- Log in
- Site search

International Relations
Entry requirements.
The minimum entry requirement for this programme is a high merit (65+) in a master’s degree in a subject relevant to the proposed research with high merit (65+) in the dissertation element, or equivalent. Applications which do not meet these criteria (or do not expect to do so on completion of any pending qualifications) are not considered eligible.
Months of entry
Course content.
About the MPhil/PhD programme
This programme offers you the chance to be part of one of the world's leading departments in the study of international relations while you undertake a substantial piece of work that is worthy of publication and which makes an original contribution to international relations. You will begin on the MPhil and be upgraded to PhD status after passing a research panel within 18 months of initial registration.
The Department is organised around four Research Clusters: International Institutions, Law and Ethics ; Theory/Area/History ; International Political Economy ; and Statecraft and Security . You will belong to at least one of these clusters during your studies and attend its weekly events. You will also have the chance to participate in the editing of a student-run journal Millennium: Journal of International Studies , which has a major role in the discipline.
The Department has particular strengths in international relations theory, security studies, international political economy, and European studies. As well as Europe, its specialist areas cover Russia, Central, Northeast and Southeast Asia, the USA, South America, the Middle East and Africa. Other areas of research strength include foreign policy analysis, nationalism, religion, historical sociology, international environmental politics and strategic and war studies. Many individuals contribute to more than one of these subjects, and there is interdisciplinary work with colleagues in the Departments of Government and International History, as well as through the many research centres at the School.
Department of International Relations
International Relations has been taught at LSE since 1924 and the department was set up three years later. We are one of the oldest as well as largest IR departments in the world, with a truly international reputation. We are ranked 2nd in the UK and 4th in the world in the QS World University Ranking by Subject 2022 tables for Politics and International Studies.
Information for international students
LSE is an international community, with over 140 nationalities represented amongst its student body. We celebrate this diversity through everything we do.
If you are applying to LSE from outside of the UK then take a look at our Information for International students .
Fees and funding
Every graduate student is charged a fee for their programme. Visit the website for more information about the fees .
The School recognises that the cost of living in London may be higher than in your home town or country, and we provide generous scholarships each year to home and overseas students.
LSE offers studentships to new PhD students in the form of LSE PhD Studentships, LSE ESRC Studentships, LAHP AHRC Studentships and LSE & III PhD Studentships on Analysing and Challenging Inequalities.
These awards are open to high calibre students of all nationalities studying across all research areas at the School.
Find out more about financial support.
Qualification, course duration and attendance options
- Campus-based learning is available for this qualification
Course contact details
Browser does not support script.
- Autumn Term events schedule
- Student Voice
- You've got this
- LSE Volunteer Centre
- Key information
- My Skills and Opportunities
- Student Wellbeing Service
- PhD Academy
- LSE Careers
- Student Services Centre
- Timetable publication information
- Students living in halls
- Faith Centre
Academic department PhD contacts
Get in touch with your department.
Doctoral programme directors (co-directors) Dr Tommaso Palermo [email protected]
Dr Xi Li [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Rebecca Baker [email protected]
Department of Accounting
Anthropology
Doctoral programme director
Professor Michael W. Scott
PhD administrative contact Yan Hinrichsen [email protected]
Department of Anthropology
Doctoral programme director Professor Maitreesh Ghatak [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Emma Taverner [email protected]
Department of Economics
Economic History
Doctoral programme director Professor Sara Horrell
PhD administrative contact Tracy Keefe [email protected]
Department of Economic History
European Institute
Doctoral programme director
Professor Jonathan Hopkin
PhD administrative contact Florence Samuels and Samson Yeung [email protected]
MPhil/PhD in European Studies
Doctoral programme director Professor Daniel Paravisini [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Mary Comben [email protected]
Department of Finance
Gender Studies
Doctoral programme director Professor Clare Hemmings [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Annie Robinson [email protected]
Gender Studies
Geography and Environment
Doctoral programme directors Professor Claire Mercer (Director of Graduate Studies) [email protected]
Dr Felipe Carozzi (Economic Geography) [email protected]
Professor Simon Dietz (Environmental Economics) [email protected]
Dr Michael Mason (Environmental Policy & Development) [email protected]
Dr Austin Zeiderman (Human Geography & Urban Studies) [email protected]
Dr Romola Sanyal (Regional Planning) [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Tom Jones
Department of Geography and Environment
Doctoral programme director Prof Sara Hobolt [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Emily Metcalf [email protected]
Department of Government
Health Policy
Doctoral programme director (co-DPDS) Professor Joan Costa-Font [email protected]
Dr Mylene Lagarde [email protected]
Dr Justin Parkhurst [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Muheez Busari [email protected]
Department of Health Policy
International Development
Doctoral programme director Dr Arjan Gjonca [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Dr Monika Kruesmann [email protected]
Department of International Development
International History
Doctoral programme director Professor Joanna Lewis [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Dr Edlira Gjonca [email protected]
Department of International History
International Relations
Doctoral programme director Professor Chris Alden [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Amy Brook and Sarah Helias [email protected]
Department of International Relations
Doctoral programme director Professor Tom Poole [email protected]
PhD administrator Rebecca Newman [email protected]
Department of Law
Doctoral programme directors Professor Ricardo Alonso (Main) [email protected]
Dr Jordi Blanes i Vidal (Economics and Management) [email protected]
Dr Jonathan Booth (Employment Relations and Human Resources) [email protected]
Dr Barbara Fasolo (Organisational Behaviour) [email protected]
Professor Om Narasimhan (Marketing) [email protected]
Dr Edgar Whitley (Information Systems and Innovation) [email protected]
PhD Programmes Manager Camilla Kennedy Harper [email protected]
Department of Management
Mathematics
Doctoral programme director Professor Luitgard Veraart [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Emily Jackson (Maternity Cover) [email protected]
Department of Mathematics
Media and Communications
Doctoral programme director Professor Ellen Helsper [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Danielle Blasse [email protected]
Department of Media and Communications
Methodology
Doctoral programme director Associate Professor Flora Cornish [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Camilya Maleh [email protected]
Department of Methodology
Philosophy, Logic and Scientific Method
Doctoral programme director Dr Kate Vredenburgh [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Anika Bloomfield [email protected]
Department of Philosophy, Logic and Scientific Method
Psychological and Behavioural Science
Doctoral programme director Dr Michael Muthukrishna [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Karine Gay [email protected]
Department of Psychological and Behavioural Science
Social Policy
Doctoral programme director Dr Timothy Hildebrandt [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Sevilay Erdogan and Craig Stewart [email protected]
Department of Social Policy
Doctoral programme director Dr Carrie Friese [email protected]
Department Research Manager Emilia Borowksa [email protected]
Department of Sociology
Doctoral programme director Prof Clifford Lam [email protected]
PhD administrative contact Muhammed Iqbal [email protected]
Department of Statistics

Our team Who's who in the PhD Academy
Browser does not support script.
- Undergraduate
- Executive education
- Study Abroad
- Summer schools
- Online certificate courses
- International students
- Meet, visit and discover LSE

Fees and funding
Scholarships, studentships, loans and tuition fees.
Each year LSE offers generous scholarships to its graduate students. There are also funding opportunities from external organisations, research councils and governments around the world.
Tuition fees
Every graduate student is charged a fee for their programme. If you receive an offer, you will be informed of the relevant tuition fee amount in your offer letter.
Tuition fee amounts
Tuition fee amounts are listed on the individual programme pages. The table of fees shows the latest tuition amounts for all programmes offered by the School.
In some cases the amount of tuition fees you will need to pay, and any financial support you are eligible for, will depend on whether you are classified as a Home or Overseas student, otherwise known as your fee status.
LSE assesses your fee status based on guidelines provided by the Department of Education.
Further information about fee status classification.
Fee reductions
Students who completed undergraduate study at LSE and are beginning taught graduate study at the School are eligible for a fee reduction of 10 per cent of the fee. Some programmes, such as executive programmes, are excluded from this fee reduction.
Further information
Alumni discount Fees and Student Finance LSE Student Fees Policy
Living costs
We broadly estimate that you should allow about £1,300-£1,400 per month for all living expenses, including accommodation, travel, food, laundry, study costs, and other personal expenses. This will vary depending on your lifestyle and requirements, so it's important you do your own research.
Please note that if you will be applying for a visa, you will have to provide evidence of sufficient funds, and these amounts may vary.
More details on living costs and making a budget .
Funding from LSE for taught master's and diploma programmes
- Graduate Support Scheme
- LSE Master's Awards
- Donor-funded awards for Home fee status students
- Programme-related funding
- Anniversary Scholarships
- LSE Access to Education Graduate Scholarship
Country based awards
The School makes available scholarships for students from specific regions of the world:
- Country-based awards for taught master's students: A - C
- Country-based awards for taught master's students: D - K
- Country-based awards for taught master's students: L - Q
- Country-based awards for taught master's students: R - Z
How to apply
See Applying for an LSE scholarship
Funding from LSE for research programmes
For 2024 entry, LSE will be offering studentships to new PhD students in the form of LSE PhD Studentships, LSE ESRC Studentships and LAHP AHRC Studentships.
These awards are open to high calibre students of all nationalities studying across all research areas at the School.
LSE PhD Studentships
LSE PhD Studentships are tenable for four years and cover full fees and an annual stipend. They are available for UK, EU and international students undertaking research in any LSE discipline, with annual renewal subject to satisfactory academic performance.
These awards will be made solely on the basis of outstanding academic merit and research potential. This relates both to your past academic record and to an assessment of your likely aptitude to complete a PhD in your chosen topic in the time allocated.
ESRC funding
LSE has an Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) Doctoral Training Partnership (DTP) and has ESRC studentships in a number of programmes across 19 departments. These studentships are available for students of all nationalities.
Studentships are tenable for three or four years, depending on the programme of study. They cover full fees (for international students, LSE will cover the difference between UK and overseas fees) and an annual stipend.
Individual programme entries detail which programme are eligible for ESRC funding.
AHRC funding
LSE is part of LAHP (London Arts and Humanities Partnership) , which is funded by the Arts and Humanities Research Council. Students of all nationalities can apply for one of these studentships.
Studentships are tenable for three years and they cover full fees (for international students, LSE will cover the difference between UK and overseas fees) and an annual stipend. LSE will also cover full fees and stipend for an additional fourth year.
LSE Departments that typically host AHRC studentships are International History, Media and Communications, Philosophy and Law, but students from other disciplines (for example, Anthropology, Gender Studies and International Development), can also apply if their research falls within the remit of AHRC, as explained here .
Department-specific funding
Check the programme-related funding page for PhD funding opportunities.
Except for LAHP studentships (see below), academic departments nominate students for the funding opportunity they may be eligible for. There is no separate application for LSE, ESRC and department-specific studentships. To be considered for this funding, you must submit your complete application for admission to LSE by a specific date. This date differs by academic department.
deadline for being considered for LSE PhD Studentships and ESRC funding for 2024 entry if you apply to a programme in the Department of Law: 1 December 2023
deadline for being considered for LSE PhD Studentships and ESRC funding for 2024 entry if you apply to a programme in the Department of Economics: 14 December 2023
deadline for being considered for ESRC funding for 2024 entry: 15 January 2024
deadline for being considered for LSE PhD Studentships for 2024 entry: this can either be 15 January 2024 and/or 25 April 2024 depending on the programme you are applying to. Details can be found on the individual programme page.
To be considered for a LAHP studentship for 2024 entry, students need to have applied for their chosen programme of studies. They will also need to submit a separate funding application to LAHP, deadline to be confirmed . Details of the application process can be found here
External funding opportunities
Uk government loans.
Postgraduate master's loan
A postgraduate master's loan from the UK government is available for eligible students. Postgraduate doctoral loan
A postgraduate doctoral loan from the UK government is available for eligible students.
External Private Loans
LSE has agreements with three loan providers who offer various packages dependent on your nationality, chosen programme of study, financial status and future earnings. The Lenders are Lendwise, Future Finance and Prodigy.
More information can be found here

PhD Studentships Find out more about our studentships

Prospective students Information on our graduate programmes, and how to apply

How to apply The application process, UCAS and when to apply

Undergraduate fees and funding Details on available scholarships, bursaries, loans and tuition fees

Contact us Get in touch with the Financial Support Office

Meet, visit and discover LSE Webinars, videos, on campus events and visits around the world
- Browse by author
- Browse by year
- Departments
- History of Thought
- Advanced search
- International Relations (301)
La Lova, Lanabi (2023) What do news media in Putin's Russia reveal about the regime’s survival strategy? PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Sepulveda Coelho Brito Filho, Tarsis Daylan (2023) Bordering humanness, securing whiteness: race, colonialism, and violence at the European borders. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Zachariades, Alexandros (2023) Greek and Cypriot foreign policy in the Middle East: small states and the limits of neoclassical realism. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Li, Andy Hanlun (2023) Territorialising the frontier: knowledge production and the emergence of modern territoriality in China. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ackah-Arthur, Jemima (2023) The state, non-state actors, and populations: security responses to insurgent attacks in Sub-Saharan Africa. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Van Wingerden, Enrike (2023) Catastrophic comparisons: International Relations through elsewhere. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Micheni, Makena Nyawira (2023) Fractured brotherhoods: ethnic identity in multi-ethnic violent political organisations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Levkovych, Oksana (2022) Liberals and protectionism: Britain's international trade policy between the wars (1902-1939). PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Hirst, Catherine (2022) Revolution, international counterrevolution and world order. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Marozzi, Armando (2022) Essays on the European Central Bank's communication. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Angioni, Giovanni Francesco (2022) Essays on the political economy of preferences for redistribution and deservingness in the age of realignments and new cleavages. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Rodehau-Noack, Johanna (2022) 'A culture of prevention': the idea of preventability and the construction of war as a governance object. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Zaidi, Asad (2022) Pakistani worldmaking in international politics: empire, decolonization and Cold War struggles 1950-1989. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ratner, McKenzie (2022) Why over-comply with international law? Exceeding international minimum standards in social, labor, and environmental policy. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Raymon, Ricky (2021) The making of Indonesia’s Global Maritime Fulcrum (GMF) grand strategy: origins and implementation. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Aboudounya, Seebal (2021) Deliberation in international institutions: the case of the International Maritime Organization. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Morlino, Irene (2021) Assessing the effectiveness of EU humanitarian aid. The cases of Myanmar, Lebanon, Mozambique. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ivanov, Helena (2021) Inside propaganda: Serbian media in the Yugoslav Wars 1991-1995. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Howlett, Marnie (2021) Nationalism in the borderlands of a borderland: a critical, cartographical, and (de)constructional analysis of contemporary Ukraine. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Vuksanovic, Vuk (2021) Systemic pressures, party politics and foreign policy: Serbia between Russia and the West, 2008-2020. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Majnemer, Jacklyn (2021) Understanding reneging: Canada's nuclear sharing commitments to NATO and NORAD during the Cold War. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Hall, Jonny (2021) The normalisation of war: from the Korean War to the War on Terror. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Heimsoeth, Eleonore (2021) The European External Action Service’s influence in European security and defence policy: understanding the role of its relational capital. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Haddadi, Anissa (2021) (Post)colonial Egypt & its simulacra of liberation a capture of revolutionary desire. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Guasti, Alessandro (2020) The systemic effects of labour rights promotion: a spatial interdependence analysis of its impact on working conditions and international trade. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Degli Esposti, Nicola (2020) Whose Kurdistan? Class politics and Kurdish nationalism in the Middle East, 1918-2018. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bertrand, Sarah (2020) Curating knowledge: international relations expertise and the end of the Cold War in East Germany. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Saint, Emma (2020) Empowering resistance? ‘Revisionist’ states and the underlying dynamics of international norm diffusion. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Fujikawa, Kentaro (2020) Serving peace and democracy? The rationales and impact of post-conflict self-determination referendums in Eritrea, East Timor, and South Sudan. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Elizalde, Pilar (2020) Human rights promotion, contestation, and politicisation in international human rights institutions: a study of the Universal Periodic Review 2008-2016. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bonnet, Tyler Alexander (2020) Russia and the rise of China: an analysis of Russian foreign policy towards China under Putin. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Shams Lahijani, Alireza (2020) Iran’s idea of Europe (1501-2015): identity, concepts, and international society. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Leigh, Joseph (2020) The emergence of global power politics: imperialism, modernity, and American expansion 1870-1914. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Winrow, Marc Sinan (2020) Reconstituting sovereignty: the Young Turks’ efforts to secure external recognition and the transition from the Ottoman Empire to the Republic of Turkey, 1908 - 1923. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Murray, Christopher Patrick (2020) Anti-imperial world politics: race, class, and internationalism in the making of post-colonial order. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Wenas Inkiriwang, Frega Ferdinand (2020) The interplay between grand strategy and defence diplomacy: examining Indonesia’s post-new order period. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Alsayed, Wafa (2019) Foreign policy making in the small Gulf states: state formation processes, ideas and identities in Kuwait and Bahrain. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Spanke, Till (2019) Nurturing dependence: the role of patron states in the state and institution building processes of de facto states. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Rogstad, Adrian (2019) Stigmatisation in international relations: Russia, the West and international society from the Cold War to Crimea. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
De Moraes Achcar, Helena (2019) The politics and anti-politics of south-south cooperation: the case of Brazil-Mozambique ProSavannah and antiretroviral factory. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Sverdrup-Thygeson, Bjørnar (2019) The identity factor in Chinese Europe policies: China’s European quest for ontological security. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Aula, Ilari (2019) Consuming conflicts: consumer responsibility for armed conflicts in DR Congo and Nigeria. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kalhousová, Irena (2019) Our Jews, our Israel! Origins of the foreign policy of Poland, the Czech Republic, and Hungary towards Israel. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ho, Benjamin Tze Ern (2019) Chinese exceptionalism: an interpretive framework to understanding China’s rise and relations with the world. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Phull, Kiran K. (2019) Polling and the pursuit of Arab public opinion. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Goettlich, Kerry (2019) From frontiers to borders: the origins and consequences of linear borders in international politics. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Garnizova, Elitsa (2018) The new political economy of trade: understanding the treatment of non-tariff measures in European Union trade policy. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Freeman, Jonathan (2018) Military assistance as a tool of 20th Century American grand strategy: the American experience in Korea and Vietnam after World War II. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Pauls, Evelyn (2018) Unravelling the poster child: the international norm against child soldiering in Sierra Leone and Myanmar. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ciflikli, Gokhan (2018) Learning conflict duration: insights from predictive modelling. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Hartnett, Liane (2018) Love in a time of empire: an engagement with the political thought of Tolstoy, Tagore and Camus. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Carrozza, Ilaria (2018) Securing the way to power: China’s rise and its normative peace and security agenda in Africa. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Haspeslagh, Sophie (2018) The effect of proscription on pre-negotiation: a comparative analysis of making peace with Colombia’s FARC before and after 9/11. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Danewid, Ida (2018) Race, capital, and the politics of solidarity: radical internationalism in the 21st century. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Wang, Ziyuan (2018) The political logic of status competition: cases from China, 1962-1979. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Dessí, Andrea T. (2018) Normalizing the Israel asset. The Reagan administration and the second cold war in the Middle East: leverage, blowback and the institutionalization of the US-Israel 'Special Relationship'. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Sharma, Rahul (2018) American civil religion and the puritan antecedents of American foreign policy. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Blanc, Emmanuelle (2018) The EU in quest for the recognition of its institutional identity: the case of the EU-US dialogues. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bareis, Luka (2018) Interstate resource conflicts: international networks and the realpolitik of natural resource acquisition. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
George, Rachel (2018) From contestation to convergence? A constructivist critique of the impact of UN Human Rights Treaty ratification on interpretations of Islam in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kaushal, Sidharth (2018) Reconceptualising strategic culture as a focal point: the impact of strategic culture on a nation’s grand strategy. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Lee, Sohyun (2017) A step toward East Asian regionalism? Comparing the negotiation approaches of South Korea and Japan in their preferential trade agreements with ASEAN. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Feist, Marian Johannes (2017) Learning in international negotiations: the strategic use of lessons in post-agreement climate finance politics. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
McKeil, Aaron (2017) Searching for a world polity: the world after international anarchy question. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Hamilton, Scott (2017) Governing through the climate: climate change, the anthropocene, and global governmentality. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Suleimanova, Neal (2017) Why keep protecting the few without external incentives? Compliance with minority rights norms after attaining IO membership in Latvia and Georgia. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Hemmings, John (2017) Quasi-alliances, managing the rise of China, and domestic politics: the US-Japan-Australia trilateral 1991-2015. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Meibauer, Gustav (2017) Doing something: neoclassical realism, US foreign policy and the no-fly zone, 1991-2016. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Schäfer, David (2017) Explaining the creation of the EU Banking Union: the interplay between interests and ideas. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Himmrich, Julia (2017) Germany’s recognition of Kosovo as an independent state in 2008. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Shaoulian-Sopher, Efrat (2017) Israeli foreign policy towards Iran 1948-1979: beyond the realist account. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
De Simone, Carolina (2017) Italy and the community of Sant’Egidio in the 1990s. ‘Coopetition’ in post-Cold War Italian foreign policy? PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Nøhr, Andreas Aagaard (2017) Tyrants of truth: a genealogy of hyper-real politics. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Delatolla, Andrew (2017) The state as a standard of civilisation: assembling the modern state in Lebanon and Syria, 1800-1944. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Papagaryfallou, Ioannis (2016) The history/theory dialectic in the thought of Herbert Butterfield, Martin Wight and E. H. Carr: a reconceptualisation of the English School of international relations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Stroikos, Dimitrios (2016) China, India in space and the orbit of international society: power, status, and order on the high frontier. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Brenner, David (2016) Insurgency as a social process: authority and armed groups in Myanmar’s changing borderlands. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Yao, Yuan (2016) Constructing the ideal river: the 19th century origins of the first international organizations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Schade, Daniel (2016) The European Union’s Latin America policy: a study of foreign policy change and coordination. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Morita-Jaeger, Minako (2016) Services trade integration in East Asia and political economy impediments in domestic decision-making: a case study of Japan-ASEAN bilateral free trade agreements. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Wang-Kaeding, Heidi (2016) Strategic concepts and interest groups in China’s environmental foreign relations (1984-2015). PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Susler, Bugra (2016) Turkey's foreign policy cooperation with the European Union during the Arab Spring, 2011-13. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Lacatus, Corina (2016) The design of national human rights institutions: global patterns of institutional diffusion and strength. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Hearson, Martin (2016) Bargaining away the tax base: the north-south politics of tax treaty diffusion. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Linsi, Lukas (2016) How the beast became a beauty: the social construction of the economic meaning of foreign direct investment inflows in advanced economies, 1960-2007. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Fotou, Maria (2016) Ethics of hospitality: envisaging the stranger in the contemporary world. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Hoeffken, Jana Ulrike (2016) Competition provisions in EU regional trade agreements: consequences for domestic reform in developing countries. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Jiang, Lu (2016) Beyond ODA: Chinese way of development cooperation with Africa: the case of agriculture. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Procopio, Maddalena (2016) Negotiating governance: Kenyan contestation, cooperation, passivity toward the Chinese. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Andersen, Morten Skumsrud (2016) A genealogy of the balance of power. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
von Weitershausen, Inez (2016) Europe between interests, institutions and ideas: crisis cooperation during the 2011 uprisings in Libya. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Frielingsdorf, Per-Axel (2016) “Machiavelli of Peace”: Dag Hammarskjöld and the political role of the Secretary-General of the United Nations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Mueller, Benjamin (2015) At cold war’s end: complexity, causes, and counterfactuals. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Guijarro Usobiaga, Borja (2015) European sanctions reconsidered: regime type, strategic bargaining, and the imposition of EU sanctions. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Terry, Jillian (2015) Towards a feminist ethics of war: rethinking moral justifications for contemporary warfare. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Dittrich, Viviane (2015) Present at the completion: creating legacies at the International Criminal Tribunals. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Nair, Deepak (2015) Saving the states’ face: an ethnography of the ASEAN secretariat and diplomatic field in Jakarta. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Koluksuz, Melissa (2015) A critical geopolitics of American “imperialism" and grand strategy (Post-9/11): the role of language and ideology. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
de Merich, Diego (2015) Empathy at the intersections of care: articulating a critical approach to the ethics of international development. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Falkiner, Daniel (2015) The erotics of empire: love, power, and tragedy in Thucydides and Hans Morgenthau. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bohnenberger-Rich, Simone (2015) China and Kazakhstan: economic hierarchy, dependency and political power? PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Crossley, Noële (2015) Humanitarian intervention: from le droit d'ingérence to the responsibility to protect. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ussar, Margit (2014) Ethics, aid, and organisational characteristics: are multilateral aid organisations more likely to be driven by ethical considerations than their bilateral counterparts? PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Sibal, Rajeev (2014) Varieties of capitalism and firm performance in emerging markets: an examination of the typological trajectories of India and Brazil. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Basedow, Johann (2014) The European Union’s international investment policy Explaining intensifying Member State cooperation in international investment regulation. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Zheng, Yixiao (2014) Complex interdependence and China’s engagement with Australia: navigating between power and vulnerability. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ohlers, Curtis (2014) Interstate warfare and the emergence of transnational insurgencies. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kramer, Reik (2014) Network-centric peace: an application of network theory to violent conflicts. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Anderson, Emily (2014) States of extraction: impacts of taxation on statebuilding in Angola and Mozambique, 1975-2013. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Muravska, Julia (2014) The institutionalisation of the European defence equipment market. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Makarem, Hadi (2014) Actually existing neoliberalism: the reconstruction of downtown Beirut in post-civil war Lebanon. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Flynn, Curran (2014) Hans Morgenthau’s scientific man versus power politics and politics among nations: a comparative analysis. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Pavese, Carolina B. (2014) Level-linkage in European Union – Brazil relations: an analysis of cooperation on climate change, trade, and human rights. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Yu, Jie (2014) Partnership or partnerships? An assessment of China-EU relations between 2001 and 2013 with cases studies on their collaborations on climate change and renewable energy. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Datzberger, Simone (2014) Peacebuilding and the depoliticisation of civil society: Sierra Leone [2002 – 2013]. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Brodersen, Rupert (2014) Rage, rancour and revenge: existentialist motives in international relations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Wirajuda, Muhammad (2014) The impact of democratisation on Indonesia’s foreign policy: regional cooperation, promotion of political values, and conflict management. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Schleifer, Philip (2014) Whose rules? The institutional diffusion and variation of private participatory governance. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Klingler-Vidra, Robyn (2014) All politics is local: sources of variance in the diffusion of venture capital policies. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Côté, Christine (2014) A chilling effect? The impact of international investment agreements on national regulatory autonomy in the areas of health, safety and the environment. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Lamprecht, Jens (2014) Bargaining power in multilateral trade negotiations: Canada and Japan in the Uruguay Round and Doha development agenda. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Barber, Laura (2014) Chinese foreign policy in the 'Going Out' era: confronting challenges and 'Adaptive Learning' in the case of China-Sudan and South Sudan Relations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Izzuddin, Mustafa (2014) Ethnic politics and Malaysia’s China Policy: from Tun Abdul Razak to Abdullah Ahmad Badawi: a neoclassical realist interpretation. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
de Felice, Damiano (2014) Explaining variation in the degree of internalisation of political conditionality: the cases of France and the United Kingdom. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kersten, Mark (2014) Justice in conflict: the ICC in Libya and Northern Uganda. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Hellmeyer, Monika (2014) The impact of the Central and Eastern European EU member states on the EU’s foreign policy, 2004 to 2013. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Schwarz, Elke (2013) The biopolitical condition: re-thinking the ethics of political violence in life-politics. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Dueben, Bjoern (2013) China-Russia relations after the Cold War: the process of institution-building and its impact on the evolution of bilateral cooperation. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Srnicek, Nick (2013) Representing complexity: the material construction of world politics. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Cheeppensook, Kasira (2013) The development of the ASEAN Charter: origins and norm codification. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bowen, Andrew (2013) Syrian-American relations, 1973 - 1977: a study of security cooperation in regional conflicts. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Tardelli, Luca (2013) When elites fight: elites and the politics of U.S. military interventions in internal conflicts. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Rahbek-Clemmensen, Jon (2013) Beyond ‘the soldier and the state’ - the theoretical framework of elite civil-military relations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Voltolini, Benedetta (2013) Lobbying in EU foreign policy-making towards the Israeli-Palestinian conflict: exploring the potential of a constructivist perspective. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Parakilas, Jacob Christopher (2013) The Mexican drug “war”: an examination into the nature of narcotics linked violence in Mexico, 2006-2012. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Laker, Frederick (2013) Rethinking internal displacement geo-political games, fragile states, & the relief industry. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Zhang, Shuxiu (2013) The dragonomic diplomacy (De)code: a study on the causal relationship between Chinese economic diplomacy preference formation and the influence of multilateral economic regimes. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Verma, Rajneesh (2013) The tiger and the dragon: a neoclassical realist perspective of India and China in the oil industry in West Africa. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Wielopolska, Anna (2013) Causes and consequences of ambivalence in Germany’s policy towards the Eastern enlargement of the European Union. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Palma, Oscar (2013) Transnational networks of insurgency and crime: explaining the spread of the revolutionary armed forces of Colombia beyond national borders. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kuroki, Maiko (2013) Nationalism in Japan’s contemporary foreign policy: a consideration of the cases of China, North Korea, and India. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Pham, Gia Son (2013) A political economy approach to the impact of the WTO’s accession process on Vietnam’s economic reform: a case of compliance? PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Niemetz, Martin (2013) Promoting a deliberative system for global peace and security: how to reform the United Nations’ decision-making procedures. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Keränen, Outi (2013) Acts of contention: local practices and dynamics of negotiated statebuilding in Bosnia and Herzegovina 1995-2010. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Dombrowski, Kathrin Irma (2013) Bridging the democratic gap: Can NGOs link local communities to international environmental institutions? PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Parks, Bradley (2013) Brokering development policy change: the parallel pursuit of millennium challenge account resources and reform. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Smith, Janel (2013) Civil society, human security, and the politics of peace-building in victor’s peace Sri Lanka (2009-2012). PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kruesman, Monika (2013) Digging for compliments: Rio Tinto Group, corporate social responsibility and the diffusion of international norms. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
de Heredia, Marta Iñiguez (2013) Everyday resistance in post-conflict statebuilding: the case of eastern Democratic Republic of Congo. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Evangelopoulos, Georgios (2013) Scientific realism in the philosophy of science and international relations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Pepino, Silvia (2013) Sovereign risk and financial crisis: the international political economy of the Euro area sovereign debt crisis. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Cho, Young (2013) Why do countries implement Basel II? An analysis of the global diffusion of Basel II implementation. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Edwards, Alex (2013) A neoclassical realist analysis of American ‘dual containment’ policy in the Persian Gulf: 1991-2001. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Jillions, Andrew (2012) From faith in rules to the rule of law: constitutional responsibilities in international society. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Orsi, Roberto (2012) Rethinking the concept of order in international politics: Carl Schmitt and Jürgen Habermas. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Markakis, Dionysius (2012) US democracy promotion in the Middle East: the pursuit of hegemony? PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Chung, Chih-tung (2012) The evolution of Taiwan’s grand strategy: from Chiang Kai-shek to Chen Shui-bian. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Fisher, Kathryn (2012) From 20th Century troubles to 21st Century international terrorism: identity, securitization, and British counterterrorism from 1968 to 2011. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Friedman, Rebekka (2012) Hybrid TRCs and national reconciliation in Sierra Leone and Peru. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Varin, Caroline (2012) Mercenaries and the state: how the hybridisation of the armed forces is changing the face of national security. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bloomfield, Michael (2012) Power, profit, and principles: industry opportunity structures and the political mobilisation of jewellers. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kirby, Paul (2012) Rethinking War/Rape: feminism, critical explanation and the study of wartime sexual violence, with special reference to the Eastern Democratic Republic of Congo. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Petersen, Alexandros (2012) Integration in energy and transport amongst Azerbaijan, Georgia and Turkey. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Méndez, Álvaro (2012) Negotiating intervention by invitation: how the Colombians shaped US participation in the genesis of Plan Colombia. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
O’Casey, Elizabeth (2012) A theory of need in international political theory: autonomy, freedom, and a global obligation. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ghulam, Faisal (2012) Accession to the World Trade Organization: factors shaping the case of Saudi Arabia’s accession (1985-2005). PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Förster, Annette (2012) Decent peace, stability and justice: John Rawls’s international theory applied. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Campanaro, Richard (2012) Socio-ecological coevolution: an ecological analysis of the historical development of international systems in the circumpolar Arctic. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Minsat, Arthur (2012) Making EU foreign policy towards a 'Pariah' state: consensus on sanctions in EU foreign policy towards Myanmar. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kaya, Zeynep (2012) Maps into nations: Kurdistan, Kurdish Nationalism and international society. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Strong, James (2012) More spinn’d against than spinning?: public opinion, political communication, and Britain’s involvement in the 2003 invasion of Iraq. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Woolfson, Alexander F. (2012) The discourse of exceptionalism and U.S. grand strategy, 1946–2009. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Dalgaard, Klaus (2012) The energy statecraft of Brazil: promoting biofuels as an instrument of Brazilian foreign policy, 2003-2010. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bennett, Hanna (2012) Leverage and limitations of the EU’s influence in the eastern neighbourhood : a study of compliance with the EU’s justice and home affairs' standards in Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Roccu, Roberto (2012) Gramsci in Cairo: neoliberal authoritarianism, passive revolution and failed hegemony in Egypt under Mubarak, 1991-2010. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Castro e Almeida, Manuel (2012) Defective polities: a history of an idea of international society. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Raimundo, Antonio Joaquim (2012) The Europeanisation of national foreign policy: Portuguese foreign policy towards Angola and Mozambique, 1978-2010. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bird, Annie (2012) US foreign policy on transitional justice: case studies on Cambodia, Liberia and Colombia. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Al Toraifi, Adel (2012) Understanding the role of state identity in foreign policy decision-making: the rise of Saudi-Iranian rapprochement (1997-2009). PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Pagliari, Natali (2012) Why are we running? Political economy of bank runs and an analysis on the 2007-09 banking crisis in the United Kingdom. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bettiza, Gregorio (2012) The global resurgence of religion and the desecularization of American foreign policy, 1990-2012. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Sabaratnam, Meera (2011) Re-thinking the liberal peace: anti-colonial thought and post-war intervention in Mozambique. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Gani, Jasmine K. (2011) Understanding and explaining US-Syrian relations: conflict and cooperation, and the role of ideology. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Pallaver, Matteo (2011) Power and its forms: hard, soft, smart. MPhil thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Masraff, Naz (2011) Why keep complying?: compliance with EU conditionality under diminished credibility in Turkey. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Dionigi, Filippo (2011) The impact of international norms on Islamist politics: the case of Hezbollah. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Homkes, Rebecca (2011) Analysing the role of public-private partnerships in global governance: institutional dynamics, variation and effects. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Moore, Candice Eleanor (2011) Governing Parties and Southern Internationalism: a neoclassical realist approach to the foreign policies of South Africa and Brazil, 1999-2010. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Topgyal, Tsering (2011) The insecurity dilemma and the Sino-Tibetan conflict. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Alves, Ana Cristina (2011) China’s oil diplomacy: comparing Chinese economic statecraft in Angola and Brazil. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Poulsen, Lauge N. Skovgaard (2011) Sacrificing sovereignty by chance: investment treaties, developing countries, and bounded rationality. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Hoover, Joseph (2011) Reconstructing human rights: a pragmatic and pluralist inquiry in global ethics. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
McFate, Sean (2011) Durable disorder: the return of private armies and the emergence of neomedievalism. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Gayoso Descalzi, Carmen Amelia (2011) Russian hegemony in the CIS region: an examination of Russian influence and of variation in consent and dissent by CIS states to regional hierarchy. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Renouf, Jean S. (2011) Understanding how the identity of international aid agencies and their approaches to security are mutually shaped. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Beaugrand, Claire Beatrix Marie (2010) Statelessness and transnationalism in northern Arabia: biduns and state building in Kuwait, 1959-2009. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Gartzke, Ulf (2010) The Boeing / McDonnell Douglas and EADS mergers: ethnocentric vs. regiocentric consolidation in the aerospace and defence industry and the implications for international relations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Oskanian, Kevork (2010) Weaving webs of insecurity: fear, weakness and power in the post-Soviet South Caucasus. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Radice, Henry (2010) The politics of humanity: humanitarianism and international political theory. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Reeves, Jeffrey (2010) Mongolian state weakness, foreign policy, and dependency on the People’s Republic of China. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Barnes, Karen (2010) Engendering peace or a gendered peace? The UN and liberal peacebuilding in Sierra Leone, 2002-2007. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Phillips, Christopher (2010) Everyday Arabism: The daily reproduction of nationalism and supranationalism in contemporary Syria and Jordan. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Wann, Joy (2010) Global financial governance and the question of influence: Examining the role private actors play in international financial standardisation. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Matsumoto, Emma (2010) Japan and the UN peace operations in the post-Cold War era: Their challenges and choices. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Pinfari, Marco (2010) Time to agree: time pressure and 'deadline diplomacy' in peace negotiations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Charnoz, Olivier (2010) The local power effects of a global governance discourse: 'Community participation' in the protection of biodiversity. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kitchen, Nicholas (2009) American power: for what? ideas, unipolarity and America’s search for purpose between the 'wars', 1991-2001. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Mills, James Robert (2009) The challenge of self-determination and emerging nationalism: the evolution of the international community’s normative responses to state fragmentation. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bulloch, Douglas (2009) Carl Schmitt: A conceptual exegesis and critique of IR theory. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Zhang, Feng (2009) Chinese primacy in East Asian history: Deconstructing the tribute system in China's early Ming Dynasty. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ankersen, Christopher (2009) Civil-military cooperation in the Canadian Army. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Henriksen, Rune (2009) Does the West still need warriors? PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Curtis, Simon J (2009) Global cities and the transformation of the international system. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Gocer, Derya (2009) Interaction between the international and the domestic: The case of the 1908 Constitutional Revolution in the Ottoman Empire. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Lennox, Corinne (2009) Mobilising for group-specific norms: Reshaping the international protection regime for minorities. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bolten, Annika (2009) Pegs, politics and petrification: exchange rate policy in Argentina and Brazil since the 1980s. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Van Criekinge, Tine (2009) Power asymmetry between the European Union and Africa? A case study of the EU's relations with Ghana and Senegal. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Cullen, Patrick Jerome (2009) Private security in international politics: Deconstructing the state's monopoly of security governance. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Pearson, John (2009) Republicanism beyond borders? Preventing domination in the absence of the state. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Barrios, Cristina (2009) Rival universalisms? American and European democracy promotion in post-Cold War international relations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Hughes, Annika Katherine (2009) World power -- to be taken (f)or granted?: The concept of political power and its significance for an analysis of power in international relations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Markarian, Tatoul (2009) The dynamics of the domestic-foreign policy relationship in transition studies. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Mahmoud, Yasser Mohamed Elwy Mohamed (2009) A political economy of Egyptian foreign policy: State, ideology, and modernisation since 1970. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kofmehl, Scott Eric (2009) The second act of victory: U.S. foreign policy and post-conflict state-building. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Vardi, Gil-li (2008) The enigma of German operational theory: the evolution of military thought in Germany, 1919-1938. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Stein, Ewan (2008) Conceptions of Israel and the formation of the Egyptian foreign policy: 1952-1981. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Singh, Rashmi (2008) Conceptualising suicide bombings and rethinking international relations theory: The case of Hamas 1987-2006. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Quinn, Adam (2008) Conquest of spirits: Ideological history as an explanatory factor in the Bush administration's resistance to balance-of-power thinking. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Wright, Christopher (2008) Environmental governance in international banking: exploring the emergence of the Equator Principles. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Stuart, Jill (2008) Exploring the relationship between outer space and world politics: English School and regime theory perspectives. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Berenskotter, Felix Sebastian (2008) From friends to strangers: A theory of interstate security cooperation applied to German-American relations, 1945-1995. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Balfour, Rosa (2008) Human rights and democracy in EU foreign policy: The cases of Ukraine and Egypt. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Mullin-Lery, Corinna (2008) Political Islam and the United States' new "Other": An analysis of the discourse on political Islam (2001-2007). PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kantz, Carola (2008) Precious stones, black gold and the extractive industries: Accounting for the institutional design of multi-stakeholder initiatives. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Fournier, Philippe (2008) Rationalities of government in contemporary America: A Foucaultian study of domestic and foreign policy (1960-2008). PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ortmann, Stefanie (2008) Re-imagining Westphalia: Identity in IR and the discursive construction of the Russian state. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Arnold, Matthew Byron (2008) The collaboration problematique: Managing frontiers of insecurity through state building interventionism. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Manea, Simona Florina (2008) A critique of the anthropomorphic conception of the state: The Romanian state as a relational, network and emergent actor. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Chitranukroh, Krirkbhumi (2008) The dynamics of preferential trade agreements and domestic institutions---an alternative route towards Asian regionalism: A case study of Singapore and Thailand's preferential trade agreements. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kamlani, Deirdre Shay (2008) The four faces of power in sovereign debt restructuring: Explaining bargaining outcomes between debtor states and private creditors since 1870. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Daehnhardt, Patricia (2008) The remaking of identity: The question of normative power in German foreign policy (1997-2007). PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Cui, Shunji (2007) Beyond rivalry?: Sino-Japanese relations and the potential for a ‘security regime’ in Northeast Asia. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Gross, Eva (2007) The Europeanization of foreign policy? The role of the EU CFSP/ESDP in crisis decision-making in Macedonia and Afghanistan. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kelley, John Robert (2007) From monologue to dialogue?: U.S. public diplomacy in the post-9/11 era. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Tosti, Padideh (2007) Global illicit sectors: An analysis of drugs in international relations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Teo, Victor E. (2007) Memories and the exigencies of national interest: an analysis of post Cold War Sino-Japanese and Sino-Russian strategic relations and perceptions. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Vinci, Anthony John (2007) Warlords in the international order: a neorealist approach. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Hinds, Kristina (2007) The activism and inclusion of civil society organisations in CARICOM on trade negotiating matters: a look at three cases. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ainley, Kirsten (2006) Rethinking agency & responsibility in contemporary international political theory. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Partrick, Neil (2006) Kuwait's foreign policy (1961-1977): Non-alignment, ideology and the pursuit of security. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Vlcek, William B. (2006) Small states and the challenge of sovereignty: Commonwealth Caribbean offshore financial centers and tax competition. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Muxagata de Carvalho Vieira, Marco Antonio (2006) Southern Africa's response(s) to international HIV/AIDS norms: The politics of assimilation. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Kissack, Robert Eoghan (2006) Who speaks for Europe in the ILO? Member state coordination and European Union representation in the International Labour Organisation. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Yuzawa, Takeshi (2005) Japan's security policy and the ASEAN Regional Forum: The search for multilateral security in the Asia Pacific. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Moghalu, Kingsley Chiedu (2005) Justice as policy and strategy: A study of the tension between political and juridical responses to violations of international humanitarian law. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Tamura, Kentaro (2005) Preference formation, negotiations and implementation: Japan and the Basle Capital Accord. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Vaquer i Fanes, Jordi (2005) Spanish policy towards Morocco (1986-2002): The impact of EC/EU membership. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Sunayama, Sonoko (2005) Syria and Saudi Arabia, 1978-1990: A study of the role of shared identities in alliance-making. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Fokas, Efterpe (2004) The role of religion in national-EU relations: the cases of Greece and Turkey. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Johnson, Rebecca (2004) The 1996 Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty: a study in post Cold War multilateral arms control negotiations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Catellani, Nicola (2004) The European Union's northern dimension: A case of foreign policy "by the backdoor"? PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Yordan, Carlos L (2004) Strategic versus communicative approaches to peacemaking: A critical assessment of the Dayton Peace Initiative. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Jayman, Jayantha (2004) A critical understanding of Japan's improved late 20th century relations in Eastern Asia. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Neves, Miguel (2003) Autonomous non-central governments in the international system: the case of Hong Kong. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Donley, Patrick Harrison (2003) Population protection in the 1990s: Managing risk in the new security environment. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Doebler-Hagedorn, Franziska (2003) The state at its borders: Germany and the Schengen negotiations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Qureshi, Saqib (2002) US Foreign Policy to Pakistan, 1947-1960: Re-constructing strategy. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Isaac, Grant E (2001) Agricultural biotechnology and transatlantic trade: An international political economy analysis of social regulatory barriers. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Correia Marques de Almeida, Joao (2001) Between anarchy and empire: An analysis and reformulation of the concept of international society in the light of the republican political tradition. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Elbe, Stefan Heinz Edward (2001) European nihilism and the meaning of the European idea: A study of Nietzsche's 'good Europeanism' in response to the debate in the post-Cold War era. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Michaels, Kevin Patrick (2001) Opening skies: The political economy of the air cargo industry in the Philippines and Taiwan. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Drossopoulos, Constantinos-John (2001) The politics of monetary integration in the European Community: Theory, practice and prospects. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Hesse, Brian Joseph (2000) Grand aims and modest means: The parallel evolution of US and South African foreign policies towards Africa in the 1990s. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Idowu, Stephen Babatunde (2000) Namibia from colonisation to statehood: The paradoxical relationship between law and power in international society. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Stubb, Alexander (1999) Flexible integration and the Amsterdam Treaty: negotiating differentiation in the 1996-97 IGC. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Viola, Donatella (1999) European foreign policy and the European Parliament in the 1990's. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Crow, Suzanne Marie (1999) Fragmented diplomacy: The impact of Russian governing institutions on foreign policy, 1991-1996. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Styan, David A. (1999) Franco-Iraqi relations and Fifth Republic foreign policy, 1958-1990. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Valde-Ugalde, Jose Luis (1999) Intervening in revolution: The US exercise of power in Guatemala, 1954. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Jacquin-Berdal, Dominique (1999) Nationalism and secession in the Horn of Africa: a critique of the ethnic interpretation. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Osman, Mohamed Awad (1999) The United Nations and peace enforcement with special reference to Kuwait, 1990-91. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Colas Krauter, Alejandro (1999) The expansion of international civil society: The case of Tunisia. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ebata, Joanne Michi (1999) The transition from war to peace: politics, political space and the peace process industry in Mozambique, 1992-1995. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Keene, Edward (1998) The colonising ethic and modern international society: A reconstruction of the Grotian tradition of international theory. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Brown, Susan (1998) The institutional evolution of the WTO Government Procurement Agreement: towards an understanding of the peripheries of domestic economic policies. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bettcher, Douglas (1997) A psychoanalytic approach to the study of international relations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Smith, Karen Elizabeth (1996) The making of foreign policy in the European Community/Union: the case of Eastern Europe, 1988-1995. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
van Walsum-Stachowicz, Judith Margaretha (1995) Corporate diplomacy and European Community information technology policies: The influence of multi-nationals and interest groups, 1980-1993. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Pinheiro, Leticia de Abreu (1995) Foreign policy decision-making under the Geisel government: The president, the military and the foreign ministry. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Khonsari, Mehrdad (1995) The National Movement of the Iranian Resistance 1979-1991: The role of a banned opposition movement in international politics. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Vervain Evans, Carol (1994) Defence industrialisation in the NICs : case studies from Brazil and India. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Taillon, Joseph Paul de Boucherville (1993) International co-operation in the use of elite military forces to counter terrorism: The British and American experience, with special reference to their respective experiences in the evolution of low-intensity operations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Chife, Aloy Chinedu (1993) The political economy of north-south relations: Japan's relations with Nigeria, 1960-1985. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Rowlands, Ian (1992) International regime formation: the politics of ozone layer depletion and global warming. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Almadhagi, Ahmed Noman Kassim (1992) YAR-US relations 1962-1990: a case study of a superpower-small state relationship. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Joao da Costa Cabral Andresen Guimaraes, Fernando (1992) The origins of the Angolan civil war. International politics and domestic political conflict 1961-1976. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Ming, Dong (1991) The principles and flexibility in China's external relations: The case of Hong Kong. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Bello, Ghaji Ismaila (1990) The international politics of famine relief operations in Ethiopia: A case study of the 1984-86 famine relief operations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Williams, Marc Andrew (1987) The group of 77 in UNCTAD: anatomy of a Third World coalition. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Suganami, Hidemi (1986) Domestic analogy in proposals for world order, 1814-1945: the transfer of legal and political principles from the domestic to the international sphere in thought on international law and relations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Linklater, Andrew (1978) Obligations beyond the state: the individual, the state and humanity in international theory. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Report a problem
Thank you, your report has been submitted. We will deal with the issue as soon as possible. If you have any other questions, please send an email to [email protected] .

Your Programmes
Mphil/phd msc bsc(hons) international relations.
1 in 9 applicants to this programme received an offer.
Data shown above is for entry in academic year 2021/22 (sources) .
Previous Years
Data sources.
- FOI Request by Albert Warren. December 2019.
- Freedom of Information (FOI) . London School of Economics. October 2022.
The acceptance rate , or offer rate, represents the fraction of applicants who received an offer. Note that this will be generally lower the acceptances rates (acceptances divided by applicants) published by many other sources. This article explains it in more detail. The acceptances generally indicate the number of offer holders who accepted the offer and fulfilled its conditions. For some universities, however, it denotes the number of applicants who accepted the offer, regardless of whether they subsequently met its conditions.
Data Reliability
Unless otherwise noted, the data presented comes from the universities and is generally reliable. However, some of the differences between years and/or courses may be due to different counting methodologies or data gathering errors. This may especially be the case if there is a sharp difference from year to year. If the data does not look right, click the "Report" button located near the top of the page.
Follow Us On Twitter/X


- About this blog
- IR Department website
- IR Department Staff
- IR Programmes of Study
LSE Department of International Relations blog
Latest posts, the un's 68th annual commission on the status of women (csw68): a report, may 14th, 2024.

Deciphering China’s ambitions in space – student event blogger report
May 29th, 2024.

European naval deployments in the Indo-Pacific: why are they there?
May 9th, 2024.
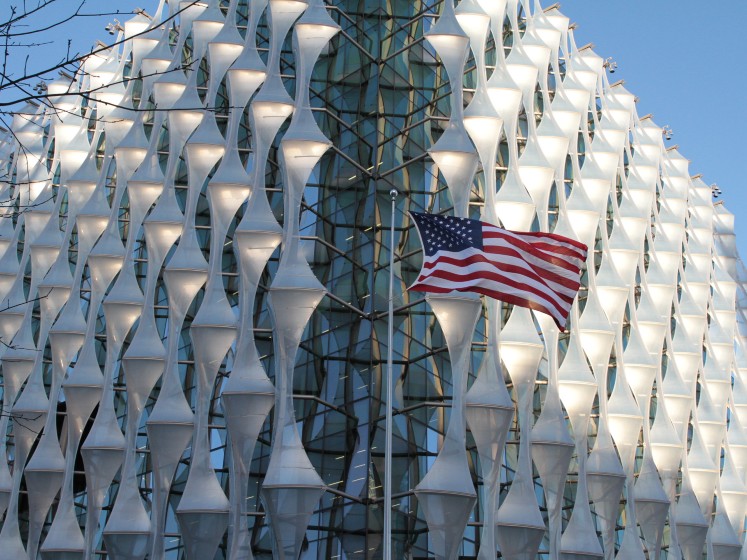

Diplomacy Day at the US Embassy in London 2024
April 30th, 2024, department news.

MSc Prizewinners 2022/23 announced
January 31st, 2024.

BSc IR Prizewinners 2022/23 announced
January 16th, 2024.
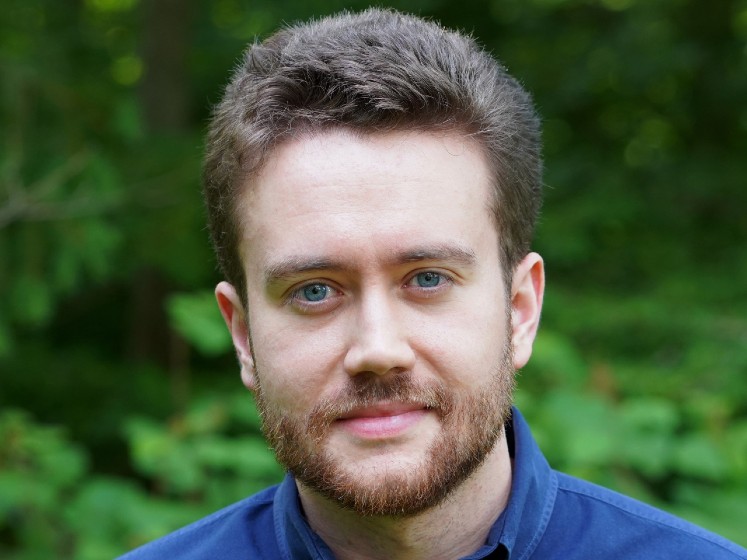

Introducing our new Assistant Professor Dr Noah Zucker joining 2023
October 3rd, 2023.

Four questions about the West’s future support for Ukraine
March 5th, 2024.

Lessons from studying the past: writing about the ethics of political commemoration
February 1st, 2024.

The Centre for International Studies (CIS): History and list of Fellows
July 21st, 2022.

Women international thinkers at LSE
July 12th, 2022.

Goldsworthy Lowes Dickinson, LSE and the origins of International Relations
February 22nd, 2022, featured alumni.

City diplomacy in the fight against climate emergency
August 17th, 2022.

From a PhD in IR at LSE to the top of a think tank
May 31st, 2022, follow us on x (twitter).

Follow us on LinkedIn

Follow us on Facebook
Our world-leading 🌏department is now in our 96th year, making us one of the oldest as well as largest in the world. #lseir 📍@londonschoolofeconomics


DPhil in International Relations
- Entry requirements
- Funding and Costs
College preference
- How to Apply
About the course
The DPhil programme is a full-time programme of doctoral research in the academic study of International Relations with an expected length of three to four years of full-time study or six to eight years of part-time study. Note that the part-time option is not a distance-learning programme; part-time students are required to attend face-to-face teaching in Oxford on up to three separate days each week during term.
As a DPhil student you will be a member of a distinguished academic community that is renowned for its cutting-edge research and its intensive and individualised teaching and supervision. The programme has received the highest level of recognition in UK national and global assessment exercises. It is a community from which you will draw support and guidance but which will also learn from your own contribution to its work.
You will have rich opportunities for connecting with fellow-students, postdoctoral fellows, and temporary and permanent academic staff involved in disciplinary and cross-disciplinary research programmes. The department attracts many of the world’s leading figures in International Relations (IR) - as visiting scholars, speakers in the regular IR Colloquium, and participants in research conferences and workshops.
Doctoral students spend the first year of full-time study, or the first two years of part-time study, in the development of, and early work on, the thesis topic; in improving knowledge of quantitative and qualitative research methods; in attendance at relevant lectures, seminars and classes; and in preparing to transfer from Probationary Research Student (PRS - the status at which you will normally be admitted - see Assessment) to full DPhil status.
An academic supervisor will advise and guide you as you progress through the different stages of your doctoral research. In addition to work for your supervisor, you will be required to take a range of coursework. In the first term this includes: Research Design and Methods (RDM) in IR, Research Design, and introductory or intermediate statistics, as well as attendance at the regular IR DPhil Research Seminar which runs through the year and at which doctoral students present their work. In the second term students continue with RDM in IR and take one course in Formal Analysis, Causal Inference or Qualitative Methods. In the third term, there are a series of short, specialised methods courses. For part-time students, these coursework obligations are distributed across six terms.
Exemptions from particular elements of the coursework can be sought on the basis of previous training. Subsequent years are largely devoted to the development of the thesis project.
Doctoral theses will normally require substantial original research, often involving archives, fieldwork, interviewing or other forms of data generation and collection. For the doctoral degree the most crucial requirement is that the thesis makes a ‘significant and substantial contribution to the field of knowledge within which it falls’. There are many ways of achieving this.
The department is committed to the rigorous use of a plurality of methods. There are many different ways of conducting research for a thesis. Any or all may be valid in a given case, depending on the subject of the research and the questions addressed. Some theses may involve an analytical-descriptive attempt at understanding different events, perspectives and traditions of thought. Others may have a strong historiographical element - exploring, for example, the relation between events and ideas, or involving an original and expert use of sources. Others may involve advancing a hypothesis about a subject and then testing it with a range of qualitative and/or quantitative approaches. Apart from meeting the highest scholarly standards, there is no set template. There is also a strong and successful tradition of normative and critical work. Oxford IR seeks to combine the best of North American political science with deep engagement with the international relations of different parts of the world and with the history of different traditions of thought on the subject.
As a doctoral student of the department, you will have access to outstanding library and computing resources within the Social Sciences Division (of which the Department of Politics and IR is a major part), elsewhere in the University and, in most cases, in your college. The division runs network events to enable DPhil students to meet and network with their colleagues not only within politics and IR but with other social science disciplines.
As a part-time student you will be required to attend classes, seminars, supervision meetings and other obligations in Oxford for a minimum of thirty days each year. There will be limited flexibility in the dates and pattern of attendance. Attendance will be required during term-time at least one day each week throughout the first two years of your study on days determined by your class and seminar attendance and by your supervisor. Attendance will be required outside of term-time on dates to be determined by mutual agreement with your supervisor. You will be required to attend fieldwork and training sessions on dates to be determined by mutual agreement with your supervisor.
Successful completion of an Oxford DPhil requires an intense and sustained level of personal motivation and focus within a world-class research and teaching environment.
Supervision
The allocation of graduate supervision for this course is the responsibility of the Department of Politics and International Relations and it is not always possible to accommodate the preferences of incoming graduate students to work with a particular member of staff. Supervisors are usually selected from the academic staff within the Department of Politics and International Relations. Under exceptional circumstances a supervisor may be found outside the Department of Politics and International Relations.
You will be assigned an academic supervisor who will advise and guide you as you progress through the different stages of your doctoral research.
Applicants are admitted to the DPhil with Probationer Research Student (PRS) status. As a PRS, you will develop your research proposal and skills, complete a programme of assessed research methods coursework, and produce a draft section or sections of the thesis, in order to apply for the Transfer of Status that will end your probationary period as a research student. The Graduate Studies Committee will require satisfactory completion of this training programme as a condition of your change of status from PRS to DPhil.
Once you have been admitted to full DPhil status, you must achieve confirmation of that status by the end of your ninth term as a full-time doctoral student, or by the end of your eighteenth term as a part-time student. Once you have completed your thesis, you will be examined viva voce .
Graduate destinations
International Relations has an outstanding placement record. The largest group of DPhil students go on to careers in academia or research. Many move on to post-doctoral fellowships in the UK, continental Europe and North America. Our doctoral students have a distinguished history of winning thesis and other prizes and of publishing their work in leading journals and with major university presses. The universities at which IR graduates have gained academic positions over recent years include: ANU, McGill, Waterloo, Sciences Po, Amsterdam, Groningen, The Graduate Institute Geneva, SAIS/JHU, ETH Zürich, The New School, Swarthmore, LSE, Oxford, Cambridge, King’s College London, University College London, Queen Mary London, St Andrews, Exeter, Reading, Warwick, PUC Santiago, and FGV São Paulo. Oxford IR DPhils also work at all levels in many of world’s leading think-tanks and research institutes in Europe and North America but also in Brazil, South Africa, and Singapore. Others still have moved to achieve leading positions in the policy and political world. The department runs regular courses on professional training, including on interviews, research grant applications and academic publishing.
DPIR is committed to engaging with its alumni community , through its Inspires alumni email newsletter and Alumni Career Conversations series of online talks.
Changes to this course and your supervision
The University will seek to deliver this course in accordance with the description set out in this course page. However, there may be situations in which it is desirable or necessary for the University to make changes in course provision, either before or after registration. The safety of students, staff and visitors is paramount and major changes to delivery or services may have to be made in circumstances of a pandemic, epidemic or local health emergency. In addition, in certain circumstances, for example due to visa difficulties or because the health needs of students cannot be met, it may be necessary to make adjustments to course requirements for international study.
Where possible your academic supervisor will not change for the duration of your course. However, it may be necessary to assign a new academic supervisor during the course of study or before registration for reasons which might include illness, sabbatical leave, parental leave or change in employment.
For further information please see our page on changes to courses and the provisions of the student contract regarding changes to courses.
Entry requirements for entry in 2024-25
Proven and potential academic excellence.
The requirements described below are specific to this course and apply only in the year of entry that is shown. You can use our interactive tool to help you evaluate whether your application is likely to be competitive .
Please be aware that any studentships that are linked to this course may have different or additional requirements and you should read any studentship information carefully before applying.
Degree-level qualifications
As a minimum, applicants should hold or be predicted to achieve the following UK qualifications or their equivalent:
- a master’s degree at distinction level in international relations, or in a closely related discipline that has prepared you to undertake advanced graduate research on your chosen thesis topic; and
- a first-class or strong upper second-class undergraduate degree with honours in politics or international relations, or in a related discipline such as economics, history, philosophy, sociology or law.
Entrance is very competitive and most successful applicants have a record of academic performance at first-class and/or distinction level.
Applicants without a master’s qualification will not normally be admitted for doctoral study.
Each application will be assessed upon its own merits, and candidates with a degree in an unrelated discipline should demonstrate the relevance of their academic background to their proposed subject or topic of study.
For applicants with a degree from the USA, the minimum GPA sought is 3.7 out of 4.0.
If your degree is not from the UK or another country specified above, visit our International Qualifications page for guidance on the qualifications and grades that would usually be considered to meet the University’s minimum entry requirements.
GRE General Test scores
No Graduate Record Examination (GRE) or GMAT scores are sought.
Other qualifications, evidence of excellence and relevant experience
- Research or work experience that is relevant to your proposed study may provide further evidence of your academic potential.
- Publications are not expected, but a peer-reviewed publication in international relations or an allied discipline may be taken as prima facie evidence of aptitude for research.
Part-time applicants
Part-time applicants will also be expected to show evidence of the ability to commit time to study and, if applicable, an employer's commitment to make time available to study, to complete coursework, and attend course and University events and modules in Oxford. Where appropriate, evidence should also be provided of permission to use employers’ data in the proposed research project. As a probationer research student, coursework requirements will necessitate attendance in Oxford for at least one day per week during full-term. It is therefore likely that part-time students are either already resident in Oxford or will live within commuting distance of the city, such as via the strong transport links along the M4 corridor and between major cities to the north (including Birmingham) and south (including Southampton).
English language proficiency
This course requires proficiency in English at the University's higher level . If your first language is not English, you may need to provide evidence that you meet this requirement. The minimum scores required to meet the University's higher level are detailed in the table below.
*Previously known as the Cambridge Certificate of Advanced English or Cambridge English: Advanced (CAE) † Previously known as the Cambridge Certificate of Proficiency in English or Cambridge English: Proficiency (CPE)
Your test must have been taken no more than two years before the start date of your course. Our Application Guide provides further information about the English language test requirement .
Declaring extenuating circumstances
If your ability to meet the entry requirements has been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic (eg you were awarded an unclassified/ungraded degree) or any other exceptional personal circumstance (eg other illness or bereavement), please refer to the guidance on extenuating circumstances in the Application Guide for information about how to declare this so that your application can be considered appropriately.
You will need to register three referees who can give an informed view of your academic ability and suitability for the course. The How to apply section of this page provides details of the types of reference that are required in support of your application for this course and how these will be assessed.
Supporting documents
You will be required to supply supporting documents with your application. The How to apply section of this page provides details of the supporting documents that are required as part of your application for this course and how these will be assessed.
Performance at interview
Interviews are not normally held as part of the admissions process.
How your application is assessed
Your application will be assessed purely on your proven and potential academic excellence and other entry requirements described under that heading.
References and supporting documents submitted as part of your application, and your performance at interview (if interviews are held) will be considered as part of the assessment process. Whether or not you have secured funding will not be taken into consideration when your application is assessed.
An overview of the shortlisting and selection process is provided below. Our ' After you apply ' pages provide more information about how applications are assessed .
Shortlisting and selection
Students are considered for shortlisting and selected for admission without regard to age, disability, gender reassignment, marital or civil partnership status, pregnancy and maternity, race (including colour, nationality and ethnic or national origins), religion or belief (including lack of belief), sex, sexual orientation, as well as other relevant circumstances including parental or caring responsibilities or social background. However, please note the following:
- socio-economic information may be taken into account in the selection of applicants and award of scholarships for courses that are part of the University’s pilot selection procedure and for scholarships aimed at under-represented groups ;
- country of ordinary residence may be taken into account in the awarding of certain scholarships; and
- protected characteristics may be taken into account during shortlisting for interview or the award of scholarships where the University has approved a positive action case under the Equality Act 2010.
Initiatives to improve access to graduate study
This course is taking part in a continuing pilot programme to improve the selection procedure for graduate applications, in order to ensure that all candidates are evaluated fairly.
For this course, socio-economic data (where it has been provided in the application form) will be used to contextualise applications at the different stages of the selection process. Further information about how we use your socio-economic data can be found in our page about initiatives to improve access to graduate study.
Processing your data for shortlisting and selection
Information about processing special category data for the purposes of positive action and using your data to assess your eligibility for funding , can be found in our Postgraduate Applicant Privacy Policy.
Admissions panels and assessors
All recommendations to admit a student involve the judgement of at least two members of the academic staff with relevant experience and expertise, and must also be approved by the Director of Graduate Studies or Admissions Committee (or equivalent within the department).
Admissions panels or committees will always include at least one member of academic staff who has undertaken appropriate training.
Other factors governing whether places can be offered
The following factors will also govern whether candidates can be offered places:
- the ability of the University to provide the appropriate supervision for your studies, as outlined under the 'Supervision' heading in the About section of this page;
- the ability of the University to provide appropriate support for your studies (eg through the provision of facilities, resources, teaching and/or research opportunities); and
- minimum and maximum limits to the numbers of students who may be admitted to the University's taught and research programmes.
Offer conditions for successful applications
If you receive an offer of a place at Oxford, your offer will outline any conditions that you need to satisfy and any actions you need to take, together with any associated deadlines. These may include academic conditions, such as achieving a specific final grade in your current degree course. These conditions will usually depend on your individual academic circumstances and may vary between applicants. Our ' After you apply ' pages provide more information about offers and conditions .
In addition to any academic conditions which are set, you will also be required to meet the following requirements:
Financial Declaration
If you are offered a place, you will be required to complete a Financial Declaration in order to meet your financial condition of admission.
Disclosure of criminal convictions
In accordance with the University’s obligations towards students and staff, we will ask you to declare any relevant, unspent criminal convictions before you can take up a place at Oxford.
The DPIR provides a stimulating research environment in which you can pursue your interests beyond the formal demands of the syllabus.
Many of the academic staff who teach on the graduate programmes also organise extracurricular research seminars for graduate students, such as, the International Relations Research.
The DPIR also hosts a wide range of research centres and programmes which actively seek to develop collaborative research activity via conferences, workshops and other academic events, and which include graduate students in their activities.
Research centres provide opportunities for you to present your own work in research seminar series and at conferences in the department and beyond. The research centres have an established and popular visitors’ programme which has allowed many scholars of international repute to participate in the DPIR’s research activities.
At Oxford you have access to an extensive range of libraries, books, journals, online resources, manuscripts and more. The Bodleian Libraries is the main library service supporting the University of Oxford. The Bodleian Libraries include the Bodleian Library, which has been a library of legal deposit for 400 years, as well as the Bodleian Social Science Library . This is located on the ground floor of the Manor Road Building and houses the main collection for Politics and International Relations alongside a wide range of other social sciences resources.
SOLO (Search Oxford Libraries Online) is the search engine for all library collections across the university. It provides access to information in over 100 libraries including college and departmental libraries as well as the Bodleian Libraries. Your Single Sign-On offers easy access to subscription resources through SOLO. The Politics and International Relations subject guide provides up-to-date advice and the contact details of your Subject Librarian for further support.

Politics and International Relations
The Department of Politics and International Relations (DPIR) at Oxford is an internationally-renowned centre of excellence for teaching and research.
The study of these disciplines at Oxford has a long and distinguished history and the DPIR is now one of the largest in the field in the UK. DPIR is ranked first for research overall in the most recent THES global university rankings for Politics and International Studies and second in the 2023 QS World University Rankings.
The department's large community of academic staff work in research areas that extend in geographical scope across the globe, cover both historical and contemporary sources, and address technical, practical, and philosophical problems in networks that extend beyond the DPIR to other departments, universities, and global and local organisations.
Graduate students have access to an unrivalled range of expertise and activity in the fields of government and politics, political theory, and international studies. Teaching is based on the most rigorous contemporary scholarship and students are trained in the highest standards of critical analysis, and in the understanding and use of rigorous research methods and techniques. The department’s graduate courses include both taught master's degrees (one-year research preparation MSc and two-year MPhil) and three- to four-year doctoral research degrees (DPhil). However, all taught degrees involve a research element, and all research degrees will involve some taught components, including quantitative and qualitative research methods. The DPIR graduate community currently numbers just over 300, with 150 students studying the taught courses and around 170 undertaking doctoral research.
View all courses View taught courses View research courses
The University expects to be able to offer over 1,000 full or partial graduate scholarships across the collegiate University in 2024-25. You will be automatically considered for the majority of Oxford scholarships , if you fulfil the eligibility criteria and submit your graduate application by the relevant December or January deadline. Most scholarships are awarded on the basis of academic merit and/or potential.
For further details about searching for funding as a graduate student visit our dedicated Funding pages, which contain information about how to apply for Oxford scholarships requiring an additional application, details of external funding, loan schemes and other funding sources.
Please ensure that you visit individual college websites for details of any college-specific funding opportunities using the links provided on our college pages or below:
Please note that not all the colleges listed above may accept students on this course. For details of those which do, please refer to the College preference section of this page.
Further information about funding opportunities for this course can be found on the department's website.
Annual fees for entry in 2024-25
Full-time study.
Further details about fee status eligibility can be found on the fee status webpage.
Part-time study
Information about course fees.
Course fees are payable each year, for the duration of your fee liability (your fee liability is the length of time for which you are required to pay course fees). For courses lasting longer than one year, please be aware that fees will usually increase annually. For details, please see our guidance on changes to fees and charges .
Course fees cover your teaching as well as other academic services and facilities provided to support your studies. Unless specified in the additional information section below, course fees do not cover your accommodation, residential costs or other living costs. They also don’t cover any additional costs and charges that are outlined in the additional information below.
Continuation charges
Following the period of fee liability , you may also be required to pay a University continuation charge and a college continuation charge. The University and college continuation charges are shown on the Continuation charges page.
Where can I find further information about fees?
The Fees and Funding section of this website provides further information about course fees , including information about fee status and eligibility and your length of fee liability .
Additional information
There are no compulsory elements of this course that entail additional costs beyond fees (or, after fee liability ends, continuation charges) and living costs. However, please note that, depending on your choice of research topic and the research required to complete it, you may incur additional expenses, such as travel and vaccination expenses, conference attendance, research expenses, and field trips. You will need to meet these additional costs, although you may be able to apply for small grants from your department and/or college to help you cover some of these expenses.
There are no compulsory elements of this course that entail additional costs beyond fees (or, after fee liability ends, continuation charges) and living costs.
Please note that you are required to attend in Oxford for a minimum of 30 days each year, and you may incur additional travel and accommodation expenses for this. Also, depending on your choice of research topic and the research required to complete it, you may incur further additional expenses, such as travel and vaccination expenses, conference attendance, research expenses, and field trips. You will need to meet these additional costs, although you may be able to apply for small grants from your department and/or college to help you cover some of these expenses.
Living costs
In addition to your course fees, you will need to ensure that you have adequate funds to support your living costs for the duration of your course.
For the 2024-25 academic year, the range of likely living costs for full-time study is between c. £1,345 and £1,955 for each month spent in Oxford. Full information, including a breakdown of likely living costs in Oxford for items such as food, accommodation and study costs, is available on our living costs page. The current economic climate and high national rate of inflation make it very hard to estimate potential changes to the cost of living over the next few years. When planning your finances for any future years of study in Oxford beyond 2024-25, it is suggested that you allow for potential increases in living expenses of around 5% each year – although this rate may vary depending on the national economic situation. UK inflationary increases will be kept under review and this page updated.
If you are studying part-time your living costs may vary depending on your personal circumstances but you must still ensure that you will have sufficient funding to meet these costs for the duration of your course.
Students enrolled on this course will belong to both a department/faculty and a college. Please note that ‘college’ and ‘colleges’ refers to all 43 of the University’s colleges, including those designated as societies and permanent private halls (PPHs).
If you apply for a place on this course you will have the option to express a preference for one of the colleges listed below, or you can ask us to find a college for you. Before deciding, we suggest that you read our brief introduction to the college system at Oxford and our advice about expressing a college preference . For some courses, the department may have provided some additional advice below to help you decide.
The following colleges accept students for full-time study on this course:
- Balliol College
- Blackfriars
- Brasenose College
- Campion Hall
- Christ Church
- Exeter College
- Green Templeton College
- Harris Manchester College
- Hertford College
- Jesus College
- Keble College
- Kellogg College
- Lady Margaret Hall
- Linacre College
- Lincoln College
- Magdalen College
- Mansfield College
- New College
- Nuffield College
- Oriel College
- Pembroke College
- Regent's Park College
- Reuben College
- St Anne's College
- St Antony's College
- St Catherine's College
- St Cross College
- St Edmund Hall
- St Hilda's College
- St Hugh's College
- St John's College
- St Peter's College
- Somerville College
- Trinity College
- University College
- Wadham College
- Wolfson College
- Worcester College
- Wycliffe Hall
The following colleges accept students for part-time study on this course:
Before you apply
Our guide to getting started provides general advice on how to prepare for and start your application. You can use our interactive tool to help you evaluate whether your application is likely to be competitive .
If it's important for you to have your application considered under a particular deadline – eg under a December or January deadline in order to be considered for Oxford scholarships – we recommend that you aim to complete and submit your application at least two weeks in advance . Check the deadlines on this page and the information about deadlines and when to apply in our Application Guide.
Application fee waivers
An application fee of £75 is payable per course application. Application fee waivers are available for the following applicants who meet the eligibility criteria:
- applicants from low-income countries;
- refugees and displaced persons;
- UK applicants from low-income backgrounds; and
- applicants who applied for our Graduate Access Programmes in the past two years and met the eligibility criteria.
You are encouraged to check whether you're eligible for an application fee waiver before you apply.
Readmission for current Oxford graduate taught students
If you're currently studying for an Oxford graduate taught course and apply to this course with no break in your studies, you may be eligible to apply to this course as a readmission applicant. The application fee will be waived for an eligible application of this type. Check whether you're eligible to apply for readmission .
Do I need to contact anyone before I apply?
You are advised to review the profiles of academic staff before you apply as successful applications always depend on the DPIR's capacity to offer appropriate supervision. A supervisor should be a permanent member of the Department of Politics and International Relations. You are not required to make contact with any prospective supervisors before you apply, as the DPIR arranges supervision for successful applicants. General questions about the course should be directed to the course administrator via the contact details provided on this page.
Completing your application
You should refer to the information below when completing the application form, paying attention to the specific requirements for the supporting documents .
For this course, the application form will include questions that collect information that would usually be included in a CV/résumé. You should not upload a separate document. If a separate CV/résumé is uploaded, it will be removed from your application .
If any document does not meet the specification, including the stipulated word count, your application may be considered incomplete and not assessed by the academic department. Expand each section to show further details.
Proposed field and title of research project
Under the 'Field and title of research project' please enter your proposed field or area of research if this is known. If the department has advertised a specific research project that you would like to be considered for, please enter the project title here instead.
You should not use this field to type out a full research proposal. You will be able to upload your research supporting materials separately if they are required (as described below).
Proposed supervisor
Under 'Proposed supervisor name' enter the name of the academic(s) who you would like to supervise your research.
You can enter the names of up to two supervisors, either in order of preference or indicating equal preference.
Referees: Three overall, academic preferred
Whilst you must register three referees, the department may start the assessment of your application if two of the three references are submitted by the course deadline and your application is otherwise complete. Please note that you may still be required to ensure your third referee supplies a reference for consideration.
Your application must be supported by academic references, ie each referee should be able to testify to your academic abilities, achievements and motivation. In most cases, the academics who have taught you or who have known your academic work during earlier university-level study will be best placed to testify to these capabilities. When that is not possible, a professional reference from a colleague who has worked with you in a research capacity or is otherwise able to comment on your academic capabilities is acceptable in place of a tutor’s reference.
Official transcript(s)
Your transcripts should give detailed information of the individual grades received in your university-level qualifications to date. You should only upload official documents issued by your institution and any transcript not in English should be accompanied by a certified translation.
More information about the transcript requirement is available in the Application Guide.
Research proposal: A minimum of 4,000 words to a maximum of 6,000 words
You should submit a detailed outline of your proposed research, written in English, covering areas such as the background to the research, methodology, expected results and the contribution to the field of learning.
The research proposal should be written in English.
If possible, please ensure that the word count is clearly displayed on the document.
This will be assessed for:
- your reasons for applying to the DPhil programme
- the coherence of the proposal
- the originality of the project
- evidence of motivation for and understanding of the proposed area of study
- the ability to present a reasoned case in English
- the feasibility of successfully completing the project in the time available for the degree (a maximum of four years)
- commitment to the subject, beyond the requirements of the degree course
- preliminary knowledge of research techniques
- capacity for sustained and intense work
- reasoning ability
- ability to absorb new ideas, often presented abstractly, at a rapid pace.
It will be normal for your ideas subsequently to change in some ways as you investigate the evidence and develop your project. You should nevertheless make the best effort you can to demonstrate the extent of your research question, sources and method at this moment.
Your proposal should focus on your research project rather than personal achievements, interests and aspirations.
Written work: Two essays, a maximum of 2,000 words each
You may submit academic essays on any subject or theme within the discipline of international relations but preferably ones that relate to your proposed area of study.
The essays may be written specially for the application or may have been produced for other purposes, for instance as a coursework submission within a previous degree programme. Essays that comprise extracts or excerpted sections from longer pieces are acceptable but should be prefaced with a brief note that places them in context.
The word count does not need to include any bibliography or brief footnotes. All written work should be in English.
This will be assessed for understanding of the subject area; understanding of problems in the area; ability to construct and defend an argument; powers of analysis; and powers of expression.
Start or continue your application
You can start or return to an application using the relevant link below. As you complete the form, please refer to the requirements above and consult our Application Guide for advice . You'll find the answers to most common queries in our FAQs.
Application Guide Apply - Full time Apply - Part time
ADMISSION STATUS
Closed to applications for entry in 2024-25
Register to be notified via email when the next application cycle opens (for entry in 2025-26)
12:00 midday UK time on:
Friday 5 January 2024 Latest deadline for most Oxford scholarships Final application deadline for entry in 2024-25
*Three-year average (applications for entry in 2021-22 to 2023-24)
Further information and enquiries
This course is offered by the Department of Politics and International Relations
- Course page on the department's website
- Funding information from the department
- Academic and research staff
- Departmental research
- Social Sciences Division
- Residence requirements for full-time courses
- Postgraduate applicant privacy policy
Course-related enquiries
Advice about contacting the department can be found in the How to apply section of this page
✉ [email protected] ☎ +44 (0)1865 278727
Application-process enquiries
See the application guide
Visa eligibility for part-time study
We are unable to sponsor student visas for part-time study on this course. Part-time students may be able to attend on a visitor visa for short blocks of time only (and leave after each visit) and will need to remain based outside the UK.

BSc International Relations and History
Introduction, preliminary readings.
This BSc International Relations and History allows you to study two complementary subjects. You’ll look at the nature of the changing dynamics between different countries and the impact of the uneven distribution of power, money, welfare and knowledge on foreign policies and international order.
For the history elements, you’ll analyse the political, economic, social and cultural developments that have shaped states and their relationships with other countries. Our history courses are distinctive for their international perspective – covering Asia, the Middle East, Africa, the Americas, Europe and Britain.
The programme draws on the combined expertise of two internationally renowned departments. As you progress, you’ll develop your analytical powers, analyse complex evidence from a variety of sources and learn how to present your findings clearly – all highly transferable skills for your future career.
This programme provides an excellent springboard for a future career in politics, government, NGOs, journalism and research.
- M Abbott History Skills (Routledge, 1996)
- A Best et al An International History of the Twentieth Century and Beyond (Routledge, 2014)
- D Cannadine What is History Now? (Palgrave, 2002)
- R Evans In Defence of History (Granta, 1997)
- D Reynolds One World Divisible (Norton, 2000)
- D Stevenson 1914-1918: the history of the First World War (Allen Lane, 2004)
- O A Westad The Global Cold War: Third World interventions and the making of our times (Cambridge University Press, 2007)
International relations
- C Alden and A Aron Foreign Policy Analysis: new approaches (Routledge, 2011)
- J Baylis, S Smith and P Owens (eds) The Globalization of World Politics: an introduction to international relations (6th edition, Oxford University Press, 2013)
- C Brown, with K Ainley Understanding International Relations (Macmillan, 2009)
- B Buzan and R Little International Systems in World History: remaking the study of international relations (Oxford University Press, 2000)
- R Jackson and G Sorensen An Introduction to International Relations: theories and approaches (5th edition, Oxford University Press, 2012)
- R Shilliam International Relations and Non-Western Thought: imperialism, colonialism and investigations of global modernity (Routledge, 2010)
- J Steans Gender & International Relations (Polity Press, 2013)
- T G Weiss and R Wilkinson (eds) International Organization and Global Governance (Routledge, 2014)
- J Young and J Kent International Relations since 1945: a global history (2nd ed, Oxford University Press, 2013)
Entry requirements
Here, you can check our entry requirements for GCSEs, A-levels (please read them alongside our information about subject combinations) and the International Baccalaureate (IB) Diploma. We also consider applications from students with a range of other UK qualifications and from overseas. Please select the overseas button below and choose your country from the dropdown list to find the equivalency to A-levels of your qualification.
For GCSEs, you’ll need a strong pre-16 academic profile such as several GCSE grades of A (or 7) and A* (or 8-9).
We also ask for a good set of GCSE grades or equivalent across a broad range of subjects, with a minimum of grade B (or 6) in GCSE English and Mathematics.
We also consider your AS grades, if available.
Contextual admissions A-level grades
Read our undergraduate admissions information to learn more about contextual admissions.
A-level subject combinations
- We consider your combination of subjects as well as your grades.
- A broad mix of traditional academic subjects provides the best preparation for studying at LSE. We expect applicants to have at least two full A-levels (or equivalent) in these subjects.
- We’re looking for students with a genuine interest in and enthusiasm for the social sciences, particularly history and international relations.
- There is no one set subject combination. Typical subject choices include History, English, Economics, Government and Politics, Sociology, modern languages and Philosophy.
- A-level History (or equivalent) is not a required subject.
- If you’ve taken Mathematics, Further Mathematics and one other subject at A-level, this may be considered a less competitive combination than a broader mix of essay-based and quantitative subjects.
Find out more about A-level subject combinations .
38 points overall , including 766 at higher level
Contextual admissions IB grades
37 points overall , including 666 at higher level
We welcome students from all walks of life at LSE. We want to recruit students with the very best academic merit, potential and motivation. So, whatever your background, please do apply. Get all the details on our general entry requirements .
Competition for places at LSE is high. We cannot guarantee you an offer of a place even if you’re predicted or achieve our standard entry requirements.
Our standard offer requirements are intended only as a guide and, in some cases, you’ll be asked for different grades.
Programme content
Why study with us.
Discover more about our students and department.
Student stories
Meet the department.

History is a wide ranging and challenging subject to study. It seeks to understand the past and to make sense of the present, adding an important dimension to the understanding of many aspects of human society. The department is world renowned in its field, offering a unique perspective on the history of relations between states, peoples and cultures. We pride ourselves on giving students the benefit of ground-breaking research throughout our teaching programmes.
Our degrees will give you a broad international perspective on the past. We give attention both to domestic and international issues and many of the courses we offer deal with major events in the history of international relations.
Since the behaviour of countries in the international arena cannot be understood without a knowledge of their distinct social, political, economic and cultural characteristics, we provide courses covering major aspects of the history of ideas and mentalities.
LSE was founded in 1895 originally as an institute of higher education for graduate students. The department reflects this tradition and takes its responsibility for undergraduate teaching and supervision very seriously. We admit nearly as many undergraduate students as master's students. We have one of the most cosmopolitan undergraduate communities in London and one of the most vibrant and dynamic.
Learn more about our programmes , research , public events and people .
Department of International History
2nd In Europe
5th In the world
1st We're ranked top university in London for the 12th year running
Carbon neutral in 2021 lse became the first carbon neutral verified university in the uk, your application, who attends.
We consider each application carefully, taking into account all the details you’ve included on your UCAS form, such as:
- academic achievement , including predicted and achieved grades (also see specific information about this programme in the "entry requirements" above)
- subjects and subject combinations (also see specific information about this programme in the "entry requirements" above)
- your personal statement
- your teacher’s reference
- educational circumstances
You may also have to provide evidence of your English proficiency, although this is not needed at the application stage. See our English language requirements page .
We’re looking for students who demonstrate:
- an equal interest in history and international relations (international society, its institutions, governance, rules and relationships)
- a willingness to read extensively
- intellectual curiosity
- an ability to evaluate and challenge conventional views
- great communication skills
- initiative and enthusiasm
- attention to detail
- self-motivation and a willingness to work hard.
Fees and funding
The table of fees shows the latest tuition fees for all programmes.
You're charged a fee for each year of your programme. Your tuition fee covers registration and examination fees payable to the School, lectures, classes and individual supervision, lectures given at other colleges under intercollegiate arrangements and, under current arrangements, membership of the Students' Union. It doesn't cover living costs or travel or fieldwork.
Your tuition fees, and eligibility for any financial support, depend on whether you’re classified as a home or an overseas student – known as your fee status. We assess your fee status based on guidelines from the UK Government’s Department for Education.
Learn more about fee status classification .
Scholarships, bursaries and loans
We recognise that the cost of living in London may be higher than in your home town or country. LSE provides generous financial support, in the form of bursaries and scholarships, to UK, EU and overseas students.
Additionally, the UK Government provides loans to UK and some EU students. Some overseas governments also offer funding.
Further information on tuition fees, living costs, loans and scholarships .
Learning and assessment
How you learn, how you're assessed.
Format: you’ll have weekly lectures and classes in small groups, totalling around eight hours per week. Hours vary depending on the course. Get a broad idea of the study time involved in the Calendar within the Teaching section of each course guide . Contact hours: you’ll need to spend around 15 to 20 hours each week on independent study during term time and holidays. This will involve reading extensively and writing between three to five essays and/or class papers per course.
LSE teaching: LSE is internationally recognised for teaching and research and you’ll be taught by academic staff and PhD students. Learn more about the teacher responsible for each course in the relevant course guide .
Academic support
Academic mentor: you’ll meet with your academic mentor regularly to discuss your work. Your mentor can provide advice and guidance on academic issues and, where appropriate, personal concerns.
Other academic support: at LSE, we offer lots of opportunities to extend your learning outside the classroom.
LSE LIFE is a great place to get advice and practise the skills you’ll need during your studies and beyond.
Through LSE LIFE, you can:
- attend workshops on developing leadership skills, finding the right study/work/life balance and preparing for the world of work
- develop your reading, academic writing and critical-thinking skills
- gain experience of working in study groups and develop your cross-cultural communication and teamwork skills.
Disability and Mental Health Service: we want all LSE students to achieve their full potential. Students can access free, confidential advice through our Disability and Mental Health Service . This is the first point of contact for students.
Your timetable
- The standard teaching day runs from 9am to 6pm, Monday to Friday. Undergraduate teaching is not normally scheduled for Wednesdays after 12 noon to allow for sports, volunteering and other extra-curricular activities.
- The lecture and seminar timetable is published in mid-August and the full academic timetable (with information on classes) is published by mid-September via the LSE timetables web pages .
- All personal undergraduate timetables are published in LSE for You (LFY) . For personal timetables to appear, you must be registered at LSE, be signed up for courses in LFY and ensured that there are no unauthorised clashes in your course selections. We try our best to minimise changes once personal timetables have been published. However, you’ll be notified about any changes by email.
Formative coursework
A ll taught courses include formative coursework, which is not assessed. This helps prepare you for summative assessment. We use a wide range of formative assessment methods, such as essays, case studies, reports, quizzes and mock exams.
Feedback on coursework is an essential part of the learning experience. Class teachers mark formative coursework and feedback is normally given within two weeks – provided the work is submitted on time.
Some history courses include written assessments and many include continuous summative assessment.
Summative assessment
This assessment counts towards your final course mark and degree award.
You’ll receive feedback on any summative coursework as part of the assessment for individual courses (except for final submitted dissertations). Feedback will normally be provided before the examination period.
Assessment on individual courses can change from year to year. Read about the current formative coursework and summative assessment for each course in the relevant course guide .
Find out more about LSE’s teaching and assessment methods .
Graduate destinations
Career support.
Through studying history you will learn how to analyse complex evidence from a variety of sources, to develop your analytical powers and to present your findings effectively. These skills and a broad knowledge of the development of the world around us are valued by many employers.
Past students have followed a range of careers in politics, journalism, media and publishing, advertising, marketing, and public relations, public administration, the foreign service, industry, the charity and development sector, finance, consulting and the legal profession, as well as in research, teaching, libraries and archives.
Further information on graduate destinations for this programme
Median salary of our undergraduate students 15 months after graduating:
Top 4 sectors our students work in:.
We're committed to supporting students' options after graduation in the world of work or futher studies by organising a careers programme tailored specifically to International History students with the help of LSE Careers . Also, many leading organisations give careers presentations at the School during the year, and LSE Careers has a wide range of resources available to assist students in their job search.
Find out more about the support available to students through LSE Careers .
Discover Uni
Every undergraduate programme of more than one year duration will have Discover Uni data. The data allows you to compare information about individual programmes at different higher education institutions.
Programmes offered by different institutions with similar names can vary quite significantly. We recommend researching the programmes you're interested in and taking into account the programme structure, teaching and assessment methods, and support services available.
Find out more
Explore lse, student life.

Student support

Accommodation

Meet, visit and discover LSE

Please enable JavaScript in your web browser to get the best experience.
Main navigation
Phd degree: politics and international studies.

- Jump to: Key information
- Jump to: Course overview
- Jump to: Structure
- Jump to: Teaching and learning
- Jump to: Fees and funding
- Jump to: Employment

Key information
Home student fees (full-time) : £4,860 per year Home student fees (part-time) : £2,430 per year Overseas student fees (full-time) : £22,490 per year Overseas student fees (part-time) : £11,245 per year
Please note that fees go up each year. See research fees for further details.
We normally require a 2.1 bachelor's degree (or its equivalent) plus a Merit-level Masters degree in Political Science or a related discipline. We also require a minimum of one reference. In exceptional cases we may accept applicants who do not meet these criteria if they show evidence of a strong Masters degree and/or appropriate level of relevant work experience. International applicants should also see Doctoral School English language requirements
Course overview
The primary aim of the PhD programme is to train students to design, research and write a successful doctoral thesis.
Those who have completed the doctorate will be familiar with the conceptual and methodological aspects of political research and qualified as experts in their field.
To be considered for entry into the PhD programme, applicants must possess a good advanced degree in Politics equivalent in level and content to the Department's MSc, although applications from individuals with related degrees in cognate disciplines will also be considered Guidelines for research proposals .
Admission takes place on a rolling basis. The application cycle opens in November and closes on 30 June for entry in October. Applicants also wishing to be considered for a SOAS scholarship or an ESRC studentship should refer to the research scholarships information for the deadlines.
Why study PhD Degree Politics and International Studies at SOAS?
- We’re ranked 5th in the UK and 17th worldwide for Politics (QS World University Rankings 2023).
- We're ranked 3rd globally for academic reputation (QS World University Rankings 2022).
Recently Completed PhD Dissertations in the Department
- Maria Ambrozy, ‘Interrogating Education Policymaking in the Rwandan Developmental State: The Politics of Changing the Language of Instruction and the Higher Education Merger’ (Phil Clark)
- Sheenah Kaliisa, ‘Opening Borders: The African Passport, Free Movement of Persons and the Integration of States’ (Phil Clark)
- Hangwei Li, ‘Global China, African Agency and the Prism of Soft Power: Media Interaction and Newsroom Politics Between China and Africa’ (Stephen Chan)
- Moudwe Daga, ‘Identity, Belonging and State Formation in Chad’ ( Professor Julia Gallagher )
- Calum Fisher, ‘Doing Democracy in Malawi: MPs and Their Constituencies’ ( Dr Alastair Fraser )
- Anna Evelyn Kensicki, ‘Jerusalem Narratives: A Phenomenological Analysis of Space and Time in 21st Century Conflict’, ( Dr Hagar Kottef )
- Dwi Kiswanto, ‘Centre-Periphery Relations: The Politics of Fiscal Transfers in Indonesia’ ( Dr Michael Buehler )
- Leon Kunz, ‘Deliberative Democracy in Social Movements in Taiwan and Hong Kong’ ( Professor Julia Strauss )
- Magsud Mammadov, ‘The State Selfie in International Politics: Ontological Insecurity, Role Making, and Nation Branding in the case of Azerbaijan, 2008-2018’ ( Dr Bhavna Dave )
The PhD programme at SOAS follows a three-year model, with the possibility to extend into a fourth year. The programme consists of research training and coursework in the first year, after which Doctoral Researchers must pass an upgrade from MPhil to PhD status through submission of an ‘Upgrade Paper’, examined by a viva exam.
This is followed by primary research/fieldwork undertaken in the second year, and the writing up of their thesis in the subsequent year. Doctoral Researchers should aim to be ready for submission by the end of the third year and must submit by the end of the fourth year at the latest.
Research training year 1
Doctoral Researchers are expected to upgrade from MPhil to PhD status within 12 months of their registration. Progression requires successful completion of the Department’s training programme consisting of:
- Politics MPhil Methods course (terms one and two);
- an Upgrade Paper Workshop (term two); and
- participation in the MPhil Research Projects Conference (term three).
Doctoral Researchers also have the opportunity to take an additional course in quantitative methods (term two). Students will produce an upgrade paper that forms the basis of a viva, which has to pass to gain PhD status. In addition to the Department’s own training, the SOAS Doctoral School offers two complementary courses for all SOAS Doctoral Researchers:
- Research Project Management (term one), and
- Technology-Enhanced Research (term 2).
Fieldwork procedure
For Doctoral Researchers who undertake fieldwork, most will generally conduct such activity in their second year. A maximum of three terms’ fieldwork is usually permitted in a full-time PhD programme. Fieldwork of longer than 12 months has to be approved by the SOAS Pro-Director for Research and Enterprise.
Training beyond year 1
Throughout the process of research design, fieldwork, and writing, Doctoral Researchers are expected to maintain regular contact with their supervisors. Writing the dissertation is the student’s work alone, supported by regular meetings with the supervisor(s) and participating in a write-up seminar for advanced PhD students.
The Department strongly encourages Doctoral Researchers to participate in workshops offered outside SOAS and to attend and present at conferences organised by the major research associations in their field (some limited funding available).
Graduate Teaching Assistant
Teaching is an important part of doctoral training for PhD Doctoral Researchers considering an academic career. The Department aims to offer advanced Doctoral Researchers the possibility to work as a Graduate Teaching Assistant (GTA) on one of the courses offered in the Department for a maximum of two years.
Duties involve seminar teaching, holding office hours, and marking. Doctoral Researchers taking on the responsibility of a GTA post are expected to have completed a GTA training module offered by the Doctoral School, typically in October.
Teaching and learning
The primary building block of the PhD programme is the relationship between student and supervisor. Students are admitted on the basis of the expressed willingness of at least one member of staff to serve as the main supervisor for the student's project.
From the student's entry in the programme, the supervisor assumes primary responsibility for monitoring and supporting the student’s progress towards the completion of the degree. Every research student also has an associate supervisor, another member of staff with a close interest in the student’s region and/or sub-field of the discipline. The Department’s research tutor oversees the PhD programme and is available for discussing general problems.
In addition to the training programme noted above, they may attend an MSc course relevant to their research. Research students are also encouraged to participate in the Department seminars, where invited scholars from other institutions give presentations, and they have access to many other seminars and lectures held throughout SOAS.
Language training
The School’s language training facilities are also available for students to develop or improve research-relevant language skills. Since 2012, research students have exclusive access to the facilities and services offered by SOAS’ Doctoral School.
Most PhD students spend some time doing fieldwork in the regions of their research. The Department and the School, through their various connections with individuals and institutions in the universities and governments of Asia, Africa and the Middle East, facilitate this work with personal contacts and introductions as well as (limited) funding.
For more information about the PhD programme in the Department of Politics and International Studies, see the MPHIL/PHD research handbook.
PDF document, 455.33KB
Important notice
The information on the website reflects the intended programme structure against the given academic session. The modules are indicative options of the content students can expect and are/have been previously taught as part of these programmes.
However, this information is published a long time in advance of enrolment and module content and availability is subject to change.
Scholarships
Fees and funding, fees for 2023/24 entrants per academic year.
Please note that fees go up each year.
See research fees for further details.
In the last REF cycle (2014-2020), about a quarter of our PhD graduates embarked on successful academic careers, taking up positions in universities in the UK and across the world, including the LSE, University of Cambridge, University of Birmingham, Queen Mary University of London, Lahore University of Management Sciences, the American University in Beirut, Korea University, Abu Dhabi University, Sabanci University, the American University of Sulaymaniyah, University of Freiburg, Sciences Po, Leiden, and the Leibniz Zentrum Moderner Orient in Berlin.
Many of our PhDs have found employment in non-academic institutions , including the Crisis Management Initiative, the Open Society Foundation, the Institute for Druze Studies in Haifa (Israel), the Institute for Security Studies in Dakar (Senegal), the Centre for Alternative Policy Research and Innovation in Freetown (Sierra Leone), the Centre for Policy Research in Delhi (India) and the Centre for International Digital Policy at Global Affairs Canada. Other PhD graduates have gone on to work as foreign-policy officials in the UK, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Nigeria, South Korea and Egypt
SOAS Voices

The Indian election: Is it still the world's largest democracy?
A SOAS student writes about the 2024 Indian election and its implications for democracy. The blog is based on an interview with Dr Simona Vittorini and the politics course 'Democracy and Authoritarianism in India'.

The year of the big vote: Do we have the world leaders we need?
More than 2 billion people in 50 countries will be invited to vote in 2024. Saleeta Akbar reports on what was discussed during latest Director’s Lecture Series on the year of the big vote.

How studying Middle East Politics helped my career as a BBC journalist
Layla Bashar Al-Kloub spoke to us about her time studying at SOAS as a Chevening Scholar, how it helped her career and what she’d advise aspiring journalists.

My study abroad experience in Jordan
Zainab reflects on her year abroad, sharing her favourite memories of travelling and how immersing herself in life in Jordan improved her confidence and language skills.

Careers: SOAS helped develop my worldview towards life and people
Dr Feroza Sanjana used her MA in International Studies and Diplomacy to deepen her knowledge of the institutions, politics and processes that underlie many of the global challenges her work now seeks to change.

Careers: "As a High Commissioner no two days are the same!"
Having grown up in a multi-cultural family in the UAE, Omar Daair knew he wanted his future career to have an international angle. Discover how his studies at lead him to his role of High Commissioner to Rwanda.
Intergenerational Justice in Eastern Africa
This research will explore intergenerational justice across the social sciences and humanities.
Reframing Justice after Atrocity
Through historical and modern case studies in Latin America, Europe and Africa and the new conceptual framework of “arenas of accountability”, this project examines justice interactions that go beyond the linear international-to-national transmission of norms and practices.
Civic Infrastructures of Torture
The project is based on exclusive access this research team has been granted to the archive of PCATI, which documents torture practices implemented by Israeli security agencies.
Constitutional Transformation
Focusing on the making of the Indian Constitution, PACT aims to build an advanced digital platform that contextualizes the Indian Constituent Assembly debates (1946-49) within wider public debates on constitution-making.
Migration Governance and Diplomacy
This project investigates how migration governance has been influenced by “refugee crises” and how crises at large shape policy responses on migration.
Pan-African Frontiers and Identities
This multi-sited collaborative research project explores the diverse deployments of pan-Africanism as a geopolitical and policy framework both on the African continent and in the diaspora.
African State Architecture
Professor Julia Gallagher and a team of researchers lead the African State Architecture project funded by a major grant from the European Research Council.
Strategic Concept for Removal of Arms and Proliferation (SCRAP)
A comprehensive approach to realising global disarmament,
ACE: Innovative approaches to anti-corruption
Finding impactful anti-corruption strategies around the world.
Recognising the women who shaped the UN Charter
Recognising the key role of women of the Global South in establishing the equality of the sexes in the UN Charter of 1945.

Book Launch | The Fate of Third Worldism in the Middle East: Iran, Palestine, and beyond
This book launch will feature a panel of presentations from contributors to the volume, a response by a scholar of Iran and Palestine, and an audience Q&A.

Dialogue with Indigenous Studies scholar and activist Dr. Jolan HSIEH(Bavaragh Dagalomai 謝若蘭)
This event is a student dialogue with Indigenous Studies scholar and activist Dr. Jolan HSIEH (Bavaragh Dagalomai 謝若蘭).

Meet the author: A dialogue with Mark O'Neill, the author of Four Books on Taiwan
From 1978 to 2006, Mark O'Neil worked as a journalist in Hong Kong, India, China, Taiwan and Japan, for Reuters and the South China Morning Post.

Book talk - Taiwan Lives: A Social and Political History
This event is a book talk on Taiwan Lives: A Social and Political History.

Revolutionary Taiwan: Making nationhood in a changing world order
This is a book talk based on the recent publish monograph, Revolutionary Taiwan: Reimagining Nationhood in a Changing World Order.

Quota Politics and Representation Gaps in Taiwan
This lecture presents how the women’s movement successfully campaigned to reform and adopt gender quotas in elections and non-electoral decision-making bodies such as government committees and commissions.
Related content
Department of Politics and International Studies
The Department provides expert grounding in the study of Politics and International Relations through deep engagement with the historical legacies, political realities, and international affairs of Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.

BA Politics
BA Politics at SOAS University of London

MA International Studies and Diplomacy
MA International Studies and Diplomacy programme at SOAS University of London

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
MPhil/PhD International Relations; Start date: 30 September 2024: Application deadline: 15 January 2024: Duration: Three to four years (minimum two) full-time. Please note that LSE allows part-time PhD study only under limited circumstances. ... Funding deadline for LSE PhD Studentships and ESRC funding: 15 January 2024. In addition to our ...
The MPhil/PhD International Relations is part of the group of accredited programmes for ESRC funding. LSE is an ESRC Doctoral Training Partnership.The programme is also eligible for LSE PhD Studentships.. Please note: There is no separate application for funding. Funding is allocated by nomination and you will automatically be considered for the award you are eligible for alongside all ...
Welcome to the world-leading Department of International Relations at LSE. We are now in our 96th year - one of the oldest as well as largest IR departments in the world, with a truly international reputation. We are ranked 2nd in the UK and 5th in the world in the QS World University Ranking by Subject 2024 tables for Politics and ...
a three-year undergraduate programme. an undergraduate General Course programme (for students wishing to substitute a year at their home university for a year at LSE) five MSc programmes. a research programme for MPhil/PhD students. plus LSE Summer School, Executive courses and online certificate courses. We are also involved in some joint ...
MSc International Relations is an advanced, academic study of the subject from a global perspective. You will have the opportunity to study a broad range of issues, including the formulation and implementation of foreign policy, relations between states and governments, international organisations and NGOs, international law, conflict and post-conflict peace-making and transitional justice ...
Learn more about MPhil/PhD International Relations Program including the program highlights, fees, scholarships, events and further course information. ... At doctoral level, LSE offers studentships to new PhD students in the form of LSE PhD Studentships, LSE ESRC Studentships, LAHP AHRC Studentships and LSE & III PhD Studentships on Analysing ...
The International Relations Department has a large PhD student body, comprising approximately 50 students. If you have any additions or amendments please contact Alison Carter. Those who have recently graduated are listed here: PhD completions. Find out all about our International Relations postgraduate PhD students and their areas of expertise.
Makena Micheni (October 2023) "Fractured brotherhoods: ethnic identity in multi-ethnic violent political organising". Thesis online. Supervisors: Milli Lake , Tomila Lankina. Samuel Dixon (July 2023) "From Hegemonic Decline to the End of History: The Transformation of International Relations, c.1970-2000."
Department of International Relations. International Relations has been taught at LSE since 1924 and the department was set up three years later. We are one of the oldest as well as largest IR departments in the world, with a truly international reputation. We are ranked 2nd in the UK and 4th in the world in the QS World University Ranking by ...
PhD students in the International Relations Department have received training in key disciplinary subjects at both LSE and leading research methods schools in the UK, Europe and North America. Our students have also gained extensive teaching experience and many will have completed the Postgraduate Certificate in Higher Education (PGCert) before ...
About us. The Department of International Relations at LSE is now in its 96th year - one of the oldest as well as largest IR departments in the world, with a truly international reputation. The ...
What do LSE graduates do? View the LSE IR graduate destination statistics. Graduates of the Department have excellent career prospects. In 2016/17, 94% of undergraduate leavers and 93% of postgraduate leavers from the Department of International Relations were in employment, completing further study or taking time out to travel just six months after graduation.
Dr Simona Milio LSE PhD European Institute 2007 and previously employed at LSE as Associate Director of the Economic and Social Policy Unit until 2015. ... Dr Rachel George LSE PhD International Relations 2018 now Senior Research Officer at the Overseas Development Institute in London, where she works in the Gender Equality and Social Inclusion ...
International Relations. Doctoral programme director Professor Chris Alden [email protected]. PhD administrative contact Amy Brook and Sarah Helias ... [email protected]. PhD Programmes Manager Camilla Kennedy Harper [email protected]. Department of Management. Mathematics.
LSE PhD Studentships are tenable for four years and cover full fees and an annual stipend. They are available for UK, EU and international students undertaking research in any LSE discipline, with annual renewal subject to satisfactory academic performance. ... They cover full fees (for international students, LSE will cover the difference ...
Bettcher, Douglas (1997) A psychoanalytic approach to the study of international relations. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science. Smith, Karen Elizabeth (1996) The making of foreign policy in the European Community/Union: the case of Eastern Europe, 1988-1995. PhD thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science.
Data sources. FOI Request by Albert Warren. December 2019. Freedom of Information (FOI).London School of Economics. October 2022. Legend. The acceptance rate, or offer rate, represents the fraction of applicants who received an offer.Note that this will be generally lower the acceptances rates (acceptances divided by applicants) published by many other sources.
BSc International Relations Durham, UK. LSE is renowned for its academic prestige and the teaching staff live up to this reputation. For an international relations student, being based in the centre of London allows you to feel closer to global affairs. ... The data was collected as part of the Graduate Outcomes survey, which is administered by ...
The new Department of International Relations at LSE was announced in June 1927 by Director William Beveridge. To mark the department's 75th anniversary in 2002, Nicholas Sims described the events leading up to the announcement and the early teaching of international relations at LSE. Between 1923 and 1930 a series of firsts occurred.
Introduction. On this programme, you'll learn about the theory and practice of politics in the contemporary world - comparing political ideologies and systems in different cultures and countries. You'll also look at the role of politics and power in international relations and examine how the international community works in terms of ...
Goldsworthy Lowes Dickinson, LSE and the origins of International Relations February 22nd, 2022. Featured alumni. Alumni news. Lessons from studying the past: writing about the ethics of political commemoration February 1st, 2024 ... From a PhD in IR at LSE to the top of a think tank
a master's degree at distinction level in international relations, or in a closely related discipline that has prepared you to undertake advanced graduate research on your chosen thesis topic; and a first-class or strong upper second-class undergraduate degree with honours in politics or international relations, or in a related discipline such as economics, history, philosophy, sociology or law.
This BSc International Relations and History allows you to study two complementary subjects. You'll look at the nature of the changing dynamics between different countries and the impact of the uneven distribution of power, money, welfare and knowledge on foreign policies and international order. For the history elements, you'll analyse the ...
The PhD programme at SOAS follows a three-year model, with the possibility to extend into a fourth year. The programme consists of research training and coursework in the first year, after which Doctoral Researchers must pass an upgrade from MPhil to PhD status through submission of an 'Upgrade Paper', examined by a viva exam.