Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
Neag School of Education

Educational Research Basics by Del Siegle
Single subject research.
“ Single subject research (also known as single case experiments) is popular in the fields of special education and counseling. This research design is useful when the researcher is attempting to change the behavior of an individual or a small group of individuals and wishes to document that change. Unlike true experiments where the researcher randomly assigns participants to a control and treatment group, in single subject research the participant serves as both the control and treatment group. The researcher uses line graphs to show the effects of a particular intervention or treatment. An important factor of single subject research is that only one variable is changed at a time. Single subject research designs are “weak when it comes to external validity….Studies involving single-subject designs that show a particular treatment to be effective in changing behavior must rely on replication–across individuals rather than groups–if such results are be found worthy of generalization” (Fraenkel & Wallen, 2006, p. 318).
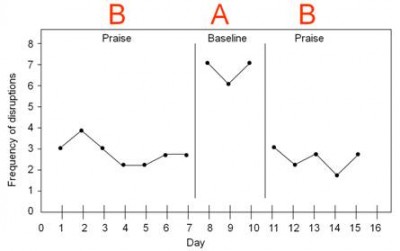
Suppose a researcher wished to investigate the effect of praise on reducing disruptive behavior over many days. First she would need to establish a baseline of how frequently the disruptions occurred. She would measure how many disruptions occurred each day for several days. In the example below, the target student was disruptive seven times on the first day, six times on the second day, and seven times on the third day. Note how the sequence of time is depicted on the x-axis (horizontal axis) and the dependent variable (outcome variable) is depicted on the y-axis (vertical axis).
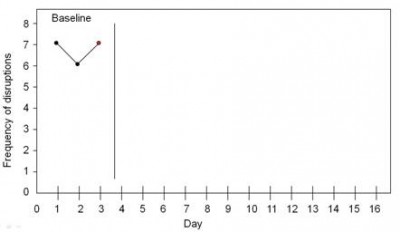
Once a baseline of behavior has been established (when a consistent pattern emerges with at least three data points), the intervention begins. The researcher continues to plot the frequency of behavior while implementing the intervention of praise.
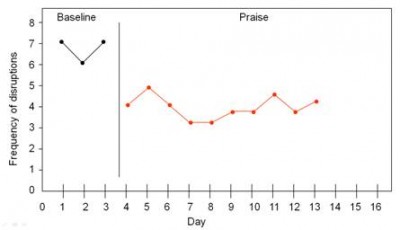
In this example, we can see that the frequency of disruptions decreased once praise began. The design in this example is known as an A-B design. The baseline period is referred to as A and the intervention period is identified as B.
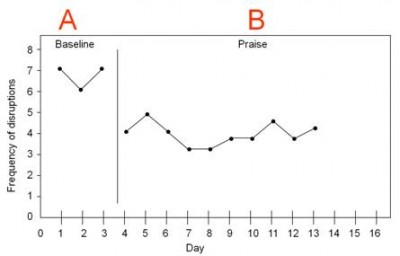
Another design is the A-B-A design. An A-B-A design (also known as a reversal design) involves discontinuing the intervention and returning to a nontreatment condition.
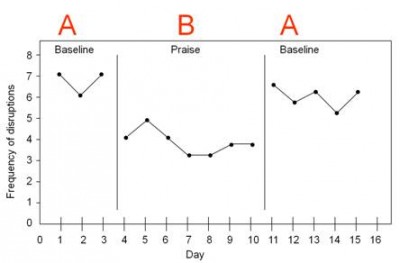
Sometimes an individual’s behavior is so severe that the researcher cannot wait to establish a baseline and must begin with an intervention. In this case, a B-A-B design is used. The intervention is implemented immediately (before establishing a baseline). This is followed by a measurement without the intervention and then a repeat of the intervention.
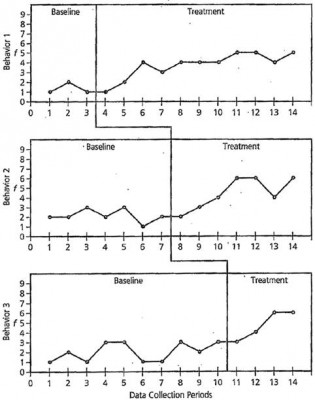
Multiple-Baseline Design
Sometimes, a researcher may be interested in addressing several issues for one student or a single issue for several students. In this case, a multiple-baseline design is used.
“In a multiple baseline across subjects design, the researcher introduces the intervention to different persons at different times. The significance of this is that if a behavior changes only after the intervention is presented, and this behavior change is seen successively in each subject’s data, the effects can more likely be credited to the intervention itself as opposed to other variables. Multiple-baseline designs do not require the intervention to be withdrawn. Instead, each subject’s own data are compared between intervention and nonintervention behaviors, resulting in each subject acting as his or her own control (Kazdin, 1982). An added benefit of this design, and all single-case designs, is the immediacy of the data. Instead of waiting until postintervention to take measures on the behavior, single-case research prescribes continuous data collection and visual monitoring of that data displayed graphically, allowing for immediate instructional decision-making. Students, therefore, do not linger in an intervention that is not working for them, making the graphic display of single-case research combined with differentiated instruction responsive to the needs of students.” (Geisler, Hessler, Gardner, & Lovelace, 2009)
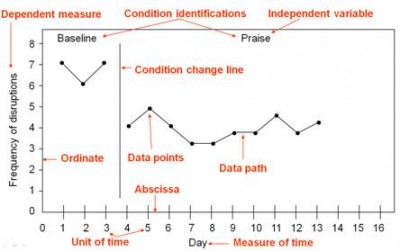
Regardless of the research design, the line graphs used to illustrate the data contain a set of common elements.
Generally, in single subject research we count the number of times something occurs in a given time period and see if it occurs more or less often in that time period after implementing an intervention. For example, we might measure how many baskets someone makes while shooting for 2 minutes. We would repeat that at least three times to get our baseline. Next, we would test some intervention. We might play music while shooting, give encouragement while shooting, or video the person while shooting to see if our intervention influenced the number of shots made. After the 3 baseline measurements (3 sets of 2 minute shooting), we would measure several more times (sets of 2 minute shooting) after the intervention and plot the time points (number of baskets made in 2 minutes for each of the measured time points). This works well for behaviors that are distinct and can be counted.
Sometimes behaviors come and go over time (such as being off task in a classroom or not listening during a coaching session). The way we can record these is to select a period of time (say 5 minutes) and mark down every 10 seconds whether our participant is on task. We make a minimum of three sets of 5 minute observations for a baseline, implement an intervention, and then make more sets of 5 minute observations with the intervention in place. We use this method rather than counting how many times someone is off task because one could continually be off task and that would only be a count of 1 since the person was continually off task. Someone who might be off task twice for 15 second would be off task twice for a score of 2. However, the second person is certainly not off task twice as much as the first person. Therefore, recording whether the person is off task at 10-second intervals gives a more accurate picture. The person continually off task would have a score of 30 (off task at every second interval for 5 minutes) and the person off task twice for a short time would have a score of 2 (off task only during 2 of the 10 second interval measures.
I also have additional information about how to record single-subject research data .
I hope this helps you better understand single subject research.
I have created a PowerPoint on Single Subject Research , which also available below as a video.
I have also created instructions for creating single-subject research design graphs with Excel .
Fraenkel, J. R., & Wallen, N. E. (2006). How to design and evaluate research in education (6th ed.). Boston, MA: McGraw Hill.
Geisler, J. L., Hessler, T., Gardner, R., III, & Lovelace, T. S. (2009). Differentiated writing interventions for high-achieving urban African American elementary students. Journal of Advanced Academics, 20, 214–247.
Del Siegle, Ph.D. University of Connecticut [email protected] www.delsiegle.info
Revised 02/02/2024

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.1 Overview of Single-Subject Research
Learning objectives.
- Explain what single-subject research is, including how it differs from other types of psychological research.
- Explain what case studies are, including some of their strengths and weaknesses.
- Explain who uses single-subject research and why.
What Is Single-Subject Research?
Single-subject research is a type of quantitative research that involves studying in detail the behavior of each of a small number of participants. Note that the term single-subject does not mean that only one participant is studied; it is more typical for there to be somewhere between two and 10 participants. (This is why single-subject research designs are sometimes called small- n designs, where n is the statistical symbol for the sample size.) Single-subject research can be contrasted with group research , which typically involves studying large numbers of participants and examining their behavior primarily in terms of group means, standard deviations, and so on. The majority of this book is devoted to understanding group research, which is the most common approach in psychology. But single-subject research is an important alternative, and it is the primary approach in some areas of psychology.
Before continuing, it is important to distinguish single-subject research from two other approaches, both of which involve studying in detail a small number of participants. One is qualitative research, which focuses on understanding people’s subjective experience by collecting relatively unstructured data (e.g., detailed interviews) and analyzing those data using narrative rather than quantitative techniques. Single-subject research, in contrast, focuses on understanding objective behavior through experimental manipulation and control, collecting highly structured data, and analyzing those data quantitatively.
It is also important to distinguish single-subject research from case studies. A case study is a detailed description of an individual, which can include both qualitative and quantitative analyses. (Case studies that include only qualitative analyses can be considered a type of qualitative research.) The history of psychology is filled with influential cases studies, such as Sigmund Freud’s description of “Anna O.” (see Note 10.5 “The Case of “Anna O.”” ) and John Watson and Rosalie Rayner’s description of Little Albert (Watson & Rayner, 1920), who learned to fear a white rat—along with other furry objects—when the researchers made a loud noise while he was playing with the rat. Case studies can be useful for suggesting new research questions and for illustrating general principles. They can also help researchers understand rare phenomena, such as the effects of damage to a specific part of the human brain. As a general rule, however, case studies cannot substitute for carefully designed group or single-subject research studies. One reason is that case studies usually do not allow researchers to determine whether specific events are causally related, or even related at all. For example, if a patient is described in a case study as having been sexually abused as a child and then as having developed an eating disorder as a teenager, there is no way to determine whether these two events had anything to do with each other. A second reason is that an individual case can always be unusual in some way and therefore be unrepresentative of people more generally. Thus case studies have serious problems with both internal and external validity.
The Case of “Anna O.”
Sigmund Freud used the case of a young woman he called “Anna O.” to illustrate many principles of his theory of psychoanalysis (Freud, 1961). (Her real name was Bertha Pappenheim, and she was an early feminist who went on to make important contributions to the field of social work.) Anna had come to Freud’s colleague Josef Breuer around 1880 with a variety of odd physical and psychological symptoms. One of them was that for several weeks she was unable to drink any fluids. According to Freud,
She would take up the glass of water that she longed for, but as soon as it touched her lips she would push it away like someone suffering from hydrophobia.…She lived only on fruit, such as melons, etc., so as to lessen her tormenting thirst (p. 9).
But according to Freud, a breakthrough came one day while Anna was under hypnosis.
[S]he grumbled about her English “lady-companion,” whom she did not care for, and went on to describe, with every sign of disgust, how she had once gone into this lady’s room and how her little dog—horrid creature!—had drunk out of a glass there. The patient had said nothing, as she had wanted to be polite. After giving further energetic expression to the anger she had held back, she asked for something to drink, drank a large quantity of water without any difficulty, and awoke from her hypnosis with the glass at her lips; and thereupon the disturbance vanished, never to return.
Freud’s interpretation was that Anna had repressed the memory of this incident along with the emotion that it triggered and that this was what had caused her inability to drink. Furthermore, her recollection of the incident, along with her expression of the emotion she had repressed, caused the symptom to go away.
As an illustration of Freud’s theory, the case study of Anna O. is quite effective. As evidence for the theory, however, it is essentially worthless. The description provides no way of knowing whether Anna had really repressed the memory of the dog drinking from the glass, whether this repression had caused her inability to drink, or whether recalling this “trauma” relieved the symptom. It is also unclear from this case study how typical or atypical Anna’s experience was.
Figure 10.2

“Anna O.” was the subject of a famous case study used by Freud to illustrate the principles of psychoanalysis.
Wikimedia Commons – public domain.
Assumptions of Single-Subject Research
Again, single-subject research involves studying a small number of participants and focusing intensively on the behavior of each one. But why take this approach instead of the group approach? There are several important assumptions underlying single-subject research, and it will help to consider them now.
First and foremost is the assumption that it is important to focus intensively on the behavior of individual participants. One reason for this is that group research can hide individual differences and generate results that do not represent the behavior of any individual. For example, a treatment that has a positive effect for half the people exposed to it but a negative effect for the other half would, on average, appear to have no effect at all. Single-subject research, however, would likely reveal these individual differences. A second reason to focus intensively on individuals is that sometimes it is the behavior of a particular individual that is primarily of interest. A school psychologist, for example, might be interested in changing the behavior of a particular disruptive student. Although previous published research (both single-subject and group research) is likely to provide some guidance on how to do this, conducting a study on this student would be more direct and probably more effective.
A second assumption of single-subject research is that it is important to discover causal relationships through the manipulation of an independent variable, the careful measurement of a dependent variable, and the control of extraneous variables. For this reason, single-subject research is often considered a type of experimental research with good internal validity. Recall, for example, that Hall and his colleagues measured their dependent variable (studying) many times—first under a no-treatment control condition, then under a treatment condition (positive teacher attention), and then again under the control condition. Because there was a clear increase in studying when the treatment was introduced, a decrease when it was removed, and an increase when it was reintroduced, there is little doubt that the treatment was the cause of the improvement.
A third assumption of single-subject research is that it is important to study strong and consistent effects that have biological or social importance. Applied researchers, in particular, are interested in treatments that have substantial effects on important behaviors and that can be implemented reliably in the real-world contexts in which they occur. This is sometimes referred to as social validity (Wolf, 1976). The study by Hall and his colleagues, for example, had good social validity because it showed strong and consistent effects of positive teacher attention on a behavior that is of obvious importance to teachers, parents, and students. Furthermore, the teachers found the treatment easy to implement, even in their often chaotic elementary school classrooms.
Who Uses Single-Subject Research?
Single-subject research has been around as long as the field of psychology itself. In the late 1800s, one of psychology’s founders, Wilhelm Wundt, studied sensation and consciousness by focusing intensively on each of a small number of research participants. Herman Ebbinghaus’s research on memory and Ivan Pavlov’s research on classical conditioning are other early examples, both of which are still described in almost every introductory psychology textbook.
In the middle of the 20th century, B. F. Skinner clarified many of the assumptions underlying single-subject research and refined many of its techniques (Skinner, 1938). He and other researchers then used it to describe how rewards, punishments, and other external factors affect behavior over time. This work was carried out primarily using nonhuman subjects—mostly rats and pigeons. This approach, which Skinner called the experimental analysis of behavior —remains an important subfield of psychology and continues to rely almost exclusively on single-subject research. For excellent examples of this work, look at any issue of the Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior . By the 1960s, many researchers were interested in using this approach to conduct applied research primarily with humans—a subfield now called applied behavior analysis (Baer, Wolf, & Risley, 1968). Applied behavior analysis plays an especially important role in contemporary research on developmental disabilities, education, organizational behavior, and health, among many other areas. Excellent examples of this work (including the study by Hall and his colleagues) can be found in the Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis .
Although most contemporary single-subject research is conducted from the behavioral perspective, it can in principle be used to address questions framed in terms of any theoretical perspective. For example, a studying technique based on cognitive principles of learning and memory could be evaluated by testing it on individual high school students using the single-subject approach. The single-subject approach can also be used by clinicians who take any theoretical perspective—behavioral, cognitive, psychodynamic, or humanistic—to study processes of therapeutic change with individual clients and to document their clients’ improvement (Kazdin, 1982).
Key Takeaways
- Single-subject research—which involves testing a small number of participants and focusing intensively on the behavior of each individual—is an important alternative to group research in psychology.
- Single-subject studies must be distinguished from case studies, in which an individual case is described in detail. Case studies can be useful for generating new research questions, for studying rare phenomena, and for illustrating general principles. However, they cannot substitute for carefully controlled experimental or correlational studies because they are low in internal and external validity.
- Single-subject research has been around since the beginning of the field of psychology. Today it is most strongly associated with the behavioral theoretical perspective, but it can in principle be used to study behavior from any perspective.
- Practice: Find and read a published article in psychology that reports new single-subject research. (A good source of articles published in the Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis can be found at http://seab.envmed.rochester.edu/jaba/jabaMostPop-2011.html .) Write a short summary of the study.
Practice: Find and read a published case study in psychology. (Use case study as a key term in a PsycINFO search.) Then do the following:
- Describe one problem related to internal validity.
- Describe one problem related to external validity.
- Generate one hypothesis suggested by the case study that might be interesting to test in a systematic single-subject or group study.
Baer, D. M., Wolf, M. M., & Risley, T. R. (1968). Some current dimensions of applied behavior analysis. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis , 1 , 91–97.
Freud, S. (1961). Five lectures on psycho-analysis . New York, NY: Norton.
Kazdin, A. E. (1982). Single-case research designs: Methods for clinical and applied settings . New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Skinner, B. F. (1938). The behavior of organisms: An experimental analysis . New York, NY: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Watson, J. B., & Rayner, R. (1920). Conditioned emotional reactions. Journal of Experimental Psychology , 3 , 1–14.
Wolf, M. (1976). Social validity: The case for subjective measurement or how applied behavior analysis is finding its heart. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 11 , 203–214.
Research Methods in Psychology Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Single-Case Experimental Designs
Introduction, general overviews and primary textbooks.
- Textbooks in Applied Behavior Analysis
- Types of Single-Case Experimental Designs
- Model Building and Randomization in Single-Case Experimental Designs
- Visual Analysis of Single-Case Experimental Designs
- Effect Size Estimates in Single-Case Experimental Designs
- Reporting Single-Case Design Intervention Research
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Action Research
- Ambulatory Assessment in Behavioral Science
- Effect Size
- Mediation Analysis
- Path Models
- Research Methods for Studying Daily Life
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Data Visualization
- Executive Functions in Childhood
- Remote Work
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Single-Case Experimental Designs by S. Andrew Garbacz , Thomas R. Kratochwill LAST REVIEWED: 29 July 2020 LAST MODIFIED: 29 July 2020 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199828340-0265
Single-case experimental designs are a family of experimental designs that are characterized by researcher manipulation of an independent variable and repeated measurement of a dependent variable before (i.e., baseline) and after (i.e., intervention phase) introducing the independent variable. In single-case experimental designs a case is the unit of intervention and analysis (e.g., a child, a school). Because measurement within each case is conducted before and after manipulation of the independent variable, the case typically serves as its own control. Experimental variants of single-case designs provide a basis for determining a causal relation by replication of the intervention through (a) introducing and withdrawing the independent variable, (b) manipulating the independent variable across different phases, and (c) introducing the independent variable in a staggered fashion across different points in time. Due to their economy of resources, single-case designs may be useful during development activities and allow for rapid replication across studies.
Several sources provide overviews of single-case experimental designs. Barlow, et al. 2009 includes an overview for the development of single-case experimental designs, describes key considerations for designing and conducting single-case experimental design research, and reviews procedural elements, assessment strategies, and replication considerations. Kazdin 2011 provides detailed coverage of single-case experimental design variants as well as approaches for evaluating data in single-case experimental designs. Kratochwill and Levin 2014 describes key methodological features that underlie single-case experimental designs, including philosophical and statistical foundations and data evaluation. Ledford and Gast 2018 covers research conceptualization and writing, design variants within single-case experimental design, definitions of variables and associated measurement, and approaches to organize and evaluate data. Riley-Tillman and Burns 2009 provides a practical orientation to single-case experimental designs to facilitate uptake and use in applied settings.
Barlow, D. H., M. K. Nock, and M. Hersen, eds. 2009. Single case experimental designs: Strategies for studying behavior change . 3d ed. New York: Pearson.
A comprehensive reference about the process of designing and conducting single-case experimental design studies. Chapters are integrative but can stand alone.
Kazdin, A. E. 2011. Single-case research designs: Methods for clinical and applied settings . 2d ed. New York: Oxford Univ. Press.
A complete overview and description of single-case experimental design variants as well as information about data evaluation.
Kratochwill, T. R., and J. R. Levin, eds. 2014. Single-case intervention research: Methodological and statistical advances . New York: Routledge.
The authors describe in depth the methodological and analytic considerations necessary for designing and conducting research that uses a single-case experimental design. In addition, the text includes chapters from leaders in psychology and education who provide critical perspectives about the use of single-case experimental designs.
Ledford, J. R., and D. L. Gast, eds. 2018. Single case research methodology: Applications in special education and behavioral sciences . New York: Routledge.
Covers the research process from writing literature reviews, to designing, conducting, and evaluating single-case experimental design studies.
Riley-Tillman, T. C., and M. K. Burns. 2009. Evaluating education interventions: Single-case design for measuring response to intervention . New York: Guilford Press.
Focuses on accelerating uptake and use of single-case experimental designs in applied settings. This book provides a practical, “nuts and bolts” orientation to conducting single-case experimental design research.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Psychology »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Abnormal Psychology
- Academic Assessment
- Acculturation and Health
- Action Regulation Theory
- Addictive Behavior
- Adolescence
- Adoption, Social, Psychological, and Evolutionary Perspect...
- Advanced Theory of Mind
- Affective Forecasting
- Affirmative Action
- Ageism at Work
- Allport, Gordon
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA)
- Animal Behavior
- Animal Learning
- Anxiety Disorders
- Art and Aesthetics, Psychology of
- Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Psychology
- Assessment and Clinical Applications of Individual Differe...
- Attachment in Social and Emotional Development across the ...
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Adults
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Childre...
- Attitudinal Ambivalence
- Attraction in Close Relationships
- Attribution Theory
- Authoritarian Personality
- Bayesian Statistical Methods in Psychology
- Behavior Therapy, Rational Emotive
- Behavioral Economics
- Behavioral Genetics
- Belief Perseverance
- Bereavement and Grief
- Biological Psychology
- Birth Order
- Body Image in Men and Women
- Bystander Effect
- Categorical Data Analysis in Psychology
- Childhood and Adolescence, Peer Victimization and Bullying...
- Clark, Mamie Phipps
- Clinical Neuropsychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Consistency Theories
- Cognitive Dissonance Theory
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Communication, Nonverbal Cues and
- Comparative Psychology
- Competence to Stand Trial: Restoration Services
- Competency to Stand Trial
- Computational Psychology
- Conflict Management in the Workplace
- Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience
- Consciousness
- Coping Processes
- Correspondence Analysis in Psychology
- Counseling Psychology
- Creativity at Work
- Critical Thinking
- Cross-Cultural Psychology
- Cultural Psychology
- Daily Life, Research Methods for Studying
- Data Science Methods for Psychology
- Data Sharing in Psychology
- Death and Dying
- Deceiving and Detecting Deceit
- Defensive Processes
- Depressive Disorders
- Development, Prenatal
- Developmental Psychology (Cognitive)
- Developmental Psychology (Social)
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM...
- Discrimination
- Dissociative Disorders
- Drugs and Behavior
- Eating Disorders
- Ecological Psychology
- Educational Settings, Assessment of Thinking in
- Embodiment and Embodied Cognition
- Emerging Adulthood
- Emotional Intelligence
- Empathy and Altruism
- Employee Stress and Well-Being
- Environmental Neuroscience and Environmental Psychology
- Ethics in Psychological Practice
- Event Perception
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Expansive Posture
- Experimental Existential Psychology
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Eyewitness Testimony
- Eysenck, Hans
- Factor Analysis
- Festinger, Leon
- Five-Factor Model of Personality
- Flynn Effect, The
- Forensic Psychology
- Forgiveness
- Friendships, Children's
- Fundamental Attribution Error/Correspondence Bias
- Gambler's Fallacy
- Game Theory and Psychology
- Geropsychology, Clinical
- Global Mental Health
- Habit Formation and Behavior Change
- Health Psychology
- Health Psychology Research and Practice, Measurement in
- Heider, Fritz
- Heuristics and Biases
- History of Psychology
- Human Factors
- Humanistic Psychology
- Implicit Association Test (IAT)
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology
- Inferential Statistics in Psychology
- Insanity Defense, The
- Intelligence
- Intelligence, Crystallized and Fluid
- Intercultural Psychology
- Intergroup Conflict
- International Classification of Diseases and Related Healt...
- International Psychology
- Interviewing in Forensic Settings
- Intimate Partner Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Introversion–Extraversion
- Item Response Theory
- Law, Psychology and
- Lazarus, Richard
- Learned Helplessness
- Learning Theory
- Learning versus Performance
- LGBTQ+ Romantic Relationships
- Lie Detection in a Forensic Context
- Life-Span Development
- Locus of Control
- Loneliness and Health
- Mathematical Psychology
- Meaning in Life
- Mechanisms and Processes of Peer Contagion
- Media Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Memories, Autobiographical
- Memories, Flashbulb
- Memories, Repressed and Recovered
- Memory, False
- Memory, Human
- Memory, Implicit versus Explicit
- Memory in Educational Settings
- Memory, Semantic
- Meta-Analysis
- Metacognition
- Metaphor, Psychological Perspectives on
- Microaggressions
- Military Psychology
- Mindfulness
- Mindfulness and Education
- Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
- Money, Psychology of
- Moral Conviction
- Moral Development
- Moral Psychology
- Moral Reasoning
- Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology
- Neuroscience of Associative Learning
- Nonergodicity in Psychology and Neuroscience
- Nonparametric Statistical Analysis in Psychology
- Observational (Non-Randomized) Studies
- Obsessive-Complusive Disorder (OCD)
- Occupational Health Psychology
- Olfaction, Human
- Operant Conditioning
- Optimism and Pessimism
- Organizational Justice
- Parenting Stress
- Parenting Styles
- Parents' Beliefs about Children
- Peace Psychology
- Perception, Person
- Performance Appraisal
- Personality and Health
- Personality Disorders
- Personality Psychology
- Person-Centered and Experiential Psychotherapies: From Car...
- Phenomenological Psychology
- Placebo Effects in Psychology
- Play Behavior
- Positive Psychological Capital (PsyCap)
- Positive Psychology
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Prejudice and Stereotyping
- Pretrial Publicity
- Prisoner's Dilemma
- Problem Solving and Decision Making
- Procrastination
- Prosocial Behavior
- Prosocial Spending and Well-Being
- Protocol Analysis
- Psycholinguistics
- Psychological Literacy
- Psychological Perspectives on Food and Eating
- Psychology, Political
- Psychoneuroimmunology
- Psychophysics, Visual
- Psychotherapy
- Psychotic Disorders
- Publication Bias in Psychology
- Reasoning, Counterfactual
- Rehabilitation Psychology
- Relationships
- Reliability–Contemporary Psychometric Conceptions
- Religion, Psychology and
- Replication Initiatives in Psychology
- Research Methods
- Risk Taking
- Role of the Expert Witness in Forensic Psychology, The
- Sample Size Planning for Statistical Power and Accurate Es...
- Schizophrenic Disorders
- School Psychology
- School Psychology, Counseling Services in
- Self, Gender and
- Self, Psychology of the
- Self-Construal
- Self-Control
- Self-Deception
- Self-Determination Theory
- Self-Efficacy
- Self-Esteem
- Self-Monitoring
- Self-Regulation in Educational Settings
- Self-Report Tests, Measures, and Inventories in Clinical P...
- Sensation Seeking
- Sex and Gender
- Sexual Minority Parenting
- Sexual Orientation
- Signal Detection Theory and its Applications
- Simpson's Paradox in Psychology
- Single People
- Single-Case Experimental Designs
- Skinner, B.F.
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Small Groups
- Social Class and Social Status
- Social Cognition
- Social Neuroscience
- Social Support
- Social Touch and Massage Therapy Research
- Somatoform Disorders
- Spatial Attention
- Sports Psychology
- Stanford Prison Experiment (SPE): Icon and Controversy
- Stereotype Threat
- Stereotypes
- Stress and Coping, Psychology of
- Student Success in College
- Subjective Wellbeing Homeostasis
- Taste, Psychological Perspectives on
- Teaching of Psychology
- Terror Management Theory
- Testing and Assessment
- The Concept of Validity in Psychological Assessment
- The Neuroscience of Emotion Regulation
- The Reasoned Action Approach and the Theories of Reasoned ...
- The Weapon Focus Effect in Eyewitness Memory
- Theory of Mind
- Therapy, Cognitive-Behavioral
- Thinking Skills in Educational Settings
- Time Perception
- Trait Perspective
- Trauma Psychology
- Twin Studies
- Type A Behavior Pattern (Coronary Prone Personality)
- Unconscious Processes
- Video Games and Violent Content
- Virtues and Character Strengths
- Women and Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM...
- Women, Psychology of
- Work Well-Being
- Workforce Training Evaluation
- Wundt, Wilhelm
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|162.248.224.4]
- 162.248.224.4
The Advantages and Limitations of Single Case Study Analysis

As Andrew Bennett and Colin Elman have recently noted, qualitative research methods presently enjoy “an almost unprecedented popularity and vitality… in the international relations sub-field”, such that they are now “indisputably prominent, if not pre-eminent” (2010: 499). This is, they suggest, due in no small part to the considerable advantages that case study methods in particular have to offer in studying the “complex and relatively unstructured and infrequent phenomena that lie at the heart of the subfield” (Bennett and Elman, 2007: 171). Using selected examples from within the International Relations literature[1], this paper aims to provide a brief overview of the main principles and distinctive advantages and limitations of single case study analysis. Divided into three inter-related sections, the paper therefore begins by first identifying the underlying principles that serve to constitute the case study as a particular research strategy, noting the somewhat contested nature of the approach in ontological, epistemological, and methodological terms. The second part then looks to the principal single case study types and their associated advantages, including those from within the recent ‘third generation’ of qualitative International Relations (IR) research. The final section of the paper then discusses the most commonly articulated limitations of single case studies; while accepting their susceptibility to criticism, it is however suggested that such weaknesses are somewhat exaggerated. The paper concludes that single case study analysis has a great deal to offer as a means of both understanding and explaining contemporary international relations.
The term ‘case study’, John Gerring has suggested, is “a definitional morass… Evidently, researchers have many different things in mind when they talk about case study research” (2006a: 17). It is possible, however, to distil some of the more commonly-agreed principles. One of the most prominent advocates of case study research, Robert Yin (2009: 14) defines it as “an empirical enquiry that investigates a contemporary phenomenon in depth and within its real-life context, especially when the boundaries between phenomenon and context are not clearly evident”. What this definition usefully captures is that case studies are intended – unlike more superficial and generalising methods – to provide a level of detail and understanding, similar to the ethnographer Clifford Geertz’s (1973) notion of ‘thick description’, that allows for the thorough analysis of the complex and particularistic nature of distinct phenomena. Another frequently cited proponent of the approach, Robert Stake, notes that as a form of research the case study “is defined by interest in an individual case, not by the methods of inquiry used”, and that “the object of study is a specific, unique, bounded system” (2008: 443, 445). As such, three key points can be derived from this – respectively concerning issues of ontology, epistemology, and methodology – that are central to the principles of single case study research.
First, the vital notion of ‘boundedness’ when it comes to the particular unit of analysis means that defining principles should incorporate both the synchronic (spatial) and diachronic (temporal) elements of any so-called ‘case’. As Gerring puts it, a case study should be “an intensive study of a single unit… a spatially bounded phenomenon – e.g. a nation-state, revolution, political party, election, or person – observed at a single point in time or over some delimited period of time” (2004: 342). It is important to note, however, that – whereas Gerring refers to a single unit of analysis – it may be that attention also necessarily be given to particular sub-units. This points to the important difference between what Yin refers to as an ‘holistic’ case design, with a single unit of analysis, and an ’embedded’ case design with multiple units of analysis (Yin, 2009: 50-52). The former, for example, would examine only the overall nature of an international organization, whereas the latter would also look to specific departments, programmes, or policies etc.
Secondly, as Tim May notes of the case study approach, “even the most fervent advocates acknowledge that the term has entered into understandings with little specification or discussion of purpose and process” (2011: 220). One of the principal reasons for this, he argues, is the relationship between the use of case studies in social research and the differing epistemological traditions – positivist, interpretivist, and others – within which it has been utilised. Philosophy of science concerns are obviously a complex issue, and beyond the scope of much of this paper. That said, the issue of how it is that we know what we know – of whether or not a single independent reality exists of which we as researchers can seek to provide explanation – does lead us to an important distinction to be made between so-called idiographic and nomothetic case studies (Gerring, 2006b). The former refers to those which purport to explain only a single case, are concerned with particularisation, and hence are typically (although not exclusively) associated with more interpretivist approaches. The latter are those focused studies that reflect upon a larger population and are more concerned with generalisation, as is often so with more positivist approaches[2]. The importance of this distinction, and its relation to the advantages and limitations of single case study analysis, is returned to below.
Thirdly, in methodological terms, given that the case study has often been seen as more of an interpretivist and idiographic tool, it has also been associated with a distinctly qualitative approach (Bryman, 2009: 67-68). However, as Yin notes, case studies can – like all forms of social science research – be exploratory, descriptive, and/or explanatory in nature. It is “a common misconception”, he notes, “that the various research methods should be arrayed hierarchically… many social scientists still deeply believe that case studies are only appropriate for the exploratory phase of an investigation” (Yin, 2009: 6). If case studies can reliably perform any or all three of these roles – and given that their in-depth approach may also require multiple sources of data and the within-case triangulation of methods – then it becomes readily apparent that they should not be limited to only one research paradigm. Exploratory and descriptive studies usually tend toward the qualitative and inductive, whereas explanatory studies are more often quantitative and deductive (David and Sutton, 2011: 165-166). As such, the association of case study analysis with a qualitative approach is a “methodological affinity, not a definitional requirement” (Gerring, 2006a: 36). It is perhaps better to think of case studies as transparadigmatic; it is mistaken to assume single case study analysis to adhere exclusively to a qualitative methodology (or an interpretivist epistemology) even if it – or rather, practitioners of it – may be so inclined. By extension, this also implies that single case study analysis therefore remains an option for a multitude of IR theories and issue areas; it is how this can be put to researchers’ advantage that is the subject of the next section.
Having elucidated the defining principles of the single case study approach, the paper now turns to an overview of its main benefits. As noted above, a lack of consensus still exists within the wider social science literature on the principles and purposes – and by extension the advantages and limitations – of case study research. Given that this paper is directed towards the particular sub-field of International Relations, it suggests Bennett and Elman’s (2010) more discipline-specific understanding of contemporary case study methods as an analytical framework. It begins however, by discussing Harry Eckstein’s seminal (1975) contribution to the potential advantages of the case study approach within the wider social sciences.
Eckstein proposed a taxonomy which usefully identified what he considered to be the five most relevant types of case study. Firstly were so-called configurative-idiographic studies, distinctly interpretivist in orientation and predicated on the assumption that “one cannot attain prediction and control in the natural science sense, but only understanding ( verstehen )… subjective values and modes of cognition are crucial” (1975: 132). Eckstein’s own sceptical view was that any interpreter ‘simply’ considers a body of observations that are not self-explanatory and “without hard rules of interpretation, may discern in them any number of patterns that are more or less equally plausible” (1975: 134). Those of a more post-modernist bent, of course – sharing an “incredulity towards meta-narratives”, in Lyotard’s (1994: xxiv) evocative phrase – would instead suggest that this more free-form approach actually be advantageous in delving into the subtleties and particularities of individual cases.
Eckstein’s four other types of case study, meanwhile, promote a more nomothetic (and positivist) usage. As described, disciplined-configurative studies were essentially about the use of pre-existing general theories, with a case acting “passively, in the main, as a receptacle for putting theories to work” (Eckstein, 1975: 136). As opposed to the opportunity this presented primarily for theory application, Eckstein identified heuristic case studies as explicit theoretical stimulants – thus having instead the intended advantage of theory-building. So-called p lausibility probes entailed preliminary attempts to determine whether initial hypotheses should be considered sound enough to warrant more rigorous and extensive testing. Finally, and perhaps most notably, Eckstein then outlined the idea of crucial case studies , within which he also included the idea of ‘most-likely’ and ‘least-likely’ cases; the essential characteristic of crucial cases being their specific theory-testing function.
Whilst Eckstein’s was an early contribution to refining the case study approach, Yin’s (2009: 47-52) more recent delineation of possible single case designs similarly assigns them roles in the applying, testing, or building of theory, as well as in the study of unique cases[3]. As a subset of the latter, however, Jack Levy (2008) notes that the advantages of idiographic cases are actually twofold. Firstly, as inductive/descriptive cases – akin to Eckstein’s configurative-idiographic cases – whereby they are highly descriptive, lacking in an explicit theoretical framework and therefore taking the form of “total history”. Secondly, they can operate as theory-guided case studies, but ones that seek only to explain or interpret a single historical episode rather than generalise beyond the case. Not only does this therefore incorporate ‘single-outcome’ studies concerned with establishing causal inference (Gerring, 2006b), it also provides room for the more postmodern approaches within IR theory, such as discourse analysis, that may have developed a distinct methodology but do not seek traditional social scientific forms of explanation.
Applying specifically to the state of the field in contemporary IR, Bennett and Elman identify a ‘third generation’ of mainstream qualitative scholars – rooted in a pragmatic scientific realist epistemology and advocating a pluralistic approach to methodology – that have, over the last fifteen years, “revised or added to essentially every aspect of traditional case study research methods” (2010: 502). They identify ‘process tracing’ as having emerged from this as a central method of within-case analysis. As Bennett and Checkel observe, this carries the advantage of offering a methodologically rigorous “analysis of evidence on processes, sequences, and conjunctures of events within a case, for the purposes of either developing or testing hypotheses about causal mechanisms that might causally explain the case” (2012: 10).
Harnessing various methods, process tracing may entail the inductive use of evidence from within a case to develop explanatory hypotheses, and deductive examination of the observable implications of hypothesised causal mechanisms to test their explanatory capability[4]. It involves providing not only a coherent explanation of the key sequential steps in a hypothesised process, but also sensitivity to alternative explanations as well as potential biases in the available evidence (Bennett and Elman 2010: 503-504). John Owen (1994), for example, demonstrates the advantages of process tracing in analysing whether the causal factors underpinning democratic peace theory are – as liberalism suggests – not epiphenomenal, but variously normative, institutional, or some given combination of the two or other unexplained mechanism inherent to liberal states. Within-case process tracing has also been identified as advantageous in addressing the complexity of path-dependent explanations and critical junctures – as for example with the development of political regime types – and their constituent elements of causal possibility, contingency, closure, and constraint (Bennett and Elman, 2006b).
Bennett and Elman (2010: 505-506) also identify the advantages of single case studies that are implicitly comparative: deviant, most-likely, least-likely, and crucial cases. Of these, so-called deviant cases are those whose outcome does not fit with prior theoretical expectations or wider empirical patterns – again, the use of inductive process tracing has the advantage of potentially generating new hypotheses from these, either particular to that individual case or potentially generalisable to a broader population. A classic example here is that of post-independence India as an outlier to the standard modernisation theory of democratisation, which holds that higher levels of socio-economic development are typically required for the transition to, and consolidation of, democratic rule (Lipset, 1959; Diamond, 1992). Absent these factors, MacMillan’s single case study analysis (2008) suggests the particularistic importance of the British colonial heritage, the ideology and leadership of the Indian National Congress, and the size and heterogeneity of the federal state.
Most-likely cases, as per Eckstein above, are those in which a theory is to be considered likely to provide a good explanation if it is to have any application at all, whereas least-likely cases are ‘tough test’ ones in which the posited theory is unlikely to provide good explanation (Bennett and Elman, 2010: 505). Levy (2008) neatly refers to the inferential logic of the least-likely case as the ‘Sinatra inference’ – if a theory can make it here, it can make it anywhere. Conversely, if a theory cannot pass a most-likely case, it is seriously impugned. Single case analysis can therefore be valuable for the testing of theoretical propositions, provided that predictions are relatively precise and measurement error is low (Levy, 2008: 12-13). As Gerring rightly observes of this potential for falsification:
“a positivist orientation toward the work of social science militates toward a greater appreciation of the case study format, not a denigration of that format, as is usually supposed” (Gerring, 2007: 247, emphasis added).
In summary, the various forms of single case study analysis can – through the application of multiple qualitative and/or quantitative research methods – provide a nuanced, empirically-rich, holistic account of specific phenomena. This may be particularly appropriate for those phenomena that are simply less amenable to more superficial measures and tests (or indeed any substantive form of quantification) as well as those for which our reasons for understanding and/or explaining them are irreducibly subjective – as, for example, with many of the normative and ethical issues associated with the practice of international relations. From various epistemological and analytical standpoints, single case study analysis can incorporate both idiographic sui generis cases and, where the potential for generalisation may exist, nomothetic case studies suitable for the testing and building of causal hypotheses. Finally, it should not be ignored that a signal advantage of the case study – with particular relevance to international relations – also exists at a more practical rather than theoretical level. This is, as Eckstein noted, “that it is economical for all resources: money, manpower, time, effort… especially important, of course, if studies are inherently costly, as they are if units are complex collective individuals ” (1975: 149-150, emphasis added).
Limitations
Single case study analysis has, however, been subject to a number of criticisms, the most common of which concern the inter-related issues of methodological rigour, researcher subjectivity, and external validity. With regard to the first point, the prototypical view here is that of Zeev Maoz (2002: 164-165), who suggests that “the use of the case study absolves the author from any kind of methodological considerations. Case studies have become in many cases a synonym for freeform research where anything goes”. The absence of systematic procedures for case study research is something that Yin (2009: 14-15) sees as traditionally the greatest concern due to a relative absence of methodological guidelines. As the previous section suggests, this critique seems somewhat unfair; many contemporary case study practitioners – and representing various strands of IR theory – have increasingly sought to clarify and develop their methodological techniques and epistemological grounding (Bennett and Elman, 2010: 499-500).
A second issue, again also incorporating issues of construct validity, concerns that of the reliability and replicability of various forms of single case study analysis. This is usually tied to a broader critique of qualitative research methods as a whole. However, whereas the latter obviously tend toward an explicitly-acknowledged interpretive basis for meanings, reasons, and understandings:
“quantitative measures appear objective, but only so long as we don’t ask questions about where and how the data were produced… pure objectivity is not a meaningful concept if the goal is to measure intangibles [as] these concepts only exist because we can interpret them” (Berg and Lune, 2010: 340).
The question of researcher subjectivity is a valid one, and it may be intended only as a methodological critique of what are obviously less formalised and researcher-independent methods (Verschuren, 2003). Owen (1994) and Layne’s (1994) contradictory process tracing results of interdemocratic war-avoidance during the Anglo-American crisis of 1861 to 1863 – from liberal and realist standpoints respectively – are a useful example. However, it does also rest on certain assumptions that can raise deeper and potentially irreconcilable ontological and epistemological issues. There are, regardless, plenty such as Bent Flyvbjerg (2006: 237) who suggest that the case study contains no greater bias toward verification than other methods of inquiry, and that “on the contrary, experience indicates that the case study contains a greater bias toward falsification of preconceived notions than toward verification”.
The third and arguably most prominent critique of single case study analysis is the issue of external validity or generalisability. How is it that one case can reliably offer anything beyond the particular? “We always do better (or, in the extreme, no worse) with more observation as the basis of our generalization”, as King et al write; “in all social science research and all prediction, it is important that we be as explicit as possible about the degree of uncertainty that accompanies out prediction” (1994: 212). This is an unavoidably valid criticism. It may be that theories which pass a single crucial case study test, for example, require rare antecedent conditions and therefore actually have little explanatory range. These conditions may emerge more clearly, as Van Evera (1997: 51-54) notes, from large-N studies in which cases that lack them present themselves as outliers exhibiting a theory’s cause but without its predicted outcome. As with the case of Indian democratisation above, it would logically be preferable to conduct large-N analysis beforehand to identify that state’s non-representative nature in relation to the broader population.
There are, however, three important qualifiers to the argument about generalisation that deserve particular mention here. The first is that with regard to an idiographic single-outcome case study, as Eckstein notes, the criticism is “mitigated by the fact that its capability to do so [is] never claimed by its exponents; in fact it is often explicitly repudiated” (1975: 134). Criticism of generalisability is of little relevance when the intention is one of particularisation. A second qualifier relates to the difference between statistical and analytical generalisation; single case studies are clearly less appropriate for the former but arguably retain significant utility for the latter – the difference also between explanatory and exploratory, or theory-testing and theory-building, as discussed above. As Gerring puts it, “theory confirmation/disconfirmation is not the case study’s strong suit” (2004: 350). A third qualification relates to the issue of case selection. As Seawright and Gerring (2008) note, the generalisability of case studies can be increased by the strategic selection of cases. Representative or random samples may not be the most appropriate, given that they may not provide the richest insight (or indeed, that a random and unknown deviant case may appear). Instead, and properly used , atypical or extreme cases “often reveal more information because they activate more actors… and more basic mechanisms in the situation studied” (Flyvbjerg, 2006). Of course, this also points to the very serious limitation, as hinted at with the case of India above, that poor case selection may alternatively lead to overgeneralisation and/or grievous misunderstandings of the relationship between variables or processes (Bennett and Elman, 2006a: 460-463).
As Tim May (2011: 226) notes, “the goal for many proponents of case studies […] is to overcome dichotomies between generalizing and particularizing, quantitative and qualitative, deductive and inductive techniques”. Research aims should drive methodological choices, rather than narrow and dogmatic preconceived approaches. As demonstrated above, there are various advantages to both idiographic and nomothetic single case study analyses – notably the empirically-rich, context-specific, holistic accounts that they have to offer, and their contribution to theory-building and, to a lesser extent, that of theory-testing. Furthermore, while they do possess clear limitations, any research method involves necessary trade-offs; the inherent weaknesses of any one method, however, can potentially be offset by situating them within a broader, pluralistic mixed-method research strategy. Whether or not single case studies are used in this fashion, they clearly have a great deal to offer.
References
Bennett, A. and Checkel, J. T. (2012) ‘Process Tracing: From Philosophical Roots to Best Practice’, Simons Papers in Security and Development, No. 21/2012, School for International Studies, Simon Fraser University: Vancouver.
Bennett, A. and Elman, C. (2006a) ‘Qualitative Research: Recent Developments in Case Study Methods’, Annual Review of Political Science , 9, 455-476.
Bennett, A. and Elman, C. (2006b) ‘Complex Causal Relations and Case Study Methods: The Example of Path Dependence’, Political Analysis , 14, 3, 250-267.
Bennett, A. and Elman, C. (2007) ‘Case Study Methods in the International Relations Subfield’, Comparative Political Studies , 40, 2, 170-195.
Bennett, A. and Elman, C. (2010) Case Study Methods. In C. Reus-Smit and D. Snidal (eds) The Oxford Handbook of International Relations . Oxford University Press: Oxford. Ch. 29.
Berg, B. and Lune, H. (2012) Qualitative Research Methods for the Social Sciences . Pearson: London.
Bryman, A. (2012) Social Research Methods . Oxford University Press: Oxford.
David, M. and Sutton, C. D. (2011) Social Research: An Introduction . SAGE Publications Ltd: London.
Diamond, J. (1992) ‘Economic development and democracy reconsidered’, American Behavioral Scientist , 35, 4/5, 450-499.
Eckstein, H. (1975) Case Study and Theory in Political Science. In R. Gomm, M. Hammersley, and P. Foster (eds) Case Study Method . SAGE Publications Ltd: London.
Flyvbjerg, B. (2006) ‘Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research’, Qualitative Inquiry , 12, 2, 219-245.
Geertz, C. (1973) The Interpretation of Cultures: Selected Essays by Clifford Geertz . Basic Books Inc: New York.
Gerring, J. (2004) ‘What is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?’, American Political Science Review , 98, 2, 341-354.
Gerring, J. (2006a) Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . Cambridge University Press: Cambridge.
Gerring, J. (2006b) ‘Single-Outcome Studies: A Methodological Primer’, International Sociology , 21, 5, 707-734.
Gerring, J. (2007) ‘Is There a (Viable) Crucial-Case Method?’, Comparative Political Studies , 40, 3, 231-253.
King, G., Keohane, R. O. and Verba, S. (1994) Designing Social Inquiry: Scientific Inference in Qualitative Research . Princeton University Press: Chichester.
Layne, C. (1994) ‘Kant or Cant: The Myth of the Democratic Peace’, International Security , 19, 2, 5-49.
Levy, J. S. (2008) ‘Case Studies: Types, Designs, and Logics of Inference’, Conflict Management and Peace Science , 25, 1-18.
Lipset, S. M. (1959) ‘Some Social Requisites of Democracy: Economic Development and Political Legitimacy’, The American Political Science Review , 53, 1, 69-105.
Lyotard, J-F. (1984) The Postmodern Condition: A Report on Knowledge . University of Minnesota Press: Minneapolis.
MacMillan, A. (2008) ‘Deviant Democratization in India’, Democratization , 15, 4, 733-749.
Maoz, Z. (2002) Case study methodology in international studies: from storytelling to hypothesis testing. In F. P. Harvey and M. Brecher (eds) Evaluating Methodology in International Studies . University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor.
May, T. (2011) Social Research: Issues, Methods and Process . Open University Press: Maidenhead.
Owen, J. M. (1994) ‘How Liberalism Produces Democratic Peace’, International Security , 19, 2, 87-125.
Seawright, J. and Gerring, J. (2008) ‘Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research: A Menu of Qualitative and Quantitative Options’, Political Research Quarterly , 61, 2, 294-308.
Stake, R. E. (2008) Qualitative Case Studies. In N. K. Denzin and Y. S. Lincoln (eds) Strategies of Qualitative Inquiry . Sage Publications: Los Angeles. Ch. 17.
Van Evera, S. (1997) Guide to Methods for Students of Political Science . Cornell University Press: Ithaca.
Verschuren, P. J. M. (2003) ‘Case study as a research strategy: some ambiguities and opportunities’, International Journal of Social Research Methodology , 6, 2, 121-139.
Yin, R. K. (2009) Case Study Research: Design and Methods . SAGE Publications Ltd: London.
[1] The paper follows convention by differentiating between ‘International Relations’ as the academic discipline and ‘international relations’ as the subject of study.
[2] There is some similarity here with Stake’s (2008: 445-447) notion of intrinsic cases, those undertaken for a better understanding of the particular case, and instrumental ones that provide insight for the purposes of a wider external interest.
[3] These may be unique in the idiographic sense, or in nomothetic terms as an exception to the generalising suppositions of either probabilistic or deterministic theories (as per deviant cases, below).
[4] Although there are “philosophical hurdles to mount”, according to Bennett and Checkel, there exists no a priori reason as to why process tracing (as typically grounded in scientific realism) is fundamentally incompatible with various strands of positivism or interpretivism (2012: 18-19). By extension, it can therefore be incorporated by a range of contemporary mainstream IR theories.
— Written by: Ben Willis Written at: University of Plymouth Written for: David Brockington Date written: January 2013
Further Reading on E-International Relations
- Identity in International Conflicts: A Case Study of the Cuban Missile Crisis
- Imperialism’s Legacy in the Study of Contemporary Politics: The Case of Hegemonic Stability Theory
- Recreating a Nation’s Identity Through Symbolism: A Chinese Case Study
- Ontological Insecurity: A Case Study on Israeli-Palestinian Conflict in Jerusalem
- Terrorists or Freedom Fighters: A Case Study of ETA
- A Critical Assessment of Eco-Marxism: A Ghanaian Case Study
Please Consider Donating
Before you download your free e-book, please consider donating to support open access publishing.
E-IR is an independent non-profit publisher run by an all volunteer team. Your donations allow us to invest in new open access titles and pay our bandwidth bills to ensure we keep our existing titles free to view. Any amount, in any currency, is appreciated. Many thanks!
Donations are voluntary and not required to download the e-book - your link to download is below.
Case Study Research Method in Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews).
The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient’s personal history). In psychology, case studies are often confined to the study of a particular individual.
The information is mainly biographical and relates to events in the individual’s past (i.e., retrospective), as well as to significant events that are currently occurring in his or her everyday life.
The case study is not a research method, but researchers select methods of data collection and analysis that will generate material suitable for case studies.
Freud (1909a, 1909b) conducted very detailed investigations into the private lives of his patients in an attempt to both understand and help them overcome their illnesses.
This makes it clear that the case study is a method that should only be used by a psychologist, therapist, or psychiatrist, i.e., someone with a professional qualification.
There is an ethical issue of competence. Only someone qualified to diagnose and treat a person can conduct a formal case study relating to atypical (i.e., abnormal) behavior or atypical development.
Famous Case Studies
- Anna O – One of the most famous case studies, documenting psychoanalyst Josef Breuer’s treatment of “Anna O” (real name Bertha Pappenheim) for hysteria in the late 1800s using early psychoanalytic theory.
- Little Hans – A child psychoanalysis case study published by Sigmund Freud in 1909 analyzing his five-year-old patient Herbert Graf’s house phobia as related to the Oedipus complex.
- Bruce/Brenda – Gender identity case of the boy (Bruce) whose botched circumcision led psychologist John Money to advise gender reassignment and raise him as a girl (Brenda) in the 1960s.
- Genie Wiley – Linguistics/psychological development case of the victim of extreme isolation abuse who was studied in 1970s California for effects of early language deprivation on acquiring speech later in life.
- Phineas Gage – One of the most famous neuropsychology case studies analyzes personality changes in railroad worker Phineas Gage after an 1848 brain injury involving a tamping iron piercing his skull.
Clinical Case Studies
- Studying the effectiveness of psychotherapy approaches with an individual patient
- Assessing and treating mental illnesses like depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD
- Neuropsychological cases investigating brain injuries or disorders
Child Psychology Case Studies
- Studying psychological development from birth through adolescence
- Cases of learning disabilities, autism spectrum disorders, ADHD
- Effects of trauma, abuse, deprivation on development
Types of Case Studies
- Explanatory case studies : Used to explore causation in order to find underlying principles. Helpful for doing qualitative analysis to explain presumed causal links.
- Exploratory case studies : Used to explore situations where an intervention being evaluated has no clear set of outcomes. It helps define questions and hypotheses for future research.
- Descriptive case studies : Describe an intervention or phenomenon and the real-life context in which it occurred. It is helpful for illustrating certain topics within an evaluation.
- Multiple-case studies : Used to explore differences between cases and replicate findings across cases. Helpful for comparing and contrasting specific cases.
- Intrinsic : Used to gain a better understanding of a particular case. Helpful for capturing the complexity of a single case.
- Collective : Used to explore a general phenomenon using multiple case studies. Helpful for jointly studying a group of cases in order to inquire into the phenomenon.
Where Do You Find Data for a Case Study?
There are several places to find data for a case study. The key is to gather data from multiple sources to get a complete picture of the case and corroborate facts or findings through triangulation of evidence. Most of this information is likely qualitative (i.e., verbal description rather than measurement), but the psychologist might also collect numerical data.
1. Primary sources
- Interviews – Interviewing key people related to the case to get their perspectives and insights. The interview is an extremely effective procedure for obtaining information about an individual, and it may be used to collect comments from the person’s friends, parents, employer, workmates, and others who have a good knowledge of the person, as well as to obtain facts from the person him or herself.
- Observations – Observing behaviors, interactions, processes, etc., related to the case as they unfold in real-time.
- Documents & Records – Reviewing private documents, diaries, public records, correspondence, meeting minutes, etc., relevant to the case.
2. Secondary sources
- News/Media – News coverage of events related to the case study.
- Academic articles – Journal articles, dissertations etc. that discuss the case.
- Government reports – Official data and records related to the case context.
- Books/films – Books, documentaries or films discussing the case.
3. Archival records
Searching historical archives, museum collections and databases to find relevant documents, visual/audio records related to the case history and context.
Public archives like newspapers, organizational records, photographic collections could all include potentially relevant pieces of information to shed light on attitudes, cultural perspectives, common practices and historical contexts related to psychology.
4. Organizational records
Organizational records offer the advantage of often having large datasets collected over time that can reveal or confirm psychological insights.
Of course, privacy and ethical concerns regarding confidential data must be navigated carefully.
However, with proper protocols, organizational records can provide invaluable context and empirical depth to qualitative case studies exploring the intersection of psychology and organizations.
- Organizational/industrial psychology research : Organizational records like employee surveys, turnover/retention data, policies, incident reports etc. may provide insight into topics like job satisfaction, workplace culture and dynamics, leadership issues, employee behaviors etc.
- Clinical psychology : Therapists/hospitals may grant access to anonymized medical records to study aspects like assessments, diagnoses, treatment plans etc. This could shed light on clinical practices.
- School psychology : Studies could utilize anonymized student records like test scores, grades, disciplinary issues, and counseling referrals to study child development, learning barriers, effectiveness of support programs, and more.
How do I Write a Case Study in Psychology?
Follow specified case study guidelines provided by a journal or your psychology tutor. General components of clinical case studies include: background, symptoms, assessments, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Interpreting the information means the researcher decides what to include or leave out. A good case study should always clarify which information is the factual description and which is an inference or the researcher’s opinion.
1. Introduction
- Provide background on the case context and why it is of interest, presenting background information like demographics, relevant history, and presenting problem.
- Compare briefly to similar published cases if applicable. Clearly state the focus/importance of the case.
2. Case Presentation
- Describe the presenting problem in detail, including symptoms, duration,and impact on daily life.
- Include client demographics like age and gender, information about social relationships, and mental health history.
- Describe all physical, emotional, and/or sensory symptoms reported by the client.
- Use patient quotes to describe the initial complaint verbatim. Follow with full-sentence summaries of relevant history details gathered, including key components that led to a working diagnosis.
- Summarize clinical exam results, namely orthopedic/neurological tests, imaging, lab tests, etc. Note actual results rather than subjective conclusions. Provide images if clearly reproducible/anonymized.
- Clearly state the working diagnosis or clinical impression before transitioning to management.
3. Management and Outcome
- Indicate the total duration of care and number of treatments given over what timeframe. Use specific names/descriptions for any therapies/interventions applied.
- Present the results of the intervention,including any quantitative or qualitative data collected.
- For outcomes, utilize visual analog scales for pain, medication usage logs, etc., if possible. Include patient self-reports of improvement/worsening of symptoms. Note the reason for discharge/end of care.
4. Discussion
- Analyze the case, exploring contributing factors, limitations of the study, and connections to existing research.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the intervention,considering factors like participant adherence, limitations of the study, and potential alternative explanations for the results.
- Identify any questions raised in the case analysis and relate insights to established theories and current research if applicable. Avoid definitive claims about physiological explanations.
- Offer clinical implications, and suggest future research directions.
5. Additional Items
- Thank specific assistants for writing support only. No patient acknowledgments.
- References should directly support any key claims or quotes included.
- Use tables/figures/images only if substantially informative. Include permissions and legends/explanatory notes.
- Provides detailed (rich qualitative) information.
- Provides insight for further research.
- Permitting investigation of otherwise impractical (or unethical) situations.
Case studies allow a researcher to investigate a topic in far more detail than might be possible if they were trying to deal with a large number of research participants (nomothetic approach) with the aim of ‘averaging’.
Because of their in-depth, multi-sided approach, case studies often shed light on aspects of human thinking and behavior that would be unethical or impractical to study in other ways.
Research that only looks into the measurable aspects of human behavior is not likely to give us insights into the subjective dimension of experience, which is important to psychoanalytic and humanistic psychologists.
Case studies are often used in exploratory research. They can help us generate new ideas (that might be tested by other methods). They are an important way of illustrating theories and can help show how different aspects of a person’s life are related to each other.
The method is, therefore, important for psychologists who adopt a holistic point of view (i.e., humanistic psychologists ).
Limitations
- Lacking scientific rigor and providing little basis for generalization of results to the wider population.
- Researchers’ own subjective feelings may influence the case study (researcher bias).
- Difficult to replicate.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources.
Because a case study deals with only one person/event/group, we can never be sure if the case study investigated is representative of the wider body of “similar” instances. This means the conclusions drawn from a particular case may not be transferable to other settings.
Because case studies are based on the analysis of qualitative (i.e., descriptive) data , a lot depends on the psychologist’s interpretation of the information she has acquired.
This means that there is a lot of scope for Anna O , and it could be that the subjective opinions of the psychologist intrude in the assessment of what the data means.
For example, Freud has been criticized for producing case studies in which the information was sometimes distorted to fit particular behavioral theories (e.g., Little Hans ).
This is also true of Money’s interpretation of the Bruce/Brenda case study (Diamond, 1997) when he ignored evidence that went against his theory.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Curtiss, S. (1981). Genie: The case of a modern wild child .
Diamond, M., & Sigmundson, K. (1997). Sex Reassignment at Birth: Long-term Review and Clinical Implications. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine , 151(3), 298-304
Freud, S. (1909a). Analysis of a phobia of a five year old boy. In The Pelican Freud Library (1977), Vol 8, Case Histories 1, pages 169-306
Freud, S. (1909b). Bemerkungen über einen Fall von Zwangsneurose (Der “Rattenmann”). Jb. psychoanal. psychopathol. Forsch ., I, p. 357-421; GW, VII, p. 379-463; Notes upon a case of obsessional neurosis, SE , 10: 151-318.
Harlow J. M. (1848). Passage of an iron rod through the head. Boston Medical and Surgical Journal, 39 , 389–393.
Harlow, J. M. (1868). Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head . Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society. 2 (3), 327-347.
Money, J., & Ehrhardt, A. A. (1972). Man & Woman, Boy & Girl : The Differentiation and Dimorphism of Gender Identity from Conception to Maturity. Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press.
Money, J., & Tucker, P. (1975). Sexual signatures: On being a man or a woman.
Further Information
- Case Study Approach
- Case Study Method
- Enhancing the Quality of Case Studies in Health Services Research
- “We do things together” A case study of “couplehood” in dementia
- Using mixed methods for evaluating an integrative approach to cancer care: a case study
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

Single-Case Design, Analysis, and Quality Assessment for Intervention Research
Michele a. lobo.
1 Biomechanics & Movement Science Program, Department of Physical Therapy, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, USA
Mariola Moeyaert
2 Division of Educational Psychology & Methodology, State University of New York at Albany, Albany, NY, USA
Andrea Baraldi Cunha
Iryna babik, background and purpose.
The purpose of this article is to describe single-case studies, and contrast them with case studies and randomized clinical trials. We will highlight current research designs, analysis techniques, and quality appraisal tools relevant for single-case rehabilitation research.
Summary of Key Points
Single-case studies can provide a viable alternative to large group studies such as randomized clinical trials. Single case studies involve repeated measures, and manipulation of and independent variable. They can be designed to have strong internal validity for assessing causal relationships between interventions and outcomes, and external validity for generalizability of results, particularly when the study designs incorporate replication, randomization, and multiple participants. Single case studies should not be confused with case studies/series (ie, case reports), which are reports of clinical management of one patient or a small series of patients.
Recommendations for Clinical Practice
When rigorously designed, single-case studies can be particularly useful experimental designs in a variety of situations, even when researcher resources are limited, studied conditions have low incidences, or when examining effects of novel or expensive interventions. Readers will be directed to examples from the published literature in which these techniques have been discussed, evaluated for quality, and implemented.
Introduction
The purpose of this article is to present current tools and techniques relevant for single-case rehabilitation research. Single-case (SC) studies have been identified by a variety of names, including “n of 1 studies” and “single-subject” studies. The term “single-case study” is preferred over the previously mentioned terms because previous terms suggest these studies include only one participant. In fact, as will be discussed below, for purposes of replication and improved generalizability, the strongest SC studies commonly include more than one participant.
A SC study should not be confused with a “case study/series “ (also called “case report”. In a typical case study/series, a single patient or small series of patients is involved, but there is not a purposeful manipulation of an independent variable, nor are there necessarily repeated measures. Most case studies/series are reported in a narrative way while results of SC studies are presented numerically or graphically. 1 , 2 This article defines SC studies, contrasts them with randomized clinical trials, discusses how they can be used to scientifically test hypotheses, and highlights current research designs, analysis techniques, and quality appraisal tools that may be useful for rehabilitation researchers.
In SC studies, measurements of outcome (dependent variables) are recorded repeatedly for individual participants across time and varying levels of an intervention (independent variables). 1 – 5 These varying levels of intervention are referred to as “phases” with one phase serving as a baseline or comparison, so each participant serves as his/her own control. 2 In contrast to case studies and case series in which participants are observed across time without experimental manipulation of the independent variable, SC studies employ systematic manipulation of the independent variable to allow for hypothesis testing. 1 , 6 As a result, SC studies allow for rigorous experimental evaluation of intervention effects and provide a strong basis for establishing causal inferences. Advances in design and analysis techniques for SC studies observed in recent decades have made SC studies increasingly popular in educational and psychological research. Yet, the authors believe SC studies have been undervalued in rehabilitation research, where randomized clinical trials (RCTs) are typically recommended as the optimal research design to answer questions related to interventions. 7 In reality, there are advantages and disadvantages to both SC studies and RCTs that should be carefully considered in order to select the best design to answer individual research questions. While there are a variety of other research designs that could be utilized in rehabilitation research, only SC studies and RCTs are discussed here because SC studies are the focus of this article and RCTs are the most highly recommended design for intervention studies. 7
When designed and conducted properly, RCTs offer strong evidence that changes in outcomes may be related to provision of an intervention. However, RCTs require monetary, time, and personnel resources that many researchers, especially those in clinical settings, may not have available. 8 RCTs also require access to large numbers of consenting participants that meet strict inclusion and exclusion criteria that can limit variability of the sample and generalizability of results. 9 The requirement for large participant numbers may make RCTs difficult to perform in many settings, such as rural and suburban settings, and for many populations, such as those with diagnoses marked by lower prevalence. 8 To rely exclusively on RCTs has the potential to result in bodies of research that are skewed to address the needs of some individuals while neglecting the needs of others. RCTs aim to include a large number of participants and to use random group assignment to create study groups that are similar to one another in terms of all potential confounding variables, but it is challenging to identify all confounding variables. Finally, the results of RCTs are typically presented in terms of group means and standard deviations that may not represent true performance of any one participant. 10 This can present as a challenge for clinicians aiming to translate and implement these group findings at the level of the individual.
SC studies can provide a scientifically rigorous alternative to RCTs for experimentally determining the effectiveness of interventions. 1 , 2 SC studies can assess a variety of research questions, settings, cases, independent variables, and outcomes. 11 There are many benefits to SC studies that make them appealing for intervention research. SC studies may require fewer resources than RCTs and can be performed in settings and with populations that do not allow for large numbers of participants. 1 , 2 In SC studies, each participant serves as his/her own comparison, thus controlling for many confounding variables that can impact outcome in rehabilitation research, such as gender, age, socioeconomic level, cognition, home environment, and concurrent interventions. 2 , 11 Results can be analyzed and presented to determine whether interventions resulted in changes at the level of the individual, the level at which rehabilitation professionals intervene. 2 , 12 When properly designed and executed, SC studies can demonstrate strong internal validity to determine the likelihood of a causal relationship between the intervention and outcomes and external validity to generalize the findings to broader settings and populations. 2 , 12 , 13
Single Case Research Designs for Intervention Research
There are a variety of SC designs that can be used to study the effectiveness of interventions. Here we discuss: 1) AB designs, 2) reversal designs, 3) multiple baseline designs, and 4) alternating treatment designs, as well as ways replication and randomization techniques can be used to improve internal validity of all of these designs. 1 – 3 , 12 – 14
The simplest of these designs is the AB Design 15 ( Figure 1 ). This design involves repeated measurement of outcome variables throughout a baseline control/comparison phase (A ) and then throughout an intervention phase (B). When possible, it is recommended that a stable level and/or rate of change in performance be observed within the baseline phase before transitioning into the intervention phase. 2 As with all SC designs, it is also recommended that there be a minimum of five data points in each phase. 1 , 2 There is no randomization or replication of the baseline or intervention phases in the basic AB design. 2 Therefore, AB designs have problems with internal validity and generalizability of results. 12 They are weak in establishing causality because changes in outcome variables could be related to a variety of other factors, including maturation, experience, learning, and practice effects. 2 , 12 Sample data from a single case AB study performed to assess the impact of Floor Play intervention on social interaction and communication skills for a child with autism 15 are shown in Figure 1 .

An example of results from a single-case AB study conducted on one participant with autism; two weeks of observation (baseline phase A) were followed by seven weeks of Floor Time Play (intervention phase B). The outcome measure Circles of Communications (reciprocal communication with two participants responding to each other verbally or nonverbally) served as a behavioral indicator of the child’s social interaction and communication skills (higher scores indicating better performance). A statistically significant improvement in Circles of Communication was found during the intervention phase as compared to the baseline. Note that although a stable baseline is recommended for SC studies, it is not always possible to satisfy this requirement, as you will see in Figures 1 – 4 . Data were extracted from Dionne and Martini (2011) 15 utilizing Rohatgi’s WebPlotDigitizer software. 78
If an intervention does not have carry-over effects, it is recommended to use a Reversal Design . 2 For example, a reversal A 1 BA 2 design 16 ( Figure 2 ) includes alternation of the baseline and intervention phases, whereas a reversal A 1 B 1 A 2 B 2 design 17 ( Figure 3 ) consists of alternation of two baseline (A 1 , A 2 ) and two intervention (B 1 , B 2 ) phases. Incorporating at least four phases in the reversal design (i.e., A 1 B 1 A 2 B 2 or A 1 B 1 A 2 B 2 A 3 B 3 …) allows for a stronger determination of a causal relationship between the intervention and outcome variables, because the relationship can be demonstrated across at least three different points in time – change in outcome from A 1 to B 1 , from B 1 to A 2 , and from A 2 to B 2 . 18 Before using this design, however, researchers must determine that it is safe and ethical to withdraw the intervention, especially in cases where the intervention is effective and necessary. 12

An example of results from a single-case A 1 BA 2 study conducted on eight participants with stable multiple sclerosis (data on three participants were used for this example). Four weeks of observation (baseline phase A 1 ) were followed by eight weeks of core stability training (intervention phase B), then another four weeks of observation (baseline phase A 2 ). Forward functional reach test (the maximal distance the participant can reach forward or lateral beyond arm’s length, maintaining a fixed base of support in the standing position; higher scores indicating better performance) significantly improved during intervention for Participants 1 and 3 without further improvement observed following withdrawal of the intervention (during baseline phase A 2 ). Data were extracted from Freeman et al. (2010) 16 utilizing Rohatgi’s WebPlotDigitizer software. 78

An example of results from a single-case A 1 B 1 A 2 B 2 study conducted on two participants with severe unilateral neglect after a right-hemisphere stroke. Two weeks of conventional treatment (baseline phases A 1, A 2 ) alternated with two weeks of visuo-spatio-motor cueing (intervention phases B 1 , B 2 ). Performance was assessed in two tests of lateral neglect, the Bells Cancellation Test (Figure A; lower scores indicating better performance) and the Line Bisection Test (Figure B; higher scores indicating better performance). There was a statistically significant intervention-related improvement in participants’ performance on the Line Bisection Test, but not on the Bells Test. Data were extracted from Samuel at al. (2000) 17 utilizing Rohatgi’s WebPlotDigitizer software. 78
A recent study used an ABA reversal SC study to determine the effectiveness of core stability training in 8 participants with multiple sclerosis. 16 During the first four weekly data collections, the researchers ensured a stable baseline, which was followed by eight weekly intervention data points, and concluded with four weekly withdrawal data points. Intervention significantly improved participants’ walking and reaching performance ( Figure 2 ). 16 This A 1 BA 2 design could have been strengthened by the addition of a second intervention phase for replication (A 1 B 1 A 2 B 2 ). For instance, a single-case A 1 B 1 A 2 B 2 withdrawal design aimed to assess the efficacy of rehabilitation using visuo-spatio-motor cueing for two participants with severe unilateral neglect after a severe right-hemisphere stroke. 17 Each phase included 8 data points. Statistically significant intervention-related improvement was observed, suggesting that visuo-spatio-motor cueing might be promising for treating individuals with very severe neglect ( Figure 3 ). 17
The reversal design can also incorporate a cross over design where each participant experiences more than one type of intervention. For instance, a B 1 C 1 B 2 C 2 design could be used to study the effects of two different interventions (B and C) on outcome measures. Challenges with including more than one intervention involve potential carry-over effects from earlier interventions and order effects that may impact the measured effectiveness of the interventions. 2 , 12 Including multiple participants and randomizing the order of intervention phase presentations are tools to help control for these types of effects. 19
When an intervention permanently changes an individual’s ability, a return to baseline performance is not feasible and reversal designs are not appropriate. Multiple Baseline Designs (MBDs) are useful in these situations ( Figure 4 ). 20 MBDs feature staggered introduction of the intervention across time: each participant is randomly assigned to one of at least 3 experimental conditions characterized by the length of the baseline phase. 21 These studies involve more than one participant, thus functioning as SC studies with replication across participants. Staggered introduction of the intervention allows for separation of intervention effects from those of maturation, experience, learning, and practice. For example, a multiple baseline SC study was used to investigate the effect of an anti-spasticity baclofen medication on stiffness in five adult males with spinal cord injury. 20 The subjects were randomly assigned to receive 5–9 baseline data points with a placebo treatment prior to the initiation of the intervention phase with the medication. Both participants and assessors were blind to the experimental condition. The results suggested that baclofen might not be a universal treatment choice for all individuals with spasticity resulting from a traumatic spinal cord injury ( Figure 4 ). 20

An example of results from a single-case multiple baseline study conducted on five participants with spasticity due to traumatic spinal cord injury. Total duration of data collection was nine weeks. The first participant was switched from placebo treatment (baseline) to baclofen treatment (intervention) after five data collection sessions, whereas each consecutive participant was switched to baclofen intervention at the subsequent sessions through the ninth session. There was no statistically significant effect of baclofen on viscous stiffness at the ankle joint. Data were extracted from Hinderer at al. (1990) 20 utilizing Rohatgi’s WebPlotDigitizer software. 78
The impact of two or more interventions can also be assessed via Alternating Treatment Designs (ATDs) . In ATDs, after establishing the baseline, the experimenter exposes subjects to different intervention conditions administered in close proximity for equal intervals ( Figure 5 ). 22 ATDs are prone to “carry-over effects” when the effects of one intervention influence the observed outcomes of another intervention. 1 As a result, such designs introduce unique challenges when attempting to determine the effects of any one intervention and have been less commonly utilized in rehabilitation. An ATD was used to monitor disruptive behaviors in the school setting throughout a baseline followed by an alternating treatment phase with randomized presentation of a control condition or an exercise condition. 23 Results showed that 30 minutes of moderate to intense physical activity decreased behavioral disruptions through 90 minutes after the intervention. 23 An ATD was also used to compare the effects of commercially available and custom-made video prompts on the performance of multi-step cooking tasks in four participants with autism. 22 Results showed that participants independently performed more steps with the custom-made video prompts ( Figure 5 ). 22

An example of results from a single case alternating treatment study conducted on four participants with autism (data on two participants were used for this example). After the observation phase (baseline), effects of commercially available and custom-made video prompts on the performance of multi-step cooking tasks were identified (treatment phase), after which only the best treatment was used (best treatment phase). Custom-made video prompts were most effective for improving participants’ performance of multi-step cooking tasks. Data were extracted from Mechling at al. (2013) 22 utilizing Rohatgi’s WebPlotDigitizer software. 78
Regardless of the SC study design, replication and randomization should be incorporated when possible to improve internal and external validity. 11 The reversal design is an example of replication across study phases. The minimum number of phase replications needed to meet quality standards is three (A 1 B 1 A 2 B 2 ), but having four or more replications is highly recommended (A 1 B 1 A 2 B 2 A 3 …). 11 , 14 In cases when interventions aim to produce lasting changes in participants’ abilities, replication of findings may be demonstrated by replicating intervention effects across multiple participants (as in multiple-participant AB designs), or across multiple settings, tasks, or service providers. When the results of an intervention are replicated across multiple reversals, participants, and/or contexts, there is an increased likelihood a causal relationship exists between the intervention and the outcome. 2 , 12
Randomization should be incorporated in SC studies to improve internal validity and the ability to assess for causal relationships among interventions and outcomes. 11 In contrast to traditional group designs, SC studies often do not have multiple participants or units that can be randomly assigned to different intervention conditions. Instead, in randomized phase-order designs , the sequence of phases is randomized. Simple or block randomization is possible. For example, with simple randomization for an A 1 B 1 A 2 B 2 design, the A and B conditions are treated as separate units and are randomly assigned to be administered for each of the pre-defined data collection points. As a result, any combination of A-B sequences is possible without restrictions on the number of times each condition is administered or regard for repetitions of conditions (e.g., A 1 B 1 B 2 A 2 B 3 B 4 B 5 A 3 B 6 A 4 A 5 A 6 ). With block randomization for an A 1 B 1 A 2 B 2 design, two conditions (e.g., A and B) would be blocked into a single unit (AB or BA), randomization of which to different time periods would ensure that each condition appears in the resulting sequence more than two times (e.g., A 1 B 1 B 2 A 2 A 3 B 3 A 4 B 4 ). Note that AB and reversal designs require that the baseline (A) always precedes the first intervention (B), which should be accounted for in the randomization scheme. 2 , 11
In randomized phase start-point designs , the lengths of the A and B phases can be randomized. 2 , 11 , 24 – 26 For example, for an AB design, researchers could specify the number of time points at which outcome data will be collected, (e.g., 20), define the minimum number of data points desired in each phase (e.g., 4 for A, 3 for B), and then randomize the initiation of the intervention so that it occurs anywhere between the remaining time points (points 5 and 17 in the current example). 27 , 28 For multiple-baseline designs, a dual-randomization, or “regulated randomization” procedure has been recommended. 29 If multiple-baseline randomization depends solely on chance, it could be the case that all units are assigned to begin intervention at points not really separated in time. 30 Such randomly selected initiation of the intervention would result in the drastic reduction of the discriminant and internal validity of the study. 29 To eliminate this issue, investigators should first specify appropriate intervals between the start points for different units, then randomly select from those intervals, and finally randomly assign each unit to a start point. 29
Single Case Analysis Techniques for Intervention Research
The What Works Clearinghouse (WWC) single-case design technical documentation provides an excellent overview of appropriate SC study analysis techniques to evaluate the effectiveness of intervention effects. 1 , 18 First, visual analyses are recommended to determine whether there is a functional relation between the intervention and the outcome. Second, if evidence for a functional effect is present, the visual analysis is supplemented with quantitative analysis methods evaluating the magnitude of the intervention effect. Third, effect sizes are combined across cases to estimate overall average intervention effects which contributes to evidence-based practice, theory, and future applications. 2 , 18
Visual Analysis
Traditionally, SC study data are presented graphically. When more than one participant engages in a study, a spaghetti plot showing all of their data in the same figure can be helpful for visualization. Visual analysis of graphed data has been the traditional method for evaluating treatment effects in SC research. 1 , 12 , 31 , 32 The visual analysis involves evaluating level, trend, and stability of the data within each phase (i.e., within-phase data examination) followed by examination of the immediacy of effect, consistency of data patterns, and overlap of data between baseline and intervention phases (i.e., between-phase comparisons). When the changes (and/or variability) in level are in the desired direction, are immediate, readily discernible, and maintained over time, it is concluded that the changes in behavior across phases result from the implemented treatment and are indicative of improvement. 33 Three demonstrations of an intervention effect are necessary for establishing a functional relation. 1
Within-phase examination
Level, trend, and stability of the data within each phase are evaluated. Mean and/or median can be used to report the level, and trend can be evaluated by determining whether the data points are monotonically increasing or decreasing. Within-phase stability can be evaluated by calculating the percentage of data points within 15% of the phase median (or mean). The stability criterion is satisfied if about 85% (80% – 90%) of the data in a phase fall within a 15% range of the median (or average) of all data points for that phase. 34
Between-phase examination
Immediacy of effect, consistency of data patterns, and overlap of data between baseline and intervention phases are evaluated next. For this, several nonoverlap indices have been proposed that all quantify the proportion of measurements in the intervention phase not overlapping with the baseline measurements. 35 Nonoverlap statistics are typically scaled as percent from 0 to 100, or as a proportion from 0 to 1. Here, we briefly discuss the Nonoverlap of All Pairs ( NAP ), 36 the Extended Celeration Line ( ECL ), the Improvement Rate Difference ( IRD) , 37 and the TauU and the TauU-adjusted, TauU adj , 35 as these are the most recent and complete techniques. We also examine the Percentage of Nonoverlapping Data ( PND ) 38 and the Two Standard Deviations Band Method, as these are frequently used techniques. In addition, we include the Percentage of Nonoverlapping Corrected Data ( PNCD ) – an index applying to the PND after controlling for baseline trend. 39
Nonoverlap of all pairs (NAP)
Each baseline observation can be paired with each intervention phase observation to make n pairs (i.e., N = n A * n B ). Count the number of overlapping pairs, n o , counting all ties as 0.5. Then define the percent of the pairs that show no overlap. Alternatively, one can count the number of positive (P), negative (N), and tied (T) pairs 2 , 36 :
Extended Celeration Line (ECL)
ECL or split middle line allows control for a positive Phase A trend. Nonoverlap is defined as the proportion of Phase B ( n b ) data that are above the median trend plotted from Phase A data ( n B< sub > Above Median trend A </ sub > ), but then extended into Phase B: ECL = n B Above Median trend A n b ∗ 100
As a consequence, this method depends on a straight line and makes an assumption of linearity in the baseline. 2 , 12
Improvement rate difference (IRD)
This analysis is conceptualized as the difference in improvement rates (IR) between baseline ( IR B ) and intervention phases ( IR T ). 38 The IR for each phase is defined as the number of “improved data points” divided by the total data points in that phase. IRD, commonly employed in medical group research under the name of “risk reduction” or “risk difference” attempts to provide an intuitive interpretation for nonoverlap and to make use of an established, respected effect size, IR B - IR B , or the difference between two proportions. 37

TauU and TauU adj
Each baseline observation can be paired with each intervention phase observation to make n pairs (i.e., n = n A * n B ). Count the number of positive (P), negative (N), and tied (T) pairs, and use the following formula: TauU = P - N P + N + τ
The TauU adj is an adjustment of TauU for monotonic trend in baseline. Each baseline observation can be paired with each intervention phase observation to make n pairs (i.e., n = n A * n B ). Each baseline observation can be paired with all later baseline observations (n A *(n A -1)/2). 2 , 35 Then the baseline trend can be computed: TauU adf = P - N - S trend P + N + τ ; S trend = P A – NA
Online calculators might assist researchers in obtaining the TauU and TauU adjusted coefficients ( http://www.singlecaseresearch.org/calculators/tau-u ).
Percentage of nonoverlapping data (PND)
If anticipating an increase in the outcome, locate the highest data point in the baseline phase and then calculate the percent of the intervention phase data points that exceed it. If anticipating a decrease in the outcome, find the lowest data point in the baseline phase and then calculate the percent of the treatment phase data points that are below it: PND = n B Overlap A n b ∗ 100 . A PND < 50 would mark no observed effect, PND = 50–70 signifies a questionable effect, and PND > 70 suggests the intervention was effective. 40 The percentage of nonoverlapping (PNDC) corrected was proposed in 2009 as an extension of the PND. 39 Prior to applying the PND, a data correction procedure is applied eliminating pre-existing baseline trend. 38
Two Standard Deviation Band Method
When the stability criterion described above is met within phases, it is possible to apply the two standard deviation band method. 12 , 41 First, the mean of the data for a specific condition is calculated and represented with a solid line. In the next step, the standard deviation of the same data is computed and two dashed lines are represented: one located two standard deviations above the mean and the other – two standard deviations below. For normally distributed data, few points (less than 5%) are expected to be outside the two standard deviation bands if there is no change in the outcome score due to the intervention. However, this method is not considered a formal statistical procedure, as the data cannot typically be assumed to be normal, continuous, or independent. 41
Statistical Analysis
If the visual analysis indicates a functional relationship (i.e., three demonstrations of the effectiveness of the intervention effect), it is recommended to proceed with the quantitative analyses, reflecting the magnitude of the intervention effect. First, effect sizes are calculated for each participant (individual-level analysis). Moreover, if the research interest lies in the generalizability of the effect size across participants, effect sizes can be combined across cases to achieve an overall average effect size estimate (across-case effect size).
Note that quantitative analysis methods are still being developed in the domain of SC research 1 and statistical challenges of producing an acceptable measure of treatment effect remain. 14 , 42 , 43 Therefore, the WWC standards strongly recommend conducting sensitivity analysis and reporting multiple effect size estimators. If consistency across different effect size estimators is identified, there is stronger evidence for the effectiveness of the treatment. 1 , 18
Individual-level effect size analysis
The most common effect sizes recommended for SC analysis are: 1) standardized mean difference Cohen’s d ; 2) standardized mean difference with correction for small sample sizes Hedges’ g ; and 3) the regression-based approach which has the most potential and is strongly recommended by the WWC standards. 1 , 44 , 45 Cohen’s d can be calculated using following formula: d = X A ¯ - X B ¯ s p , with X A ¯ being the baseline mean, X B ¯ being the treatment mean, and s p indicating the pooled within-case standard deviation. Hedges’ g is an extension of Cohen’s d , recommended in the context of SC studies as it corrects for small sample sizes. The piecewise regression-based approach does not only reflect the immediate intervention effect, but also the intervention effect across time:
i stands for the measurement occasion ( i = 0, 1,… I ). The dependent variable is regressed on a time indicator, T , which is centered around the first observation of the intervention phase, D , a dummy variable for the intervention phase, and an interaction term of these variables. The equation shows that the expected score, Ŷ i , equals β 0 + β 1 T i in the baseline phase, and ( β 0 + β 2 ) + ( β 1 + β 3 ) T i in the intervention phase. β 0 , therefore, indicates the expected baseline level at the start of the intervention phase (when T = 0), whereas β 1 marks the linear time trend in the baseline scores. The coefficient β 2 can then be interpreted as an immediate effect of the intervention on the outcome, whereas β 3 signifies the effect of the intervention across time. The e i ’s are residuals assumed to be normally distributed around a mean of zero with a variance of σ e 2 . The assumption of independence of errors is usually not met in the context of SC studies because repeated measures are obtained within a person. As a consequence, it can be the case that the residuals are autocorrelated, meaning that errors closer in time are more related to each other compared to errors further away in time. 46 – 48 As a consequence, a lag-1 autocorrelation is appropriate (taking into account the correlation between two consecutive errors: e i and e i –1 ; for more details see Verbeke & Molenberghs, (2000). 49 In Equation 1 , ρ indicates the autocorrelation parameter. If ρ is positive, the errors closer in time are more similar; if ρ is negative, the errors closer in time are more different, and if ρ equals zero, there is no correlation between the errors.
Across-case effect sizes
Two-level modeling to estimate the intervention effects across cases can be used to evaluate across-case effect sizes. 44 , 45 , 50 Multilevel modeling is recommended by the WWC standards because it takes the hierarchical nature of SC studies into account: measurements are nested within cases and cases, in turn, are nested within studies. By conducting a multilevel analysis, important research questions can be addressed (which cannot be answered by single-level analysis of SC study data), such as: 1) What is the magnitude of the average treatment effect across cases? 2) What is the magnitude and direction of the case-specific intervention effect? 3) How much does the treatment effect vary within cases and across cases? 4) Does a case and/or study level predictor influence the treatment’s effect? The two-level model has been validated in previous research using extensive simulation studies. 45 , 46 , 51 The two-level model appears to have sufficient power (> .80) to detect large treatment effects in at least six participants with six measurements. 21
Furthermore, to estimate the across-case effect sizes, the HPS (Hedges, Pustejovsky, and Shadish) , or single-case educational design ( SCEdD)-specific mean difference, index can be calculated. 52 This is a standardized mean difference index specifically designed for SCEdD data, with the aim of making it comparable to Cohen’s d of group-comparison designs. The standard deviation takes into account both within-participant and between-participant variability, and is typically used to get an across-case estimator for a standardized change in level. The advantage of using the HPS across-case effect size estimator is that it is directly comparable with Cohen’s d for group comparison research, thus enabling the use of Cohen’s (1988) benchmarks. 53
Valuable recommendations on SC data analyses have recently been provided. 54 , 55 They suggest that a specific SC study data analytic technique can be chosen based on: (1) the study aims and the desired quantification (e.g., overall quantification, between-phase quantifications, randomization, etc.), (2) the data characteristics as assessed by visual inspection and the assumptions one is willing to make about the data, and (3) the knowledge and computational resources. 54 , 55 Table 1 lists recommended readings and some commonly used resources related to the design and analysis of single-case studies.
Recommend readings and resources related to the design and analysis of single-case studies.
Quality Appraisal Tools for Single-Case Design Research
Quality appraisal tools are important to guide researchers in designing strong experiments and conducting high-quality systematic reviews of the literature. Unfortunately, quality assessment tools for SC studies are relatively novel, ratings across tools demonstrate variability, and there is currently no “gold standard” tool. 56 Table 2 lists important SC study quality appraisal criteria compiled from the most common scales; when planning studies or reviewing the literature, we recommend readers consider these criteria. Table 3 lists some commonly used SC quality assessment and reporting tools and references to resources where the tools can be located.
Summary of important single-case study quality appraisal criteria.
Quality assessment and reporting tools related to single-case studies.
When an established tool is required for systematic review, we recommend use of the What Works Clearinghouse (WWC) Tool because it has well-defined criteria and is developed and supported by leading experts in the SC research field in association with the Institute of Education Sciences. 18 The WWC documentation provides clear standards and procedures to evaluate the quality of SC research; it assesses the internal validity of SC studies, classifying them as “Meeting Standards”, “Meeting Standards with Reservations”, or “Not Meeting Standards”. 1 , 18 Only studies classified in the first two categories are recommended for further visual analysis. Also, WWC evaluates the evidence of effect, classifying studies into “Strong Evidence of a Causal Relation”, “Moderate Evidence of a Causal Relation”, or “No Evidence of a Causal Relation”. Effect size should only be calculated for studies providing strong or moderate evidence of a causal relation.
The Single-Case Reporting Guideline In BEhavioural Interventions (SCRIBE) 2016 is another useful SC research tool developed recently to improve the quality of single-case designs. 57 SCRIBE consists of a 26-item checklist that researchers need to address while reporting the results of SC studies. This practical checklist allows for critical evaluation of SC studies during study planning, manuscript preparation, and review.
Single-case studies can be designed and analyzed in a rigorous manner that allows researchers strength in assessing causal relationships among interventions and outcomes, and in generalizing their results. 2 , 12 These studies can be strengthened via incorporating replication of findings across multiple study phases, participants, settings, or contexts, and by using randomization of conditions or phase lengths. 11 There are a variety of tools that can allow researchers to objectively analyze findings from SC studies. 56 While a variety of quality assessment tools exist for SC studies, they can be difficult to locate and utilize without experience, and different tools can provide variable results. The WWC quality assessment tool is recommended for those aiming to systematically review SC studies. 1 , 18
SC studies, like all types of study designs, have a variety of limitations. First, it can be challenging to collect at least five data points in a given study phase. This may be especially true when traveling for data collection is difficult for participants, or during the baseline phase when delaying intervention may not be safe or ethical. Power in SC studies is related to the number of data points gathered for each participant so it is important to avoid having a limited number of data points. 12 , 58 Second, SC studies are not always designed in a rigorous manner and, thus, may have poor internal validity. This limitation can be overcome by addressing key characteristics that strengthen SC designs ( Table 2 ). 1 , 14 , 18 Third, SC studies may have poor generalizability. This limitation can be overcome by including a greater number of participants, or units. Fourth, SC studies may require consultation from expert methodologists and statisticians to ensure proper study design and data analysis, especially to manage issues like autocorrelation and variability of data. 2 Fifth, while it is recommended to achieve a stable level and rate of performance throughout the baseline, human performance is quite variable and can make this requirement challenging. Finally, the most important validity threat to SC studies is maturation. This challenge must be considered during the design process in order to strengthen SC studies. 1 , 2 , 12 , 58
SC studies can be particularly useful for rehabilitation research. They allow researchers to closely track and report change at the level of the individual. They may require fewer resources and, thus, can allow for high-quality experimental research, even in clinical settings. Furthermore, they provide a tool for assessing causal relationships in populations and settings where large numbers of participants are not accessible. For all of these reasons, SC studies can serve as an effective method for assessing the impact of interventions.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Institute of Health, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health & Human Development (1R21HD076092-01A1, Lobo PI) and the Delaware Economic Development Office (Grant #109).
Some of the information in this manuscript was presented at the IV Step Meeting in Columbus, OH, June 2016.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Triangulation in Research – Types, Methods and...

Focus Groups – Steps, Examples and Guide

Exploratory Research – Types, Methods and...

Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and...

Applied Research – Types, Methods and Examples

Correlational Research – Methods, Types and...
Single Case Research Design
- First Online: 04 January 2024
Cite this chapter

- Stefan Hunziker 3 &
- Michael Blankenagel 3
562 Accesses
2 Citations
This chapter addresses single-case research designs’ peculiarities, characteristics, and significant fallacies. A single case research design is a collective term for an in-depth analysis of a small non-random sample. The focus of this design is in-depth. This characteristic distinguishes the case study research from other research designs that understand the individual case as a relatively insignificant and interchangeable aspect of a population or sample. Also, researchers find relevant information on writing a single case research design paper and learn about typical methods used for this research design. The chapter closes by referring to overlapping and adjacent research designs.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Barratt, M., Choi, T. Y., & Li, M. (2011). Qualitative case studies in operations management: Trends, research outcomes, and future research implications. Journal of Operations Management, 29 (4), 329–342.
Google Scholar
Baškarada, S. (2014). Qualitative case studies guidelines. The Qualitative Report, 19 (40), 1–25.
Berg, B., & Lune, H. (2012). Qualitative research methods for the social sciences . Pearson.
Berry, L. L., Conant, J. S. & Parasuraman, A. (1991), “A framework for conducting a servicemarketing audit”. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 19 , 255–266.
Bryman, A. (2004). Social research methods 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, 592.
Burns, R. B. (2000). Introduction to research methods . United States of America.
Boos, M., (1992). A Typologie of Case Studies, in: M. O’S´uilleabhain, E.A. Stuhler, D. de Tombe (Eds.), Research on Cases and Theories , (Vol. I), München.
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Qualitative inquiry and research design. Choosing among five approaches (3rd ed.). SAGE.
Darke, P., Shanks, G., & Broadbent, M. (1998). Successfully completing case study research: Combining rigour, relevance and pragmatism. Inform Syst J, 8 (4), 273–289.
Article Google Scholar
Dey, I. (1999). Grounding grounded theory: Guidelines for qualitative inquiry . Academic Press.
Dick, B. (2005). Grounded theory: A thumbnail sketch. Retrieved 11 June 2021 from http://www.scu.edu.au/schools/gcm/ar/arp/grounded.html .
Dooley, L. M. (2002). Case study research and theory building. Advances in Developing Human Resources, 4 (3), 335–354.
Dubé, L., & Paré, G. (2003). Rigor in information systems positivist case research: Current practices, trends, and recommendations. MIS Quarterly, 27, 597–635.
Edmonds, W. A., & Kennedy, T. D. (2012). An applied reference guide to research designs: Quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods . Sage.
Edmondson, A. & McManus, S. (2007). Methodological fit in management field research. The Academy of Management Review, 32 (4), 1155–1179.
Eisenhardt, K. M. (1989). Building theories from case study research. Academy of Management Review, 14 (4), 532–550.
Flynn, B. B., Sakakibara, S., Schroeder, R. G., Bates, K. A., & Flynn, E. J. (1990). Empirical research methods in operations management. Journal of Operations Management, 9 (2), 250–284.
Flyvbjerg, B. (2001). Making social science matter: Why social inquiry fails and how it can succeed again . Cambridge University Press.
Flyvbjerg, B. (2006). Five misunderstandings about case-study research. Qualitative Inquiry, 12 (2), 219–245.
General Accounting Office. (1990). Case study evaluations. Retrieved May 15, 2021, from https://www.gao.gov/assets/pemd-10.1.9.pdf .
Gerring, J. (2004). What is a case study and what is it good for? American Political Science Review, 98 (2), 341–354.
Glaser, B. G. (1978). Theoretical sensitivity: Advances in the methodology of grounded theory . Sociology Press.
Glaser, B., & Strauss, A. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research . Sociology Press.
Gomm, R. (2000). Case study method. Key issues, key texts . SAGE.
Halaweh, M., Fidler, C., & McRobb, S. (2008). Integrating the Grounded Theory Method and Case Study Research Methodology Within IS Research: A Possible ‘Road Map’, ICIS 2008 Proceedings
Halaweh, M. (2012). Integration of grounded theory and case study: An exemplary application from e-commerce security perception research. Journal of Information Technology Theory and Application (JITTA), 13 (1).
Hancock, D., & Algozzine, B. (2016). Doing case study research: A practical guide for beginning researchers (3rd ed.). Teachers College Press.
Hekkala, R. (2007). Grounded theory—the two faces of the methodology and their manifestation in IS research. In Proceedings of the 30th Information Systems Research Seminar in Scandinavia IRIS, 11–14 August, Tampere, Finland (pp. 1–12).
Horton, J., Macve, R., & Struyven, G. (2004). Qualitative Research: Experiences in Using Semi-Structured Interviews. In: Humphrey, Christopher and Lee, Bill H. K., (eds.) The Real Life Guide to Accounting Research: a Behind-The-Scenes View of Using Qualitative Research Methods. Elsevier Science (Firm) , (pp. 339–358 ), Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
Hyett, N., Kenny, A., & Dickson-Swift, V. (2014). Methodology or method? A critical review of qualitative case study reports. International Journal of Qualitative Studies on Health and Well-Being, 9, 23606.
Keating, P. J. (1995). A framework for classifying and evaluating the theoretical contributions of case research in management accounting. Journal of Management Accounting Research, 7, 66.
Levy, J. S. (2008). Case studies: Types, designs, and logics of inference. Conflict Management and Peace Science, 25 (1), 1–18.
Maoz, Z. (2002). Case study methodology in international studies: from storytelling to hypothesis testing. In F. P. Harvey & M. Brecher (Eds.). Evaluating methodology in international studies . University of Michigan Press.
Mayring, P. (2010). Design. In G. Mey & K. Mruck (Hrsg.), Handbuch qualitative Forschung in der Psychologie (S. 225–237). VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften.
May, T. (2011). Social research: Issues, methods and process . Open University Press/Mc.
Merriam, S. B. (2002). Qualitative Research in Practice: Examples For discussion and Analysis . Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Merriam, S. B. (2009). Qualitative research in practice: Examples for discussion and analysis . Jossey-Bass publishers.
Meyer, J.-A., & Kittel-Wegner, E. (2002a). Die Fallstudie in der betriebswirtschaftlichen Forschung und Lehre . Stiftungslehrstuhl für ABWL, insb. kleine und mittlere Unternehmen, Universität.
Meyer, J.-A., & Kittel-Wegner, E. (2002b). Die Fallstudie in der betriebswirtschaftlichen Forschung und Lehre, Schriften zu Management und KMU, Nr. 2/02, Universität Flensburg, Mai 2002.
Mitchell, J. C. (1983). Case and situation analysis. The Sociological Review, 31 (2), 187–211.
Ng. (2005). A principal-distributor collaboration moden in the crane industry. Ph.D. Thesis, Graduate College of Management, Southern Cross University, Australia.
Ng, Y. N. K. & Hase, S. (2008). Grounded suggestions for doing a grounded theory business research. Electronic Journal on Business Research Methods, 6 (2).
Otley, D., Anthony J.B. (1994), “Case study research in management accounting and control”. Management Accounting Research, 5 , 45–65.
Onwuegbuzie, A. J., Leech, N. L., & Collins, K. M. (2012). Qualitative analysis techniques for the review of the literature. Qualitative Report, 17 (56).
Piekkari, R., Welch, C., & Paavilainen, E. (2009). The case study as disciplinary convention. Organizational Research Methods, 12 (3), 567–589.
Ridder, H.-G. (2016). Case study research. Approaches, methods, contribution to theory. Sozialwissenschaftliche Forschungsmethoden (vol. 12). Rainer Hampp Verlag.
Ridder, H.-G. (2017). The theory contribution of case study research designs. Business Research, 10 (2), 281–305.
Stake, R. E. (1995). The art of case study research . Sage.
Stake, R. E. (2005). Qualitative case studies. The SAGE handbook of qualitative research (3rd ed.), eds. N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (pp. 443–466).
Strauss, A. L., & Corbin, J. (1990). Basics of qualitative research: Grounded theory procedures and techniques . Sage publications.
Strauss, A. L., & Corbin, J. (1998). Basics of qualitative research techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory . Sage.
Tight, M. (2003). Researching higher education . Society for Research into Higher Education; Open University Press.
Tight, M. (2010). The curious case of case study: A viewpoint. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 13 (4), 329–339.
Walsham, G. (1995). Interpretive case studies in IS research: nature and method. Eur J Inf Syst 4, 74–81.
Walsham, G. (2006). Doing interpretive research. European Journal of Information Systems, 15 (3), 320–330.
Welch, C., Piekkari, R., Plakoyiannaki, E., & Paavilainen-Mäntymäki, E. (2011). Theorising from case studies: Towards a pluralist future for international business research. Journal of International Business Studies, 42 (5), 740–762.
Woods, M. (2009). A contingency theory perspective on the risk management control system within Birmingham city council. Management Accounting Research, 20 (1), 69–81.
Yin, R. K. (1994). Discovering the future of the case study. Method in evaluation research. American Journal of Evaluation, 15 (3), 283–290.
Yin, R. K. (2004). Case study research: Design and methods (3rd ed.). Chongqing University Press.
Yin, R. K. (2009). Case study research: Design and methods (4th ed.). SAGE.
Yin, R. K. (2014). Case study research. Design and methods (5th ed.). SAGE.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Wirtschaft/IFZ, Campus Zug-Rotkreuz, Hochschule Luzern, Zug-Rotkreuz, Zug, Switzerland
Stefan Hunziker & Michael Blankenagel
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Stefan Hunziker .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Hunziker, S., Blankenagel, M. (2024). Single Case Research Design. In: Research Design in Business and Management. Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-42739-9_8
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-42739-9_8
Published : 04 January 2024
Publisher Name : Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN : 978-3-658-42738-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-658-42739-9
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Case Study vs. Single-Case Experimental Designs
What's the difference.
Case study and single-case experimental designs are both research methods used in psychology and other social sciences to investigate individual cases or subjects. However, they differ in their approach and purpose. Case studies involve in-depth examination of a single case, such as an individual, group, or organization, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon being studied. On the other hand, single-case experimental designs focus on studying the effects of an intervention or treatment on a single subject over time. These designs use repeated measures and control conditions to establish cause-and-effect relationships. While case studies provide rich qualitative data, single-case experimental designs offer more rigorous experimental control and allow for the evaluation of treatment effectiveness.
Further Detail
Introduction.
When conducting research in various fields, it is essential to choose the appropriate study design to answer research questions effectively. Two commonly used designs are case study and single-case experimental designs. While both approaches aim to provide valuable insights into specific phenomena, they differ in several key attributes. This article will compare and contrast the attributes of case study and single-case experimental designs, highlighting their strengths and limitations.
Definition and Purpose
A case study is an in-depth investigation of a particular individual, group, or event. It involves collecting and analyzing qualitative or quantitative data to gain a comprehensive understanding of the subject under study. Case studies are often used to explore complex phenomena, generate hypotheses, or provide detailed descriptions of unique cases.
On the other hand, single-case experimental designs are a type of research design that focuses on studying a single individual or a small group over time. These designs involve manipulating an independent variable and measuring its effects on a dependent variable. Single-case experimental designs are particularly useful for examining cause-and-effect relationships and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions or treatments.
Data Collection and Analysis
In terms of data collection, case studies rely on various sources such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts. Researchers often employ multiple methods to gather rich and diverse data, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of the case. The data collected in case studies are typically qualitative in nature, although quantitative data may also be included.
In contrast, single-case experimental designs primarily rely on quantitative data collection methods. Researchers use standardized measures and instruments to collect data on the dependent variable before, during, and after the manipulation of the independent variable. This allows for a systematic analysis of the effects of the intervention or treatment on the individual or group being studied.
Generalizability
One of the key differences between case studies and single-case experimental designs is their generalizability. Case studies are often conducted on unique or rare cases, making it challenging to generalize the findings to a larger population. The focus of case studies is on providing detailed insights into specific cases rather than making broad generalizations.
On the other hand, single-case experimental designs aim to establish causal relationships and can provide evidence for generalizability. By systematically manipulating the independent variable and measuring its effects on the dependent variable, researchers can draw conclusions about the effectiveness of interventions or treatments that may be applicable to similar cases or populations.
Internal Validity
Internal validity refers to the extent to which a study accurately measures the cause-and-effect relationship between variables. In case studies, establishing internal validity can be challenging due to the lack of control over extraneous variables. The presence of multiple data sources and the potential for subjective interpretation may also introduce bias.
In contrast, single-case experimental designs prioritize internal validity by employing rigorous control over extraneous variables. Researchers carefully design the intervention or treatment, implement it consistently, and measure the dependent variable under controlled conditions. This allows for a more confident determination of the causal relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
Time and Resources
Case studies often require significant time and resources due to their in-depth nature. Researchers need to spend considerable time collecting and analyzing data from various sources, conducting interviews, and immersing themselves in the case. Additionally, case studies may involve multiple researchers or a research team, further increasing the required resources.
On the other hand, single-case experimental designs can be more time and resource-efficient. Since they focus on a single individual or a small group, data collection and analysis can be more streamlined. Researchers can also implement interventions or treatments in a controlled manner, reducing the time and resources needed for data collection.
Ethical Considerations
Both case studies and single-case experimental designs require researchers to consider ethical implications. In case studies, researchers must ensure the privacy and confidentiality of the individuals or groups being studied. Informed consent and ethical guidelines for data collection and analysis should be followed to protect the rights and well-being of the participants.
Similarly, in single-case experimental designs, researchers must consider ethical considerations when implementing interventions or treatments. The well-being and safety of the individual or group being studied should be prioritized, and informed consent should be obtained. Additionally, researchers should carefully monitor and evaluate the potential risks and benefits associated with the intervention or treatment.
Case studies and single-case experimental designs are valuable research approaches that offer unique insights into specific phenomena. While case studies provide in-depth descriptions and exploratory analyses of individual cases, single-case experimental designs focus on establishing causal relationships and evaluating interventions or treatments. Researchers should carefully consider the attributes and goals of their study when choosing between these two designs, ensuring that the selected approach aligns with their research questions and objectives.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.
- International
Donald Trump found guilty of all 34 charges in hush money trial
By CNN's Kara Scannell, Lauren Del Valle and Jeremy Herb in the courthouse
Our live coverage has ended. Follow the latest news on Donald Trump's guilty verdict or read through the updates below.
Stormy Daniels' attorney says she was "really emotional" after verdict
From CNN's Kaanita Iyer
Stormy Daniels' attorney Clark Brewster said his client was "really emotional" following former President Donald Trump's guilty verdict in the hush money case.
He told CNN's Kaitlan Collins that Daniels faced the "realization of the finality" and had "a lot of emotions flowing."
Brewster also responded to Trump attorney Todd Blanche saying he'd raise Daniels' testimony in appeal, arguing that "it was straightforward" and "they had an opportunity to cross examine her."
Stormy Daniels' friend said "it's a joyous day" after Trump's guilty verdict
From CNN's Piper Hudspeth Blackburn

Alana Evans, friend of Stormy Daniels and an adult film star told CNN’s Abby Phillip that she — and Daniels — absolutely feels vindicated by Trump’s guilty verdict, calling it a “joyous day.”
"We were deemed credible, and it's heartwarming in that way because so many people judge us for who we are — our backgrounds — it's something that's thrown in our faces again and again ... it isn't a reflection of who we are as people," Evans said. Evans added that she's "really happy simply because it meant that at the end of the day, it really is a adult film star who is stepping forward and being the person to put that man to the truth."
Here's what happens now that Trump has been convicted in his hush money criminal case
From CNN's Devan Cole

A New York jury convicting Donald Trump on 34 felony counts of falsifying business records brought the former president’s weekslong trial to a close but ushered in a new phase of the historic case.
Now in the unique position of being the first former US president convicted of a felony, Trump faces the possibility of a prison sentence or probation for his crimes stemming from a hush money payment scheme he helped facilitate ahead of the 2016 presidential election.
Trump – who is known for mounting lengthy appeals of court rulings against him – has said he will appeal the conviction, which can be done after he is sentenced.
Here’s what to know about the case following Trump’s conviction:
When will Trump be sentenced?
Judge Juan Merchan has set Trump’s sentencing for 10 a.m. ET on July 11. For now, the former president will remain out of prison as he awaits his sentencing. Prosecutors did not ask for Trump to post any bond.
Can Trump appeal his conviction?
Shortly after Trump was convicted, his attorney Todd Blanche asked Merchan for an acquittal of the charges notwithstanding the guilty verdict. The judge rejected the pro forma request.
Can Trump still be elected president?
Nothing in the US Constitution bars a convicted criminal from running for the nation’s highest office, University of California, Los Angeles law professor Richard L. Hasen has consistently said.
“The Constitution contains only limited qualifications for running for office (being at least 35 years old, a natural born citizen, and at least 14 years a resident of the U.S.),” Hasen continued.
Will the conviction cost Trump his right to vote?
Trump is a Florida resident. When it comes to the Manhattan guilty verdict just rendered, Trump’s right to vote in Florida in November’s election will depend on whether he is sentenced to a term in prison and if he has finished serving that prison sentence by the time of the election.
Florida’s felon voting prohibitions apply to people with out-of-state convictions. However, if a Floridian’s conviction is out of state, Florida defers to that state’s laws for how felon can regain their voting rights.
Read more on the aftermath of Trump's guilty verdict.
Correction: This post has been updated to reflect when Trump is allowed to file an appeal.
In pictures: Trump convicted in hush money case
For the first time in history, a former US president has been convicted of a felony.
A jury on Thursday found Donald Trump guilty on 34 charges of falsifying business records. Prosecutors alleged that the former president engaged in a cover-up scheme to hide reimbursement payments made to his former attorney, Michael Cohen, who had paid hush money to adult film star Stormy Daniels to stop her from going public about a past affair with Trump before the 2016 presidential election. Trump has denied the affair.
See more photos from the trial .

Trump is facing 3 other criminal cases while running again for president
From CNN’s Devan Cole, Amy O'Kruk and Curt Merrill

The hush money criminal case against former President Donald Trump was only one of four criminal cases he is juggling while running again for president.
The former president still faces criminal indictments in Georgia, Washington, DC, and Florida. Trump has pleaded not guilty to every charge in these cases.
Here's a recap of each case:
- Hush money: Trump was first indicted in March 2023 by the Manhattan district attorney on state charges related to a hush-money payment to an adult film star in 2016. Prosecutors alleged Trump was part of an illegal conspiracy to undermine the integrity of the 2016 election. Further, they alleged he was part of an unlawful plan to suppress negative information, including the $130,000 payment. He was found guilty of all 34 counts on Thursday.
- Classified documents: Trump was indicted in June 2023 by a federal grand jury in Miami for taking classified national defense documents from the White House after he left office and resisting the government’s attempts to retrieve the materials. The National Archives said in early 2022 that at least 15 boxes of White House records were recovered from the estate, including some that were classified . The charges were brought by special counsel Jack Smith. However, Judge Aileen Cannon has indefinitely postponed the trial , citing significant issues around classified evidence that would need to be worked out before the federal criminal case goes to a jury.
- Federal election interference: Smith separately charged the former president last August with four crimes over his efforts to reverse the 2020 election results. The indictment alleges Trump and a co-conspirator "attempted to exploit the violence and chaos at the Capitol by calling lawmakers to convince them ... to delay the certification" of the election. That case is currently on hold as the Supreme Court weighs Trump’s claims of presidential immunity in the matter.
- Fulton County: State prosecutors in Georgia brought a similar election subversion case against Trump and others. An Atlanta-based grand jury on August 14, 2023, indicted Trump and 18 others on state charges stemming from their alleged efforts to overturn the former president’s 2020 electoral defeat. A trial date has not yet been set in that case.
Track the criminal cases against Trump.
The post was updated with details from Thursday's verdict.
Melania Trump is in New York City, source says
From CNN's Kristen Holmes
Former first lady Melania Trump and her son, Barron Trump, are currently in New York, a source familiar with the matter told CNN. The two were already in New York when the verdict was read earlier Thursday, although it was not immediately clear when they arrived in the city.
Melania Trump did not attend a fundraiser dinner with Trump at a private residence Thursday night in New York City.
She was not seen at court during the trial.
Schumer says “no one is above the law” after Trump verdict
From CNN's Morgan Rimmer
Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer posted a brief statement about the verdict in former President Donald Trump's hush money trial on social media.
"No one is above the law. The verdict speaks for itself," the New York Democrat said.
Trump attorney Todd Blanche outlines appeal arguments

Donald Trump's attorney Todd Blanche told CNN's Kaitlan Collins Thursday that the former president's legal team plans to argue in its appeal of the verdict that the jury was biased against Trump and the timing of the trial was unfair.
"Every single person on the jury knew Donald Trump as president, as candidate, from 'The Apprentice' so I don't accept that this was a fair place to try President Trump," Blanche said.
He added: "There was so much publicity around the witnesses and around – leading up to the trial that our system of justice isn't supposed to be a system where every person who walks into the courtroom knows about the case."
"The law says a person is entitled to a fair trial in front of a jury of their peers and we just think that because of everything around the lead up this trial, it made it very difficult for the jury to evaluate the evidence kind of independent of what they knew coming in," Blanche said.
Blanche previewed that Trump's legal team will now "vigorously fight" with motions due in a few weeks. And "if that is not successful," the attorney said they will appeal following the sentencing in July.
Please enable JavaScript for a better experience.
Will closing arguments make a difference to the jury in Donald Trump’s hush-money trial?
- Search Search
Jurors in the criminal trial of Donald Trump heard closing arguments Tuesday. A Northeastern law expert explains why they are important.
- Copy Link Link Copied!

Jurors in the criminal trial of Donald Trump heard closing arguments Tuesday from the former president’s defense lawyer and the prosecutor of the hush-money case.
In accordance with New York law, the defense delivered its statement first.
This is the first criminal trial in American history involving a former president. Trump has been charged with 34 felony counts of falsifying business records in order to conceal damaging information that could hurt his 2016 presidential election campaign.
In particular, it is alleged that Trump concealed a $130,000 payment via his then-lawyer Michael Cohen to Stephanie Clifford, the adult film actor known as Stormy Daniels.
Featured Stories

Dominique Biron turned weaknesses into strengths on her way to the NCAA track and field championships

Your podcast needs a theme song. Good Dog Licensing can help

‘Republic Day’ event at Northeastern celebrates the 78th anniversary of democracy in Italy

Bicultural staff can better boost chances of success in international negotiations, Northeastern researcher explains
The trial started on April 15, and the jury heard 22 witnesses across 16 days of testimony. The case is expected to go to the jury on Wednesday. Judge Juan M. Merchan will give instructions to the jury before deliberations.
Northeastern Global News spoke to Rose Zoltek-Jick , an associate teaching professor at the Northeastern University School of Law, about the purpose of closing arguments at a trial and the impact they can have on jurors deciding a case.
What is the role of closing arguments in the whole process of a trial?
A closing is not evidence, but it is an argument where the lawyer gets to put together the case that they have presented or refute the case that the other side has presented, or try to poke holes in it.

It is a story. At trial, evidence comes in piece by piece, document by document, witness by witness. Opening and closing arguments are the two chances that a lawyer has to build a story that puts it all together.
So a closing is a chance to say this is what has happened in the trial, and this is how to understand it.
Does a closing argument impact the jury?
Yes, of course it does, because it helps the jury understand the whole story. In this case [Trump’s hush-money trial], the case has gone on for several weeks, the prosecution called [more than] 20 witnesses. It’s hard to put it all together or remember it all.
The person who has the burden of proof, in this case the prosecution, tried to show that they had proven the case against President Trump beyond a reasonable doubt. So they have to put all the evidence together to show that one piece of evidence relates to another piece of evidence, and how the whole thing hangs together because some evidence doesn’t become clear until other evidence also comes in.
What does the term ‘burden of proof’ mean?
The prosecution has to show on its own and in its own case or through the trial that the defendant has committed a crime on the books beyond a reasonable doubt. Every criminal case must be proven beyond a reasonable doubt by the evidence.
And how would you explain what is reasonable doubt?
[It means] that there is no reason to doubt the case. There is no reasonable reason for the jury not to believe the prosecution’s proof, that the case has been proven to the level of moral certainty, that they can convict and feel confident that they have made the right decision.
In a criminal case, one of the arguments available to [defense] is that the prosecutor has not produced enough evidence or enough quality evidence, or enough evidence that is credible to meet their burden that the case has been proven beyond a reasonable doubt.
It’s a difficult term to define, and judges and courts have struggled with the definition. It refers to the quantity and quality of the evidence that the jury chooses to believe is true.
Does the order in which closing arguments are delivered matter?
In New York, the defendant goes first. In many jurisdictions, the prosecutor goes first and the defendant answers. The prosecution may on occasion get a chance to do a very short rebuttal of anything new that the defendant has raised in their closing.
But New York is unusual in having the defendant go first. The reasoning for that is that the prosecution bears the burden of proof and that they should have the last chance to tell the jury that they have in fact met that burden.
Other jurisdictions see it in the opposite way. That the prosecution should go first, but the defendant should have the last word under the theory that the person who has the last word has a real chance to have their argument stick with the jury as they go into the jury room.
It’s a different sort of psychology as to whether going first is more important or going last is more important, and which order most conforms with the responsibility of the prosecution. The constitutional duty that the prosecution has under the due process clause [is] to satisfy the burden of proof. There’s an argument as to which order is congruent or aligns with that burden.

Recent Stories

- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Trump is found guilty on 34 felony counts. Read the counts here

Ximena Bustillo
Hilary Fung
Jurors in the New York criminal trial against former President Donald Trump have convicted him of 34 felony counts of falsified business records.

4 takeaways from the historic felony conviction of Donald Trump

Legal experts say Trump's conviction is unlikely to lead to a prison sentence
This is the first time a former or sitting U.S. president has been convicted of criminal charges.
The jurors said they unanimously agreed that Trump falsified business records to conceal a $130,000 hush money payment to adult film star Stormy Daniels to influence the outcome of the 2016 election.
Here are the details of those 34 felony counts:

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 10: Single-Subject Research
Overview of Single-Subject Research
Learning Objectives
- Explain what single-subject research is, including how it differs from other types of psychological research.
- Explain what case studies are, including some of their strengths and weaknesses.
- Explain who uses single-subject research and why.
What Is Single-Subject Research?
Single-subject research is a type of quantitative research that involves studying in detail the behaviour of each of a small number of participants. Note that the term single-subject does not mean that only one participant is studied; it is more typical for there to be somewhere between two and 10 participants. (This is why single-subject research designs are sometimes called small- n designs, where n is the statistical symbol for the sample size.) Single-subject research can be contrasted with group research , which typically involves studying large numbers of participants and examining their behaviour primarily in terms of group means, standard deviations, and so on. The majority of this textbook is devoted to understanding group research, which is the most common approach in psychology. But single-subject research is an important alternative, and it is the primary approach in some areas of psychology.
Before continuing, it is important to distinguish single-subject research from two other approaches, both of which involve studying in detail a small number of participants. One is qualitative research, which focuses on understanding people’s subjective experience by collecting relatively unstructured data (e.g., detailed interviews) and analyzing those data using narrative rather than quantitative techniques. Single-subject research, in contrast, focuses on understanding objective behaviour through experimental manipulation and control, collecting highly structured data, and analyzing those data quantitatively.
It is also important to distinguish single-subject research from case studies. A case study is a detailed description of an individual, which can include both qualitative and quantitative analyses. (Case studies that include only qualitative analyses can be considered a type of qualitative research.) The history of psychology is filled with influential cases studies, such as Sigmund Freud’s description of “Anna O.” (see Note 10.5 “The Case of “Anna O.””) and John Watson and Rosalie Rayner’s description of Little Albert (Watson & Rayner, 1920) [1] , who learned to fear a white rat—along with other furry objects—when the researchers made a loud noise while he was playing with the rat. Case studies can be useful for suggesting new research questions and for illustrating general principles. They can also help researchers understand rare phenomena, such as the effects of damage to a specific part of the human brain. As a general rule, however, case studies cannot substitute for carefully designed group or single-subject research studies. One reason is that case studies usually do not allow researchers to determine whether specific events are causally related, or even related at all. For example, if a patient is described in a case study as having been sexually abused as a child and then as having developed an eating disorder as a teenager, there is no way to determine whether these two events had anything to do with each other. A second reason is that an individual case can always be unusual in some way and therefore be unrepresentative of people more generally. Thus case studies have serious problems with both internal and external validity.
The Case of “Anna O.”
Sigmund Freud used the case of a young woman he called “Anna O.” to illustrate many principles of his theory of psychoanalysis (Freud, 1961) [2] . (Her real name was Bertha Pappenheim, and she was an early feminist who went on to make important contributions to the field of social work.) Anna had come to Freud’s colleague Josef Breuer around 1880 with a variety of odd physical and psychological symptoms. One of them was that for several weeks she was unable to drink any fluids. According to Freud,
She would take up the glass of water that she longed for, but as soon as it touched her lips she would push it away like someone suffering from hydrophobia.…She lived only on fruit, such as melons, etc., so as to lessen her tormenting thirst. (p. 9)
But according to Freud, a breakthrough came one day while Anna was under hypnosis.
[S]he grumbled about her English “lady-companion,” whom she did not care for, and went on to describe, with every sign of disgust, how she had once gone into this lady’s room and how her little dog—horrid creature!—had drunk out of a glass there. The patient had said nothing, as she had wanted to be polite. After giving further energetic expression to the anger she had held back, she asked for something to drink, drank a large quantity of water without any difficulty, and awoke from her hypnosis with the glass at her lips; and thereupon the disturbance vanished, never to return. (p.9)
Freud’s interpretation was that Anna had repressed the memory of this incident along with the emotion that it triggered and that this was what had caused her inability to drink. Furthermore, her recollection of the incident, along with her expression of the emotion she had repressed, caused the symptom to go away.
As an illustration of Freud’s theory, the case study of Anna O. is quite effective. As evidence for the theory, however, it is essentially worthless. The description provides no way of knowing whether Anna had really repressed the memory of the dog drinking from the glass, whether this repression had caused her inability to drink, or whether recalling this “trauma” relieved the symptom. It is also unclear from this case study how typical or atypical Anna’s experience was.

Assumptions of Single-Subject Research
Again, single-subject research involves studying a small number of participants and focusing intensively on the behaviour of each one. But why take this approach instead of the group approach? There are several important assumptions underlying single-subject research, and it will help to consider them now.
First and foremost is the assumption that it is important to focus intensively on the behaviour of individual participants. One reason for this is that group research can hide individual differences and generate results that do not represent the behaviour of any individual. For example, a treatment that has a positive effect for half the people exposed to it but a negative effect for the other half would, on average, appear to have no effect at all. Single-subject research, however, would likely reveal these individual differences. A second reason to focus intensively on individuals is that sometimes it is the behaviour of a particular individual that is primarily of interest. A school psychologist, for example, might be interested in changing the behaviour of a particular disruptive student. Although previous published research (both single-subject and group research) is likely to provide some guidance on how to do this, conducting a study on this student would be more direct and probably more effective.
A second assumption of single-subject research is that it is important to discover causal relationships through the manipulation of an independent variable, the careful measurement of a dependent variable, and the control of extraneous variables. For this reason, single-subject research is often considered a type of experimental research with good internal validity. Recall, for example, that Hall and his colleagues measured their dependent variable (studying) many times—first under a no-treatment control condition, then under a treatment condition (positive teacher attention), and then again under the control condition. Because there was a clear increase in studying when the treatment was introduced, a decrease when it was removed, and an increase when it was reintroduced, there is little doubt that the treatment was the cause of the improvement.
A third assumption of single-subject research is that it is important to study strong and consistent effects that have biological or social importance. Applied researchers, in particular, are interested in treatments that have substantial effects on important behaviours and that can be implemented reliably in the real-world contexts in which they occur. This is sometimes referred to as social validity (Wolf, 1976) [3] . The study by Hall and his colleagues, for example, had good social validity because it showed strong and consistent effects of positive teacher attention on a behaviour that is of obvious importance to teachers, parents, and students. Furthermore, the teachers found the treatment easy to implement, even in their often-chaotic elementary school classrooms.
Who Uses Single-Subject Research?
Single-subject research has been around as long as the field of psychology itself. In the late 1800s, one of psychology’s founders, Wilhelm Wundt, studied sensation and consciousness by focusing intensively on each of a small number of research participants. Herman Ebbinghaus’s research on memory and Ivan Pavlov’s research on classical conditioning are other early examples, both of which are still described in almost every introductory psychology textbook.
In the middle of the 20th century, B. F. Skinner clarified many of the assumptions underlying single-subject research and refined many of its techniques (Skinner, 1938) [4] . He and other researchers then used it to describe how rewards, punishments, and other external factors affect behaviour over time. This work was carried out primarily using nonhuman subjects—mostly rats and pigeons. This approach, which Skinner called the experimental analysis of behaviour —remains an important subfield of psychology and continues to rely almost exclusively on single-subject research. For excellent examples of this work, look at any issue of the Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behaviour . By the 1960s, many researchers were interested in using this approach to conduct applied research primarily with humans—a subfield now called applied behaviour analysis (Baer, Wolf, & Risley, 1968) [5] . Applied behaviour analysis plays an especially important role in contemporary research on developmental disabilities, education, organizational behaviour, and health, among many other areas. Excellent examples of this work (including the study by Hall and his colleagues) can be found in the Journal of Applied Behaviour Analysis .
Although most contemporary single-subject research is conducted from the behavioural perspective, it can in principle be used to address questions framed in terms of any theoretical perspective. For example, a studying technique based on cognitive principles of learning and memory could be evaluated by testing it on individual high school students using the single-subject approach. The single-subject approach can also be used by clinicians who take any theoretical perspective—behavioural, cognitive, psychodynamic, or humanistic—to study processes of therapeutic change with individual clients and to document their clients’ improvement (Kazdin, 1982) [6] .
Key Takeaways
- Single-subject research—which involves testing a small number of participants and focusing intensively on the behaviour of each individual—is an important alternative to group research in psychology.
- Single-subject studies must be distinguished from case studies, in which an individual case is described in detail. Case studies can be useful for generating new research questions, for studying rare phenomena, and for illustrating general principles. However, they cannot substitute for carefully controlled experimental or correlational studies because they are low in internal and external validity.
- Single-subject research has been around since the beginning of the field of psychology. Today it is most strongly associated with the behavioural theoretical perspective, but it can in principle be used to study behaviour from any perspective.
- Practice: Find and read a published article in psychology that reports new single-subject research. ( An archive of articles published in the Journal of Applied Behaviour Analysis can be found at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/journals/309/) Write a short summary of the study.
- Describe one problem related to internal validity.
- Describe one problem related to external validity.
- Generate one hypothesis suggested by the case study that might be interesting to test in a systematic single-subject or group study.
Media Attributions
- Pappenheim 1882 by unknown is in the Public Domain .
- Watson, J. B., & Rayner, R. (1920). Conditioned emotional reactions. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 3 , 1–14. ↵
- Freud, S. (1961). Five lectures on psycho-analysis . New York, NY: Norton. ↵
- Wolf, M. (1976). Social validity: The case for subjective measurement or how applied behaviour analysis is finding its heart. Journal of Applied Behaviour Analysis, 11 , 203–214. ↵
- Skinner, B. F. (1938). T he behaviour of organisms: An experimental analysis . New York, NY: Appleton-Century-Crofts. ↵
- Baer, D. M., Wolf, M. M., & Risley, T. R. (1968). Some current dimensions of applied behaviour analysis. Journal of Applied Behaviour Analysis, 1 , 91–97. ↵
- Kazdin, A. E. (1982). Single-case research designs: Methods for clinical and applied settings . New York, NY: Oxford University Press. ↵
A type of quantitative research that involves studying the behaviour of each small number of participants in detail.
The study of large numbers of participants and examining their behaviour primarily in terms of group means, standard deviations, and so on.
A detailed description of an individual, which can include both qualitative and quantitative analyses.
The study of strong and consistent effects that can be implemented reliably in the real-world contexts in which they occur.
Laboratory methods that rely on single-subject research; based upon B. F. Skinner’s philosophy of behaviourism which posits that everything organisms do is behaviour.
Starting in the 1960s, researchers began using single-subject techniques to conduct applied research with human subjects.
Research Methods in Psychology - 2nd Canadian Edition Copyright © 2015 by Paul C. Price, Rajiv Jhangiani, & I-Chant A. Chiang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Advertisement
Trump on Trial
‘guilty,’ and history is made.
A single word rings out in a Manhattan courtroom as Donald Trump becomes the first American president convicted of a crime.
- Share full article

By Jesse McKinley
The single word that rang out in a Manhattan courtroom a little past 5 p.m. on Thursday afternoon shook the country, making Donald Trump the first American president convicted of a crime.
It was a landmark — and, for Trump’s supporters, a black mark — in American history.
The word “guilty” actually was heard 34 times, as the jury — seven men and five women — found the former president guilty of 34 felony counts of falsifying business records to cover up a $130,000 hush-money payment to Stormy Daniels.
The verdict shattered a late afternoon languor inside the Manhattan courthouse where Trump’s trial had played out over the last month and a half, during which time the jury heard a sweeping and sometimes sordid tale of sex, payoffs and presidential politics.
How the outcome affects the 2024 presidential campaign remains to be seen. Trump could use the conviction to galvanize his base and fund-raising, as he has after arrests in other cases, three of which are still pending. On Thursday, after the verdict was read, he assailed what he called “a rigged trial by a conflicted judge who is corrupt.”
“A disgrace,” he said.
Biden’s warning
Shortly after the verdict was read aloud in court, President Biden posted a fund-raising appeal, saying that the verdict alone would not be enough to derail Trump or his supporters.
“There’s only one way to keep Donald Trump out of the Oval Office: At the ballot box,” Biden wrote.
That was one thing Biden and Trump agreed on: Trump told reporters that “the real verdict is going to be Nov. 5 by the people.”
It is not clear what Trump’s legal status will be on Election Day. He is almost certain to appeal today’s verdict, and that process could take months or even longer. In the meantime, Trump will confront the nitty-gritty of the New York State criminal justice system: a meeting with the Probation Department, a pre-sentence report, and then — at 10 a.m. on July 11 — his sentencing.
Trump, a first-time offender, faces probation or up to four years in prison.
That decision will fall to the judge, Juan Merchan, who has been the target of Trump’s attacks during the trial. Trump also attacked the judge’s daughter — a political consultant who has worked with prominent Democrats — prompting Justice Merchan to expand a gag order before the trial began, barring the former president from attacking members of his family. The order also protected witnesses and jurors, both of whom were targets of Trump’s vitriol.
A triumph for Bragg
The verdict was a victory for Alvin Bragg, the Manhattan district attorney who staked his reputation on a prosecution that many legal analysts questioned. But in the end, his strategy was a winning one. The verdict also provided vindication for two crucial witnesses: Michael Cohen, Trump’s former lawyer and fixer; and Daniels, the porn star who testified about a brief, unpleasant sexual encounter with Trump in Lake Tahoe, Nev., in 2006. That encounter led to the $130,000 payoff from Cohen, which led — in turn — to his reimbursement, which led — in turn — to the falsification of business records for which Trump was convicted.
That cascading narrative spanned a decade, from the hotel encounter to the days before the 2016 election, and spilled out in a trial that subjected both Cohen and Daniels to often blistering cross-examination.
Trump denied ever having sex with Daniels, despite her precise details about the night of their encounter — what was in his bathroom, how he waited for her in his boxers, sitting on a bed. Trump’s lawyers were aggressive in suggesting she was lying, even as she stood fast. But defense lawyers rested their hopes on destroying the credibility of Cohen, whom they painted as a pathetic sycophant and money-hungry opportunist. He, too, largely remained steady, despite admitting to many lies during his life, and career, as Trump’s fixer.
In the end, it appeared that the jury was not swayed by the defense’s attacks. Though the testimony lasted more than five weeks, the jury took less than two full days of deliberations to find the former president guilty.
Trump’s initial reaction was muted: He sat in the courtroom, in a red pleather chair, placidly listening as the jury foreman repeated the same word over and over. As the individual jurors were polled, he looked over at the jury box.
Moments later, those 12 New Yorkers — drawn from the many neighborhoods of Manhattan, where Trump made his name as a brash businessman — left the courtroom, walking right past the man they had just convicted.
Get live updates.
Your questions.
We’re asking readers what they’d like to know about the Trump cases: the charges, the procedure, the important players or anything else. You can send us your question by filling out this form.
Is it legal for a felon to run for president? — Laura Downs, Florence, Italy
Answer: This question, which has been bouncing around since the prospect of a criminal trial of Trump first arose, obviously takes on new importance after today’s verdict. But the answer remains the same: Yes.
There is no constitutional or legal prohibition to a felon running for — or even serving as — president, unlike some other elected positions. Whether voters decide to make that happen, of course, remains to be seen.
Jesse McKinley is a Times reporter covering upstate New York, courts and politics. More about Jesse McKinley
What was Trump found guilty of? See the 34 business records the jury decided he falsified

Donald Trump was found guilty of 34 felony counts of falsifying business records after prosecutors successfully convinced a jury he disguised hush money reimbursement as legal expenses. He is the first former president to be convicted of a crime.
Each count is tied to a different business record that prosecutors demonstrated Trump is responsible for changing to conceal or commit another crime .
Those records include 11 checks paid to former lawyer Michael Cohen , 11 invoices from Michael Cohen and 12 entries in Trump's ledgers.
The jury found that Trump authorized a plan to reimburse Cohen for the $130,000 hush money payment issued to Stormy Daniels and spread the payments across 12 months disguised as legal expenses.
Live updates: Former President Donald Trump found guilty on all counts in hush money case
Prep for the polls: See who is running for president and compare where they stand on key issues in our Voter Guide
Breakdown of 34 counts of falsifying business records
Here are the 34 business records Trump was found guilty of falsifying, as described in Judge Juan Merchan 's jury instructions :
- Count 1: Michael Cohen's invoice dated Feb. 14, 2017
- Count 2: Entry in the Detail General Ledger for the Donald J. Trump Revocable Trust dated Feb. 14, 2017
- Count 3: Entry in the Detail General Ledger for the Donald J. Trump Revocable Trust dated Feb. 14, 2017
- Count 4: A Donald J. Trump Revocable Trust Account check and check stub dated Feb. 14, 2017
- Count 5: Michael Cohen's invoice dated March 16, 2017
- Count 6: Entry in the Detail General Ledger for the Donald J. Trump Revocable Trust dated March 17, 2017
- Count 7: A Donald J. Trump Revocable Trust Account check and check stub dated March 17, 2017
- Count 8: Michael Cohen's invoice dated April 13, 2017
- Count 9: Entry in the Detail General Ledger for Donald J. Trump dated June 19, 2017
- Count 10: A Donald J. Trump account check and check stub dated June 19, 2017
- Count 11: Michael Cohen's invoice dated May 22, 2017
- Count 12: Entry in the Detail General Ledger for Donald J. Trump dated May 22, 2017
- Count 13: A Donald J. Trump account check and check stub May 23, 2017
- Count 14: Michael Cohen's invoice dated June 16, 2017
- Count 15: Entry in the Detail General Ledger for Donald J. Trump dated June 19, 2017
- Count 16: A Donald J. Trump account check and check stub dated June 19, 2017
- Count 17: Michael Cohen's invoice dated July 11, 2017
- Count 18: Entry in the Detail General Ledger for Donald J. Trump dated July 11, 2017
- Count 19: A Donald J. Trump account check and check stub dated July 11, 2017
- Count 20: Michael Cohen's invoice dated Aug. 1, 2017
- Count 21: Entry in the Detail General Ledger for Donald J. Trump dated Aug. 1, 2017
- Count 22: A Donald J. Trump account check and check stub dated Aug. 1, 2017
- Count 23: Michael Cohen's invoice dated Sept. 11, 2017
- Count 24: Entry in the Detail General Ledger for Donald J. Trump dated Sept. 11, 2017
- Count 25: A Donald J. Trump account check and check stub dated Sept. 12, 2017
- Count 26: Michael Cohen's invoice dated Oct. 18, 2017
- Count 27: Entry in the Detail General Ledger for Donald J. Trump dated Oct. 18, 2017
- Count 28: A Donald J. Trump account check and check stub dated Oct. 18, 2017
- Count 29: Michael Cohen's invoice dated Nov. 20, 2017
- Count 30: Entry in the Detail General Ledger for Donald J. Trump dated Nov. 20, 2017
- Count 31: A Donald J. Trump account check and check stub dated Nov. 21, 2017
- Count 32: Michael Cohen's invoice dated Dec. 1, 2017
- Count 33: Entry in the Detail General Ledger for Donald J. Trump dated Dec. 1, 2017
- Count 34: A check and check stub dated Dec. 5 2017
Jurors saw copies of these records entered as evidence. Evidence from the entire trial is available on the New York Courts website .
Contributing: Aysha Bagchi

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An added benefit of this design, and all single-case designs, is the immediacy of the data. Instead of waiting until postintervention to take measures on the behavior, single-case research prescribes continuous data collection and visual monitoring of that data displayed graphically, allowing for immediate instructional decision-making.
Key Takeaways. Single-subject research—which involves testing a small number of participants and focusing intensively on the behavior of each individual—is an important alternative to group research in psychology. Single-subject studies must be distinguished from case studies, in which an individual case is described in detail.
A single case research design is not the same as researching a "case". Everything can be considered a "case" in most languages and certainly in English: a product, a patient, a business, an industry, a country, a currency, an ethnicity, a social group etc. Researching such a "case" does not make your research design a case study.
Within a case study research, one may study a single case or multiple cases. Single case studies are most common in case study researches. ... (2004, pp. 33-34), the case study became an instant hit as 'it was the first one to use and give operational meaning to terms such as 'upper-upper class, 'lower-upper class and so on'. Warner ...
Single-case designs are usually appropriate where the case represents a critical case (it meets all the necessary conditions for testing a theory), where it is an extreme or unique case, where it is a revelatory case, or where the research is exploratory (Yin 1994, pp. 38-40). Single cases allow researchers to investigate phenomena in-depth to ...
What is a case study? Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue.
Single case research typically requires a large amount of data since the justification of. using one case is often unusual access to a level of granular detail not permitted by multiple. cases. Researchers can generally collect three types of qualitative data: (1) interviews, (2) archival data, and (3) observations.
The application of single-case research methods is entering a new phase of scientific relevance. Researchers in an increasing array of disciplines are finding single-case methods useful for the questions they are asking and the clinical needs in their fields (Kratochwill et al., 2010; Maggin et al., 2017; Maggin & Odom, 2014; Riley-Tillman, Burns, & Kilgus, 2020).
In designing single-case research studies, it is essential that researchers select the appropriate research design for the specific research question and dependent variable. ... In some cases, this may mean collecting dozens of data points prior to implementing any interventions or procedures, which may be resource intensive and potentially ...
Single-case experimental designs are a family of experimental designs that are characterized by researcher manipulation of an independent variable and repeated measurement of a dependent variable before (i.e., baseline) and after (i.e., intervention phase) introducing the independent variable. In single-case experimental designs a case is the ...
Single-subject design. In design of experiments, single-subject curriculum or single-case research design is a research design most often used in applied fields of psychology, education, and human behaviour in which the subject serves as his/her own control, rather than using another individual/group. Researchers use single-subject design ...
The single-case experiment has a storied history in psychology dating back to the field's founders: Fechner (1889), Watson (1925), and Skinner (1938).It has been used to inform and develop theory, examine interpersonal processes, study the behavior of organisms, establish the effectiveness of psychological interventions, and address a host of other research questions (for a review, see ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
The single case study is the most basic form of case-oriented research, but researchers may also conduct a series of case studies, each study building on the previous, or conduct simultaneous studies of several instances of the same phenomenon (as in comparative research). The key commonality of these different case-oriented approaches is that ...
As demonstrated above, there are various advantages to both idiographic and nomothetic single case study analyses - notably the empirically-rich, context-specific, holistic accounts that they have to offer, and their contribution to theory-building and, to a lesser extent, that of theory-testing.
Case studies are in-depth investigations of a person, group, event, or community. Typically, data is gathered from various sources using several methods (e.g., observations & interviews). The case study research method originated in clinical medicine (the case history, i.e., the patient's personal history). In psychology, case studies are ...
Single-case studies can provide a viable alternative to large group studies such as randomized clinical trials. Single case studies involve repeated measures, and manipulation of and independent variable. They can be designed to have strong internal validity for assessing causal relationships between interventions and outcomes, and external ...
Defnition: A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
Policies and ethics. This chapter addresses single-case research designs' peculiarities, characteristics, and significant fallacies. A single case research design is a collective term for an in-depth analysis of a small non-random sample. The focus of this design is in-depth.
Single Case Research Methodology, 3 rd Edition presents a thorough, technically sound, user-friendly, and comprehensive discussion of single case research methodology. This book can serve as a detailed and complex reference tool for students, researchers, and practitioners who intend to conduct single case research design studies; interpret findings of single case design studies; or write ...
One of the key differences between case studies and single-case experimental designs is their generalizability. Case studies are often conducted on unique or rare cases, making it challenging to generalize the findings to a larger population. The focus of case studies is on providing detailed insights into specific cases rather than making ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Single Case Research, Differences between single case & Group designs, Nomothetic vs. Idiographic Approach and more. ... -group designs focus on average importance-just because a statistic accurately describes a group doesn't mean that it accurately describes an individual ...
A New York jury convicting Donald Trump on 34 felony counts of falsifying business records brought the former president's weekslong trial to a close but ushered in a new phase of the historic case.
12:30-3:30 pm -- DH Research Fellows' Showcase. 12:30 - 1:50 PM : The Meaning and Measurement of Place. with presentations from: Matt Randolph (PhD Candidate in History): "Bringing AI to Archibald Grimké's Archive: A Case Study of Artificial Intelligence for Histories of Race and Slavery". This digital project builds upon two years of research ...
Jurors in the criminal trial of Donald Trump heard closing arguments Tuesday from the former president's defense lawyer and the prosecutor of the hush-money case. In accordance with New York law, the defense delivered its statement first. This is the first criminal trial in American history involving a former president.
Jurors in the New York criminal trial against former President Donald Trump have convicted him of 34 felony counts of falsified business records. This is the first time a former or sitting U.S ...
There are over 25, 000 studies on the Bible, Marriage, Parenting, and more. Right now, also has an extensive catalog of professional development courses on leadership, team building, community, diversity, and conflict resolution. In fact, Baylor has made the full library, the video library available to all of our faculty and staff.
Key Takeaways. Single-subject research—which involves testing a small number of participants and focusing intensively on the behaviour of each individual—is an important alternative to group research in psychology. Single-subject studies must be distinguished from case studies, in which an individual case is described in detail.
By Jesse McKinley. May 30, 2024. "Guilty.". The single word that rang out in a Manhattan courtroom a little past 5 p.m. on Thursday afternoon shook the country, making Donald Trump the first ...
Here are the 34 business records Trump was found guilty of falsifying, as described in Judge Juan Merchan 's jury instructions: Count 1: Michael Cohen's invoice dated Feb. 14, 2017. Count 2: Entry ...