educational research techniques
Research techniques and education.


Research Purpose, Hypotheses, and Questions
Four key components to a research project are the purpose statement, research questions, hypotheses, and research objectives. In this post, we will define each of these.
Definitions

The purpose of this study is to examine the relationship between college completion and organizational commitment of undergraduate students in Thailand.
Here is an example of a qualitative purpose statement.
The purpose of this study is to explore student experiences at a university in Thailand about completing their tertiary degree.
Both of these examples are short one-sentence responses to what the study will attempt to do. This is a critical first step in shaping the study.
Research Question
The research question(s) in a quantitative or qualitative study narrows the purpose down to a specific question(s) for the researcher to find answers. Below are examples from both the quantitative and qualitative perspective. We are continuing the research themes from the previous section on the purpose statement.
Quantitative
Does organizational commitment affect college completion of students?
Qualitative
What kinds of experiences have students had while completing their degree?
On closer examination, you may have noticed that the research questions sound a lot like the purpose statement. Research questions often split a part a long complex purpose statement into several questions. This is why questions sound so redundant when compared to the purpose statement. Despite this apparent problem, this thought process helps researchers to organize their thinking and proceed in a manner that is much more efficient.
The next two components only relate to quantitative research and they are the hypotheses and research objective(s). For this reason our illustration of qualitative concepts will stop at this point.
Hypotheses are statements a researcher makes about the potential outcome(s) of a study based on the examination of literature. Below is an example from the same theme as before.
Students who have a higher perception of organizational commitment will also have a higher likelihood of completing college.
Again, the wording of the research questions, hypotheses and purpose statement are similarly. The difference is only slightly and is due to context. Seeing these similarities quickly will help you to move faster in finishing a study. The difference between these elements is a matter of perspective rather than a strong difference, as they do sound awfully similar.
Research Objectives
Research objectives are the goals a researcher has for a study. This component is not always included in a study. Below is an example.
To examine the correlation between organizational commitment and the rate of college completion
Share this:
10 thoughts on “ research purpose, hypotheses, and questions ”.
This is the wrong use of the word, it should be “their” not “there”.
The purpose of this study is to explore student experiences at a university in Thailand about completing there tertiary degree.
Whoops, thanks for catching that
Thank you for this, very helpful 🙂
This has been helpful.
This was helpful. Thank you
Pingback: Developing a Data Analysis Plan | educational research techniques
This was helpful.
Glad to be of service
As an emerging researcher, my worry is that I have six objectives but five research questions and hypotheses. Am I correct or they must all be the same in times of numbers? Thank you
Thank you, this information helped me so much.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Discover more from educational research techniques.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Chapter 1: Home
- Narrowing Your Topic
- Problem Statement
Purpose Statement Overview
Best practices for writing your purpose statement, writing your purpose statement, sample purpose statements.
- Student Experience Feedback Buttons
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Quantitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative & Quantitative Research Support with the ASC This link opens in a new window
- Library Research Consultations This link opens in a new window
Jump to DSE Guide
The purpose statement succinctly explains (on no more than 1 page) the objectives of the research study. These objectives must directly address the problem and help close the stated gap. Expressed as a formula:

Good purpose statements:
- Flow from the problem statement and actually address the proposed problem
- Are concise and clear
- Answer the question ‘Why are you doing this research?’
- Match the methodology (similar to research questions)
- Have a ‘hook’ to get the reader’s attention
- Set the stage by clearly stating, “The purpose of this (qualitative or quantitative) study is to ...
In PhD studies, the purpose usually involves applying a theory to solve the problem. In other words, the purpose tells the reader what the goal of the study is, and what your study will accomplish, through which theoretical lens. The purpose statement also includes brief information about direction, scope, and where the data will come from.
A problem and gap in combination can lead to different research objectives, and hence, different purpose statements. In the example from above where the problem was severe underrepresentation of female CEOs in Fortune 500 companies and the identified gap related to lack of research of male-dominated boards; one purpose might be to explore implicit biases in male-dominated boards through the lens of feminist theory. Another purpose may be to determine how board members rated female and male candidates on scales of competency, professionalism, and experience to predict which candidate will be selected for the CEO position. The first purpose may involve a qualitative ethnographic study in which the researcher observes board meetings and hiring interviews; the second may involve a quantitative regression analysis. The outcomes will be very different, so it’s important that you find out exactly how you want to address a problem and help close a gap!
The purpose of the study must not only align with the problem and address a gap; it must also align with the chosen research method. In fact, the DP/DM template requires you to name the research method at the very beginning of the purpose statement. The research verb must match the chosen method. In general, quantitative studies involve “closed-ended” research verbs such as determine , measure , correlate , explain , compare , validate , identify , or examine ; whereas qualitative studies involve “open-ended” research verbs such as explore , understand , narrate , articulate [meanings], discover , or develop .
A qualitative purpose statement following the color-coded problem statement (assumed here to be low well-being among financial sector employees) + gap (lack of research on followers of mid-level managers), might start like this:
In response to declining levels of employee well-being, the purpose of the qualitative phenomenology was to explore and understand the lived experiences related to the well-being of the followers of novice mid-level managers in the financial services industry. The levels of follower well-being have been shown to correlate to employee morale, turnover intention, and customer orientation (Eren et al., 2013). A combined framework of Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory and the employee well-being concept informed the research questions and supported the inquiry, analysis, and interpretation of the experiences of followers of novice managers in the financial services industry.
A quantitative purpose statement for the same problem and gap might start like this:
In response to declining levels of employee well-being, the purpose of the quantitative correlational study was to determine which leadership factors predict employee well-being of the followers of novice mid-level managers in the financial services industry. Leadership factors were measured by the Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) assessment framework by Mantlekow (2015), and employee well-being was conceptualized as a compound variable consisting of self-reported turnover-intent and psychological test scores from the Mental Health Survey (MHS) developed by Johns Hopkins University researchers.
Both of these purpose statements reflect viable research strategies and both align with the problem and gap so it’s up to the researcher to design a study in a manner that reflects personal preferences and desired study outcomes. Note that the quantitative research purpose incorporates operationalized concepts or variables ; that reflect the way the researcher intends to measure the key concepts under study; whereas the qualitative purpose statement isn’t about translating the concepts under study as variables but instead aim to explore and understand the core research phenomenon.
Always keep in mind that the dissertation process is iterative, and your writing, over time, will be refined as clarity is gradually achieved. Most of the time, greater clarity for the purpose statement and other components of the Dissertation is the result of a growing understanding of the literature in the field. As you increasingly master the literature you will also increasingly clarify the purpose of your study.
The purpose statement should flow directly from the problem statement. There should be clear and obvious alignment between the two and that alignment will get tighter and more pronounced as your work progresses.
The purpose statement should specifically address the reason for conducting the study, with emphasis on the word specifically. There should not be any doubt in your readers’ minds as to the purpose of your study. To achieve this level of clarity you will need to also insure there is no doubt in your mind as to the purpose of your study.
Many researchers benefit from stopping your work during the research process when insight strikes you and write about it while it is still fresh in your mind. This can help you clarify all aspects of a dissertation, including clarifying its purpose.
Your Chair and your committee members can help you to clarify your study’s purpose so carefully attend to any feedback they offer.
The purpose statement should reflect the research questions and vice versa. The chain of alignment that began with the research problem description and continues on to the research purpose, research questions, and methodology must be respected at all times during dissertation development. You are to succinctly describe the overarching goal of the study that reflects the research questions. Each research question narrows and focuses the purpose statement. Conversely, the purpose statement encompasses all of the research questions.
Identify in the purpose statement the research method as quantitative, qualitative or mixed (i.e., “The purpose of this [qualitative/quantitative/mixed] study is to ...)
Avoid the use of the phrase “research study” since the two words together are redundant.
Follow the initial declaration of purpose with a brief overview of how, with what instruments/data, with whom and where (as applicable) the study will be conducted. Identify variables/constructs and/or phenomenon/concept/idea. Since this section is to be a concise paragraph, emphasis must be placed on the word brief. However, adding these details will give your readers a very clear picture of the purpose of your research.
Developing the purpose section of your dissertation is usually not achieved in a single flash of insight. The process involves a great deal of reading to find out what other scholars have done to address the research topic and problem you have identified. The purpose section of your dissertation could well be the most important paragraph you write during your academic career, and every word should be carefully selected. Think of it as the DNA of your dissertation. Everything else you write should emerge directly and clearly from your purpose statement. In turn, your purpose statement should emerge directly and clearly from your research problem description. It is good practice to print out your problem statement and purpose statement and keep them in front of you as you work on each part of your dissertation in order to insure alignment.
It is helpful to collect several dissertations similar to the one you envision creating. Extract the problem descriptions and purpose statements of other dissertation authors and compare them in order to sharpen your thinking about your own work. Comparing how other dissertation authors have handled the many challenges you are facing can be an invaluable exercise. Keep in mind that individual universities use their own tailored protocols for presenting key components of the dissertation so your review of these purpose statements should focus on content rather than form.
Once your purpose statement is set it must be consistently presented throughout the dissertation. This may require some recursive editing because the way you articulate your purpose may evolve as you work on various aspects of your dissertation. Whenever you make an adjustment to your purpose statement you should carefully follow up on the editing and conceptual ramifications throughout the entire document.
In establishing your purpose you should NOT advocate for a particular outcome. Research should be done to answer questions not prove a point. As a researcher, you are to inquire with an open mind, and even when you come to the work with clear assumptions, your job is to prove the validity of the conclusions reached. For example, you would not say the purpose of your research project is to demonstrate that there is a relationship between two variables. Such a statement presupposes you know the answer before your research is conducted and promotes or supports (advocates on behalf of) a particular outcome. A more appropriate purpose statement would be to examine or explore the relationship between two variables.
Your purpose statement should not imply that you are going to prove something. You may be surprised to learn that we cannot prove anything in scholarly research for two reasons. First, in quantitative analyses, statistical tests calculate the probability that something is true rather than establishing it as true. Second, in qualitative research, the study can only purport to describe what is occurring from the perspective of the participants. Whether or not the phenomenon they are describing is true in a larger context is not knowable. We cannot observe the phenomenon in all settings and in all circumstances.
It is important to distinguish in your mind the differences between the Problem Statement and Purpose Statement.
The Problem Statement is why I am doing the research
The Purpose Statement is what type of research I am doing to fit or address the problem
The Purpose Statement includes:
- Method of Study
- Specific Population
Remember, as you are contemplating what to include in your purpose statement and then when you are writing it, the purpose statement is a concise paragraph that describes the intent of the study, and it should flow directly from the problem statement. It should specifically address the reason for conducting the study, and reflect the research questions. Further, it should identify the research method as qualitative, quantitative, or mixed. Then provide a brief overview of how the study will be conducted, with what instruments/data collection methods, and with whom (subjects) and where (as applicable). Finally, you should identify variables/constructs and/or phenomenon/concept/idea.
Qualitative Purpose Statement
Creswell (2002) suggested for writing purpose statements in qualitative research include using deliberate phrasing to alert the reader to the purpose statement. Verbs that indicate what will take place in the research and the use of non-directional language that do not suggest an outcome are key. A purpose statement should focus on a single idea or concept, with a broad definition of the idea or concept. How the concept was investigated should also be included, as well as participants in the study and locations for the research to give the reader a sense of with whom and where the study took place.
Creswell (2003) advised the following script for purpose statements in qualitative research:
“The purpose of this qualitative_________________ (strategy of inquiry, such as ethnography, case study, or other type) study is (was? will be?) to ________________ (understand? describe? develop? discover?) the _________________(central phenomenon being studied) for ______________ (the participants, such as the individual, groups, organization) at __________(research site). At this stage in the research, the __________ (central phenomenon being studied) will be generally defined as ___________________ (provide a general definition)” (pg. 90).
Quantitative Purpose Statement
Creswell (2003) offers vast differences between the purpose statements written for qualitative research and those written for quantitative research, particularly with respect to language and the inclusion of variables. The comparison of variables is often a focus of quantitative research, with the variables distinguishable by either the temporal order or how they are measured. As with qualitative research purpose statements, Creswell (2003) recommends the use of deliberate language to alert the reader to the purpose of the study, but quantitative purpose statements also include the theory or conceptual framework guiding the study and the variables that are being studied and how they are related.
Creswell (2003) suggests the following script for drafting purpose statements in quantitative research:
“The purpose of this _____________________ (experiment? survey?) study is (was? will be?) to test the theory of _________________that _________________ (compares? relates?) the ___________(independent variable) to _________________________(dependent variable), controlling for _______________________ (control variables) for ___________________ (participants) at _________________________ (the research site). The independent variable(s) _____________________ will be generally defined as _______________________ (provide a general definition). The dependent variable(s) will be generally defined as _____________________ (provide a general definition), and the control and intervening variables(s), _________________ (identify the control and intervening variables) will be statistically controlled in this study” (pg. 97).
- The purpose of this qualitative study was to determine how participation in service-learning in an alternative school impacted students academically, civically, and personally. There is ample evidence demonstrating the failure of schools for students at-risk; however, there is still a need to demonstrate why these students are successful in non-traditional educational programs like the service-learning model used at TDS. This study was unique in that it examined one alternative school’s approach to service-learning in a setting where students not only serve, but faculty serve as volunteer teachers. The use of a constructivist approach in service-learning in an alternative school setting was examined in an effort to determine whether service-learning participation contributes positively to academic, personal, and civic gain for students, and to examine student and teacher views regarding the overall outcomes of service-learning. This study was completed using an ethnographic approach that included observations, content analysis, and interviews with teachers at The David School.
- The purpose of this quantitative non-experimental cross-sectional linear multiple regression design was to investigate the relationship among early childhood teachers’ self-reported assessment of multicultural awareness as measured by responses from the Teacher Multicultural Attitude Survey (TMAS) and supervisors’ observed assessment of teachers’ multicultural competency skills as measured by the Multicultural Teaching Competency Scale (MTCS) survey. Demographic data such as number of multicultural training hours, years teaching in Dubai, curriculum program at current school, and age were also examined and their relationship to multicultural teaching competency. The study took place in the emirate of Dubai where there were 14,333 expatriate teachers employed in private schools (KHDA, 2013b).
- The purpose of this quantitative, non-experimental study is to examine the degree to which stages of change, gender, acculturation level and trauma types predicts the reluctance of Arab refugees, aged 18 and over, in the Dearborn, MI area, to seek professional help for their mental health needs. This study will utilize four instruments to measure these variables: University of Rhode Island Change Assessment (URICA: DiClemente & Hughes, 1990); Cumulative Trauma Scale (Kira, 2012); Acculturation Rating Scale for Arabic Americans-II Arabic and English (ARSAA-IIA, ARSAA-IIE: Jadalla & Lee, 2013), and a demographic survey. This study will examine 1) the relationship between stages of change, gender, acculturation levels, and trauma types and Arab refugees’ help-seeking behavior, 2) the degree to which any of these variables can predict Arab refugee help-seeking behavior. Additionally, the outcome of this study could provide researchers and clinicians with a stage-based model, TTM, for measuring Arab refugees’ help-seeking behavior and lay a foundation for how TTM can help target the clinical needs of Arab refugees. Lastly, this attempt to apply the TTM model to Arab refugees’ condition could lay the foundation for future research to investigate the application of TTM to clinical work among refugee populations.
- The purpose of this qualitative, phenomenological study is to describe the lived experiences of LLM for 10 EFL learners in rural Guatemala and to utilize that data to determine how it conforms to, or possibly challenges, current theoretical conceptions of LLM. In accordance with Morse’s (1994) suggestion that a phenomenological study should utilize at least six participants, this study utilized semi-structured interviews with 10 EFL learners to explore why and how they have experienced the motivation to learn English throughout their lives. The methodology of horizontalization was used to break the interview protocols into individual units of meaning before analyzing these units to extract the overarching themes (Moustakas, 1994). These themes were then interpreted into a detailed description of LLM as experienced by EFL students in this context. Finally, the resulting description was analyzed to discover how these learners’ lived experiences with LLM conformed with and/or diverged from current theories of LLM.
- The purpose of this qualitative, embedded, multiple case study was to examine how both parent-child attachment relationships are impacted by the quality of the paternal and maternal caregiver-child interactions that occur throughout a maternal deployment, within the context of dual-military couples. In order to examine this phenomenon, an embedded, multiple case study was conducted, utilizing an attachment systems metatheory perspective. The study included four dual-military couples who experienced a maternal deployment to Operation Iraqi Freedom (OIF) or Operation Enduring Freedom (OEF) when they had at least one child between 8 weeks-old to 5 years-old. Each member of the couple participated in an individual, semi-structured interview with the researcher and completed the Parenting Relationship Questionnaire (PRQ). “The PRQ is designed to capture a parent’s perspective on the parent-child relationship” (Pearson, 2012, para. 1) and was used within the proposed study for this purpose. The PRQ was utilized to triangulate the data (Bekhet & Zauszniewski, 2012) as well as to provide some additional information on the parents’ perspective of the quality of the parent-child attachment relationship in regards to communication, discipline, parenting confidence, relationship satisfaction, and time spent together (Pearson, 2012). The researcher utilized the semi-structured interview to collect information regarding the parents' perspectives of the quality of their parental caregiver behaviors during the deployment cycle, the mother's parent-child interactions while deployed, the behavior of the child or children at time of reunification, and the strategies or behaviors the parents believe may have contributed to their child's behavior at the time of reunification. The results of this study may be utilized by the military, and by civilian providers, to develop proactive and preventive measures that both providers and parents can implement, to address any potential adverse effects on the parent-child attachment relationship, identified through the proposed study. The results of this study may also be utilized to further refine and understand the integration of attachment theory and systems theory, in both clinical and research settings, within the field of marriage and family therapy.
Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Problem Statement
- Next: Alignment >>
- Last Updated: Oct 23, 2024 6:26 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1006886

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information
From John W. Creswell \(2016\). 30 Essential Skills for the Qualitative Researcher \ . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Thesis and Purpose Statements
Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements.
In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools.
A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be restricted or clarified and eventually worked into an introduction.
As you revise your paper, try to phrase your thesis or purpose statement in a precise way so that it matches the content and organization of your paper.
Thesis statements
A thesis statement is a sentence that makes an assertion about a topic and predicts how the topic will be developed. It does not simply announce a topic: it says something about the topic.
Good: X has made a significant impact on the teenage population due to its . . . Bad: In this paper, I will discuss X.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic.
A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire paragraph.
A thesis statement is focused and specific enough to be proven within the boundaries of the paper. Key words (nouns and verbs) should be specific, accurate, and indicative of the range of research, thrust of the argument or analysis, and the organization of supporting information.
Purpose statements
A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be.
Common beginnings include:
“This paper examines . . .,” “The aim of this paper is to . . .,” and “The purpose of this essay is to . . .”
A purpose statement makes a promise to the reader about the development of the argument but does not preview the particular conclusions that the writer has drawn.
A purpose statement usually appears toward the end of the introduction. The purpose statement may be expressed in several sentences or even an entire paragraph.
A purpose statement is specific enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. Purpose statements are common in research papers in some academic disciplines, while in other disciplines they are considered too blunt or direct. If you are unsure about using a purpose statement, ask your instructor.
This paper will examine the ecological destruction of the Sahel preceding the drought and the causes of this disintegration of the land. The focus will be on the economic, political, and social relationships which brought about the environmental problems in the Sahel.
Sample purpose and thesis statements
The following example combines a purpose statement and a thesis statement (bold).
The goal of this paper is to examine the effects of Chile’s agrarian reform on the lives of rural peasants. The nature of the topic dictates the use of both a chronological and a comparative analysis of peasant lives at various points during the reform period. . . The Chilean reform example provides evidence that land distribution is an essential component of both the improvement of peasant conditions and the development of a democratic society. More extensive and enduring reforms would likely have allowed Chile the opportunity to further expand these horizons.
For more tips about writing thesis statements, take a look at our new handout on Developing a Thesis Statement.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Research Questions & Hypotheses
Generally, in quantitative studies, reviewers expect hypotheses rather than research questions. However, both research questions and hypotheses serve different purposes and can be beneficial when used together.
Research Questions
Clarify the research’s aim (farrugia et al., 2010).
- Research often begins with an interest in a topic, but a deep understanding of the subject is crucial to formulate an appropriate research question.
- Descriptive: “What factors most influence the academic achievement of senior high school students?”
- Comparative: “What is the performance difference between teaching methods A and B?”
- Relationship-based: “What is the relationship between self-efficacy and academic achievement?”
- Increasing knowledge about a subject can be achieved through systematic literature reviews, in-depth interviews with patients (and proxies), focus groups, and consultations with field experts.
- Some funding bodies, like the Canadian Institute for Health Research, recommend conducting a systematic review or a pilot study before seeking grants for full trials.
- The presence of multiple research questions in a study can complicate the design, statistical analysis, and feasibility.
- It’s advisable to focus on a single primary research question for the study.
- The primary question, clearly stated at the end of a grant proposal’s introduction, usually specifies the study population, intervention, and other relevant factors.
- The FINER criteria underscore aspects that can enhance the chances of a successful research project, including specifying the population of interest, aligning with scientific and public interest, clinical relevance, and contribution to the field, while complying with ethical and national research standards.
- The P ICOT approach is crucial in developing the study’s framework and protocol, influencing inclusion and exclusion criteria and identifying patient groups for inclusion.
- Defining the specific population, intervention, comparator, and outcome helps in selecting the right outcome measurement tool.
- The more precise the population definition and stricter the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the more significant the impact on the interpretation, applicability, and generalizability of the research findings.
- A restricted study population enhances internal validity but may limit the study’s external validity and generalizability to clinical practice.
- A broadly defined study population may better reflect clinical practice but could increase bias and reduce internal validity.
- An inadequately formulated research question can negatively impact study design, potentially leading to ineffective outcomes and affecting publication prospects.
Checklist: Good research questions for social science projects (Panke, 2018)
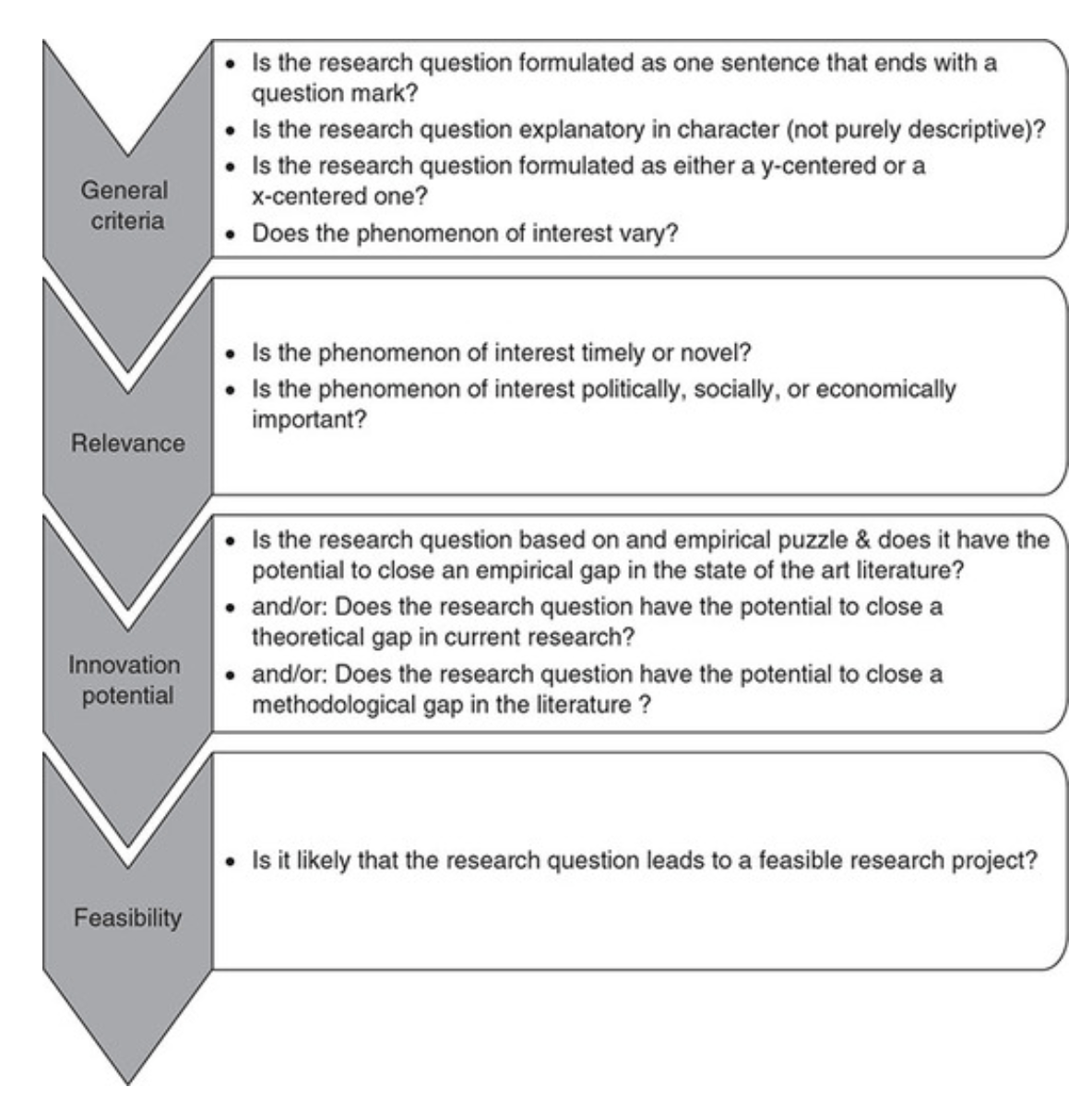
Research Hypotheses
Present the researcher’s predictions based on specific statements.
- These statements define the research problem or issue and indicate the direction of the researcher’s predictions.
- Formulating the research question and hypothesis from existing data (e.g., a database) can lead to multiple statistical comparisons and potentially spurious findings due to chance.
- The research or clinical hypothesis, derived from the research question, shapes the study’s key elements: sampling strategy, intervention, comparison, and outcome variables.
- Hypotheses can express a single outcome or multiple outcomes.
- After statistical testing, the null hypothesis is either rejected or not rejected based on whether the study’s findings are statistically significant.
- Hypothesis testing helps determine if observed findings are due to true differences and not chance.
- Hypotheses can be 1-sided (specific direction of difference) or 2-sided (presence of a difference without specifying direction).
- 2-sided hypotheses are generally preferred unless there’s a strong justification for a 1-sided hypothesis.
- A solid research hypothesis, informed by a good research question, influences the research design and paves the way for defining clear research objectives.
Types of Research Hypothesis
- In a Y-centered research design, the focus is on the dependent variable (DV) which is specified in the research question. Theories are then used to identify independent variables (IV) and explain their causal relationship with the DV.
- Example: “An increase in teacher-led instructional time (IV) is likely to improve student reading comprehension scores (DV), because extensive guided practice under expert supervision enhances learning retention and skill mastery.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: The dependent variable (student reading comprehension scores) is the focus, and the hypothesis explores how changes in the independent variable (teacher-led instructional time) affect it.
- In X-centered research designs, the independent variable is specified in the research question. Theories are used to determine potential dependent variables and the causal mechanisms at play.
- Example: “Implementing technology-based learning tools (IV) is likely to enhance student engagement in the classroom (DV), because interactive and multimedia content increases student interest and participation.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: The independent variable (technology-based learning tools) is the focus, with the hypothesis exploring its impact on a potential dependent variable (student engagement).
- Probabilistic hypotheses suggest that changes in the independent variable are likely to lead to changes in the dependent variable in a predictable manner, but not with absolute certainty.
- Example: “The more teachers engage in professional development programs (IV), the more their teaching effectiveness (DV) is likely to improve, because continuous training updates pedagogical skills and knowledge.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: This hypothesis implies a probable relationship between the extent of professional development (IV) and teaching effectiveness (DV).
- Deterministic hypotheses state that a specific change in the independent variable will lead to a specific change in the dependent variable, implying a more direct and certain relationship.
- Example: “If the school curriculum changes from traditional lecture-based methods to project-based learning (IV), then student collaboration skills (DV) are expected to improve because project-based learning inherently requires teamwork and peer interaction.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: This hypothesis presumes a direct and definite outcome (improvement in collaboration skills) resulting from a specific change in the teaching method.
- Example : “Students who identify as visual learners will score higher on tests that are presented in a visually rich format compared to tests presented in a text-only format.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis aims to describe the potential difference in test scores between visual learners taking visually rich tests and text-only tests, without implying a direct cause-and-effect relationship.
- Example : “Teaching method A will improve student performance more than method B.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis compares the effectiveness of two different teaching methods, suggesting that one will lead to better student performance than the other. It implies a direct comparison but does not necessarily establish a causal mechanism.
- Example : “Students with higher self-efficacy will show higher levels of academic achievement.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis predicts a relationship between the variable of self-efficacy and academic achievement. Unlike a causal hypothesis, it does not necessarily suggest that one variable causes changes in the other, but rather that they are related in some way.
Tips for developing research questions and hypotheses for research studies
- Perform a systematic literature review (if one has not been done) to increase knowledge and familiarity with the topic and to assist with research development.
- Learn about current trends and technological advances on the topic.
- Seek careful input from experts, mentors, colleagues, and collaborators to refine your research question as this will aid in developing the research question and guide the research study.
- Use the FINER criteria in the development of the research question.
- Ensure that the research question follows PICOT format.
- Develop a research hypothesis from the research question.
- Ensure that the research question and objectives are answerable, feasible, and clinically relevant.
If your research hypotheses are derived from your research questions, particularly when multiple hypotheses address a single question, it’s recommended to use both research questions and hypotheses. However, if this isn’t the case, using hypotheses over research questions is advised. It’s important to note these are general guidelines, not strict rules. If you opt not to use hypotheses, consult with your supervisor for the best approach.
Farrugia, P., Petrisor, B. A., Farrokhyar, F., & Bhandari, M. (2010). Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Canadian journal of surgery. Journal canadien de chirurgie , 53 (4), 278–281.
Hulley, S. B., Cummings, S. R., Browner, W. S., Grady, D., & Newman, T. B. (2007). Designing clinical research. Philadelphia.
Panke, D. (2018). Research design & method selection: Making good choices in the social sciences. Research Design & Method Selection , 1-368.

Research Problem vs. Research Question
What's the difference.
Research problem and research question are two essential components of any research study. The research problem refers to the issue or gap in knowledge that the researcher aims to address through their study. It identifies the area of research that requires further investigation and highlights the significance of the study. On the other hand, the research question is a specific inquiry that the researcher formulates to guide their investigation. It is a concise and focused query that helps to narrow down the research problem and provides a clear direction for the study. While the research problem sets the broader context, the research question provides a specific and measurable objective for the research study.
Further Detail
Introduction.
Research is a systematic process that involves the exploration and investigation of a particular topic or issue. It aims to generate new knowledge, solve problems, or answer specific questions. In any research endeavor, it is crucial to clearly define the research problem and research question. While they are closely related, they have distinct attributes that shape the research process. This article will delve into the characteristics of research problems and research questions, highlighting their similarities and differences.
Research Problem
A research problem is the foundation of any research study. It refers to an area of concern or a gap in knowledge that requires investigation. Identifying a research problem is the initial step in the research process, as it sets the direction and purpose of the study. A research problem should be specific, clear, and well-defined to guide the research process effectively.
One of the key attributes of a research problem is that it should be significant. It should address an issue that has practical or theoretical implications and contributes to the existing body of knowledge. A significant research problem has the potential to make a positive impact on society, industry, or academia.
Furthermore, a research problem should be researchable. This means that it should be feasible to investigate and gather relevant data to address the problem. It should be within the researcher's capabilities and resources to conduct the study. A research problem that is too broad or vague may hinder the research process and lead to inconclusive results.
Additionally, a research problem should be specific and well-defined. It should clearly state the variables or concepts under investigation and provide a clear focus for the study. A well-defined research problem helps in formulating research questions and hypotheses, as it narrows down the scope of the study.
Lastly, a research problem should be original. It should contribute to the existing body of knowledge by addressing a gap or extending previous research. Originality ensures that the research study adds value and novelty to the field, making it relevant and interesting to researchers and practitioners.
Research Question
A research question is a specific inquiry that guides the research process and aims to provide an answer or solution to the research problem. It is derived from the research problem and helps in focusing the study, collecting relevant data, and analyzing the findings. A well-formulated research question is crucial for conducting a successful research study.
Similar to a research problem, a research question should be clear and specific. It should be concise and focused on a particular aspect of the research problem. A clear research question helps in determining the appropriate research design, methodology, and data collection techniques.
Furthermore, a research question should be answerable. It should be feasible to gather data and evidence to address the research question. An answerable research question ensures that the research study is practical and achievable within the given constraints.
A research question should also be relevant. It should directly relate to the research problem and contribute to the existing body of knowledge. A relevant research question ensures that the study has significance and value in the field, making it meaningful to researchers and stakeholders.
Lastly, a research question should be specific to the research context. It should consider the scope, objectives, and limitations of the study. A specific research question helps in avoiding ambiguity and ensures that the research study remains focused and coherent.
While research problems and research questions share some similarities, they also have distinct attributes that differentiate them. Both research problems and research questions should be clear, specific, and relevant to the research study. They should address a gap in knowledge and contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
However, a research problem is broader in scope compared to a research question. It sets the overall direction and purpose of the study, while a research question focuses on a specific aspect or inquiry within the research problem. A research problem provides a broader context for the study, while a research question narrows down the focus and guides the investigation.
Another difference lies in their formulation. A research problem is typically formulated as a statement or a declarative sentence, highlighting the area of concern or gap in knowledge. On the other hand, a research question is formulated as an interrogative sentence, posing a specific inquiry that needs to be answered or explored.
Furthermore, a research problem is often derived from a literature review or an analysis of existing research. It identifies the gap or area of concern based on the current state of knowledge. On the contrary, a research question is derived from the research problem itself. It is formulated to address the specific aspect or inquiry identified in the research problem.
Lastly, a research problem is usually stated at the beginning of a research study, while research questions are developed during the research design phase. The research problem sets the foundation for the study, while research questions are refined and finalized based on the research problem and objectives.
In conclusion, research problems and research questions are essential components of any research study. While they share similarities in terms of being clear, specific, and relevant, they also have distinct attributes that shape the research process. A research problem sets the overall direction and purpose of the study, while research questions focus on specific inquiries within the research problem. Both are crucial in guiding the research process, collecting relevant data, and generating new knowledge. By understanding the attributes of research problems and research questions, researchers can effectively design and conduct their studies, contributing to the advancement of knowledge in their respective fields.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.

- Research Group
- Job Seekers

Research Tips
Understanding the Difference between Research Questions and Objectives
January 13, 2023
When conducting research, clearly understanding the difference between research questions and objectives is important. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they refer to two distinct aspects of the research process.
Research questions are broad statements that guide the overall direction of the research. They identify the main problem or area of inquiry that the research will address. For example, a research question might be, "What is the impact of social media on teenage mental health?" This question sets the stage for the research and helps to define the scope of the study.

- Research questions are more general and open-ended, while objectives are specific and measurable.
- Research questions identify the main problem or area of inquiry, while objectives define the specific outcomes that the researcher is looking to achieve.
- Research questions help define the study's scope, while objectives help guide the research process.
- Research questions are often used to generate hypotheses or identify gaps in existing knowledge, while objectives are used to establish clear and achievable targets for the research.
- Research questions and objectives are not mutually exclusive, but well-defined research questions should lead to specific objectives necessary to answer the question.
On the other hand, research objectives are specific, measurable goals that the research aims to achieve. They are used to guide the research process and help to define the specific outcomes that the researcher is looking to achieve. For example, an objective for the above research question might be "To determine the correlation between social media usage and rates of depression in teenagers." This objective is more specific and measurable than the research question and helps define the specific outcomes that the researcher is looking to achieve.
It is important to note that research questions and objectives are not mutually exclusive; a study can have one or several questions and objectives. A well-defined research question should lead to specific objectives necessary to answer the question.
In summary, research questions and objectives are two distinct aspects of the research process. Research questions are broad statements that guide the overall direction of the research, while research objectives are specific, measurable goals that the research aims to achieve. Understanding these two terms' differences is essential for conducting effective and meaningful research.

Organizing Academic Research Papers: The Research Problem/Question
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
A research problem is a statement about an area of concern, a condition to be improved, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or in practice that points to the need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation. In some social science disciplines the research problem is typically posed in the form of a question. A research problem does not state how to do something, offer a vague or broad proposition, or present a value question.
Importance of...
The purpose of a problem statement is to:
- Introduce the reader to the importance of the topic being studied . The reader is oriented to the significance of the study and the research questions or hypotheses to follow.
- Places the problem into a particular context that defines the parameters of what is to be investigated.
- Provides the framework for reporting the results and indicates what is probably necessary to conduct the study and explain how the findings will present this information.
In the social sciences, the research problem establishes the means by which you must answer the "So What?" question. The "So What?" question refers to a research problem surviving the relevancy test [the quality of a measurement procedure that provides repeatability and accuracy]. Note that answering the "So What" question requires a commitment on your part to not only show that you have researched the material, but that you have thought about its significance.
To survive the "So What" question, problem statements should possess the following attributes:
- Clarity and precision [a well-written statement does not make sweeping generalizations and irresponsible statements],
- Identification of what would be studied, while avoiding the use of value-laden words and terms,
- Identification of an overarching question and key factors or variables,
- Identification of key concepts and terms,
- Articulation of the study's boundaries or parameters,
- Some generalizability in regards to applicability and bringing results into general use,
- Conveyance of the study's importance, benefits, and justification [regardless of the type of research, it is important to address the “so what” question by demonstrating that the research is not trivial],
- Does not have unnecessary jargon; and,
- Conveyance of more than the mere gathering of descriptive data providing only a snapshot of the issue or phenomenon under investigation.
Castellanos, Susie. Critical Writing and Thinking . The Writing Center. Dean of the College. Brown University; Ellis, Timothy J. and Yair Levy Nova Framework of Problem-Based Research: A Guide for Novice Researchers on the Development of a Research-Worthy Problem. Informing Science: the International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline 11 (2008); Thesis and Purpose Statements . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Thesis Statements . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Types and Content
There are four general conceptualizations of a research problem in the social sciences:
- Casuist Research Problem -- this type of problem relates to the determination of right and wrong in questions of conduct or conscience by analyzing moral dilemmas through the application of general rules and the careful distinction of special cases.
- Difference Research Problem -- typically asks the question, “Is there a difference between two or more groups or treatments?” This type of problem statement is used when the researcher compares or contrasts two or more phenomena.
- Descriptive Research Problem -- typically asks the question, "what is...?" with the underlying purpose to describe a situation, state, or existence of a specific phenomenon.
- Relational Research Problem -- suggests a relationship of some sort between two or more variables to be investigated. The underlying purpose is to investigate qualities/characteristics that are connected in some way.
A problem statement in the social sciences should contain :
- A lead-in that helps ensure the reader will maintain interest over the study
- A declaration of originality [e.g., mentioning a knowledge void, which would be supported by the literature review]
- An indication of the central focus of the study, and
- An explanation of the study's significance or the benefits to be derived from an investigating the problem.
II. Sources of Problems for Investigation
Identifying a problem to study can be challenging, not because there is a lack of issues that could be investigated, but due to pursuing a goal of formulating a socially relevant and researchable problem statement that is unique and does not simply duplicate the work of others. To facilitate how you might select a problem from which to build a research study, consider these three broad sources of inspiration:
Deductions from Theory This relates to deductions made from social philosophy or generalizations embodied in life in society that the researcher is familiar with. These deductions from human behavior are then fitted within an empirical frame of reference through research. From a theory, the research can formulate a research problem or hypothesis stating the expected findings in certain empirical situations. The research asks the question: “What relationship between variables will be observed if theory aptly summarizes the state of affairs?” One can then design and carry out a systematic investigation to assess whether empirical data confirm or reject the hypothesis and hence the theory.
Interdisciplinary Perspectives Identifying a problem that forms the basis for a research study can come from academic movements and scholarship originating in disciplines outside of your primary area of study. A review of pertinent literature should include examining research from related disciplines, which can expose you to new avenues of exploration and analysis. An interdisciplinary approach to selecting a research problem offers an opportunity to construct a more comprehensive understanding of a very complex issue than any single discipline might provide.
Interviewing Practitioners The identification of research problems about particular topics can arise from formal or informal discussions with practitioners who provide insight into new directions for future research and how to make research findings increasingly relevant to practice. Discussions with experts in the field, such as, teachers, social workers, health care providers, etc., offers the chance to identify practical, “real worl” problems that may be understudied or ignored within academic circles. This approach also provides some practical knowledge which may help in the process of designing and conducting your study.
Personal Experience Your everyday experiences can give rise to worthwhile problems for investigation. Think critically about your own experiences and/or frustrations with an issue facing society, your community, or in your neighborhood. This can be derived, for example, from deliberate observations of certain relationships for which there is no clear explanation or witnessing an event that appears harmful to a person or group or that is out of the ordinary.
Relevant Literature The selection of a research problem can often be derived from an extensive and thorough review of pertinent research associated with your overall area of interest. This may reveal where gaps remain in our understanding of a topic. Research may be conducted to: 1) fill such gaps in knowledge; 2) evaluate if the methodologies employed in prior studies can be adapted to solve other problems; or, 3) determine if a similar study could be conducted in a different subject area or applied to different study sample [i.e., different groups of people]. Also, authors frequently conclude their studies by noting implications for further research; this can also be a valuable source of problems to investigate.
III. What Makes a Good Research Statement?
A good problem statement begins by introducing the broad area in which your research is centered and then gradually leads the reader to the more narrow questions you are posing. The statement need not be lengthy but a good research problem should incorporate the following features:
Compelling topic Simple curiosity is not a good enough reason to pursue a research study. The problem that you choose to explore must be important to you and to a larger community you share. The problem chosen must be one that motivates you to address it. Supports multiple perspectives The problem most be phrased in a way that avoids dichotomies and instead supports the generation and exploration of multiple perspectives. A general rule of thumb is that a good research problem is one that would generate a variety of viewpoints from a composite audience made up of reasonable people. Researchable It seems a bit obvious, but you don't want to find yourself in the midst of investigating a complex research project and realize that you don't have much to draw on for your research. Choose research problems that can be supported by the resources available to you. Not sure? Seek out help from a librarian!
NOTE: Do not confuse a research problem with a research topic. A topic is something to read and obtain information about whereas a problem is something to solve or framed as a question that must be answered.
IV. Mistakes to Avoid
Beware of circular reasoning . Don’t state that the research problem as simply the absence of the thing you are suggesting. For example, if you propose, "The problem in this community is that it has no hospital."
This only leads to a research problem where:
- The need is for a hospital
- The objective is to create a hospital
- The method is to plan for building a hospital, and
- The evaluation is to measure if there is a hospital or not.
This is an example of a research problem that fails the "so what?" test because it does not reveal the relevance of why you are investigating the problem of having no hospital in the community [e.g., there's a hospital in the community ten miles away] and because the research problem does not elucidate the significance of why one should study the fact that no hospital exists in the community [e.g., that hospital in the community ten miles away has no emergency room].
Choosing and Refining Topics . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Ellis, Timothy J. and Yair Levy Nova Framework of Problem-Based Research: A Guide for Novice Researchers on the Development of a Research-Worthy Problem. Informing Science: the International Journal of an Emerging Transdiscipline 11 (2008); How to Write a Research Question . The Writing Center. George Mason University; Invention: Developing a Thesis Statement . The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; Problem Statements PowerPoint Presentation . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Procter, Margaret. Using Thesis Statements . University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Trochim, William M.K. Problem Formulation . Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Thesis and Purpose Statements . The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Thesis Statements . The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
- << Previous: Background Information
- Next: Theoretical Framework >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON

The Research Problem & Statement

I f you’re new to academic research, you’re bound to encounter the concept of a “ research problem ” or “ problem statement ” fairly early in your learning journey. Having a good research problem is essential, as it provides a foundation for developing high-quality research, from relatively small research papers to a full-length PhD dissertations and theses.
In this post, we’ll unpack what a research problem is and how it’s related to a problem statement . We’ll also share some examples and provide a step-by-step process you can follow to identify and evaluate study-worthy research problems for your own project.
Overview: Research Problem 101
What is a research problem.
- What is a problem statement?
Where do research problems come from?
- How to find a suitable research problem
- Key takeaways
A research problem is, at the simplest level, the core issue that a study will try to solve or (at least) examine. In other words, it’s an explicit declaration about the problem that your dissertation, thesis or research paper will address. More technically, it identifies the research gap that the study will attempt to fill (more on that later).
Let’s look at an example to make the research problem a little more tangible.
To justify a hypothetical study, you might argue that there’s currently a lack of research regarding the challenges experienced by first-generation college students when writing their dissertations [ PROBLEM ] . As a result, these students struggle to successfully complete their dissertations, leading to higher-than-average dropout rates [ CONSEQUENCE ]. Therefore, your study will aim to address this lack of research – i.e., this research problem [ SOLUTION ].
A research problem can be theoretical in nature, focusing on an area of academic research that is lacking in some way. Alternatively, a research problem can be more applied in nature, focused on finding a practical solution to an established problem within an industry or an organisation. In other words, theoretical research problems are motivated by the desire to grow the overall body of knowledge , while applied research problems are motivated by the need to find practical solutions to current real-world problems (such as the one in the example above).
As you can probably see, the research problem acts as the driving force behind any study , as it directly shapes the research aims, objectives and research questions , as well as the research approach. Therefore, it’s really important to develop a very clearly articulated research problem before you even start your research proposal . A vague research problem will lead to unfocused, potentially conflicting research aims, objectives and research questions .

What is a research problem statement?
As the name suggests, a problem statement (within a research context, at least) is an explicit statement that clearly and concisely articulates the specific research problem your study will address. While your research problem can span over multiple paragraphs, your problem statement should be brief , ideally no longer than one paragraph . Importantly, it must clearly state what the problem is (whether theoretical or practical in nature) and how the study will address it.
Here’s an example of a statement of the problem in a research context:
Rural communities across Ghana lack access to clean water, leading to high rates of waterborne illnesses and infant mortality. Despite this, there is little research investigating the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects within the Ghanaian context. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the effectiveness of such projects in improving access to clean water and reducing rates of waterborne illnesses in these communities.
As you can see, this problem statement clearly and concisely identifies the issue that needs to be addressed (i.e., a lack of research regarding the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects) and the research question that the study aims to answer (i.e., are community-led water supply projects effective in reducing waterborne illnesses?), all within one short paragraph.
Need a helping hand?
Wherever there is a lack of well-established and agreed-upon academic literature , there is an opportunity for research problems to arise, since there is a paucity of (credible) knowledge. In other words, research problems are derived from research gaps . These gaps can arise from various sources, including the emergence of new frontiers or new contexts, as well as disagreements within the existing research.
Let’s look at each of these scenarios:
New frontiers – new technologies, discoveries or breakthroughs can open up entirely new frontiers where there is very little existing research, thereby creating fresh research gaps. For example, as generative AI technology became accessible to the general public in 2023, the full implications and knock-on effects of this were (or perhaps, still are) largely unknown and therefore present multiple avenues for researchers to explore.
New contexts – very often, existing research tends to be concentrated on specific contexts and geographies. Therefore, even within well-studied fields, there is often a lack of research within niche contexts. For example, just because a study finds certain results within a western context doesn’t mean that it would necessarily find the same within an eastern context. If there’s reason to believe that results may vary across these geographies, a potential research gap emerges.
Disagreements – within many areas of existing research, there are (quite naturally) conflicting views between researchers, where each side presents strong points that pull in opposing directions. In such cases, it’s still somewhat uncertain as to which viewpoint (if any) is more accurate. As a result, there is room for further research in an attempt to “settle” the debate.
Of course, many other potential scenarios can give rise to research gaps, and consequently, research problems, but these common ones are a useful starting point. If you’re interested in research gaps, you can learn more here .
How to find a research problem
Given that research problems flow from research gaps , finding a strong research problem for your research project means that you’ll need to first identify a clear research gap. Below, we’ll present a four-step process to help you find and evaluate potential research problems.
If you’ve read our other articles about finding a research topic , you’ll find the process below very familiar as the research problem is the foundation of any study . In other words, finding a research problem is much the same as finding a research topic.
Step 1 – Identify your area of interest
Naturally, the starting point is to first identify a general area of interest . Chances are you already have something in mind, but if not, have a look at past dissertations and theses within your institution to get some inspiration. These present a goldmine of information as they’ll not only give you ideas for your own research, but they’ll also help you see exactly what the norms and expectations are for these types of projects.
At this stage, you don’t need to get super specific. The objective is simply to identify a couple of potential research areas that interest you. For example, if you’re undertaking research as part of a business degree, you may be interested in social media marketing strategies for small businesses, leadership strategies for multinational companies, etc.
Depending on the type of project you’re undertaking, there may also be restrictions or requirements regarding what topic areas you’re allowed to investigate, what type of methodology you can utilise, etc. So, be sure to first familiarise yourself with your institution’s specific requirements and keep these front of mind as you explore potential research ideas.
Step 2 – Review the literature and develop a shortlist
Once you’ve decided on an area that interests you, it’s time to sink your teeth into the literature . In other words, you’ll need to familiarise yourself with the existing research regarding your interest area. Google Scholar is a good starting point for this, as you can simply enter a few keywords and quickly get a feel for what’s out there. Keep an eye out for recent literature reviews and systematic review-type journal articles, as these will provide a good overview of the current state of research.
At this stage, you don’t need to read every journal article from start to finish . A good strategy is to pay attention to the abstract, intro and conclusion , as together these provide a snapshot of the key takeaways. As you work your way through the literature, keep an eye out for what’s missing – in other words, what questions does the current research not answer adequately (or at all)? Importantly, pay attention to the section titled “ further research is needed ”, typically found towards the very end of each journal article. This section will specifically outline potential research gaps that you can explore, based on the current state of knowledge (provided the article you’re looking at is recent).
Take the time to engage with the literature and develop a big-picture understanding of the current state of knowledge. Reviewing the literature takes time and is an iterative process , but it’s an essential part of the research process, so don’t cut corners at this stage.
As you work through the review process, take note of any potential research gaps that are of interest to you. From there, develop a shortlist of potential research gaps (and resultant research problems) – ideally 3 – 5 options that interest you.

Step 3 – Evaluate your potential options
Once you’ve developed your shortlist, you’ll need to evaluate your options to identify a winner. There are many potential evaluation criteria that you can use, but we’ll outline three common ones here: value, practicality and personal appeal.
Value – a good research problem needs to create value when successfully addressed. Ask yourself:
- Who will this study benefit (e.g., practitioners, researchers, academia)?
- How will it benefit them specifically?
- How much will it benefit them?
Practicality – a good research problem needs to be manageable in light of your resources. Ask yourself:
- What data will I need access to?
- What knowledge and skills will I need to undertake the analysis?
- What equipment or software will I need to process and/or analyse the data?
- How much time will I need?
- What costs might I incur?
Personal appeal – a research project is a commitment, so the research problem that you choose needs to be genuinely attractive and interesting to you. Ask yourself:
- How appealing is the prospect of solving this research problem (on a scale of 1 – 10)?
- Why, specifically, is it attractive (or unattractive) to me?
- Does the research align with my longer-term goals (e.g., career goals, educational path, etc)?
Depending on how many potential options you have, you may want to consider creating a spreadsheet where you numerically rate each of the options in terms of these criteria. Remember to also include any criteria specified by your institution . From there, tally up the numbers and pick a winner.
Step 4 – Craft your problem statement
Once you’ve selected your research problem, the final step is to craft a problem statement. Remember, your problem statement needs to be a concise outline of what the core issue is and how your study will address it. Aim to fit this within one paragraph – don’t waffle on. Have a look at the problem statement example we mentioned earlier if you need some inspiration.
Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- A research problem is an explanation of the issue that your study will try to solve. This explanation needs to highlight the problem , the consequence and the solution or response.
- A problem statement is a clear and concise summary of the research problem , typically contained within one paragraph.
- Research problems emerge from research gaps , which themselves can emerge from multiple potential sources, including new frontiers, new contexts or disagreements within the existing literature.
- To find a research problem, you need to first identify your area of interest , then review the literature and develop a shortlist, after which you’ll evaluate your options, select a winner and craft a problem statement .

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
I APPRECIATE YOUR CONCISE AND MIND-CAPTIVATING INSIGHTS ON THE STATEMENT OF PROBLEMS. PLEASE I STILL NEED SOME SAMPLES RELATED TO SUICIDES.
Very pleased and appreciate clear information.
Your videos and information have been a life saver for me throughout my dissertation journey. I wish I’d discovered them sooner. Thank you!
Very interesting. Thank you. Please I need a PhD topic in climate change in relation to health.
Your posts have provided a clear, easy to understand, motivating literature, mainly when these topics tend to be considered “boring” in some careers.
Thank you, but i am requesting for a topic in records management
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This entry was posted in Research and tagged research on December 14, 2014. Four key components to a research project are the purpose statement, research questions, hypotheses, and research objectives. In this post, we will define each of these. Definitions The purpose statement provides the reader with the overall focus and direction of a study.
between the purpose statement, the research problem, and the research questions. The purpose statement sets forth the intent of the study, not the problem or issue leading to a need for the study (see Chapter 5). The purpose is also not the research questions—those questions that the data collection will attempt to answer (discussed in ...
Good purpose statements: Flow from the problem statement and actually address the proposed problem. Are concise and clear. Answer the question 'Why are you doing this research?'. Match the methodology (similar to research questions) Have a 'hook' to get the reader's attention.
Research Questions and Hypotheses I nvestigators place signposts to carry the reader through a plan for a study. The first signpost is the purpose statement, which establishes the central direction for the study. From the broad, general purpose state-ment, the researcher narrows the focus to specific questions to be
The purpose statement is the overall objective or intent of the study. In some projects it is called the "study aim.". It is the most important statement in your qualitative study. It is a statement that conveys the essence of a project. A central question is a single general question that reframes the purpose into a specific question.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic. A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire ...
Research Aims: Examples. True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording "this research aims to…", "this research seeks to…", and so on. For example: "This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.". "This study sets out to assess the interaction between student ...
The primary research question should originate from the hypothesis, not the data, and be established before starting the study. Formulating the research question and hypothesis from existing data (e.g., a database) can lead to multiple statistical comparisons and potentially spurious findings due to chance.
for designing a research question), purpose statements, research ques-tions, keywords, data collection strategies, and data collection tools. Table 2.1 outlines the foundational connections between the research design, guiding questions, and the purpose statement. In this table (2.1), the purpose statement is presented as an . example. Table 2. ...
esearch question for a study, depending on the complex-ity and breadth of your proposed work. Each question should be clear and specific, refer to the problem or phenomenon, reflect an inter. ention in experimental work, and note the target population or participants (see Figure 2.1). Identifying a research question will provide greater focus ...
Research Question; Definition: A statement that identifies an area of concern or knowledge gap to be addressed through research. ... Identifying a research problem is the initial step in the research process, as it sets the direction and purpose of the study. A research problem should be specific, clear, and well-defined to guide the research ...
A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement. A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Chapter six includes a discussion of problem and purpose statements with examples of each. Research questions and hypotheses are included with examples from qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods research designs.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
Research questions are more general and open-ended, while objectives are specific and measurable. Research questions identify the main problem or area of inquiry, while objectives define the specific outcomes that the researcher is looking to achieve. Research questions help define the study's scope, while objectives help guide the research ...
A research problem is a statement about an area of concern, a condition to be improved, a difficulty to be eliminated, or a troubling question that exists in scholarly literature, in theory, or in practice that points to the need for meaningful understanding and deliberate investigation. In some social science disciplines the research problem is typically posed in the form of a question.
Purpose Statement. The importance of a clearly articulated purpose statement cannot be underestimated. First and foremost, the purpose statement informs the reader of the primary reason for conducting the research study. In a research article, the purpose statement is most commonly found at the end of the background/literature review section.
Consistency in the title, problem, purpose, and research question improve the logic and transparency of research. When these components of research are aligned research design and planning are more coherent and research reports are more readable.This article reviews the process for checking for and improving consistency.Numerous examples of consistency among these four components of research ...
From there, tally up the numbers and pick a winner. Step 4 - Craft your problem statement. Once you've selected your research problem, the final step is to craft a problem statement. Remember, your problem statement needs to be a concise outline of what the core issue is and how your study will address it.