetables started from 1000 BC to 7000 BC. And is when agriculture started developing. As time passed trade grew.

At this point of time, China is the largest producer of vegetables. China exports a large no. of vegetables to other countries. India is the second largest producer in vegetables but it doesn’t export a large no. of vegetables because the vegetables produced are consumed within the country itself.
Vegetables are a very important constituent of our diet. Without vegetables no meal is complete. Vegetables can be cooked to provide a nutrition full meal. It can be eaten with breads like naan, roti, puri, and bedmi. It can also be eaten with rice.
Some vegetables can be consumed raw, in a salad while some need to be cooked before consumption. Vegetables grow on different parts of trees. For e.g. Onion, reddish and carrot grow in the roots of plants and vegetables like spinach are the leaves of a plant. The cauliflower is obtained from the flower of a tree. Vegetables like gourd, bitter gourd are grown on grapevine like structures.
Thus we see that we have a lot of variety in vegetables. We should concentrate on the consuming portions of vegetables. This provides the body adequate nutrients for its functioning since different vegetables provide the body with different kinds of vitamins and minerals.
Also consumption is a must especially for children who are in their growing stage. Parents should make sure that the children consume a nutrient rich diet and less of junk food. This will make their body strong and will help in the development of their brains and bodies.
Also vegetables increase the immunity of children towards countering diseases. At an early age, they are especially vulnerable to diseases. But the right amount of nutrition helps to fight diseases.
The advantages of consuming vegetables are many. First of all, vegetables help in weight management. Vegetables like potato and cauliflower can help you to gain weight. While vegetables like spinach and green vegetables can help immensely in weight reduction.
From time immemorial, our elders have promoted the consumption of green vegetables. This is because of the fact that green vegetables have a lot of iron in it. They help in the development of bones and muscles. It is actually good for us to consume vegetables at regular intervals so as to protect our body from any diseases.
Vegetables can help your body to fight against some particular type of cancers. Also a healthy intake of vegetables helps to burn the layers of fat in our body this ultimately improves the blood flow and helps in managing the blood pressure of a person. Consumption of vegetables also keeps cholesterol in check.

Also eating vegetables increases your life span by keeping you healthy, in general. Also their frequent intake ensures that we stay rejuvenated throughout the day and we don’t experience any drowsiness or nausea. Vegetables are the fuel to your well-being just like petrol is a fuel to a car.
Vegetables also contains a lot of fibers. Fiber is not a nutrient itself but it helps in the digestive system in our body. To lead a healthy life, one needs to make sure to intake the correct amount of iron or else, the consequences afterwards will be worse. Iron helps the body immensely in carrying out the daily chores.
Also anemia that means lack of hemoglobin in blood can also be cured through the right intake of vegetables. Nevertheless green vegetables also contain folic acid which works wonders on the health of pregnant women.
Make sure to consume healthy and nutritious food which keeps you fit as a fiddle and satiates your body and soul in every way possible, in every way you have ever wanted. Life is short and every moment of it should be made worth living. What is a life without health? Nothing.
As we say, Health is wealth . You cannot enjoy moments in your life without maintaining a healthy lifestyle. And to maintain a healthy lifestyle, you should consume vegetables. Even in old days of your life, you will have a healthy and disease free life, thanking the temptations of junk food you did not give into.
No we should also remember one thing. Vegetables are comparatively cheaper to non vegetarian sources of proteins. Although some trainers do recommend non-vegetarian food but doctors and dieticians worldwide have stuck on a unanimous opinion.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Top Trending Essays in March 2021
- Essay on Pollution
- Essay on my School
- Summer Season
- My favourite teacher
- World heritage day quotes
- my family speech
- importance of trees essay
- autobiography of a pen
- honesty is the best policy essay
- essay on building a great india
- my favourite book essay
- essay on caa
- my favourite player
- autobiography of a river
- farewell speech for class 10 by class 9
- essay my favourite teacher 200 words
- internet influence on kids essay
- my favourite cartoon character
Brilliantly
Content & links.
Verified by Sur.ly
Essay for Students
- Essay for Class 1 to 5 Students
Scholarships for Students
- Class 1 Students Scholarship
- Class 2 Students Scholarship
- Class 3 Students Scholarship
- Class 4 Students Scholarship
- Class 5 students Scholarship
- Class 6 Students Scholarship
- Class 7 students Scholarship
- Class 8 Students Scholarship
- Class 9 Students Scholarship
- Class 10 Students Scholarship
- Class 11 Students Scholarship
- Class 12 Students Scholarship
STAY CONNECTED
- About Study Today
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
Scholarships
- Apj Abdul Kalam Scholarship
- Ashirwad Scholarship
- Bihar Scholarship
- Canara Bank Scholarship
- Colgate Scholarship
- Dr Ambedkar Scholarship
- E District Scholarship
- Epass Karnataka Scholarship
- Fair And Lovely Scholarship
- Floridas John Mckay Scholarship
- Inspire Scholarship
- Jio Scholarship
- Karnataka Minority Scholarship
- Lic Scholarship
- Maulana Azad Scholarship
- Medhavi Scholarship
- Minority Scholarship
- Moma Scholarship
- Mp Scholarship
- Muslim Minority Scholarship
- Nsp Scholarship
- Oasis Scholarship
- Obc Scholarship
- Odisha Scholarship
- Pfms Scholarship
- Post Matric Scholarship
- Pre Matric Scholarship
- Prerana Scholarship
- Prime Minister Scholarship
- Rajasthan Scholarship
- Santoor Scholarship
- Sitaram Jindal Scholarship
- Ssp Scholarship
- Swami Vivekananda Scholarship
- Ts Epass Scholarship
- Up Scholarship
- Vidhyasaarathi Scholarship
- Wbmdfc Scholarship
- West Bengal Minority Scholarship
- Click Here Now!!
Mobile Number
Have you Burn Crackers this Diwali ? Yes No
Essay Service Examples Medicine Importance of Food
Essay about Importance of Vegetables
- Proper editing and formatting
- Free revision, title page, and bibliography
- Flexible prices and money-back guarantee

Our writers will provide you with an essay sample written from scratch: any topic, any deadline, any instructions.
Cite this paper
Related essay topics.
Get your paper done in as fast as 3 hours, 24/7.
Related articles

Most popular essays
- Importance of Food
A popular disorder that affects millions of people is an eating disorder. It's estimated that at...
Who doesn't want to eat food? Probably, no one. Food is a necessity for every human being on the...
Women athletes are likely to be monitored for eating disorders these days. Representatives of...
- Food Safety
According to dictionary, a food is any nutritious substance that people or animals eat or drink or...
We live in a time of reckoning when it comes to body image and particularly female body image....
- Adolescence
There has been research-proven by scientists that there needs to be a balance between stress...
This paper will discuss and explain the topic of eating disorders. This paper will explain how and...
In this research, assumptions about the causes of eating disorders were examined among those with...
Living in a culture where body image is an important component to a person’s character, the...
Join our 150k of happy users
- Get original paper written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
Fair Use Policy
EduBirdie considers academic integrity to be the essential part of the learning process and does not support any violation of the academic standards. Should you have any questions regarding our Fair Use Policy or become aware of any violations, please do not hesitate to contact us via [email protected].
We are here 24/7 to write your paper in as fast as 3 hours.
Provide your email, and we'll send you this sample!
By providing your email, you agree to our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy .
Say goodbye to copy-pasting!
Get custom-crafted papers for you.
Enter your email, and we'll promptly send you the full essay. No need to copy piece by piece. It's in your inbox!
Student Essays

4 Essays on Vegetables & their Importance for our Health
Vegetables are an important part of our diet. They provide essential nutrients that keep us healthy and strong. Vegetables are low in calories and high in fiber, which makes them a perfect food for weight loss. They also contain antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that protect us from disease.
Most vegetables are easy to prepare and can be eaten raw, cooked, or juiced. Vegetables can be added to soups, stews, salads, and stir-fries, or they can be enjoyed as a healthy snack.
There are many different types of vegetables, including leafy greens, root vegetables, cruciferous vegetables, and nightshades. Each type of vegetable has its own unique nutritional benefits. Leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They are also a good source of fiber.
>>>> Read Also : ” Paragraph On Impacts of Junk Food”
Root vegetables, such as carrots and potatoes, are an excellent source of vitamins and minerals. They are also a good source of fiber. Cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli and cauliflower, are a good source of fiber and antioxidants. They also contain compounds that help protect against cancer. Nightshades, such as tomatoes and bell peppers, are a good source of vitamins and minerals. They also contain antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds.
Vegetables are an important part of a healthy diet. They are low in calories and fat, and they are a good source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. including leafy greens, root vegetables, cruciferous vegetables, and nightshades. Each type of vegetable has its own unique nutritional benefits.
Eating a diet rich in vegetables may help to protect against certain chronic diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, cancer, and type 2 diabetes.
Eating vegetables is a great way to improve your health. They are low in calories and high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Vegetables also contain antioxidants, which help protect against disease. A diet rich in vegetables may help to prevent chronic diseases and make us healthy and fit.
Importance of Vegetables:
Vegetables are an essential part of the human diet. They provide numerous health benefits and are packed with nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that our bodies need to function properly. Despite their importance, many people do not consume enough vegetables in their daily diet.
One of the main reasons for this is the misconception that vegetables are bland or unappetizing. However, with the right preparation and cooking methods, vegetables can be delicious and add flavor to any meal. Moreover, there is a wide variety of vegetables available that cater to different taste preferences.
Apart from being tasty, vegetables are also crucial for maintaining good health. They contain high levels of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and helps to prevent constipation. Additionally, they are low in calories, making them an excellent choice for people looking to manage their weight or lose some pounds.
Vegetables are also rich in antioxidants, which help protect our bodies against diseases and infections. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals, which are harmful molecules that can damage cells and lead to chronic illnesses such as cancer and heart disease.
Another essential nutrient found in vegetables is Vitamin C. This vitamin is vital for strengthening the immune system and maintaining healthy bones, teeth, and blood vessels. It also acts as an antioxidant, protecting our cells from damage.
Moreover, vegetables contain a variety of minerals such as potassium, magnesium, and calcium, which are essential for various bodily functions. Potassium helps to regulate blood pressure while magnesium and calcium are crucial for strong bones and teeth.
Eating a diet rich in vegetables has also been linked to a lower risk of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and heart disease. This is because vegetables are low in saturated fats and cholesterol, making them heart-healthy foods.
In addition to the health benefits, consuming a variety of vegetables also adds color and diversity to our meals. Eating a rainbow of vegetables ensures that we are getting a wide range of nutrients and vitamins, which is essential for overall health and wellbeing.
>>>> Read Also : “A Paragraph on Flowers”
In conclusion, vegetables are a vital part of our diet and should be consumed regularly to reap their numerous health benefits. Whether cooked or eaten raw, incorporating a variety of vegetables into our meals can help us maintain good health and prevent chronic diseases
Short Essay on Vegetables:
Vegetables are an essential part of our diet, providing us with the necessary nutrients to keep us healthy and active. They are a rich source of vitamins, minerals, fiber and antioxidants that help in maintaining our overall well-being. From leafy greens to root vegetables, each type of vegetable offers unique health benefits.
One of the main advantages of including vegetables in our diet is their low calorie content. This makes them an ideal food choice for weight management and maintaining a healthy body weight. Vegetables are also packed with fiber, which promotes digestive health and helps in keeping us feeling full for longer periods of time.
Eating a variety of vegetables also ensures that we receive a wide range of nutrients essential for our body’s proper functioning. For example, dark leafy greens like spinach and kale are rich in iron, while brightly colored vegetables like bell peppers and carrots provide us with vitamin C and beta-carotene. Including a variety of vegetables in our diet helps in preventing nutrient deficiencies and reduces the risk of chronic diseases.
Apart from their nutritional benefits, vegetables also add flavor, texture, and color to our meals. They can be cooked in various ways – steamed, roasted, stir-fried or grilled – making them versatile and easy to incorporate into different dishes. They are also affordable and readily available throughout the year.
In addition to being nutritious and delicious, vegetables also have a positive impact on our environment. Growing vegetables requires less resources and produces fewer greenhouse gases compared to raising livestock for meat consumption. Therefore, by choosing to include more vegetables in our diet, we can contribute towards a more sustainable and eco-friendly world.
In conclusion, vegetables are an integral part of a healthy and balanced diet. They provide us with essential nutrients, aid in weight management, prevent diseases, add variety to our meals, and have a positive impact on the environment. It is important to include a variety of vegetables in our daily meals to reap their numerous health benefits and lead a healthier lifestyle
Essay on Vegetables for Class 1,2,3
Vegetables are a crucial part of our daily lives and they play a vital role in keeping us healthy. They provide us with essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that help our bodies function properly. In this essay, we will learn about the different types of vegetables and their importance in our diet.
Vegetables are classified into five main groups – dark green vegetables, starchy vegetables, red and orange vegetables, beans and peas, and other vegetables. Dark green vegetables include spinach, kale, and broccoli which are rich in iron, calcium, and vitamin C. Starchy vegetables like potatoes, corn, and peas are high in carbohydrates that give us energy to carry out our daily activities.
Red and orange vegetables such as carrots, sweet potatoes, and pumpkin are packed with beta carotene, which is converted into vitamin A in our bodies. This vitamin is essential for maintaining good eyesight and a healthy immune system. Beans and peas, like lentils, chickpeas, and kidney beans, are a great source of protein for vegetarians.
Other vegetables like onions, tomatoes, and bell peppers provide us with various vitamins and minerals that are essential for our overall health. They are also low in calories, making them a great addition to any weight-loss diet.
Vegetables not only provide us with important nutrients, but they also help prevent various diseases like heart disease, obesity, and certain types of cancer. They are an excellent source of fiber which aids in digestion and keeps our digestive system healthy.
In conclusion, vegetables are an important part of a balanced diet and should be included in our meals daily. Whether raw, steamed, or cooked, they provide us with numerous health benefits that cannot be ignored. So let’s make sure to eat our veggies and stay healthy! Remember, it’s never too early to start incorporating vegetables into our diets, so even young students can make a positive impact on their health by choosing to eat a variety of vegetables every day. So let’s all pledge to eat our veggies and be healthy!
Q: What is the importance of vegetables?
A: Vegetables are important because they provide essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals for a healthy diet. They also add variety to meals and contribute to overall well-being.
Q: What is the short information about vegetables?
A: Vegetables are edible plants that provide a wide range of nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and fiber. They are a crucial part of a balanced diet.
Q: What is a vegetable and its uses?
A: A vegetable is an edible plant or part of a plant. It is used for human consumption in various forms, such as salads, side dishes, soups, and as ingredients in a wide range of recipes.
Q: What are vegetables for Class 1?
A: For a Class 1 audience, you can explain that vegetables are healthy foods that grow in the ground and help make our bodies strong and fit. They come in many colors and shapes and can be delicious when prepared in different ways
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Agriculture in India
Essay on vegetables: top 4 essays | agriculture.
Here is an essay on ‘Vegetables’ for class 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Vegetables’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay # 1. Introduction to Vegetables:
The noun vegetable usually means an edible plant or part of a plant other than a sweet fruit or seed.
However, the word is not scientific, and its meaning is largely based on culinary and cultural tradition. Therefore, the application of the word is somewhat arbitrary and subjective. For example, some people consider mushrooms to be vegetables, while others consider them a separate food category.
Some vegetables can be consumed raw, and some may (or must) be cooked in various ways, most often in non- sweet (savory or salty) dishes. However, a few vegetables are often used in desserts and other sweet dishes, such as rhubarb pies and carrot cakes.
As an adjective, the word vegetable is used in scientific and technical contexts with a different and much broader meaning, namely of ‘related to plants’ in general, edible or not — as in vegetable matter, vegetable kingdom, vegetable origin, etc. The meaning of ‘vegetable’ as ‘plant grown for food’ was not established until the 18th century.
There are three definitions relating to fruits and vegetables:
i. Fruit (scientific): the ovary of a seed-bearing plant;
ii. Fruit (culinary): any edible part of a plant with a sweet flavour;
iii. Vegetable: any edible part of a plant with a savory flavour.
In everyday, grocery-store, culinary language, the words ‘fruit’ and ‘vegetable’ are mutually exclusive; plant products that are called fruits are hardly ever classified as vegetables, and vice versa. For scientists, the word ‘fruit’ has a precise botanical meaning (a part that developed from the ovary of a flowering plant), which is considerably different from its common meaning, and includes many poisonous fruits.
While peaches, plums, and oranges are ‘fruits’ in both senses, many items commonly called ‘vegetables’ — such as eggplants, bell peppers, and tomatoes — are technically fruits, as are most cereals, as well as some spices like black pepper and chillies. Some plant products, such as corn or peas, may be considered vegetables only while still unripe.
The question of whether the tomato is a fruit or a vegetable found its way into the United States Supreme Court in 1893. The court ruled unanimously in Nix v. Hedden that a tomato is correctly identified as, and thus taxed as, a vegetable, for the purposes of the 1883 Tariff Act on imported produce. The court did acknowledge, however, that, botanically speaking, a tomato is a fruit.
Languages other than English often have categories that can be identified with the common English meanings of ‘fruit’ and ‘vegetable’, but their precise meaning often depends on local culinary traditions. For example, in Brazil the avocado is traditionally consumed with sugar as a dessert or in milk shakes, and hence regarded as a fruit; whereas in other countries (including Mexico and the United States) it is used in salads and dips, and hence considered a vegetable.
The list of food items called ‘vegetable’ is quite long, and includes many different parts of plants.
‘Vegetable’ comes from the Latin vegetabilis (animated) and from vegetare (enliven), which is derived from vegetus (active), in reference to the process of a plant growing. This in turn derives from the Proto-Indo-European base *weg- or *wog-, which is also the source of the English wake, meaning ‘become (or stay) alert’.
The word ‘vegetable’ was first recorded in English in the 15th century, but applied to any plant. This is still the sense of the adjective ‘vegetable’ in science. The related term vegetation also has a similarly broad scope.
Essay # 2. Nutrition in Vegetables:
Vegetables are eaten in a variety of ways, as part of main meals and as snacks. The nutritional content of vegetables varies considerably, though generally they contain little protein or fat, and varying proportions of vitamins, pro-vitamins, dietary minerals, fiber and carbohydrates. Vegetables contain a great variety of other phytochemicals, some of which have been claimed to have antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral and anti-carcinogenic properties.
However, vegetables often also contain toxins and anti-nutrients such as a-solanine, a-chaconine, enzyme inhibitors (of cholinesterase, protease, amylase, etc.), cyanide and cyanide precursors, oxalic acid, and more. Depending on the concentration, such compounds may reduce the edibility, nutritional value, and health benefits of dietary vegetables. Cooking and/or other processing may be necessary to eliminate or reduce them.
Essay # 3. Colour Pigments Present in Vegetables:
The green colour of leafy vegetables is due to the presence of the green pigment chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is affected by pH and changes to olive green in acid conditions, and bright green in alkaline conditions. Some of the acids are released in steam during cooking, particularly if cooked without a cover.
The yellow/orange colours of fruits and vegetables are due to the presence of carotenoids, which are also affected by normal cooking processes or changes in pH.
The red/blue colouring of some fruits and vegetables (e.g. blackberries and red cabbage) are due to anthocyanin’s which are sensitive to changes in pH. When pH is neutral, the pigments are purple, when acidic, red, and when alkaline, blue. These pigments are very water soluble.
For food safety, the CDC recommends proper fruit handling and preparation to reduce the risk of food contamination and foodborne illness. Fresh fruits and vegetables should be carefully selected. At the store, they should not be damaged or bruised and pre-cut pieces should be refrigerated or surrounded by ice.
All fruits and vegetables should be rinsed before eating. This recommendation also applies to produce with rinds or skins that are not eaten. It should be done just before preparing or eating to avoid premature spoilage. Fruits and vegetables should be kept separate from raw foods like meat, poultry, and seafood, as well as any cooking utensils or surfaces that may have come into contact with them (e.g. cutting boards).
Fruits and vegetables, if they are not going to be cooked, should be thrown away if they have touched raw meat, poultry, seafood or eggs. All cut, peeled, or cooked fruits and vegetables should be refrigerated within 2 hours. After a certain time, harmful bacteria may grow on them and increase the risk of foodborne illness.
Essay # 4. Storage Care for Vegetables :
Proper post-harvest storage aimed at extending and ensuring shelf life is best effected by efficient cold chain application. All vegetables benefit from proper post-harvest care.
Many root and non-root vegetables that grow underground can be stored through winter in a root cellar or other similarly cool, dark and dry place to prevent mold, greening and sprouting. Care should be taken in understanding the properties and vulnerabilities of the particular roots to be stored. These vegetables can last through to early spring and be nearly as nutritious as when fresh.
During storage, leafy vegetables lose moisture, and the vitamin C in them degrades rapidly. They should be stored for as short a time as possible in a cool place, in a container or plastic bag.
Related Articles:
- Essay on the Cottage Gardens: Top Essays | Agriculture
- Essay on Gardens: Top 15 Essays | Plants | Agriculture
Essay , Agriculture , Vegetables , Essay on Vegetables
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Importance of Vegetables
Do you like to eat vegetables? Not all people in this world prefer to be vegetarians . They might prefer the delicious non-vegetarian foods like meat, fish, etc., over the vegetables. The fact is, even though some of the seafood and other non-vegetarian dishes are nutritious, they will never be able to compete with the nutritional value of the vegetables. There are different types of vegetables, such as leafy vegetables, cereals, pulses, etc.
One of the most important factors to have a healthy life is a well-balanced diet. The type of food we consume decides the quality of our life. The vegetables contain all the necessary proteins, vitamins, fiber, and other minerals which have a very important role in our lives.

There are many people who do not realize the vital role of vegetables in their life. Hence, it is important to keep in mind the below-mentioned points which help us to understand the importance of vegetables.
- Vegetables help to reduce the risk of diabetes by producing the necessary micronutrients required for the regulation of the blood sugar. They also help to reduce the glycemic load of the meals. The fiber contained in them slow down the absorption of sugar in our body. Hence, consuming more vegetables makes us less prone to diabetes by reducing the energy density of your diet.
- The micronutrients present in the vegetables are the best foods to prevent cardiovascular diseases.
- The vegetables rich in potassium, calcium, and magnesium help to regulate the blood pressure.
- The antioxidants present in them reduce the oxidative stress and maintains the healthy body fat levels.
- The fiber content in the vegetables helps in curing the digestive problems.
- Vegetables containing calcium, magnesium, phosphorous, chromium, and vitamin K promote the bone health in people. The various studies show that the vegetables are far more effective than the dairy products in preventing the bone problems.
- The fiber present in the vegetables also helps to prevent colorectal cancer.
- The chlorophyll found in the plants alleviate the carcinogenic properties of heme iron found in the red meat.
- The presence of various nutrients and the low-caloric value in the vegetables alleviates the problems of obesity.
- The vitamin A present in them keeps our skin and eyes healthy.
- The vitamin C in the vegetables helps to keep the gums and teeth healthy.
- The vegetables give protection against the infections and also help in healing wounds faster.
- The antioxidants in the vegetable prevent cell damage and also cures diseases like Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and atherosclerosis.
- The potassium content in the vegetables prevents bone loss and kidney stone.
- The nutrient called folate present in the vegetables are essential for pregnant women. The folate reduces the risk of neural tube defects in the fetus.
- The carotenoids present in the vegetables like carrots, sweet potato, beetroot, etc., and dark green vegetables like spinach, broccoli, etc., improve our overall immune system.
- Foods containing diallyl sulfide, such as garlic, shallots, leeks, onions, etc., give protection against stomach ulcer.
- The vitamin B present in the vegetables like sweet potato, carrot, broccoli, green pepper, etc., improves our immune system and also the nervous functions.
- Vitamin K present in the vegetables like cauliflower, broccoli, cabbage, kale, turnip greens and other dark green leafy vegetables improves our metabolism and is also involved in blood clotting.
- The copper content in the leafy vegetables promotes the formation of red blood cells.
Vegetables are, in short, the powerhouse of various nutrients, vitamins, and minerals. They not only help in improving our metabolism but also reduces the risk posed by the various high-caloric value food products. A lot of people in the current world are trying to reduce their excess body weight and remain healthy. The vegetables are the boon to those types of dieters.
The different types of vegetables focus on the different organs in your body. Thus, consuming vegetables in our daily life maintains the development and functioning of each and every organ in our body. They also fight against the fatal diseases like cancer, which is very common nowadays.
Whether you consume other types of food products or not, it is essential to include the nutritious vegetables in your diet. The majority of our health problems can easily be tackled with the help of vegetables. Hence, vegetables play a very crucial role in our overall health and are indispensable. We have to remember that a healthy population is the keystone of a healthy economy.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Captcha: 9320

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center

What is the nutritional value of vegetables?
What are the main types of vegetables.
- What does a potato plant look like?
- What is corn?
- Why do corn kernels pop?

Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health - Vegetables and Fruits
- Live Science - What's the difference between fruit and vegetables?
- University of Minnesota Extension - Vegetable
- Medicine LibreTexts - Vegetable Nutrition, Storage and Preparation
- WebMD - Health Benefits of Vegetables
- vegetable - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- vegetable - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)

What is a vegetable?
In common usage, the term vegetable usually refers to the edible portions of certain herbaceous plants. These plant parts are either eaten fresh or prepared in several ways.
Most vegetables are low in calories and have a water content of over 70 percent, with only about 3.5 percent protein and less than 1 percent fat. Vegetables are good sources of minerals, especially calcium and iron, and vitamins, principally A and C. Nearly all vegetables are rich in dietary fiber and antioxidants.
What parts of plants are eaten as vegetables?
The root, stem, leaf and leafstalk, flower, fruits, and seeds are the parts of plants that are eaten as vegetables.
Vegetables are usually classified on the basis of the part of the plant that is used for food. There are root vegetables, stem vegetables, edible tubers (underground stems), leaf and leafstalk vegetables, bulb vegetables, head or flower vegetables, fruits commonly considered vegetables by virtue of their use (cucumbers, eggplants, sweet corn), and seed vegetables (peas, beans).

vegetable , in the broadest sense, any kind of plant life or plant product, namely “vegetable matter”; in common, narrow usage, the term vegetable usually refers to the fresh edible portions of certain herbaceous plants— roots , stems , leaves , flowers , fruit , or seeds . These plant parts are either eaten fresh or prepared in a number of ways, usually as a savory, rather than sweet , dish.
A brief treatment of vegetables and vegetable farming follows. For in-depth treatment of vegetable cultivation, see vegetable farming . For treatment of the nutrient composition and processing of vegetables, see vegetable processing .

Virtually all of the more important vegetables were cultivated among the ancient civilizations of either the Old or the New World and have long been noted for their nutritional importance. Most fresh vegetables are low in calories and have a water content in excess of 70 percent, with only about 3.5 percent protein and less than 1 percent fat . Vegetables are good sources of minerals, especially calcium and iron , and vitamins, principally A and C . Nearly all vegetables are rich in dietary fibre and antioxidants .

Vegetables are usually classified on the basis of the part of the plant that is used for food . The root vegetables include beets , carrots , radishes , sweet potatoes , and turnips . Stem vegetables include asparagus and kohlrabi . Among the edible tubers , or underground stems, are potatoes . The leaf and leafstalk vegetables include brussels sprouts , cabbage , celery , lettuce , rhubarb , and spinach . Among the bulb vegetables are garlic , leeks , and onions . The head, or flower, vegetables include artichokes , broccoli , and cauliflower . The fruits commonly considered vegetables by virtue of their use include cucumbers , eggplant , okra , sweet corn , squash , peppers , and tomatoes . Seed vegetables are usually legumes, such as peas and beans .
Modern vegetable farming ranges from small-scale production for local sale to vast commercial operations utilizing the latest advances in automation and technology. In addition, vegetables can be grown conventionally or using organic farming methods. Most vegetables are planted by seeding in the fields where they are to be grown, but occasionally they are germinated in a nursery or greenhouse and transplanted as seedlings to the field. During the growing season synthetic or organic herbicides , pesticides , and fungicides are commonly used to inhibit damage by weeds , insects , and diseases , respectively. Depending on the crop , harvesting operations are usually mechanized in well-developed countries, but the practice of harvesting by hand is still employed in some areas or is used in conjunction with machine operations. Another concern of the vegetable farmer is postharvest storage, which may require refrigerated facilities.

Vegetables may be washed, sorted, graded, cut, and packaged for sale as fresh products. Fresh vegetables are subject to quick aging and spoilage, but their storage life can be extended by such preservation processes as dehydration, canning , freezing, fermenting, or pickling.
Vegetables and Fruits

- Vegetables and fruits are an important part of a healthy diet, and variety is as important as quantity.
- No single fruit or vegetable provides all of the nutrients you need to be healthy. Eat plenty every day.
A diet rich in vegetables and fruits can lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke, prevent some types of cancer, lower risk of eye and digestive problems, and have a positive effect upon blood sugar, which can help keep appetite in check. Eating non-starchy vegetables and fruits like apples, pears, and green leafy vegetables may even promote weight loss. [1] Their low glycemic loads prevent blood sugar spikes that can increase hunger.
At least nine different families of fruits and vegetables exist, each with potentially hundreds of different plant compounds that are beneficial to health. Eat a variety of types and colors of produce in order to give your body the mix of nutrients it needs. This not only ensures a greater diversity of beneficial plant chemicals but also creates eye-appealing meals.

Tips to eat more vegetables and fruits each day
- Keep fruit where you can see it . Place several ready-to-eat washed whole fruits in a bowl or store chopped colorful fruits in a glass bowl in the refrigerator to tempt a sweet tooth.
- Explore the produce aisle and choose something new . Variety and color are key to a healthy diet. On most days, try to get at least one serving from each of the following categories: dark green leafy vegetables; yellow or orange fruits and vegetables; red fruits and vegetables; legumes (beans) and peas; and citrus fruits.
- Skip the potatoes . Choose other vegetables that are packed with different nutrients and more slowly digested carbohydrates .
- Make it a meal . Try cooking new recipes that include more vegetables. Salads, soups, and stir-fries are just a few ideas for increasing the number of tasty vegetables in your meals.

5 common questions about fruits and vegetables.
Vegetables, fruits, and disease, cardiovascular disease.
There is compelling evidence that a diet rich in fruits and vegetables can lower the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- A meta-analysis of cohort studies following 469,551 participants found that a higher intake of fruits and vegetables is associated with a reduced risk of death from cardiovascular disease, with an average reduction in risk of 4% for each additional serving per day of fruit and vegetables. [2]
- The largest and longest study to date, done as part of the Harvard-based Nurses’ Health Study and Health Professionals Follow-up Study, included almost 110,000 men and women whose health and dietary habits were followed for 14 years.
- The higher the average daily intake of fruits and vegetables, the lower the chances of developing cardiovascular disease. Compared with those in the lowest category of fruit and vegetable intake (less than 1.5 servings a day), those who averaged 8 or more servings a day were 30% less likely to have had a heart attack or stroke. [3]
- Although all fruits and vegetables likely contributed to this benefit, green leafy vegetables, such as lettuce, spinach, Swiss chard, and mustard greens, were most strongly associated with decreased risk of cardiovascular disease. Cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, Brussels sprouts , bok choy, and kale ; and citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruit (and their juices) also made important contributions. [3]
- When researchers combined findings from the Harvard studies with several other long-term studies in the U.S. and Europe, and looked at coronary heart disease and stroke separately, they found a similar protective effect: Individuals who ate more than 5 servings of fruits and vegetables per day had roughly a 20% lower risk of coronary heart disease [4] and stroke, [5] compared with individuals who ate less than 3 servings per day.
Blood pressure
- The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) study [6] examined the effect on blood pressure of a diet that was rich in fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products and that restricted the amount of saturated and total fat. The researchers found that people with high blood pressure who followed this diet reduced their systolic blood pressure (the upper number of a blood pressure reading) by about 11 mm Hg and their diastolic blood pressure (the lower number) by almost 6 mm Hg—as much as medications can achieve.
- A randomized trial known as the Optimal Macronutrient Intake Trial for Heart Health (OmniHeart) showed that this fruit and vegetable-rich diet lowered blood pressure even more when some of the carbohydrate was replaced with healthy unsaturated fat or protein. [7]
- In 2014 a meta-analysis of clinical trials and observational studies found that consumption of a vegetarian diet was associated with lower blood pressure. [8]
Numerous early studies revealed what appeared to be a strong link between eating fruits and vegetables and protection against cancer . Unlike case-control studies, cohort studies , which follow large groups of initially healthy individuals for years, generally provide more reliable information than case-control studies because they don’t rely on information from the past. And, in general, data from cohort studies have not consistently shown that a diet rich in fruits and vegetables prevents cancer.
- For example, over a 14-year period in the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study, men and women with the highest intake of fruits and vegetables (8+ servings a day) were just as likely to have developed cancer as those who ate the fewest daily servings (under 1.5). [3]
- A meta-analysis of cohort studies found that a higher fruit and vegetable intake did not decrease the risk of deaths from cancer. [2]
A more likely possibility is that some types of fruits and vegetables may protect against certain cancers.
- A study by Farvid and colleagues followed a Nurses’ Health Study II cohort of 90,476 premenopausal women for 22 years and found that those who ate the most fruit during adolescence (about 3 servings a day) compared with those who ate the lowest intakes (0.5 servings a day) had a 25% lower risk of developing breast cancer. There was a significant reduction in breast cancer in women who had eaten higher intakes of apples, bananas , grapes, and corn during adolescence, and oranges and kale during early adulthood. No protection was found from drinking fruit juices at younger ages. [9]
- Farvid and colleagues followed 90, 534 premenopausal women from the Nurses’ Health Study II over 20 years and found that higher fiber intakes during adolescence and early adulthood were associated with a reduced risk of breast cancer later in life. When comparing the highest and lowest fiber intakes from fruits and vegetables, women with the highest fruit fiber intake had a 12% reduced risk of breast cancer; those with the highest vegetable fiber intake had an 11% reduced risk. [10]
- After following 182,145 women in the Nurses’ Health Study I and II for 30 years, Farvid’s team also found that women who ate more than 5.5 servings of fruits and vegetables each day (especially cruciferous and yellow/orange vegetables) had an 11% lower risk of breast cancer than those who ate 2.5 or fewer servings. Vegetable intake was strongly associated with a 15% lower risk of estrogen-receptor-negative tumors for every two additional servings of vegetables eaten daily. A higher intake of fruits and vegetables was associated with a lower risk of other aggressive tumors including HER2-enriched and basal-like tumors. [11]
- A report by the World Cancer Research Fund and the American Institute for Cancer Research suggests that non-starchy vegetables—such as lettuce and other leafy greens, broccoli, bok choy, cabbage, as well as garlic, onions, and the like—and fruits “probably” protect against several types of cancers, including those of the mouth, throat, voice box, esophagus, and stomach. Fruit probably also protects against lung cancer. [12]
Specific components of fruits and vegetables may also be protective against cancer. For example:
- A line of research stemming from a finding from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study suggests that tomatoes may help protect men against prostate cancer, especially aggressive forms of it. [12] One of the pigments that give tomatoes their red hue—lycopene—could be involved in this protective effect. Although several studies other than the Health Professionals Study have also demonstrated a link between tomatoes or lycopene and prostate cancer, others have not or have found only a weak connection. [14]
- Taken as a whole, however, these studies suggest that increased consumption of tomato-based products (especially cooked tomato products) and other lycopene-containing foods may reduce the occurrence of prostate cancer. [12] Lycopene is one of several carotenoids (compounds that the body can turn into vitamin A) found in brightly colored fruits and vegetables, and research suggests that foods containing carotenoids may protect against lung, mouth, and throat cancer. [12] But more research is needed to understand the exact relationship between fruits and vegetables, carotenoids, and cancer.
Some research looks specifically at whether individual fruits are associated with risk of type 2 diabetes. While there isn’t an abundance of research into this area yet, preliminary results are compelling.
- A study of over 66,000 women in the Nurses’ Health Study, 85,104 women from the Nurses’ Health Study II, and 36,173 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study—who were free of major chronic diseases—found that greater consumption of whole fruits—especially blueberries, grapes, and apples—was associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. Another important finding was that greater consumption of fruit juice was associated with a higher risk of type 2 diabetes. [15]
- Additionally a study of over 70,000 female nurses aged 38-63 years, who were free of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes, showed that consumption of green leafy vegetables and fruit was associated with a lower risk of diabetes. While not conclusive, research also indicated that consumption of fruit juices may be associated with an increased risk among women. (16)
- A study of over 2,300 Finnish men showed that vegetables and fruits, especially berries, may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. [17]
Data from the Nurses’ Health Studies and the Health Professional’s Follow-up Study show that women and men who increased their intakes of fruits and vegetables over a 24-year period were more likely to have lost weight than those who ate the same amount or those who decreased their intake. Berries, apples, pears, soy, and cauliflower were associated with weight loss while starchier vegetables like potatoes, corn, and peas were linked with weight gain. [1] However, keep in mind that adding more produce into the diet won’t necessarily help with weight loss unless it replaces another food, such as refined carbohydrates of white bread and crackers.
Gastrointestinal health
Fruits and vegetables contain indigestible fiber, which absorbs water and expands as it passes through the digestive system. This can calm symptoms of an irritable bowel and, by triggering regular bowel movements, can relieve or prevent constipation. [18] The bulking and softening action of insoluble fiber also decreases pressure inside the intestinal tract and may help prevent diverticulosis. [19]
Eating fruits and vegetables can also keep your eyes healthy, and may help prevent two common aging-related eye diseases—cataracts and macular degeneration—which afflict millions of Americans over age 65. [20-23] Lutein and zeaxanthin, in particular, seem to reduce risk of cataracts. [24]
- Bertoia ML, Mukamal KJ, Cahill LE, Hou T, Ludwig DS, Mozaffarian D, Willett WC, Hu FB, Rimm EB. Changes in intake of fruits and vegetables and weight change in United States men and women followed for up to 24 years: analysis from three prospective cohort studies. PLoS medicine . 2015 Sep 22;12(9):e1001878.
- Wang X, Ouyang Y, Liu J, Zhu M, Zhao G, Bao W, Hu FB. Fruit and vegetable consumption and mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMJ . 2014 Jul 29;349:g4490.
- Hung HC, Joshipura KJ, Jiang R, Hu FB, Hunter D, Smith-Warner SA, Colditz GA, Rosner B, Spiegelman D, Willett WC. Fruit and vegetable intake and risk of major chronic disease. Journal of the National Cancer Institute . 2004 Nov 3;96(21):1577-84.
- He FJ, Nowson CA, Lucas M, MacGregor GA. Increased consumption of fruit and vegetables is related to a reduced risk of coronary heart disease: meta-analysis of cohort studies. Journal of human hypertension . 2007 Sep;21(9):717.
- He FJ, Nowson CA, MacGregor GA. Fruit and vegetable consumption and stroke: meta-analysis of cohort studies. The Lancet . 2006 Jan 28;367(9507):320-6.
- Appel LJ, Moore TJ, Obarzanek E, Vollmer WM, Svetkey LP, Sacks FM, Bray GA, Vogt TM, Cutler JA, Windhauser MM, Lin PH. A clinical trial of the effects of dietary patterns on blood pressure. New England Journal of Medicine . 1997 Apr 17;336(16):1117-24.
- Appel LJ, Sacks FM, Carey VJ, Obarzanek E, Swain JF, Miller ER, Conlin PR, Erlinger TP, Rosner BA, Laranjo NM, Charleston J. Effects of protein, monounsaturated fat, and carbohydrate intake on blood pressure and serum lipids: results of the OmniHeart randomized trial. JAMA . 2005 Nov 16;294(19):2455-64.
- Yokoyama Y, Nishimura K, Barnard ND, Takegami M, Watanabe M, Sekikawa A, Okamura T, Miyamoto Y. Vegetarian diets and blood pressure: a meta-analysis. JAMA internal medicine. 2014 Apr 1;174(4):577-87.
- Farvid MS, Chen WY, Michels KB, Cho E, Willett WC, Eliassen AH. Fruit and vegetable consumption in adolescence and early adulthood and risk of breast cancer: population based cohort study. BMJ . 2016 May 11;353:i2343.
- Farvid MS, Eliassen AH, Cho E, Liao X, Chen WY, Willett WC. Dietary fiber intake in young adults and breast cancer risk. Pediatrics . 2016 Mar 1;137(3):e20151226.
- Farvid MS, Chen WY, Rosner BA, Tamimi RM, Willett WC, Eliassen AH. Fruit and vegetable consumption and breast cancer incidence: Repeated measures over 30 years of follow‐up. International journal of cancer . 2018 Jul 6.
- Wiseman M. The Second World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research Expert Report. Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity, and the Prevention of Cancer: A Global Perspective: Nutrition Society and BAPEN Medical Symposium on ‘Nutrition support in cancer therapy’. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society . 2008 Aug;67(3):253-6.
- Giovannucci E, Liu Y, Platz EA, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC. Risk factors for prostate cancer incidence and progression in the health professionals follow‐up study. International journal of cancer . 2007 Oct 1;121(7):1571-8.
- Kavanaugh CJ, Trumbo PR, Ellwood KC. The US Food and Drug Administration’s evidence-based review for qualified health claims: tomatoes, lycopene, and cancer. Journal of the National Cancer Institute . 2007 Jul 18;99(14):1074-85.
- Muraki I, Imamura F, Manson JE, Hu FB, Willett WC, van Dam RM, Sun Q. Fruit consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes: results from three prospective longitudinal cohort studies. BMJ . 2013 Aug 29;347:f5001.
- Bazzano LA, Li TY, Joshipura KJ, Hu FB. Intake of fruit, vegetables, and fruit juices and risk of diabetes in women. Diabetes Care . 2008 Apr 3.
- Mursu J, Virtanen JK, Tuomainen TP, Nurmi T, Voutilainen S. Intake of fruit, berries, and vegetables and risk of type 2 diabetes in Finnish men: the Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study–. The American journal of clinical nutrition . 2013 Nov 20;99(2):328-33.
- Lembo A, Camilleri M. Chronic constipation. New England Journal of Medicine . 2003 Oct 2;349(14):1360-8.
- Aldoori WH, Giovannucci EL, Rockett HR, Sampson L, Rimm EB, Willett AW. A prospective study of dietary fiber types and symptomatic diverticular disease in men. The Journal of nutrition . 1998 Oct 1;128(4):714-9.
- Brown L, Rimm EB, Seddon JM, Giovannucci EL, Chasan-Taber L, Spiegelman D, Willett WC, Hankinson SE. A prospective study of carotenoid intake and risk of cataract extraction in US men–. The American journal of clinical nutrition . 1999 Oct 1;70(4):517-24.
- Christen WG, Liu S, Schaumberg DA, Buring JE. Fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of cataract in women–. The American journal of clinical nutrition . 2005 Jun 1;81(6):1417-22.
- Moeller SM, Taylor A, Tucker KL, McCullough ML, Chylack Jr LT, Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Jacques PF. Overall adherence to the dietary guidelines for Americans is associated with reduced prevalence of early age-related nuclear lens opacities in women. The Journal of nutrition . 2004 Jul 1;134(7):1812-9.
- Cho E, Seddon JM, Rosner B, Willett WC, Hankinson SE. Prospective study of intake of fruits, vegetables, vitamins, and carotenoidsand risk of age-related maculopathy. Archives of Ophthalmology . 2004 Jun 1;122(6):883-92.
- Christen WG, Liu S, Glynn RJ, Gaziano JM, Buring JE. Dietary carotenoids, vitamins C and E, and risk of cataract in women: a prospective study. Archives of Ophthalmology . 2008 Jan 1;126(1):102-9.
Terms of Use
The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products.
- Diet & Weight Management
- Popular Diet Plans
- Healthy Weight Resources
- Vitamins and Nutrients
- Understanding Fats
- Calorie Counting
- Best & Worst Choices
- View Full Guide
Health Benefits of Vegetables

Vegetable is a broad term that refers to the edible parts of plants, which are usually their leaves, roots, fruits, or seeds. Vegetables are a staple food across the world and are a fundamental part of modern agriculture.
Since they’re low in calories but high in nutrients, most health experts recommend that you consume vegetables daily. There’s a scientific consensus that a balanced, rotating diet of different varieties of vegetables is one of the best ways to source nutrients from your food starting at a young age.
Health Benefits
Vegetables are full of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that provide many important health benefits to your body. For instance, carrots are known for being very high in vitamin A , which plays an important role in eye health, as you grow older.
Vegetables also offer many other health benefits like:
Improved Digestive Health
Vegetables are a good source of dietary fiber, a type of carbohydrate that helps pass food through your digestive system. Studies show that fiber may also improve vitamin and mineral absorption in the body, which could potentially raise your daily energy levels.
Lower Blood Pressure
Many green leafy vegetables like kale, spinach , and chard contain potassium. Potassium helps your kidneys filter sodium out of your body more efficiently, which can reduce your blood pressure.
Lower Risk of Heart Disease
Green leafy vegetables also contain vitamin K, which is believed to prevent calcium from building up in your arteries. This can lower your risk of arterial damage and help prevent many heart health complications in the future.
Diabetes Control
Vegetables are particularly high in fiber, which is needed for optimal digestion. They have a low glycemic index, so your blood sugar won’t rise quickly after a meal. The American Diabetes Association recommends at least 3 to 5 servings per day of non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, carrots, or cauliflower.
Vegetables are a rich source of folate , a B vitamin that helps your body make new red blood cells. Folate is especially important for children’s health and may also reduce the risk of cancer and depression.
Vegetables are also great sources of essential minerals like:
- Phosphorous
Nutrients per Serving
The nutritional content of vegetables naturally depends on which kind you’re eating. For instance, calories range from 6.5 calories per celery stalk to 67 calories per 1/2 cup of peas.
Portion Sizes
While portion sizes also vary depending on the specific vegetables, the USDA recommends that adults eat between one and three cups of vegetables per day.
How to Prepare Vegetables
Many varieties of vegetables can be found in grocery and health food stores across the country. They can be bought in both organic and conventionally grown varieties. Experts recommend eating a varied diet of vegetables regularly to maximize their nutrient potential.
Vegetables are a versatile food that can be steamed, roasted, mixed into stir-fry, and more. They’re an essential part of cuisines all around the world that are served as either a main dish or a side dish in countless recipes.
Here are some easy ways to incorporate vegetables in your diet:
- Try a mixed salad with kale , cabbage, and brussels sprouts
- Cook onions, peppers, and zucchini together for a vegetable kabob meal
- Roast your tomatoes in the oven with olive oil, parmesan cheese, and basil
- Create a fresh Mediterranean garden salad with lettuce, sweet peas, peppers, and cherry tomatoes
- Fry vegetables with oil in a wok with chicken or tofu to create a delicious stir-fry
- Create a vegetable melt by adding asparagus , mushrooms, and peppers to toasted cheese bread

Top doctors in ,
Find more top doctors on, related links.
- Diet & Weight Management Home
- Diet Medical Reference
- Diet Plans A-Z
- Healthy Weight Guide
- Health Tools & Calculators
- Healthy Eating & Nutrition
- Best & Worst Health Choices
- All Health Guide Topics
- Weight Loss & Obesity
- Fitness & Exercise
- Food & Recipes
- Food Calculator
- BMI Calculator
- Cholesterol Management
- More Related Topics
College of Agricultural, Consumer & Environmental Sciences
Illinois Extension
- Beef Cattle
- Community Planning
- Environment
- Local Government Education
- Rainfall Management
- Fruit Trees
- Vegetable Gardening
- Newsletters
- Online Courses
- Publications
- Summer Resources
- Contact Staff
- Find an Office
- Social Media
- Administration and Educator Teams
- Geographic Organizational Leadership
- Communications and Information Technology
- Planning, Reporting, and Evaluation
- Volunteer and Career Development
- Energy Education Council
- Illini Science Policy Program
- Illinois Indiana Sea Grant
- Master Gardeners
- Master Naturalists
- Plant Clinic
- Research and Education Centers
- Home and Community Education
- Annual Reports
- Economic and Functional Impact
- 2024 Extension Collaboration Grants
- Agriculture and AgriBusiness Impact
- Community and Economic Development Impact
- Family and Consumer Sciences Impact
- Integrated Health Disparities Impact
- Natural Resources, Environment, and Energy Impact
- SNAP-Education Impact
- Extension Funded Research Projects
- Extension Councils
- FYI Internal Communications
- Professional Associations
- Partnerships
- Strategic Planning
Grow your own vegetables to benefit your health and the environment

There are many reasons to grow your vegetables, including health benefits, better flavor, and environmental protection. The health benefits are exponential with the combination of nutrients, sunshine, and exercise gained through vegetable gardening.
Studies show that those who garden are more likely to eat more vegetables. Vegetables are a good source of essential nutrients such as calcium, vitamin A, potassium, and fiber for example. As you work outside in the sunshine, you are aiding your body in the production of vitamin D.
Walking, bending, lifting, and pulling movements that happen while gardening fit into the moderate excise category that can increase your body's immune system function. See this fact sheet about Training your Immune System for more information.
Certain vegetables such as broccoli, cabbage, and Brussel's sprouts produce a disease-fighting compound called sulfurane when cut. Colorful vegetables provide antioxidants such as lycopene and beta carotene. Diversity in the types of vegetables ensures balanced nutrition.
Freshly picked vegetables that you grew in your garden seem to taste better. Several factors determine taste. Different varieties of vegetables have different flavors. You can choose varieties for your garden to suit your tastes.
The flavor is also based on biochemical changes that happen to the produce once it is harvested. "Sugar stored in sweet corn kernels is being converted to starch as soon as the ear is harvested," says Nicole Flowers-Kimmerle, horticulture educator with the University of Illinois Extension serving Fulton, Mason, Peoria, and Tazewell counties. “Cook sweet corn as soon as you can for the most sweetness.”
Harvest time can also affect the flavor of the vegetable. In your garden, you can harvest your vegetables at their peak to ensure maximum flavor. For more information on the perfect time to harvest different vegetables go to the University of Illinois Extension A Taste of Gardening website .
Vegetable gardens benefit the environment in many ways. Locally grown vegetables reduce carbon emissions from burning fossil fuels. No plastic packaging is required when you harvest vegetables straight from the garden, which also reduces fossil fuel inputs. Pesticide and other chemical inputs can be much less in a small, well-tended garden than even a small farm.
Instead of your kitchen and yard waste going to a landfill, start a compost pile. A bonus is you are creating your own soil amendment to increase your garden's productivity. Visit the University of Illinois Extension site Composting Central for more information on composting for the home garden.
These health and environmental benefits can last even longer when you plant vegetables for fall harvest. Vegetables that grow well in cool weather such as leaf lettuce, radish, spinach, and turnips can be planted throughout August for a fall harvest. Visit the Illinois Extension website “Vegetable Garden Guide” at web.extension.illinois.edu/vegguide for planting dates.
For more information on how to start a vegetable garden, contact your local University of Illinois Extension office or visit the website extension.illinois.edu/ .
MEET THE AUTHOR
Nicole Flowers-Kimmerle is a Agriculture and Natural Resources (Horticulture) Educator for Fulton, Mason, Peoria and Tazewell counties. She completed a bachelors of science degree in crop science at the University of Illinois, and a master’s of science degree in agronomy with an emphasis in weed science at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. She has also worked at Montana State University as a research associate where she worked on weed control in sugar beets and barley. She taught high school chemistry and other science classes where she was able to teach students in both the school garden and greenhouse. She works with both the Extension Master Gardeners and Extension Master Naturalists.
ABOUT THE BLOG
ILRiverHort is a blog that helps people connect to nature and grow.

Related Content

Essay on My Favourite Vegetable
Students are often asked to write an essay on My Favourite Vegetable in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on My Favourite Vegetable
Introduction.
My favourite vegetable is the carrot. It is a root vegetable, often orange in colour, though purple, black, red, and yellow varieties exist.
Reasons for My Preference
Carrots are not only tasty but also packed with health benefits. They are rich in vitamins, fibre, and antioxidants.
Usage in Various Dishes
Carrots can be used in a variety of dishes. They can be eaten raw, cooked, or used in salads, soups, and even desserts like carrot cake.
In conclusion, my favourite vegetable, the carrot, is versatile, delicious, and healthy.
250 Words Essay on My Favourite Vegetable
The versatility of potatoes.
Potatoes are the epitome of versatility. They can be baked, boiled, mashed, fried, or roasted, each method unlocking a unique flavour and texture. This adaptability extends beyond culinary uses. In the scientific realm, potatoes have been grown in controlled environments as part of research for potential crop cultivation in space.
Nutritional Value
Despite being stigmatized for their carbohydrate content, potatoes are nutritionally dense. They are a good source of vitamin C, vitamin B6, potassium, and dietary fiber, especially when consumed with their skin. They also provide essential minerals and antioxidants, contributing to overall health and well-being.
Cultural Significance
Potatoes have a profound cultural significance. Originating in South America, they were brought to Europe in the 16th century and have since become a staple in many cuisines. They symbolize sustenance and comfort in several cultures, and their global cultivation attests to their universal appeal.
In conclusion, the potato, in its simplicity and versatility, embodies the essence of my favourite vegetable. Its nutritional value, coupled with its cultural significance, makes it not just a dietary staple but also a testament to human innovation and adaptability. The humble potato, therefore, stands as a symbol of the intersection between food, culture, and science.
500 Words Essay on My Favourite Vegetable
The allure of the aubergine.
Choosing a favourite vegetable may seem like a trivial exercise to some, but to me, it is a reflection of personal taste, culinary preferences, and even cultural background. My favourite vegetable is the aubergine, or eggplant, as it is known in some parts of the world. Its versatility, nutritional value, and the depth it adds to various dishes make it stand out among the plethora of vegetables available to us.
Versatility in the Kitchen
Nutritional powerhouse.
The aubergine is not just a culinary delight; it is also a nutritional powerhouse. It is low in calories and high in dietary fibre, making it an excellent choice for those looking to maintain a healthy lifestyle. It also contains essential nutrients such as potassium, vitamin C, and vitamin B6. The skin of the aubergine is rich in antioxidants, specifically nasunin, which is known for its potential protective effects against free radical damage. This balance of taste and health benefits makes the aubergine an appealing choice for the health-conscious food lover.
The Depth of Flavour
The aubergine’s unique flavour profile is another reason why it is my favourite vegetable. When raw, it has a somewhat bitter taste and a spongy texture. However, when cooked, it undergoes a transformation that is nothing short of culinary magic. It becomes tender and develops a complex flavour profile that is smoky, slightly sweet, and utterly delicious. This depth of flavour makes the aubergine a delight to cook with and eat.
The Cultural Significance
In conclusion, the aubergine, with its versatility, nutritional value, depth of flavour, and cultural significance, is my favourite vegetable. It is a testament to the fact that vegetables can be as exciting and delightful as any other food group. The aubergine’s rich history and wide usage across different cuisines make it not just a vegetable, but a culinary ambassador, breaking barriers and bringing people together through the universal language of food.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Recent Posts / Worksheets
- Ask AI – How to Write Leave letters for absence Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
- Create School Worksheets with AI – Generating a Grade 3 Math Worksheet
- [PowerPoint] How to Add Space Between Bullet and Bullet Text
- [Excel] How to Insert Multiple Pictures in Each Column with Names – Using VBA
- How to copy a text or shape in a slide to all slides of Powerpoint using Macro
Our Popular Works
- 25 Phrases with Example Sentences
- Pronouns Worksheets – He, She, It and They…
- Reading Comprehension for Grade 2
- Self Introduction Worksheet for kids
- Reading Comprehension Passages for Grade 3 or 4…
- Chart on Collective Nouns
- My Aim In Life is to Become a Cricketer
- Shapes Names with Pictures
- Living Things and Non-living Things Chart
- Present perfect tense form of verbs worksheet
Importance of Vegetables
- Your Home Teacher
- October 1, 2015
- No Comments
Importance of Vegetables:
- Vegetables are a rich source of nutrients
- Adding vegetables to our daily food routine makes a healthy diet
- Having more vegetables instead of oily foods and junk foods helps in weight management
- Eating all the varieties of vegetables increases our immune
- It is good to eat vegetables regularly to protect our body from diseases.
Importance of Vegetables: (Short Essay)
Our food we intake daily is the source of all essentials namely vitamins, minerals, fibers and phytochemicals . All food we have nowadays does not do well to our body. Since time being, vegetables are said to be the source of nutrients and immunity. One who takes right amount of fruits and vegetables is immune to diseases. Vegetables form a healthy diet which keeps our stomach full for a longer time. As a result, one doesn’t gain weight even if he overeats vegetables every day. Vegetables that are healthy and easy to be added in daily food are tomatoes, garlic, broccoli, carrot, spinach and so on.
Importance of Vegetables: (Brief Essay)
Vegetables are said to be the best food for our body. Vegetables have all the essential nutrients namely vitamins, minerals, fibers and phytochemicals that form resistance to diseases naturally. Unfortunately, we fail to add these healthy vegetables in our daily meal. The importance of vegetables can be summarized as follows:
- The nutrients rich vegetables maintain the health of our body in a regular pace. Having vegetables daily ensures the immunity of our body. A meal with vegetables added reduces the possibilities of Arthritis, Stroke, Heart Diseases and many other serious complications which we think vegetables cannot resist.
- Vegetables do not add more calories to your body. Eating a plate full of vegetables is good for your health; at the same time helps in weight management. As you eat more vegetables, we do not tend to get hungry easily.
- Most of the vegetables have anti-aging properties. Regular consumption of such vegetables ensures a young look and healthy feeling to our body. Younger looks gives us more confidence.
- Vegetables keep our biological cycle very regular. Vegetables regularize the digestive system and maintain the appetite throughout the day. This keeps us mentally and physically fresh than ever.
The vegetables that can be added in our daily food are spinach, garlic, onions, tomatoes, carrots, green peas and many more. The more the vegetables we consume, the more the healthier we become. As in the saying, “ Prevention is better than cure ”, having vegetables today will reduce the risk of many unexpected diseases in the future.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

10 lines on vegetables in English - Short essay on Vegetables
Today, we are sharing ten lines essay on vegetables . This article can help the students who are looking for information about vegetables in English . This essay is very simple and easy to remember. The level of this essay is moderate so any students can write on this topic. This article is generally useful for class 1, class 2, and class 3 .

10 lines on vegetables in English
- Green vegetables are very important for our health.
- Eating green vegetables keep both bodies and mind healthy.
- Green vegetables have a great contribution to a balanced diet.
- Green vegetables contain many types of vitamins and minerals.
- Some vegetables we cook and some we eat them by making a raw salad.
- Spinach, beans, peas, tomatoes, okra, Loki, brinjals, carrots, radish, etc., are green vegetables.
- There are more than 80 types of vegetables all over the world.
- It is most important to have green vegetables in our food.
- Doctors advise us to eat green vegetables.
- Eating green vegetables increases the immunity of our body.

Children in school, are often asked to write 10 lines about vegetables in English . We help the students to do their homework in an effective way. If you liked this article, then please comment below and tell us how you liked it. We use your comments to further improve our service. We hope you have got some learning on the above subject. You can also visit my YouTube channel that is https://www.youtube.com/synctechlearn. You can also follow us on Facebook https://www.facebook.com/synctechlearn .
You might like

not good points
Post a Comment
Contact form.

- healthy living
The benefits of fruits and vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are an essential part of a healthy diet. Not only do these colourful foods add flavour and variety to your meals, but they also pack a powerful nutritional punch, providing vitamins, minerals, fibre and antioxidants. In this article, we will explore the health benefits of eating fruits and vegetables, how much and the best types to eat and answer some commonly asked questions about fruits.
What is the difference between fruits and vegetables?
Fruits and vegetables are classified from both a botanical and culinary standpoint. The botanical classification is based on the plant’s physiological characteristics, like its structure, function and organisation. 1 A botanical fruit has at least one seed and grows from the flower of the plant. Examples of botanical fruits include apples, strawberries, peaches, but also tomatoes , cucumbers and peppers . A botanical vegetable, on the other hand, does not have a set definition but is more of a general term encompassing all other edible aspects of the plant, the roots, the stems and the leaves. Examples include foods such as spinach, broccoli and carrots.
The culinary classification is based on the way the plants are used and their flavour profiles. Culinary fruits have a softer texture, tend to be either sweet or tart and are often enjoyed raw or in desserts or jams. In contrast, a culinary vegetable usually has a tougher texture, blander taste and often requires cooking. The culinary classification may be more useful in our day-to-day lives as foods from the same botanical family may not have the same nutritional composition. For example, cantaloupe melons, watermelons, butternut squash, cucumbers and pumpkins all belong to the same botanical family but have different nutritional values.

What are the health benefits of fruits and vegetables?
Most people know that fruits and vegetables are good for us. Both fruits and vegetables are high in dietary fibre as well as vitamins and minerals , and other bioactive plant compounds, including many with antioxidant properties such as polyphenols or beta-carotene. Fruits and vegetables contain, for example, vitamin A , B5 , folate , C , E & K and are a rich source of calcium , iron , magnesium , manganese and potassium . 2 The amounts and types of nutrients vary between different types of fruits and vegetables. Fruits and vegetables are also high in water, ranging from 75-90% of their weight. This fact explains their low energy content. Fruits and vegetables usually contain traces of fats and protein, with a few exceptions such as avocados, which have a high fat content. There is no evidence that organic fruits and vegetables are more nutritious compared to conventional varieties. 3-5
Eating a lot of fruits and vegetables is strongly associated with a lower risk of premature deaths and non-communicable diseases ; particularly, cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary heart disease and stroke, and certain cancers i.e., of the mouth, pharynx, larynx, oesophagus and colorectum. 6-8 A meta-analysis looking at 95 prospective studies found that each additional 200 grams of fruits and vegetables per day was associated with an 8% lower risk of coronary heart disease, 16% lower risk of stroke, 8% lower risk of cardiovascular disease, 3% lower risk of cancer and 10% lower risk of premature death. 9 Eating fruits and vegetables was associated with these reduced risks up to intakes of 800 grams per day except cancer, where no further reductions in risk were observed above 600 grams per day.
Eating fruits and vegetables is also linked to a lower risk of other diseases, including dementia, certain eye diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, depression, pancreatic diseases and hip fractures, although with a lower strength of evidence. 6 , 7 Furthermore, diets high in fruits and vegetables may prevent weight gain, the most important risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
How much fruit and vegetables should I eat per day?
The World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends eating at least 400 g of fruits and vegetables per day. 10 This is often translated to five 80 g portions (also commonly known as “5-a-day”). Almost all fruits and vegetables count towards this recommended daily amount, with a few exceptions: potatoes and other starchy tubers such as cassava; tinned or canned fruits and vegetables with added sugar or salt; more than one portion of dried fruit (30 grams); and more than 150 ml of 100% fruit or vegetable juice or smoothie. In other words, dried fruit and fruit/vegetable juices and smoothies only count for one of your 5-a-day even if you eat or drink more portions.
Should I avoid eating fruits and vegetables because of ‘anti-nutrients’?
No, fruits and vegetables are healthy choices, despite containing anti-nutrients.
Anti-nutrients are chemicals that are found in plant-based foods that can interfere with how your body absorbs nutrients. 11 Examples of anti-nutrients found in fruits and vegetables include lectins (e.g., in tomatoes and aubergines), oxalates (e.g., in spinach, Swiss chard and beetroot), goitrogens (e.g., in kale, Brussels sprouts, cabbage and broccoli) and tannins (e.g., in grapes, berries, apples and stone fruits). 12 Other examples of anti-nutrients you may have heard of include phytates (e.g., in legumes, whole grains and nuts and seeds) and phytoestrogens (e.g., in soy and soy products and flaxseeds) but these two groups are not found in significant quantities in fruit and vegetables. Although evidence is limited, some suggested implications of these anti-nutrients include altered gut function and inflammation (lectins), reduced absorption of calcium (oxalates), and iron (tannins) and reduced absorption of iodine, hypothyroidism and/or goitre (goitrogens). 12
Some studies have shown that anti-nutrients may cause negative health effects when eaten in very high amounts, without any form of food processing, or in isolated form (e.g. not as part of a food). However, often the health effects seen in these studies are not easily comparable to potential effects of eating them as part of our every diet. For example, much of the research on anti-nutrients linking them to negative health outcomes is performed in animals, which cannot tell us what happens in humans. 12 Moreover, how our bodies absorb nutrients from our diets likely significantly different that how it reacts to isolated compounds used in some research studies. This is because the diverse and complex interactions of all the chemicals in our foods and food combinations affect how our body digests and absorbs nutrients, and any resulting health effects. 11 , 12
There is however consistent evidence showing that a eating a lot of fruits and vegetables is linked to a reduced risk of various diseases. So, although fruits and vegetables contain anti-nutrients, the health benefits of eating them outweighs any potential negative nutritional effects. Food processing techniques such as boiling, steaming or peeling the skins (specifically for fruits high in tannins) can also reduce the amount of anti-nutrients present in fruits and vegetables.
In a small number of people who have or are at high risk for certain illnesses, anti-nutrients might cause problems (e.g., oxalates in kidney stone formation and goitrogens in thyroid disease). 12 In this case, it is best to consult with a registered dietitian or GP for individualised and safe advice.
What fruit or vegetable is best for health?
No single fruit or vegetable is best for health. All fruits and vegetables are good for health and provide different nutrients. Eating a variety of types and colours provides us with a range of different nutrients the body needs.
Some studies have found that specific fruits and vegetables may be more strongly related to reducing our disease risk. 9 These include apples and pears, citrus fruits, green leafy vegetables (e.g., kale, spinach and pak choi) and salads and cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, Brussels sprouts and cabbage) for cardiovascular disease and mortality and green-yellow vegetables and cruciferous vegetables for total cancer risk.
Are fresh fruits and vegetables better than frozen?
Both fresh and frozen fruits and vegetables are nutritious choices and count towards the recommended daily intake. Generally, produce picked at peak ripeness offers the highest amount of vitamins and minerals. During sorting, transporting and distribution, fruits and vegetables lose some of their vitamins and minerals. Frozen fruits and vegetables are often frozen within a few hours of harvesting at peak ripeness, and so they retain the most nutrients. However, some vegetables are blanched before freezing, which reduces the levels of less stable water-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins B1 and C, as well as antioxidants. 13 Other nutrients such as fat-soluble vitamins A and E are less easily lost, and processing may make these even more available to our bodies. 14
Frozen fruits and vegetables are convenient, often cheaper than fresh and allow us greater variety year-round. They can help to reduce food waste. When choosing frozen produce, choose ones that don’t have added salt or sugar.
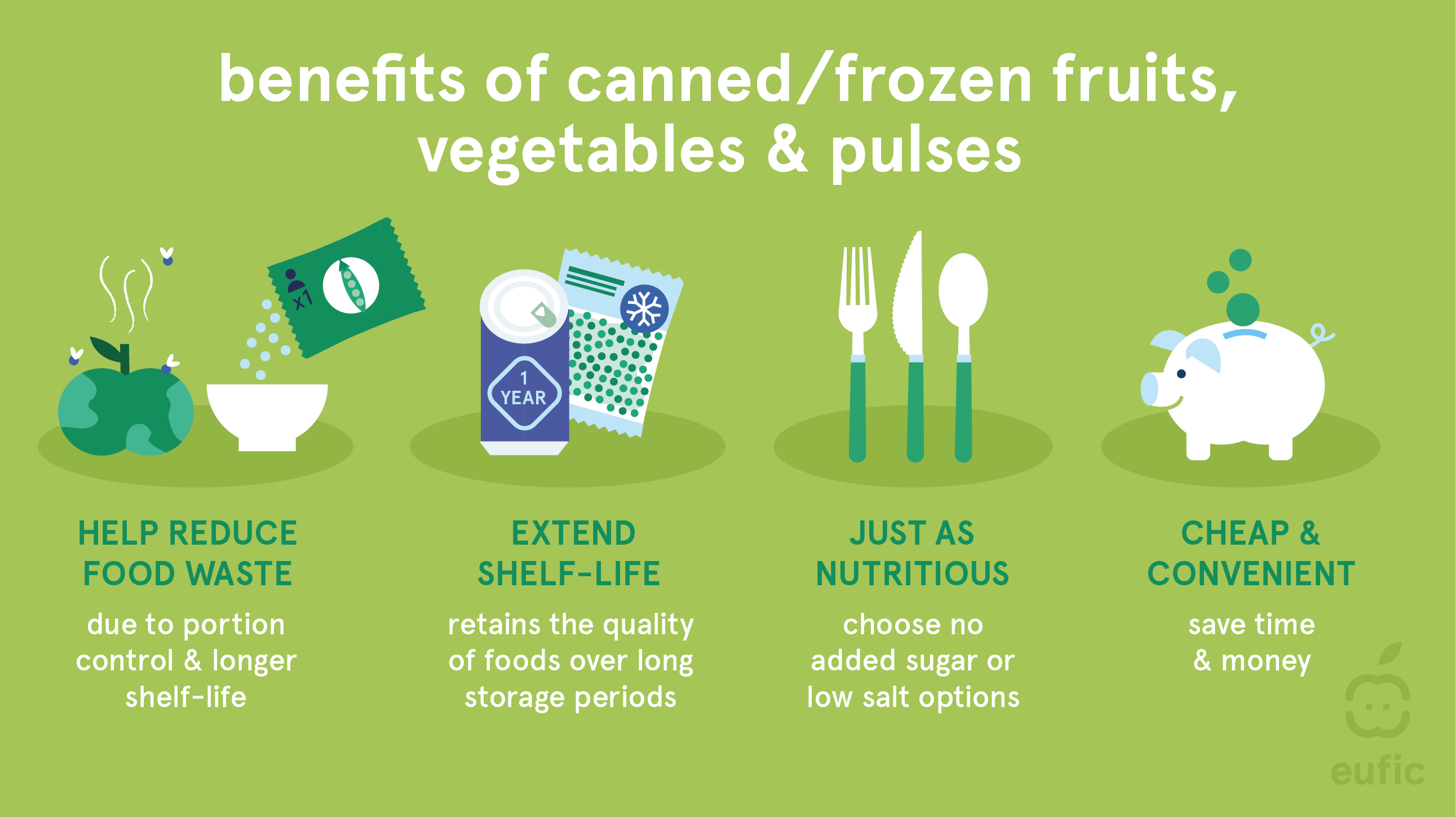
When should you eat fruits? Can you eat fruits at night?
Fruits are a healthy choice at any time of the day. The myth that eating fruits at night is bad for you stems from the idea that eating fruit will raise your blood glucose levels and that if your body does not have time to stabilise those levels before bed, it may lead to weight gain. However, there is no evidence to suggest that eating fruit at night is harmful or leads to weight gain.
Any carbohydrate-containing food, including fruits but also vegetables, bread, pasta and pulses, will temporarily increase your blood sugar while glucose is being absorbed by the body, regardless of the time of day. Some studies indicate that our body’s glucose control is influenced by our internal body clock and that eating carbohydrates earlier in the day is associated with better glucose control. 15 However only a small number of studies have looked at this so far and more studies are needed to understand the mechanisms and whether there is any impact on health.
Importantly, glucose control is also dependent on a person’s overall diet and the amount and type of carbohydrate consumed. For example, pairing fruit with a source of protein or fat can help slow down the absorption of sugar and mitigate any potential spikes in blood sugar levels. It’s also important to consider overall calorie intake, as consuming excessive calories from any source can lead to weight gain over time.
Is sugar in fruit bad for you?
No, sugar in fruit is not bad for you. Foods in which sugars naturally occur, such as fruit, vegetables, grains or pulses, usually also contain fibre and other health-promoting nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals. As such they are better for our health than foods containing predominantly free or added sugars and few other nutrients. Indeed, high intake of free and added sugars is a risk factor for many preventable diseases, 16 , 17 whereas overall, high fruit and vegetable intake is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases, cancers and premature death. 9
How to safely handle fruits and vegetables?
Since they are often eaten raw, fresh fruit and vegetables can sometimes be a source of foodborne illness. This is because they can pick up microbes from manure or water used during production, or at other stages of picking, storage and transport. However, basic food hygiene can reduce this risk so we can enjoy a wide variety of fresh fruits and vegetables:
- Wash your hands before and after preparing fruits and vegetables;
- Wash or scrub their skin with water before eating or preparing (products marketed as fruit and vegetable washes are not necessary);
- ‘prewashed’ fruits and vegetables don’t need to be washed again;
- Store them properly and throw away produce that looks or smells spoiled

Fruits and vegetables are an essential part of a healthy diet. They are rich in nutrients and can lower our risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases and certain cancers. Eating a variety of fruits and vegetables will help ensure that you are getting a range of nutrients. Whether you choose fresh or frozen or eat them in the morning or at night, fruits and vegetables are a great way to boost your health. Eating 400 g of fruits and vegetables a day may seem ambitious but here are some helpful tips to help you:
- Keep fruit easy to reach;
- Take fruits and vegetables with you to have as snacks;
- (re)discover new or forgotten vegetables;
- Check what is in season where you are (& try new recipes);
- Swap your old favourites to increase variety.

- Pennington JAT & Fisher RA (2009). Classification of fruits and vegetables. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 22S:S23-S31.
- Public Health England. 2019. McCance and Widdowson’s Composition of Foods Integrated Dataset.
- Dangour AD, Dodhia SK, Hayter A, Allen E, Lock K & Uauy R (2009). Nutritional quality of organic foods: a systematic review. American Journal Clinical Nutrition. 90:680-685.
- Bourn D & Prescott J (2002). A comparison of the nutritional value, sensory qualities, and food safety of organically and conventionally produced foods. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 42:1-34.
- Worthington V (1998). Effect of agricultural methods on nutritional quality: A comparison of organic with conventional crops. Alternative Therapies in Health & Medicine 4:58-69.
- Angelino, D. et al. (2019). Fruit and vegetable consumption and health outcomes: An umbrella review of observational studies. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 70(6), 652-667
- Boeing, H., Bechthold, A., Bub, A., Ellinger, S., Haller, D., Kroke, A., ... & Watzl, B. (2012). Critical review: vegetables and fruit in the prevention of chronic diseases. European journal of nutrition, 51, 637-663.
- World Cancer Research Fund International. (2018). Wholegrains, vegetables and fruit and the risk of cancer. Continuous Update Project Expert Report.
- Aune, D. et al. (2017). Fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer and all-cause mortality—a systematic review and dose-response meta-ananalysis of prospective studies. International journal of epidemiology, 46(3)
- World Health Organization. (2020). Healthy diet. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/healthy-diet
- López-Moreno, M., Garcés-Rimón, M., & Miguel, M. (2022). Antinutrients: Lectins, goitrogens, phytates and oxalates, friends or foe?. Journal of Functional Foods, 89, 104938.
- Petroski, W., & Minich, D. M. (2020). Is there such a thing as “anti-nutrients”? A narrative review of perceived problematic plant compounds. Nutrients, 12(10), 2929.
- Rickman JC, Barrett DM & Bruhn CM. (2007). Nutritional comparison of fresh, frozen and canned fruits and vegetables. Part I. Vitamins C and B and phenolic compounds. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 87:930-944.
- Rickman JC, Barrett DM & Bruhn CM. (2007). Nutritional comparison of fresh, frozen and canned fruits and vegetables. Part II. Vitamin A and carotenoids, vitamin E, minerals and fiber. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 87:1185-1196.
- Zhao, L., Hutchison, A. T., & Heilbronn, L. K. (2021). Carbohydrate intake and circadian synchronicity in the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care, 24(4), 342-348.
- Gakidou E, et al. (2017). Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016
- Mann J (2007). Dietary carbohydrate: relationship to cardiovascular disease and disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. European Journal of Nutrition 61:S100-S111.
Don't miss any news from us!
You may also like….
Rue Belliard 2A (3rd floor), 1040 Brussels, Belgium
VAT: BE0456866931
- Healthy living
- What’s in food?
- Food production
- Food safety
- Understanding science
About EUFIC
- How we work
- Work at EUFIC
Using this website
- Privacy policy
- Terms of use
© eufic 2024 - design: FWD - illustration: Pouce-pied
- Members' Area

- Competitions
- Press releases
- Spokespeople
- Share your story
- Vegan insight panel
- Plant milk market
- Meat alternative market
- Definition of veganism
- Go vegan for animals
- Go vegan for the environment
- Go vegan for your health
- How many animals would I save?
- The honey industry
- Meal planning
- Take the Vegan Pledge
- VeGuide App - Go Vegan the Easy Way
- Become a Member
- Donate Today
- Leaving A Gift In Your Will
- Giving in Loving Memory
- Run for The Vegan Society
- Walk for The Vegan Society
- Collection tins
- Fundraising ideas
- Shop ethically with our affinity partners
- Vegan and Thriving 77 Challenge
- Volunteer Roles
- Volunteer Profiles
- Community Network
- Join our newsletter
- Our Manifesto for Veganism
- Planting Value in the Food System
- How We Influence Policy
- COP27 Policy Briefing
- Climate Crisis
- Research News
- Research Advisory Committee
- Researcher Network
- On the Pulse Webinars
- Publications
- Research Day 2024: Vegan Pasts, Presents and Futures
- Empathy Index
- About the IRN
- What rights do vegans have?
- Veganism in the workplace
- Currently experiencing problems?
- International Vegan Rights Conference 2024
- Veganise your town
- Discount list
- Wholesale opportunities
- Offer a competition
- World Vegan Month
- Nutrition overview
- Life stages
- Bone health
- Vegan Supplementation
- Medications
- Allergen labelling
- Nutrition Network
- Fuelling an active lifestyle
- Vegan and Thriving
- Vegan shoes
- Vegan tattoos
- Sandwich and wrap fillings
- Vegan-friendly options in UK chains
- Vegan on a budget
- Trademark search
- Lists of vegan items in UK supermarkets
- The Vegan magazine
- The Vegan Pod
- General FAQs
- Vegan Trademark
- VEG 1 Vegan Supplements
- Gifts & Accessories
Why we should grow our own veg
You are here, discover the many benefits, both personal and environmental, that come of growing your own vegetables. freya partridge discusses reasons for getting green fingered and how you can do this whether you have a garden or not..
Wrapped in copious amounts of plastic, transported long distances before reaching the chopping board, and grown using chemical pesticides. A large proportion of shop-bought fruit and vegetables are responsible for causing significant environmental damage, leaving us with an ethical dilemma to contend with whenever we go to the supermarket. One solution that arguably resolves each of these issues is to start growing our own food.
There are many reasons why tending a vegetable garden could bring both personal and environmental benefits. Although the success of such an endeavour in part depends on the amount of time you can commit to it, it’s hard to deny that the benefits of growing your own food make the hours spent planting, watering, and weeding worthwhile.
It would be remiss not to recognise the challenges associated with finding a space suitable for growing fruit and vegetables. Not all of us have access to a garden or local allotment, and this can seem like a hurdle too high to overcome. Luckily, it is possible to find plant species that do well in pots placed in windows or on balconies. If you dream of eating greens brought into existence by your own labour, lacking a garden doesn’t have to stop you from achieving this goal.
Detailed below are just some positives of nurturing your own fruit and vegetable plants.

Control over pesticide use
Although a recent change in European law means that a range of chemicals harmful to pollinators are no longer used on crops grown in these countries, scientists are worried that replacement pesticides are no safer for bee populations.
It is vital that continued action is taken to protect these insects, not least because global food production is dependent on bees pollinating crops. When growing your own fruit and vegetables, decisions regarding the use of pesticides are in your hands. It is possible to affordably grow organic produce without the use of harmful chemicals. To help bee populations further, you might decide to plant bee-friendly flowers in another part of your garden.
Creating your own vegetable patch puts you in control of the practices used to grow the food you eat, providing a great opportunity to effect positive environmental change.
Reduced carbon footprint
An additional environmental benefit of starting a vegetable garden is that it allows you to cook with vegetables that are grown as close to home as possible, whether that be in your back garden or at a community allotment. By reducing your consumption of food grown hundreds, if not thousands, or miles away, your carbon footprint will decrease.
In order to provide customers with a wide and varied range of produce, supermarkets often bring in fruit and vegetables that originate from either a distant part of the country or a different country altogether. Although this certainly has its benefits, allowing us to cook meals with ingredients that might not otherwise be available to us, the energy required to transport these goods contributes significantly to climate change . After harvesting your own vegetables, they need only be carried from garden to kitchen.
No need for plastic
In many places, it can be difficult to find produce that isn’t wrapped in plastic, particularly if you are also looking to buy organic. Although supermarkets are increasingly making efforts to reduce their use of plastic, the need to keep fruit and vegetables fresh – particularly when they must be transported across the globe – means that these businesses face difficulties in eradicating such packaging from their shelves.
Produce grown in your back garden or local allotment is the definition of fresh. With no need for it to be tightly packaged for transit, home grown produce causes no increase in plastic waste.
Other environmental benefits that come from tending your own vegetable garden include reduced food waste. Rather than sending your vegetable cuttings to landfill, why not start composting? You’ll be able to make use of this compost to improve the quality of your plants, creating a circular system that reduces the amount of day to day waste you produce.
Improved mental health and wellbeing
Growing your own fruit and vegetables might take some time out of your day, but it is certainly time well spent. Gardening is a great way to combat stress and anxiety, with fresh air and exercise being widely recommended to people suffering with mental health . The various tasks involved in producing greens for your kitchen table, from planting seeds to harvesting vegetables, are sure to increase your daily activity.
A great sense of accomplishment can also be found in successfully nurturing a plant from its beginnings as a seedling up to its growth of vegetables ripe for picking. If you’re lucky, you might end up with enough food to share with your friends, family and local community, helping to spread a love of home grown produce.

Choosing to grow your own food might seem like a daunting prospect, but there is lots of information available about the easiest plants to grow and how best to start. Creating a vegetable garden is a great opportunity to have a positive impact on your own health as well as that of animals, while reducing the negative impact that food production can have on the environment. Learning more about the foods you eat every day might unlock a whole new area of personal interest, and possibly inspire a lifelong hobby.
If growing plants outdoors simply isn’t an option for you – it’s often the case that allotment waiting lists are many years long – it is possible to keep some plant species inside your home. Those with a balcony space might choose to get hold of some pots and start small – there is certainly no requirement to start by planting every tomato variety under the sun.
If you are struggling to find a suitable green space but remain determined to start growing your own fruit and vegetables, why not raise the issue of allotment shortages with your local council? There is no such thing as too many community vegetable gardens.
By Freya Partridge
- Jen Jones's blog
The views expressed by our bloggers are not necessarily the views of The Vegan Society.
Sign-up for our newsletter
Join our newsletter to receive monthly competitions, offers and information on all things vegan.
Congratulations! Your order qualifies for free shipping Spend $25 more for free shipping
Your cart is empty.
Continue browsing
Shipping & taxes calculated at checkout

What are the Benefits of Growing a Vegetable Garden?
What are the benefits of growing your own vegetables? Vegetables are so easy to grow, especially with the help of two simple things: tools we use in the garden and sunny spots. And you don’t need a large yard to build a vegetable garden. Even the tiniest slice of space can be transformed into a lush, thriving garden.
If you love the idea of growing your own produce then building a vegetable garden will save you hundreds of dollars on grocery. You’ll also have the peace of mind knowing that the vegetables you eat are grown with lots of TLC! Still torn about the idea of building a vegetable patch? In today’s post, we are outlining all the amazing benefits of growing your own vegetables:
Contents [ hide ]
Improve your health, save money on food, it’s eco-friendly, effective and enjoyable workout, healthy, sustainable food, minimize waste.

Fresh vegetables are a central part of a healthy diet. Vegetables are loaded with essential nutrients that promote better health, including antioxidants and vitamins. Adding fresh vegetables to your daily meals is the best way to boost your health, and your loved ones’ health too.
Children, in particular, will benefit from the health-giving nutrients of fresh vegetables. Studies show that children who are fed with homegrown produce are twice more likely to eat 5 servings of fresh fruits and vegetable a day compared to children who rarely or never ate homegrown veggies. Unfortunately, kids are not great fans of greens. Starting them young is a great way to get the kids to appreciate vegetables early on.
Stocking up on fresh produce grown from the yard means having more food to enjoy for weeks, even months, without spending a dime on store-bought vegetables. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, an average household spends about $550 per month on food, spending more on fresh produce compared to eggs, dairy, sugar, and other staples. If you’d like to reduce your grocery expenses, try growing your own crops. You won’t believe how much money you will save from growing your own food!
Most households spend 60% of their food budget on meals and snacks. A small packet of seeds costs about a few cents. Growing vegetables from seeds allow you to plant a huge variety of vegetables, which you can harvest at different seasons. If your pantry is overflowing with vegetables, you can always preserve these so you can enjoy healthy veggies even after the growing season is over!
Gardening is inherently eco-friendly, more so if you are growing vegetables without using any type of chemical. Growing food organically means sparing the earth of water, soil, and air pollution. Since you are buying less produce from the supermarket, you are not contributing to the use of fossil fuel from transporting fruits and vegetables to your local grocery. If you are growing crops without using pesticides or herbicides, toxic chemicals won’t seep into the soil and waterways. You can enjoy the earth’s bounty without harming the environment.

One of the benefits of growing your own vegetables is that it keeps you fit. Most people want to work out but not all of us are comfortable at the idea of lifting weights or enrolling in a fitness class at the local gym. Gardening is a wonderful hobby for anyone who’d like to achieve a trim and healthy physique. All that weeding, planting, watering, and harvesting tone the muscles and build strength. If you don’t like lifting weights, completing all your gardening activities is similar to working out but it’s much more organic and enjoyable because you are doing something that nourishes your soul. If you are always stressed out and you don’t or won’t go to the local spa to de-stress, try gardening. Doing something meaningful or purposeful is a great stress reliever. Going out there and getting some fresh air and sunshine certainly helps soothe frazzled nerves!

Dining out or having takeouts is nice every once in a while but restaurant food and fast foods pale in comparison to homemade meals made from fresh, sustainable ingredients. Usually, resto meals and fast foods are high in sodium, sugar, and additives that are bad for the health. Also, there is no way to say if the ingredients are organically grown.
Organically grown vegetables are healthier, more flavorful compared to store-bought meals. Unfortunately, organic produce is more expensive than your average fruits and vegetables. Wouldn’t it be great to have access to organically produced vegetables at home? Growing your own food allows you to enjoy sustainable fruits and vegetables whenever. You can prepare your meals and have total control over the quality of the ingredients while spending less money on food.
Did you know that the average American household throws about $600 worth of food every year? Most people are so used to accessing food conveniently, never thinking about the hard work that comes from growing the said food. It’s much harder to waste food when you grew your own food.
When you are growing your own food, you are less likely to take fruits and vegetables for granted. You are also likely to preserve or use up your supply before it spoils. Building a vegetable garden is also a great way to teach your children about the importance of utilizing whatever bounty the earth has provided to its fullest and avoiding waste!

To make your vegetable garden even more sustainable, you can build your own compost pile using kitchen scraps and organic garden debris. By building a compost pile, you can turn organic scraps into natural fertilizers for your garden.
Building a vegetable garden takes a lot of hard work and commitment but as long as you are devoted to growing your own food, you will reap the benefits of growing your own vegetables! It’s also easy to turn any available space into a garden patch. Just use small containers if your garden space is limited. Found these gardening tips useful? Tune in for more! Subscribe to our newsletter to get the latest gardening resources
← Older Post Newer Post →
Featured Blogs

Creating a Sensory Garden for Relaxation and Therapy

Perfect Companion Plants for Your Potatoes

Companion Planting Tips: Finding the Right Plants to Grow Next to Each Other
- Share full article

Is a Writer a Kind of Spy?
In her new novel, Rachel Kushner invents a secret agent who’s not really all that different from a novelist.
Ms. Kushner said she set out to explore a character “who thinks they are authoring the world around them.” Credit... Kate Warren for The New York Times
Supported by
By Kate Dwyer
Reporting from Delaware County, N.Y., and Los Angeles
- Aug. 31, 2024
Rachel Kushner had warned me that there might be snakes and one very mean turkey on the farm. There would also be mud; she recommended rubber boots. And, as far as she remembered, there was no cell service.
The property in Delaware County, N.Y., belonged to her cousin, who did not want to be named in this article but greeted me with a saxophone performance on the porch of a green cottage. Across the way was the house where Ms. Kushner, a novelist whose work often explores society’s gritty margins, was staying for a few days early this summer.
“I was weeding for hours and hours yesterday,” she said.
Everyone who visits the farm must work. Over the years, even garage-rock band members recording music in the barn’s grain elevator have traversed rows of root vegetables in their jeans.
Ms. Kushner, 55, was used to it: In her 20s, shortly after her cousin purchased the land, she helped rescue the guesthouse from “a state of total abandon” and lived there on the weekends for a while. Years later, when her husband, a professor, received a fellowship at Cornell University, they would visit often with their young son, who learned from Ms. Kushner’s cousin how to ride a tractor and catch fish.
More recently, the farm provided some inspiration for her fourth novel, “Creation Lake,” a sexy, noirish thriller about a 34-year-old American woman, a spy-for-hire, who infiltrates an eco-commune in the south of France.
Her mission is to disrupt the group’s plans to sabotage the French government’s efforts to bring corporate agriculture to the area, but she finds herself occasionally distracted by warm six-packs of beer, a mysterious cave-dwelling philosopher and a communard she seduces.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
250 Words Essay on Vegetables Introduction to Vegetables. Vegetables, the fundamental building blocks of our diets, are imbued with a rich assortment of nutrients that are essential for our well-being. They originate from various parts of plants including leaves, stems, roots, tubers, bulbs, and flowers, and exhibit a wide range of colors ...
Essay on Vegetables in 10 Lines - Examples. 1. Vegetables are an essential part of a healthy diet, providing vitamins, minerals, and fiber. 2. They come in a variety of colors, shapes, and sizes, offering a wide range of nutrients. 3. Some popular vegetables include broccoli, carrots, spinach, and bell peppers. 4.
First of all, vegetables help in weight management. Vegetables like potato and cauliflower can help you to gain weight. While vegetables like spinach and green vegetables can help immensely in weight reduction. From time immemorial, our elders have promoted the consumption of green vegetables.
Keeping them open minded about these issues is a good thing. In the study of Beate, and Slavin (2012), vegetables are important because they have a lot of vitamins and nutrients, such as vitamin A, which is good for avoiding cancer while, and vitamin C is good for the vision, teeth, skin, skeletal tissue. Additionally, According to Huybrechts ...
500 Words Essay on Importance of Vegetables Introduction. Vegetables, the cornerstone of a balanced diet, are indispensable for maintaining optimal health. They are rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, and play a crucial role in promoting overall well-being. This essay delves into the importance of ...
500 Words Essay on Fruits And Vegetables Introduction to Fruits and Vegetables. Fruits and vegetables are an important part of what we eat every day. They come in many shapes, sizes, colors, and tastes. Some are sweet, like oranges, while others are not, like spinach. They are nature's treats packed with vitamins, minerals, and other ...
Essay on Vegetables for Class 1,2,3. Vegetables are a crucial part of our daily lives and they play a vital role in keeping us healthy. They provide us with essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that help our bodies function properly. In this essay, we will learn about the different types of vegetables and their importance in our diet. ...
Essay # 2. Nutrition in Vegetables: Vegetables are eaten in a variety of ways, as part of main meals and as snacks. The nutritional content of vegetables varies considerably, though generally they contain little protein or fat, and varying proportions of vitamins, pro-vitamins, dietary minerals, fiber and carbohydrates. Vegetables contain a ...
The vitamin B present in the vegetables like sweet potato, carrot, broccoli, green pepper, etc., improves our immune system and also the nervous functions. Vitamin K present in the vegetables like cauliflower, broccoli, cabbage, kale, turnip greens and other dark green leafy vegetables improves our metabolism and is also involved in blood ...
Vegetables are usually classified on the basis of the part of the plant that is used for food. The root vegetables include beets, carrots, radishes, sweet potatoes, and turnips. Stem vegetables include asparagus and kohlrabi. Among the edible tubers, or underground stems, are potatoes. The leaf and leafstalk vegetables include brussels sprouts ...
A diet rich in vegetables and fruits can lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke, prevent some types of cancer, lower risk of eye and digestive problems, and have a positive effect upon blood sugar, which can help keep appetite in check. Eating non-starchy vegetables and fruits like apples, pears, and green leafy ...
Nutrition. Vegetables are a rich source of folate, a B vitamin that helps your body make new red blood cells. Folate is especially important for children's health and may also reduce the risk of ...
The word vegetable was first recorded in English in the early 15th century. It comes from Old French, [1] and was originally applied to all plants; the word is still used in this sense in biological contexts. [2] It derives from Medieval Latin vegetabilis "growing, flourishing" (i.e. of a plant), a semantic change from a Late Latin meaning "to be enlivening, quickening".
Certain vegetables such as broccoli, cabbage, and Brussel's sprouts produce a disease-fighting compound called sulfurane when cut. Colorful vegetables provide antioxidants such as lycopene and beta carotene. Diversity in the types of vegetables ensures balanced nutrition. Freshly picked vegetables that you grew in your garden seem to taste better.
Somehow they all do the same thing. They develop the theory that helps people to do things faster and easier. Somehow they are always the ones that change the world and make it a better place. Thinking as a visionary myself, the idea of growing our own vegetables would be an innovation that would make things easier for people, faster, and cheaper.
250 Words Essay on My Favourite Vegetable Introduction. Vegetables are an integral part of our diet, providing essential nutrients and promoting good health. Among the myriad of vegetables, my favourite is the humble potato, a versatile tuber with a rich history and cultural significance. The Versatility of Potatoes
Importance of Vegetables: (Short Essay) Our food we intake daily is the source of all essentials namely vitamins, minerals, fibers and phytochemicals. All food we have nowadays does not do well to our body. Since time being, vegetables are said to be the source of nutrients and immunity. One who takes right amount of fruits and vegetables is ...
Spinach, beans, peas, tomatoes, okra, Loki, brinjals, carrots, radish, etc., are green vegetables. There are more than 80 types of vegetables all over the world. It is most important to have green vegetables in our food. Doctors advise us to eat green vegetables. Eating green vegetables increases the immunity of our body.
Most people know that fruits and vegetables are good for us. Both fruits and vegetables are high in dietary fibre as well as vitamins and minerals, and other bioactive plant compounds, including many with antioxidant properties such as polyphenols or beta-carotene. Fruits and vegetables contain, for example, vitamin A, B5, folate, C, E & K and ...
Improved mental health and wellbeing. Growing your own fruit and vegetables might take some time out of your day, but it is certainly time well spent. Gardening is a great way to combat stress and anxiety, with fresh air and exercise being widely recommended to people suffering with mental health. The various tasks involved in producing greens ...
In today's post, we are outlining all the amazing benefits of growing your own vegetables: Contents [hide] Improve Your Health. Save Money on Food. It's Eco-Friendly. Effective and Enjoyable Workout. Healthy, Sustainable Food. Minimize Waste.
Essay On Vegetable Garden. 1351 Words6 Pages. HOW TO BUILD A KITCHEN GARDEN Growing your own vegetables is both fun and rewarding. All you really need to get started is some decent soil and a few plants. But to be a really successful vegetable gardener — and to do it organically — you'll need to understand what it takes to keep your plants ...
In her essay collection, "The Hard Crowd," which partly chronicles her coming-of-age in the Bay Area, she describes falling in with some "ratty delinquents" who skip school, take drugs and ...