Geography Notes
Essay on the earth: structure and gradients | solar system | geography.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Here is a compilation of essays on the ‘Earth’ for class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on the ‘Earth’ especially written for school and college students.

Essay on the Earth
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Geothermal Gradients in the Earth
Essay # 1. Origin of the Earth:
Earth is the third planet in the Solar system and lies at an average distance of approximately 149 billion km from the Sun. The Earth is presumed to be as old as five or six billion years. The Earth was initially a fiery spinning ball of hot gases and vapours. Gradually, through millions of years, the gases condensed into a molten core and the different elements got stratified according to their density.
The heavy elements like iron and nickel sank to the centre and formed the core of the Earth, while the lighter elements such as silicon and aluminium formed the middle shell, while the lightest elements like helium, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon settled at the surface and formed the gaseous atmosphere. This atmosphere was very different from what it is today.
The temperature of the Earth was estimated to be about 5000 – 6000°C. At such high temperatures, elements like hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen could not exist in Free State. These combined among themselves or with metals forming oxides, carbides and nitrides.
These compounds existed in gaseous state. Water was also present as super-heated steam. Such an atmosphere composed of ammonia, methane, steam, cyanides, carbon dioxide, free hydrogen and without free oxygen is described as a reducing type of atmosphere.
As cooling occurred gradually, the gases liquified and some of the liquids turned into solids. Steam condensed into water and resulted in rain that evaporated on approaching the heated surface.
This continued for millions of years and resulted in the cooling of the Earth’s surface. Water bodies came into existence. They contained dissolved ammonia and methane. There occurred dissolution of mineral rocks leading to the accumulation of minerals and salts in the oceanic water.
ADVERTISEMENTS: (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); Essay # 2. Age of the Earth:
Scientists have estimated the age of the Earth by measuring the amount of decay of certain radioactive isotopes that has taken place in rocks. For example, radioactive potassium, 40K decays into argon (40A) and calcium ( 40 Ca).
About 90 percent of 40K decays to 40 A and ten percent to 40 Ca. It is safe to assume that argon would not have been present when the rocks formed because this element occurs as a gas and would have been excluded from rocks. Any argon now present in rocks must therefore have derived from the decay of 40 K after their formation.
The half-life of 40K is 1.26 × 10 9 years. Knowing this, one can compute the age of the particular rock by measuring how much of the 40 K has decayed to 40 A, that is, by measuring the ratio of 40 A to 40 K.
In addition to the potassium-argon method of dating, the age of rocks can be estimated from the ratio of rubidium to strontium or by the uranium-thorium-lead method. The three dating methods all give about the same age for the oldest rocks, 4.6 × 10 9 years. This is generally accepted as the age of the Earth. Formation of the Earth is believed to have occurred by aggregation of particles ranging in size from dust to asteroids over a period of millions of years.
The process still continues with the capture from space of dust and meteors by the Earth’s gravity. Contrary to earlier views, it is now generally believed that the surface of Earth was not molten when the Earth was formed, which means that the surface temperature remained below 900°C. This is important because it means that simple organic materials, which are known to be present outside the Earth, might have been included during formation of the Earth and survived to become a part of the primitive Earth.
Essay # 3. Structure of the Earth’s Interior:
In this article we will discuss about the structure of the earth’s interior, explained with the help of a suitable diagram.
It is the uppermost shell of earth that extends to variable depths below mountains, continents and oceans. The thickness of crust is believed to be 0.90 km and several substances like limestone, coal, gold, petroleum etc. are found in the crust.
It is the second concentric shell of earth that lies below the crust. The upper rigid part of the mantle extends up to 100 km below the separating crust and contains mainly iron and magnesium. The crust and upper mantle form the ‘lithosphere’.
The lower mantle extending up to 2900 km below the earth’s surface is less rigid and is hotter. This is known as ‘asthenosphere’ and is capable of being deformed. The movement of lithosphere over the asthenosphere results in the ‘phenomenon of plate tectonics’ i.e. movement of the earth’s crust.
It is the innermost concentric shell of the earth. The core boundary begins at a depth of 2900 km from the surface and extends to the centre of the earth at 6370 km. This layer is further subdivided into outer core and inner core.
The outer core comprises the region from a depth of 2900 km to 5200 km below the earth’s surface and behaves mere like a liquid. The inner core with a thickness of around 1170 km is believed to be a solid metallic body, containing nickel-iron alloy.
The hot molten rock of the mantle is called Magma.
Essay # 4. Earth Rotation and Revolution:
The term ‘Earth rotation’ refers to the spinning of the Earth on its axis. One rotation takes exactly twenty-four hours and is called a mean solar day. If you could look down at the Earth’s North Pole from space you would notice that the direction of rotation is counterclockwise. The opposite is true if you viewed the Earth from the South Pole.
The orbit of the Earth around the Sun is called Earth revolution. This celestial motion takes 365 1/4 days to complete one cycle. Further, the Earth’s orbit around the Sun is not circular, but elliptical. An elliptical orbit causes the Earth’s distance from the Sun to vary annually. However, this phenomenon does not cause the seasons!
This annual variation in the distance from the Sun does influence the amount of solar radiation intercepted by the Earth by approximately 6%. On January 3rd, perihelion, the Earth is closest to the Sun (147.5 million kilometers). The Earth is farthest from the Sun on July 4th, or aphelion. The average distance of the Earth from the Sun over a one year period is 150 million kilometers.
The Earth’s axis is not perpendicular to the plane of the ecliptic, but inclined at a fixed angle of 23.5°. Moreover, the northern end of the Earth’s axis always points to the same place in space (North Star). Figure 3.2 shows an animation of the Earth revolving around the Sun. In this animation the Earth’s axis is coloured red. Note that the angle of the Earth’s axis in relation to the plane of the ecliptic remains unchanged.
However, the relative position of the Earth’s axis to the Sun does change during this cycle. This circumstance is responsible for the annual changes in the height of the Sun above the horizon. It also causes the seasons, by controlling the intensity and duration of sunlight received by locations on the Earth.
The Earth from a position in space is above the North Pole at the summer solstice, the winter solstice, and the two equinoxes. Note how the position of the North Pole on the Earth’s surface does not change. However, its position relative to the Sun does change and this shift is responsible for the seasons. The red circle on each of the Earths represents the Arctic Circle (66.5° N).
During the summer solstice, the area above the Arctic Circle is experiencing 24 hours of daylight because the North Pole is tilted 23.5° toward the Sun. The Arctic Circle experiences 24 hours of night when the North Pole is tilted 23.5° away from the Sun in the winter solstice. During the two equinoxes, the circle of illumination cuts through the polar axis and all locations on the Earth experience 12 hours of day and night.
On June 21 or 22, the summer solstice, the Earth is positioned in its orbit so that the North Pole is leaning 23.5° toward the Sun. During the summer solstice, all locations north of the equator have day lengths greater than twelve hours, while all locations south of the equator have day lengths less than twelve hours.
On December 21 or 22, the winter solstice, the Earth is positioned so that the South Pole is leaning 23.5° toward the Sun. During the winter solstice, all locations north of the equator have day lengths less than twelve hours, while all locations south of the equator have day lengths greater than twelve hours.
On September 22 or 23, the autumnal equinox, neither pole is tilted towards the Sun. March 20 or 21 marks the arrival of the spring or vernal equinox when once again the poles are not tilted towards the Sun. Day lengths on both of these days, regardless of latitude, are exactly 12 hours.
Essay # 5. Axis Tilt and Solar Altitude:
The annual change in the relative position of the Earth’s axis in relationship to the Sun causes the height of the Sun (solar altitude) to vary in our skies. The total variation in maximum solar altitude for any location on the Earth over a one year period is 47° (2 x 23.5 = 47). For example, at 50° north, maximum solar altitude varies from 63.5° on the summer solstice to 16.5° on the winter solstice.
Maximum solar height at the equator goes from 66.5° above the northern end of the horizon during the summer solstice, to directly overhead on the fall equinox, and then down to 66.5° above the southern end of the horizon during the summer solstice.
The location on the Earth where the Sun is directly overhead at solar noon is known as the sub-solar point. The sub-solar point occurs on the equator during the equinoxes. During the summer solstice, the sub-solar point moves to the Tropic of Cancer because at this time the North Pole is tilted 23.5° toward the Sun. The sub-solar point is located at the Tropic of Capricorn on the winter solstice. On this date, the South Pole is now tilted toward the Sun.
Figure 3.7 shows the relationship of maximum Sun height to the latitude for the equinox (left) and summer solstice (right). The red values on the right of the globes are maximum solar altitudes at solar noon. Black numbers on the left indicate the location of the equator, Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N), Tropic of Capricorn (23.5°S), Arctic Circle (66.5°N), and the Antarctic Circle (66.5°S). The location of the North and South Poles are also identified. During the equinox, the equator is the location on the Earth with a Sun angle of 90° for solar noon. Note how maximum Sun height declines with latitude as you move away from the equator.
For each degree of latitude traveled, maximum Sun height decreases by the same amount. At equinox, you can also calculate the noon angle by subtracting the location’s latitude from 90. During the summer solstice, the Sun is now directly overhead at the Tropic of Cancer. All locations above this location have maximum Sun heights that are 23.5° higher from the equinox situation.
Places above the Arctic Circle are in 24 hours of daylight. Below the Tropic of Cancer the noon angle of the Sun drops one degree in height for each degree of latitude traveled. At the Antarctic Circle, maximum Sun height becomes 0° and locations south of this point on the Earth are in 24 hours of darkness.
The following table describes the changes in solar altitude at solar noon for the two solstices and equinoxes. All measurements are in degrees (horizon has 180 degrees from True North to True South) and are measured from either True North or True South (whatever is closer).
Finally, the altitude of the Sun at solar noon can also be calculated with the following simple equation:
Altitude A = 90 – Latitude L +/- Declination D
In this equation, L is the latitude of the location in degrees and D is the declination. The equation is simplified to A = 90 – L if Sun angle determinations are being made for either equinox date. If the Sun angle determination is for a solstice date, declination (D) is added to latitude (L) if the location is experiencing summer (northern latitudes = summer solstice; southern latitudes = winter solstice) and subtracted from latitude (L) if the location is experiencing winter (northern latitudes = winter solstice; southern latitudes = summer solstice).
All answers from this equation are given relative to True North for southern latitudes and True South for northern latitudes. For our purposes only the declinations of the two solstices and two equinoxes are important.
These values are – Summer Solstice D = 23.5, Winter Solstice D = 23.5, Autumnal Equinox D = 0, and Vernal Equinox D = 0. When using the above equation in tropical latitudes, Sun altitude values greater than 90° may occur for some calculations. When this occurs, the noonday Sun is actually behind you when looking towards the equator.
Under these circumstances, Sun altitude should be recalculated as follows:
Altitude A = 90 – (originally calculated Altitude A – 90)
Essay # 6. Energy of Earth-Heat Flux :
Earth is in a state of thermal equilibrium. The energy received from sun is lost at night. The small amount of energy generated by the decay of unstable isotopes of uranium, thorium etc. is dissipated from earth’s interior to oceans and atmosphere.
The heat generated within earth is around 2700 GW:
i. The heat energy in earth’s interior is due to radioactivity. Regions of higher radioactivity have higher heat flux and are potential geothermal sites.
ii. Earth’s surface consists of about one dozen tectonic plates (e.g., American plate, Arabian plate, Indian plate, Philippine plate, Pacific plate etc.). Each of these plates has thickness around 100 km and thousands of kilometres area. Earth’s interior is unable to lose heat, by conduction, as rapidly as it is generated by ‘radioactivity’. This leads to “convective instabilities” which means that these plates are continuously in motion with respect to each other.
A variety of processes along the margins of the plates lead to partial melting at depths between 15 and 200 km. The molten masses penetrate the surrounding rocks and rise towards earth at rates varying from a few cms per day to a few cms per year, thus resulting in volcanic activity. The molten masses which do not reach earth’s surface come to rest in the middle or upper part of earth’s crust at depths less than 20 km. These liquid magmas may have temperatures around 1000°C.
The crystallisation of these liquid magmas produces intrusive igneous bodies. The cooling and crystallisation of igneous bodies give rise to local heat flux. This heat flux constitutes the geothermal energy which may be used for a variety of purposes including generation of electricity.
The local heat fluxes continue for thousands of years and form an ‘inexhaustible source of energy’.
iii. The majority of active geothermal areas tend to concentrate around the margins of major lithospheric plates.
Essay # 7. Geothermal Gradients in the Earth :
The temperature difference within the earth depends on:
1. The thermal properties of earth’s interior and their radial and lateral variation.
2. Movement of fluids or solid rock materials occurring at rates of more than a few millimetres per year.
A potential geothermal source region should have high thermal gradient. Thermal gradient is defined as the ratio of heat flux and thermal conductivity.
Fig. 7.3 shows the Geothermal gradients. The figures are based on measurements within a few km of earth’s surface.
Curve 1: It represents average uniform gradient.
Curve 2: It represents theoretical increase in the boiling point of water at increasing depths due to higher pressures, allowing for reduced density due to higher temperatures.
Curve 3: It represents thermal gradients of such regions in which water percolates through upper crust into lower hot region and hot water flows vigorously upwards forming ‘hot springs’.
Curve 4: It represents the effect of solid impermeable rock. The rock forms insulating cap on geothermal reserves and does not allow heat flow to upper part.
Curve 5: It represents leaks in the solid impermeable rocks in the form of springs of hot boiling water discharged in large quantities to ground surface. In some locations production of steam occurs at lower depths and the steam is released to the surface in the form of fumaroles and geysers as shown in curve 5. Such locations are very few in number.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Solar Radiation: Top 8 Essays on Solar Radiation | Geography
- Essay on the Earth: Top 8 Essays on Earth |Solar System | Geography
- The Best Essay on Hydrosphere | Earth | Solar System | Geography
- The Best Essay on Lithosphere | Earth | Solar System | Geography
Essay , Geography , Solar System , Earth , Essay on the Earth
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
- Growth & Development
- Play & Activities
- Life Skills
- Play & Learning
- Learning & Education
- Rhymes & Songs
- Preschool Locator

Essay On ‘Save The Earth’ – 10 Lines, Short And Long Essay For Children
Key Points To Remember When Writing An Essay On ‘Save The Earth’ For Lower Primary Classes
10 lines on ‘save the earth’ for kids, a paragraph on ‘save the earth’, short essay on ‘save the earth’ in english for children, long essay on ‘save the earth’ for children, what will your child learn from the ‘save the earth’ essay.
Practising essay writing from a young age helps young learners develop an understanding of sentence formation and appropriate words. It also allows children to expand their vocabulary and learn new words. Learning new words and using them in sentences helps them improve their writing skills. Our planet is rich in natural resources, but it is rapidly depleting due to human greed. Writing an essay on saving the earth in English makes children aware of their surroundings and familiarises them with the steps that can be taken to improve the situation. This article provides some pointers and examples to help students write a good essay on saving the earth for classes 1, 2, and 3.
Writing an essay on ‘save the earth’ can be interesting, provided certain things are kept in mind. Following these tips enables your children to write an essay that is different and unique from others. If you, too, are wondering about how to write an essay on this topic, here are some tips for you:
- Start with an introductory paragraph giving a general introduction about our planet earth and why is it beneficial for us to save it from depletion. The introduction should be such that it provides a flow to the entire content ahead.
- The second part of the essay should be its body. The body should be divided into smaller paragraphs, each focusing on a different aspect. For instance, one paragraph can talk about all the problems faced by our planet; the second can talk about the reasons behind the same.
- It is always advised to summarise your thoughts in a concluding paragraph.
Saving our planet, mother earth, is the need of the hour. We should understand our responsibility and do our bit to improve this world. Here are a few lines on save earth that can be used to write a good essay for class 1 and 2 kids:
- Earth is the only planet in the universe that has life in this universe.
- The planet has given us abundant natural resources like water, air, sunlight and more.
- Humans have been exploiting the planet for their greed.
- This has caused a lot of adversity such as global warming, unnatural disasters etc.
- All of us should work towards protecting and saving our planet.
- We should plant more trees.
- We should stop hunting animals to meet our selfish needs, affecting the ecological balance.
- We should follow the three R’s, i.e., Reduce, Reduce and Recycle.
- Saving natural resources, water, and the environment should be our primary goal.
- We should also spread awareness regarding saving the earth among the public.
Short paragraphs help children of lower classes to read and understand easily. It also guides kids to write a good essay on saving the earth for their classroom activities or even competitions. Given below is a short paragraph on save earth:
As we all know, the earth is the only planet in the universe where life exists. Not only that, but the earth also provides us with numerous natural resources such as sunlight, water, air, minerals, and so on. Humans, however, have depleted almost all natural resources due to greed. They have also hunted down many wildlife animals, causing the majority of species to become extinct. “Save the Earth” is a phrase that should be used to raise public awareness. We must plant more trees, reduce pollution, and conserve natural resources to save the planet. We should also reduce exploiting the gift of nature and follow the 3R’s, i.e., Reduce, Reuse and Recycle.
Saving the earth is very crucial at this point. Writing a short essay on this topic allows the children to be more aware of their surroundings and also allows them to take steps to protect the environment. Given below is a save earth essay for classes 1,2 and 3:

We often refer to our planet earth as “Mother Nature”, but when it comes to treating it like a mother, we fail to do so. Our planet is the home of many living creatures such as mammals, reptiles, plants and many more and all beings need to sustain an ecological balance. However, due to the unfavourable activities of humans, the ecological balance of the earth is being destroyed. Humans are cutting down trees, creating pollution as a result of which global warming is increasing. We all should take individual steps to save our planet. The government has taken steps to protect the environment, such as banning plastics and plastic products, running campaigns to reduce waste and keep our surroundings clean, and so on. We must also take steps such as planting more trees, replacing large vehicles with bicycles, limiting air conditioners, and using LED lights. We can save our planet if we follow at least a few of these steps.
Writing an essay on ‘save the earth’ helps children understand the world’s serious situation and encourages them to help find solutions. A long essay for class 3 kids is provided below to help them understand what points to include when writing an essay:
“Earth provides enough to satisfy every man’s needs, but not enough to satisfy every man’s greed,” Mahatma Gandhi once said. Although he made this statement many years ago, it is still valid. Mother Nature, as we fondly refer to our planet Earth, provides us with a wide range of natural resources such as sunlight, minerals, and water, to name a few. Humans have used these resources for a long time and have exploited them to a large extent.
Why Is It Necessary To Save Earth?
Our planet earth is facing plenty of problems due to mindless human behaviour, which has resulted in a difficult position. We have cut down trees to build industrial factories, buildings, and townships, among other things. These industrial plants emit hazardous chemicals that pollute the air and water. Population growth is also a significant contributor to the earth’s depleting condition. The increased number of cars on the road has resulted in pollution and the emission of harmful greenhouse gases, all of which contribute to global warming. As a result, seasons have been pushed back, monsoons have disappeared in some areas while flooding has occurred in others, and glaciers are melting.
Easy Ways To Save Earth
Saving the earth is not difficult if we all contribute our tiny bits towards it. Some of the easy steps that we can take in our daily lives to save our planet are:
- We should reduce our use of plastic in our daily routine.
- We need to plant more trees.
- We should prioritise water conservation. Bathing in a bucket rather than a shower can save litres of water.
- We should use carpools or shared vehicles to travel daily because it reduces pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- We should adhere to the 3Rs, which emphasise reducing, reusing, and recycling.
- We should use LED bulbs.
- We should reduce our electricity consumption by not unnecessarily leaving fans, lights, or other electrical appliances on.
- We should also concentrate on solar and renewable energy sources, such as solar panels.
This essay will help your children learn more about their surroundings while also making them aware of why we need to save our planet. This also encourages them to participate in various Earth-saving campaigns organised by multiple groups.
Earth has provided us with numerous resources that have been extremely beneficial to humanity over the years. It is our turn to repay our planet by taking steps to protect it.
Essay On Save Electricity for Kids Essay On Save The Environment for Children Save Water (Water Conservation) Essay for Kids
- Essays for Class 1
- Essays for Class 2
- Essays for Class 3
How Your Screen Time Directly Impacts Your Child
13 helpful tips to get your child to listen to you, how to build a healthy relationship with food for your child, leave a reply cancel reply.
Log in to leave a comment

Most Popular
Why playing alone is recommended for kids, recent comments.

FirstCry Intelli Education is an Early Learning brand, with products and services designed by educators with decades of experience, to equip children with skills that will help them succeed in the world of tomorrow.

The FirstCry Intellikit `Learn With Stories` kits for ages 2-6 brings home classic children`s stories, as well as fun activities, specially created by our Early Learning Educators.
For children 6 years and up, explore a world of STEAM learning, while engaging in project-based play to keep growing minds busy!

Build a love for reading through engaging book sets and get the latest in brain-boosting toys, recommended by the educators at FirstCry Intellitots.

Our Comprehensive 2-year Baby Brain Development Program brings to you doctor-approved toys for your baby`s developing brain.

Our Preschool Chain offers the best in education across India, for children ages 2 and up.
©2024 All rights reserved
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use

Welcome to the world of Intelli!
We have some FREE Activity E-books waiting for you. Fill in your details below so we can send you tailor- made activities for you and your little one.
Parent/Guardian's Name
Child's DOB
What would you like to receive other than your Free E-book? I would like information, discounts and offers on toys, books and products I want to find a FirstCry Intellitots Preschool near me I want access to resources for my child's development and/or education

Welcome to the world of intelli!
FREE guides and worksheets coming your way on whatsapp. Subscribe Below !!
THANK YOU!!!
Here are your free guides and worksheets.
- Paragraph Writing
- Paragraph On Earth
Paragraph on Earth - Check Samples for 100, 150, 200, 250 Words
For so many years, Earth has been the only planet that made life possible. Now, due to overpopulation and other reasons, the Earth is in the process of depletion. Owing to this condition, scientists and astronauts are trying to find neighbouring planets that could support life. Read through the article to learn more about the Earth and the need to conserve the planet. You can also try writing a paragraph on Earth after you have gone through the sample paragraphs given in the article.
Table of Contents
Paragraph on earth in 100 words, paragraph on earth in 150 words, paragraph on earth in 200 words, paragraph on earth in 250 words, frequently asked questions on paragraph on earth.
The Earth is the third planet from the sun. It is also called the blue plane. The Earth is the only planet that supports life because of the availability of air, water, and gases needed for survival. The climate of the Earth is mild. However, due to the overuse and wastage of resources, the planet is in danger, and global warming is increasing. This is affecting the survival conditions for human beings and all living things. In order to save our Earth, we will have to take major steps to conserve what is left on the planet because life is not possible on other planets.
The sphere or spheroid-shaped Earth is the third planet in the solar system and is the only life-supporting planet. When seen from the Earth’s outer surface, it looks blue in colour due to the presence of water and hence is called the blue planet. The Earth provides all its inhabitants with the basic amenities which are required for survival. The sad fact is that human beings have been exploiting all the resources which have been made available to us all this while mindlessly. If this continues, we will put ourselves and all living things in great danger. It is high time we took steps to save our planet. Afforestation, using biodegradable products and reducing pollution are some measures you could take to preserve the beauty and quality of life on Earth.
The third planet from the sun is the Earth. Because of the availability of air, water, and gases required for survival, the Earth is the only planet that sustains life. The planet has all the necessary amenities and a mild climate that is suitable for all the inhabitants of the planet. The underlying concept of harmony is at the heart of the Earth’s living processes. There is perfect coordination between the biosphere, lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and the many levels and realms of life. Because of this coordination and synchronisation, we are able to live a healthy life on Earth. However, there has been massive exploitation of resources due to various anthropogenic activities, and now, it has become a threat to our planet. It is so disheartening that the gifts of nature are being mishandled and exploited, thereby threatening our survival on the whole. So, it is important that all of us understand the need to preserve our natural resources and see to it that our future generations also get to enjoy what we do.
The Earth, spherical in shape, is the third planet from the Sun in the solar system and is the only one that has sustainable living conditions. Because of the existence of water, the Earth appears blue when viewed from outer space, earning it the nickname “blue planet.” We must be extremely cautious about its preservation because life is not possible on any of the planets other than Earth.
Earth has provided us with all of the essential resources we require for living, but we have been exploiting these resources since the beginning. It has now become a major concern as it has led to the depletion and total destruction of the plant on the whole. Unprecedented and unexpected natural calamities like forest fires, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis and cyclones are the effects of our actions. There has been a perfect balance in the ecosystem, but activities such as deforestation, disposal of sewage and waste into water bodies, improper waste management systems, etc., have disturbed this. Australia’s ‘Black Summer’ bushfires of 2019-20 that killed almost one to three billion animals and destroyed many million hectares of native vegetation is an example of the kind of damage the planet is bound to face if we do not take measures to curb the effects of pollution and other activities. This is the only way we can restrain from putting the life of the entire planet in jeopardy. There is no more time to be wasted thinking of actions to be taken, you have to step out and act now if you want to continue living on this sustainable and all-providing planet.
How are resources on our Earth depleting?
The resources on our Earth are depleting due to overpopulation, global warming, pollution, etc. The ice is melting; forests are burning, fields are empty and dry, the oceans are unstable, and the water is not clean – all these are signs that our resources on Earth are depleting, and it is high time to save our Earth.
Why is the Earth called a blue planet?
The Earth is called the blue planet because, when observed from outer space, it seems to be blue in colour due to the amount of water present.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Essay on Environment for Students and Children
500+ words essay on environment.
Essay on Environment – All living things that live on this earth comes under the environment. Whether they live on land or water they are part of the environment. The environment also includes air, water, sunlight, plants, animals, etc.
Moreover, the earth is considered the only planet in the universe that supports life. The environment can be understood as a blanket that keeps life on the planet sage and sound.

Importance of Environment
We truly cannot understand the real worth of the environment. But we can estimate some of its importance that can help us understand its importance. It plays a vital role in keeping living things healthy in the environment.
Likewise, it maintains the ecological balance that will keep check of life on earth. It provides food, shelter, air, and fulfills all the human needs whether big or small.
Moreover, the entire life support of humans depends wholly on the environmental factors. In addition, it also helps in maintaining various life cycles on earth.
Most importantly, our environment is the source of natural beauty and is necessary for maintaining physical and mental health.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Benefits of the Environment
The environment gives us countless benefits that we can’t repay our entire life. As they are connected with the forest, trees, animals, water, and air. The forest and trees filter the air and absorb harmful gases. Plants purify water, reduce the chances of flood maintain natural balance and many others.
Moreover, the environment keeps a close check on the environment and its functioning, It regulates the vital systems that are essential for the ecosystem. Besides, it maintains the culture and quality of life on earth.
The environment regulates various natural cycles that happen daily. These cycles help in maintaining the natural balance between living things and the environment. Disturbance of these things can ultimately affect the life cycle of humans and other living beings.
The environment has helped us and other living beings to flourish and grow from thousands of years. The environment provides us fertile land, water, air, livestock and many essential things for survival.
Cause of Environmental Degradation
Human activities are the major cause of environmental degradation because most of the activities humans do harm the environment in some way. The activities of humans that causes environmental degradation is pollution, defective environmental policies, chemicals, greenhouse gases, global warming, ozone depletion, etc.
All these affect the environment badly. Besides, these the overuse of natural resources will create a situation in the future there will be no resources for consumption. And the most basic necessity of living air will get so polluted that humans have to use bottled oxygen for breathing.

Above all, increasing human activity is exerting more pressure on the surface of the earth which is causing many disasters in an unnatural form. Also, we are using the natural resources at a pace that within a few years they will vanish from the earth. To conclude, we can say that it is the environment that is keeping us alive. Without the blanket of environment, we won’t be able to survive.
Moreover, the environment’s contribution to life cannot be repaid. Besides, still what the environment has done for us, in return we only have damaged and degraded it.
FAQs about Essay on Environment
Q.1 What is the true meaning of the environment?
A.1 The ecosystem that includes all the plants, animals, birds, reptiles, insects, water bodies, fishes, human beings, trees, microorganisms and many more are part of the environment. Besides, all these constitute the environment.
Q.2 What is the three types of the environment?
A.2 The three types of environment includes the physical, social, and cultural environment. Besides, various scientists have defined different types and numbers of environment.

Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 3 Landforms and Life
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 3 Landforms and Life updated and modified for academic session 2024-25. The question answers of Class 6 Social Science Exploring Society – India and Beyond India Beyond Geography Chapter 3 is given here based on NEP 2020.
Class 6 Social Science Chapter 3 Landforms and Life Question Answers
- Class 6 Social Science Chapter 3 Solutions
- Class 6 Social Science Chapter 3 NCERT
- Class 6 Social Science NCERT Solutions
- Class 6 all Subject’s NCERT Solutions
Landforms are natural features on Earth’s surface that vary greatly from place to place. The three main types of landforms are mountains, plateaus, and plains. These landforms are formed over millions of years and have a significant impact on the environment and the way people live. As you travel across different regions, such as from Jharkhand to Uttarakhand in India, you’ll notice changes in the landscape due to the presence of these landforms. Each landform has its unique climate, vegetation, and animal life, and humans have adapted to live in all these different environments.

Mountains: The Majestic Heights Mountains are towering landforms with steep slopes and a narrow peak. They are often found in long chains or ranges, such as the Himalayas in Asia or the Andes in South America. Mountains can be covered in snow at high altitudes, which melts in the summer to feed rivers. Some of the world’s tallest mountains, like Mount Everest and Mount Kanchenjunga, are part of the Himalayan range. Mountains are rich in natural resources and are home to a variety of wildlife, including animals like the snow leopard and the yak. People living in mountainous regions often rely on activities like farming, herding, and tourism for their livelihood.
Living in the mountains comes with its challenges. The rugged terrain and steep slopes make farming difficult, but people have found ways to cultivate the land by creating terraces on the slopes. Many mountain communities also depend on tourism, as visitors are drawn to the fresh air, scenic views, and opportunities for outdoor activities like skiing and mountaineering. However, mountain life can be dangerous due to natural hazards like landslides, avalanches, and flash floods. Despite these challenges, many people continue to live in the mountains, adapting to the harsh conditions with resilience and ingenuity.
Plateaus: Elevated Plains Plateaus are flat, elevated areas of land that rise sharply above the surrounding landscape. Some plateaus, like the Tibetan Plateau, are known as the “Roof of the World” because of their high elevation. Others, like the Deccan Plateau in India, are rich in minerals and have been formed through volcanic activity. Plateaus are important sources of minerals like coal, iron, and gold, making mining a major economic activity in these regions. However, the rocky soil of plateaus often makes them less suitable for farming, except for volcanic plateaus, which have fertile black soil.
While plateaus may not be as fertile as plains, they still support a variety of human activities. In addition to mining, people on plateaus often engage in farming and herding. Some plateaus are also famous for their stunning waterfalls, such as the Victoria Falls in Africa and the Jog Falls in India. The diverse landscapes of plateaus offer opportunities for tourism as well. However, the harsh climate and rocky terrain can make life on plateaus challenging, and people living in these regions must adapt to these conditions.
Plains: The Fertile Lands Plains are vast, flat areas of land that are usually very fertile, making them ideal for agriculture. Many of the world’s earliest civilizations developed in the fertile plains around rivers, where the soil was rich and suitable for growing crops. In India, the Ganga Plain supports a large population and is known for its agricultural productivity. People in the plains grow a variety of crops, including rice, wheat, and cotton, and the plains are also home to diverse wildlife. The flat terrain of plains makes them ideal for transportation and trade, further contributing to their importance in human society.
The Earth’s surface is made up of a complex variety of landforms, each offering different challenges and opportunities for human life. From the towering mountains to the elevated plateaus and the fertile plains, each landform has shaped the way people live, work, and interact with their environment. Understanding these landforms helps us appreciate the diversity of life on Earth and the ways in which humans have adapted to their surroundings. Whether it’s the resilience of mountain communities or the agricultural productivity of the plains, the connection between landforms and life is a fundamental aspect of our world.

Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education


10 Lines on Earth
Earth is our mother planet which provides habitat to millions of species of plants and animals. Earth is the only planet that has atmosphere in the entire solar system. Earth’s atmosphere nourishes life and protects it from harmful UV rays and meteorites. Earth is our planet and we should take all the necessary steps to maintain the continuity of life. As a responsible person, we should participate in volunteering the activities that would make our earth a sustainable planet for future generations.
Ten Lines on Earth in English
We are providing 10 lines, 5 lines, 20 lines, few lines and sentences on Earth in English for Class 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. You can add these lines in your essay and paragraph writing in your exams as well as in the school competitions. So, let’s start reading and getting the one best for you:
1) Earth is one of the eight planets of our solar system that revolves around the sun.
2) Earth is the only known planet supporting life in the entire solar system.
3) Many scientists claim that earth is supposed to be 4.5 billion years old.
4) Around 73% of the surface of the earth is covered with water.
5) Earth has an atmosphere containing 21% oxygen which helps in the survival of living beings.
6) The gases like nitrogen, CO2, and oxygen in earth’s atmosphere help plants to grow.
7) Earth‘s rocky surface known as the crust is made up of silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium and magnesium.
8) Earth is spheroid in shape and is larger than other planets like Mercury, Venus, and Mars.
9) Earth completes its orbit around the sun in 365.256 days which creates leap year once in 4 years.
10) The earth is a habitat for the millions of species of plants and animals.
10 Lines and Sentences on Earth
1) The coldest place on earth is Antarctica and the hottest place in Libya.
2) Earth provides us air, water, food and shelter to live.
3) It is our moral responsibility to protect our earth from pollution and global warming.
4) We should not waste natural resources like coal, water, and minerals found on earth.
5) Conservation of natural resources is important for the sustainability of planet earth.
6) More than 7 billion people are currently residing on planet earth.
7) Earth Day is observed every year on 22 nd April in order to protect the environment.
8) Earth generates a powerful magnetic field due to its rotation and iron core.
9) Only 3% of the earth’s water is freshwater rest 97 percent of water is saline in nature.
10) Earth’s only natural satellite is the moon which revolves around the earth.

5 Lines on Earth
1) Earth is one of the planets in our solar system.
2) It is the only planet supporting life.
3) Earth is bigger than Mars, Mercury, and Venus.
4) It is covered with 71% of water.
5) It is also called the blue planet.
20 Lines on Earth
1) Earth is a planet of Sun which is also called Blue Planet because of the availability of water and it looks blue when observed from the space.
2) The entire surface area of the Earth is 510,072,000 sq km, of which the land area is approx. 148,940,000 sq km and the aquatic area is about 361,132,000 sq km.
3) 97% of the water on the earth is saline or not potable and only 3% is clean water which mankind uses for their need.
4) Only 11 percent of the Earth’s terrain is used to produce food i.e. in agriculture.
5) The Earth is tilted at an angle of 23.5 0 on its own axis and due to this inclination of the earth, the weather changes.
6) There is a very dense atmosphere around the Earth and it contains about 78.09% nitrogen, 20.91% oxygen and 1% other gases.
7) On the surface of the earth, there are huge mountains, somewhere rugged plateau and fertile plains are found elsewhere.
8) The surface of the Earth constantly changes during time period due to plate tectonics and erosion.
9) Changes at the bottom due to plate tectonics have an effect on weather, rainfall, heat cycle and chemical changes.
10) These changes occur on the surface due to many factors such as freezing, coastal erosion, formation of coral reefs and large meteor bodies falling on the earth.
11) According to Indian mythology, the name Prithvi is derived from the legend king Maharajah (his Highness) Prithu.
12) In English, it is also known as Earth.
13) The word ‘Earth’ has been taken from the German language which means ‘ground’.
14) Earth is the 5th largest planet in size and is the only planet in the solar system that has life.
15) The planet Earth was formed about 4.54 billion years ago and life started to develop hereafter one billion years of this event.
16) Earth’s radius is about 6,371 kilometers and is the fifth largest body in the solar system by size.
17) The Earth is located approximately 150 million kilometers from the Sun and this distance is known as Astronomical Unit.
18) It takes about 8.3 minutes for sunlight to reach the Earth.
19) The Earth completes a circle around the Sun in an elliptical path in 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes and 45.51 seconds, which is called its rotational motion.
20) On 22 nd April 1970, the first Earth Day was celebrated in America and after this day is celebrated as Earth Day all over the world.
Earth is the only planet that supports life. Earth gives us all the necessary things like food, water, the shelter needed for the survival of life. Hence, it is our prime responsibility to protect the earth by saving greenery and the environment. We should not waste natural resources in abundance for our own greed. As a human being, we should volunteer for the activities that help in reducing pollution and global warming thereby making it a sustainable planet to live.
Related Posts
10 lines on mahatma gandhi, 10 lines on patriotism, 10 lines on nationalism, 10 lines on national flag of india, 10 lines on importance of national flag, 10 lines on importance of national festivals of india, 10 lines on national festivals of india, 10 lines on national festivals celebration, 10 lines on a.p.j. abdul kalam, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- Social Science
- The Earth Our Habitat

Solutions for NCERT Geography Class 6 (The Earth Our Habitat) - FREE PDF Download
The NCERT Geography Class 6 Solutions offers clear and detailed answers to all the questions in the textbook. These solutions help students straightforwardly understand important geographical concepts. The Earth Our Habitat is a crucial part of this subject. This book helps to understand the wonders of our planet. It covers various topics, including the Earth's formation, landforms, water bodies, and climatic conditions, providing a comprehensive overview of our natural environment.

NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science is also great for exam preparation, covering all key topics and questions from the textbook. By using CBSE Class 6 Social Science Syllabus , students can clear up any doubts, reinforce their understanding, and build a strong base in Geography. This resource is designed to improve performance, making it essential for Class 6 students.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography Chapter-wise Links - Download the FREE PDF
S.No. | NCERT Solutions Class 6 Geography Chapter-wise List |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
6 |
|
Below is the pictorial representation of the Class 6 NCERT Geography Syllabus for better understanding.
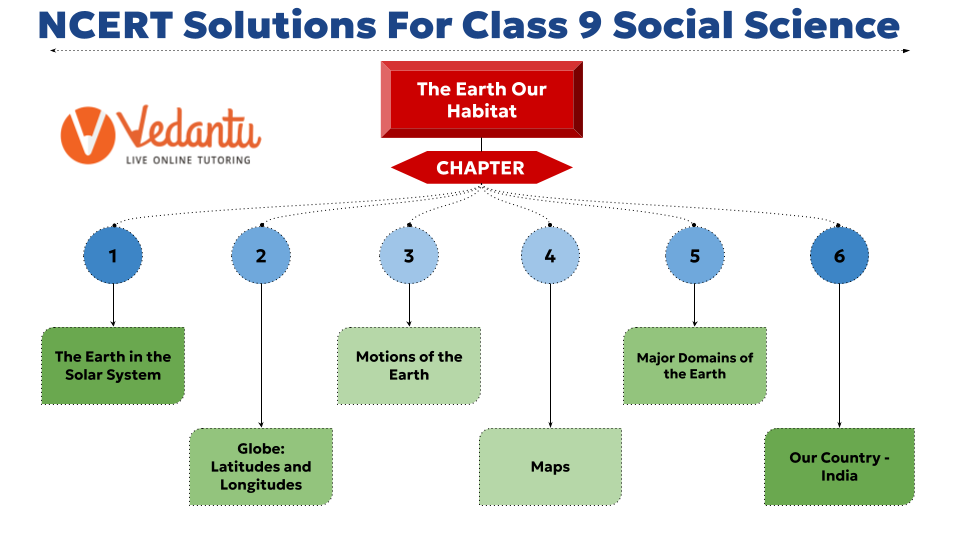
Quick Overview of NCERT Solutions Class 6 Geography
NCERT Geography Class 6 provides answers to all chapters in the NCERT textbook, ensuring complete coverage.
NCERT Class 6 Geography solutions help students practise and evaluate their understanding of Geography concepts, aiding in better retention and clarity.
In the Geography NCERT Class 6, Each solution offers detailed explanations, including step-by-step methods and relevant examples, facilitating effective learning and revision.
This resource is essential for exam preparation, helping students build a strong foundation in Geography NCERT Class 6 and their confidence in tackling exam questions.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography: Chapter Details, Concepts, and Important Links
Chapter 1 - the earth in the solar system.
NCERT Solutions for Geography NCERT Class 6 Chapter 1 examines the concept of The Earth in the Solar System and its societal importance.
In NCERT Geography Class 6 Chapter 1 The Earth in the Solar System, discovers the sun, the star at the centre, and its eight planetary companions, including our very own Earth.
Learn about the planets – fiery Mercury, scorching Venus, rusty Mars, giant Jupiter and Saturn, icy Uranus and Neptune, and even the dwarf planet Pluto (is it still a planet?).
Find out what makes Earth special and why it's the only known planet to support life as we know it.
Learn about the Earth's movements in space – rotation on its axis (day and night) and revolution around the Sun (seasons).
Unravel the secrets of our natural satellite, the Moon. Why do we always see the same side? How does it affect Earth?
Get a glimpse of other celestial bodies like asteroids, meteoroids, and comets that zip around the solar system.
Important Topics Covered in Chapter 1: The Earth in the Solar System
The Solar System
Along with Class 6 Geography NCERT Solution, you can also refer to Class 6 The Earth in the Solar System Revision Notes .
Chapter 2 - Globe: Latitudes and Longitudes
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography Chapter 2 examines the concept of Globe: Latitudes and Longitudes and its societal importance.
In NCERT Geography Class 6 Chapter 2 Globe: Latitudes and Longitudes, discover the wonder of globes! How they act as mini Earth, helping us visualise our planet.
Learn about graticules – the imaginary lines that create a grid system on the globe.
Unravel the mystery of parallels of latitude – imaginary lines that run east-west, marking distance north or south from the equator. Climate zones – hot, warm, and cold – come into play here!
Explore meridians of longitude – imaginary lines running north-south, marking east or west from a special meridian called the Prime Meridian. Get ready for time zone adventures!
Learn the secret code for pinpointing any place on Earth – using latitude and longitude! It's like a treasure hunt to find any location on the globe.
Discover important imaginary circles like the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, and the Arctic and Antarctic Circles. They're not just lines on a map – they tell us about the sun's path and Earth's climate zones.
Important Topics Covered in Chapter 2: Globe: Latitudes and Longitudes
Important Parallels of Latitudes
Heat Zone of The Earth
What are Longitudes
Longitude and Time
Why Do We Have Standard Time
Along with Class 6 Geography NCERT Solution, you can also refer to Class 6 Globe: Latitudes and Longitudes Revision Notes .
Chapter 3 - Motions of the Earth
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography Chapter 3 examines the concept of Motions of the Earth and its societal importance.
In NCERT Geography Class 6 Chapter 3 Motions of the Earth, explore Earth's rotation on its axis, causing day and night.
Uncover Earth's revolution around the Sun, leading to the changing seasons.
Discover the Earth's tilted axis, the secret ingredient behind the seasons we experience.
Learn why some days are longer and some are shorter, depending on your location.
Find out how long it takes for Earth to complete one revolution around the Sun (hint: it's not exactly 365 days!).
Important Topics Covered in Chapter 3: Motions of the Earth
Orbital Plane
Circle of Illumination
Elliptical Orbit
Summer Solstice
Winter Solstice
Along with Class 6 Geography NCERT Solution, you can also refer to Class 6 Motions of the Earth Revision Notes .
Chapter 4 - Maps
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 examines the concept of Maps and their societal importance.
In NCERT Geography Class 6 Chapter 4 Maps, discover maps, the amazing tools that help us navigate and understand our planet.
Learn about the three key components of any map – distance, direction, and symbols.
Explore cardinal directions (north, south, east, west) and intermediate directions never to get lost on a map.
Grasp the concept of map scale – how a map represents actual distances on the ground.
Understand why maps are more practical than globes for everyday use.
Uncover different types of maps – physical maps showing landforms, political maps showing countries and boundaries, and thematic maps focusing on specific information like climate or population.
Learn how to interpret symbols used on maps to understand the information they convey.
Important Topics Covered in Chapter 4: Maps
Physical Map
Political Map
Thematic Map
Along with Class 6 Geography NCERT Solution, you can also refer to Class 6 Maps Revision Notes .
Chapter 5 - Major Domains of the Earth
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography Chapter 5 examines the concept of Major Domains of the Earth and their societal importance.
In NCERT Geography Class 6 Chapter 5 Major Domains of the Earth, embark on a journey to explore the Earth's major domains - the fundamental building blocks that make up our planet!
Focus on the world of land (lithosphere), water (hydrosphere), and air (atmosphere) - each playing a crucial role in sustaining life.
Uncover the secrets of the lithosphere - the solid, rocky outer layer of Earth, including mountains, plains, and valleys.
Explore the vast hydrosphere - the water layer covering most of Earth's surface, encompassing oceans, lakes, rivers, and groundwater.
Focus on the atmosphere - the layer of gases surrounding Earth, essential for respiration and regulating temperature.
Discover the interconnectedness of these domains - how they interact and influence each other to create the perfect conditions for life to thrive.
Important Topics Covered in Chapter 5: Major Domains of the Earth
Lithosphere
Hydrosphere
Biosphere - The Domain Of Life
Along with Class 6 Geography NCERT Solution, you can also refer to Class 6 Major Domains of the Earth Revision Notes .
Chapter 6 - Our Country India
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography Chapter 6 examines the concept of Our Country India and its societal importance.
In NCERT Geography Class 6 Chapter 6 Our Country India, unveil the vast and vibrant landmass called India – your home country!
Explore the diverse landscapes of India – towering Himalayas, fertile plains, gushing rivers, and stunning coastlines.
Decipher the map of India, learning about its states, union territories, and their capitals.
Discover the variations in India's climate, from the hot deserts to the snow-capped mountains.
Navigate along the mighty rivers of India – the lifeline of the nation – the Ganges, Yamuna, Indus, Brahmaputra, and more!
Important Topics Covered in Chapter 6: Our Country India
Locational Settings
India’s Neighbours
Political And Administrative Divisions
Physical Divisions
Along with Class 6 Geography NCERT Solution, you can also refer to Class 6 Our Country India Revision Notes .
Benefits of Referring to Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography (The Earth Our Habitat)
Geography Class 6 provides clear and extensive explanations for each topic, allowing students to better understand the concepts.
These solutions cover all important topics and questions from the textbook, which is helpful for thorough exam preparation.
Problems are solved step-by-step, making it simple for students to learn and apply problem-solving techniques.
Practising these solutions can help students improve their speed and accuracy, aiding in better time management during exams.
The solutions help clear up any doubts students may have, ensuring a strong grasp of Geography principles.
Regular practice with Geography Class 6 solutions builds students' confidence, making them well-prepared for their exams.
Class 6 Geography : The Earth Our Habitat isn't just memorising facts, it's an explorer's guide to our amazing planet. Students will travel the solar system, decipher maps, discover Earth's building blocks, and explore diverse landscapes, all while building a foundation for future studies and becoming a responsible citizen who appreciates the wonder of our world.
Related Important Links for Class 6 Geography
Along with this, students can also download additional study materials provided by Vedantu for CBSE Class 6 Geography–
S.No. | Important Links for Class 6 Geography |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography 2024-25
1. What is the crux of content given in NCERT Solutions Class 6 Geography?
Here the crux of content given in NCERT Class 6 Geography solution is students can build up their knowledge on various aspects of the universe like the solar system, natural vegetation and wildlife, landforms, maps, etc.
2. What do we understand by Chapter 6 Class 6 Our India?
NCERT Class 6 Geography Solutions Chapter 6 Our India discusses Our country in detail. Students can understand the concept of the chapter by going through NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography by Vedantu. Practising the important questions will help students to reap the utmost benefit of scoring well in exams. Vedantu provides PDF Class 6 Geography where all the notes are prepared by subject experts giving the best out of the best to its students. Important topics like The Arabian Sea, The Bay of Bengal, and the Indian Peninsula are covered under NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography Chapter 6.
3. How many chapters does the NCERT Solutions Class 6 Geography have?
The NCERT textbook for class 6 Geography has eight chapters. These chapters cover essential topics from our solar system to the geography of India. These topics are important for creating a strong base for CBSE students for higher classes. The NCERT Solutions for class 6 Geography has solutions to all the questions from the NCERT textbook to help students better understand the concepts and the chapter. The NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography are available for all students download on the Vedantu website.
4. What does Chapter 1 of Class 6 Geography focus on?
The NCERT Solutions provide the students with step by step solutions to all questions for each chapter in CBSE prescribed syllabus for all classes. The first chapter of Geography for class 6 is The Earth in the Solar System. The chapter discusses the different planets and celestial bodies in our solar system. It aims at providing an introduction to the solar system and how the Earth is a unique planet in the solar system. All the questions from the textbook are answered in the solution pdf which is available for download online at free of cost from the Vedantu website and the Vedantu app.
5. What is the ideal study plan for class 6 Geography?
Class 6 is the class in which the students are introduced to different divisions in social science- Geography, History and Political science. This helps students to get familiarised with how they would be taught in higher classes as well and build a strong foundation. The students should make a timetable and divide their time equally for each part and chapter. The NCERT solutions for each chapter subject wise will provide the students with summaries, solved questions and extra questions for practice.
6. Is the NCERT Solution PDF for Class 6 Geography enough to prepare for the final exam?
The NCERT textbook is the best book prescribed by the CBSE to prepare for exams. It is from where most questions are asked in the exam. The NCERT Solutions PDF available for download by Vedantu provides answers to all NCERT questions in simple language for all the students to understand the concepts. The students can refer to the PDF to understand the concepts and practice extra questions as well. The students can revise from the PDF as well as all the important information is provided in a concise form.
7. What is NCERT Solutions Class 6 Geography?
NCERT Solutions are answer guides for textbooks published by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) in India. These solutions provide explanations and answers to the exercise questions found at the end of each chapter in the textbook.
8. Are NCERT Class 6 Geography solutions available online for FREE?
While NCERT doesn't officially publish its solutions online, there are many websites and educational platforms that offer NCERT Solutions for various subjects, including Class 6 Social Science: The Earth Our Habitat. It's important to be cautious about copyright restrictions when using these resources.
9. Are NCERT Class 6 Geography solutions necessary to understand the content in ‘The Earth Our Habitat’?
NCERT Solutions can be a helpful tool for students who need extra explanation or clarification on concepts covered in the textbook. However, they shouldn't be a substitute for actively reading and understanding the content yourself. The textbook itself provides clear explanations and engaging activities.
NCERT SOLUTIONS FOR CLASS 6
Cbse class 6 study materials.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Locating Places on the Earth Class 6 MCQ Online Test Social Science Chapter 1
August 21, 2024 by Veerendra
Class 6 Social Science Chapter 1 MCQ Locating Places on the Earth
MCQ Questions for Class 6 Social Science SST Chapter 1 Locating Places on the Earth
1. Choose the correct option in the following questions:
Question 1. Map showing the distribution of forests. (a) Political map (b) Physical map (c) Thematic map (d) Colourful map. Answer: (c) Thematic map
Question 2. A scale is necessary. (a) for a plan (b) for symbols (c) for accuracy (d) for a map. Answer: (d) for a map.
Question 3. Grid is a network of: (a) lines of latitude (b) lines converging at the poles (c) total number of longitudes (d) parallels of latitudes and Meridians of longitudes. Answer: (d) parallels of latitudes and Meridians of longitudes.
Question 4. The longest circle drawn midway between the two poles. (a) The Prime Meridian (b) The Equator (c) The Tropic of Cancer (d) The Tropic of Capricorn. Answer: (b) The Equator
Question 5. The Equator does not pass through which of the following continents: (a) Europe (b) Africa (c) Asia (d) South America. Answer: (a) Europe
2. Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
Question 1. The Earth rotates from _________ to _________ Answer: West/East
Question 2. Each degree of longitude corresponds to a time difference of _________ minutes. Answer: 4 minutes
Question 3. International Date Line passes through the _________ Ocean. Answer: Pacific
Question 4. Prime Meridian passes through Greenwich near _________. Answer: London
Question 5. Standard Meridian of India _________. Answer: 82VT° E longitude
3. State whether the statements given below are True or False:
Question 1. Distance between two points represented on maps depend on symbols and colours that a map is using. Answer: False
Question 2. Both latitudes and longitudes are expressed in degrees. Answer: True
Question 3. It takes the Earth 365 days to complete one spin on its axis called rotation. Answer: False
Question 4. India’s (Bharat’s) Prime Meridian many centuries ago was called ‘madhya rekha’ and passed through the city of Ujjain. Answer: True
Question 5. India’s latitudes extras approximately from 8°N to 37°N and longitudes from 68°E to 97°E. Answer: True
4. Match the following items given in Column A with that in Column B:
Question 1.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Coordinates | a. Scale |
| 2. Distance | b. North |
| 3. Cardinal directions | c. Latitudes and Longitudes |
| 4. Axis | d. Model of Earth |
| 5. Globe | e. 23½° |
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Coordinates | c. Latitudes and Longitudes |
| 2. Distance | a. Scale |
| 3. Cardinal directions | b. North |
| 4. Axis | e. 23½° |
| 5. Globe | d. Model of Earth |
Class 6 Social Science MCQ
Free resources.
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources

IMAGES
COMMENTS
500 Words Essay On Earth. The earth is the planet that we live on and it is the fifth-largest planet. It is positioned in third place from the Sun. This essay on earth will help you learn all about it in detail. Our earth is the only planet that can sustain humans and other living species. The vital substances such as air, water, and land make ...
This essay on earth is for kids from class 3 to 6 to understand about our planet. July 5, 2021. Earth is the only planet of the solar system that provides all the necessities required to survive. In short, it is the only planet that has life on it. It is the third planet of the solar system and the fifth largest planet among all the planets.
500+ Words Essay on Save Earth. Earth and the resources of earth make life possible on it. If we were to imagine our lives without these resources, that would not be possible. As life cannot function without sunshine, air, vegetation, and water. However, this is soon going to be our reality if we do not save the earth now.
Earth is the 3rd planet from the Sun, and it has one Moon. It is the only planet in our Solar System which is suitable for sustaining life. The composition of the Earth's surface is 70% water and only 30% land. Water bodies such as oceans, rivers, lakes, glaciers and seas make up 70% of the water content on Earth.
500+ Words Essay on Save Earth. Taking care of our Earth is no longer an option - it is a necessity. There is no other alternative planet where life is possible other than Earth. Since the beginning of our existence, we have exploited nature by cutting innumerable trees to build infrastructure and killing animals for food.
Short Essay on Earth of 100 Words. The Earth, often referred to as the "Blue Planet," is a remarkable celestial body in our solar system. It's situated at just the right distance from the Sun, allowing it to maintain a stable climate and support a wide variety of life forms. Earth's diverse landscapes, from towering mountains to vast ...
Learn about Save Earth Essay topic of english in details explained by subject experts on vedantu.com. Register free for online tutoring session to clear your doubts. ... CBSE Notes for class 6. Essay on Save Earth. Each living being on Earth knows the importance of Earth in our lives. Without Earth, we cannot even imagine living.
500+ Words Climate Change Essay. Climate change refers to the change in the environmental conditions of the earth. This happens due to many internal and external factors. The climatic change has become a global concern over the last few decades. Besides, these climatic changes affect life on the earth in various ways.
Essay # 1. Origin of the Earth: Earth is the third planet in the Solar system and lies at an average distance of approximately 149 billion km from the Sun. The Earth is presumed to be as old as five or six billion years. The Earth was initially a fiery spinning ball of hot gases and vapours.
The save earth essay emphasises issues faced by the planet and measures we can take to save it from hazardous activities. Earth is a beautiful place full of life. Unfortunately, our activities are harming our world. As the population increases, we rely too much on our vehicles rather than public transportation, which harms the environment.
Here are a few lines on save earth that can be used to write a good essay for class 1 and 2 kids: Earth is the only planet in the universe that has life in this universe. The planet has given us abundant natural resources like water, air, sunlight and more. Humans have been exploiting the planet for their greed.
Essay on Save Environment Day. The environment is the surrounding area of our dwelling. It plays a crucial role in our survival and existence. It is in the "environment" where a living thing has its chances of birth, growth, development, and life itself. The cues present in that environment gradually shape their survivability and habitation.
In Class 6 Chapter 1 Geography the orbit of a planet (or satellite) is the specific and precise elliptical route in which it constantly travels (or satellite). A planet is a celestial body that spins in an orbit around a single star and receives all of its light from that star. Earth is a planetary system.
10 Lines Essay on Earth (100 - 120 Words) 1) Planet Earth is positioned third from the Sun in solar system. 2) The only known planet to support life in solar system is Earth. 3) It looks bright blue and green in color. 4) It ranks fifth in size among the planets of our solar system.
In order of their distance from the sun, they are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. All eight planets of the solar system move around the sun in fixed paths. These paths are called orbits. Mercury is nearest to the sun. It takes only about 88 days to complete one round along its orbit.
The Earth in the Solar System Class 6 Notes Social Science Geography Chapter 1. Solar System. The sun, nine planets, satellites, asteroids and meteoroids form the solar system. The Sun. The sun is in the center of the solar system. It is made up of extremely hot gases. The sun is about 150 million km away from the earth.
Paragraph on Earth in 250 Words. The Earth, spherical in shape, is the third planet from the Sun in the solar system and is the only one that has sustainable living conditions. Because of the existence of water, the Earth appears blue when viewed from outer space, earning it the nickname "blue planet.". We must be extremely cautious about ...
Essay on Save Earth in 150 words. Earth stands alone in this vast universe as the sole haven for life as we know it. It offers a unique blend of essential elements like oxygen, water, and the necessary gravitational pull, creating an environment conducive to life. However, the urgency to preserve our planet has never been greater.
500+ Words Essay on Environment. Essay on Environment - All living things that live on this earth comes under the environment. Whether they live on land or water they are part of the environment. The environment also includes air, water, sunlight, plants, animals, etc. Moreover, the earth is considered the only planet in the universe that ...
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10; CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11; CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12; ... The question answers of Class 6 Social Science Exploring Society - India and Beyond India Beyond Geography Chapter 3 is given here based on NEP 2020. ... The Earth's surface is made up of a complex variety of landforms, each offering ...
10 Lines on Earth. 1) Earth is one of the eight planets of our solar system that revolves around the sun. 2) Earth is the only known planet supporting life in the entire solar system. 3) Many scientists claim that earth is supposed to be 4.5 billion years old. 4) Around 73% of the surface of the earth is covered with water.
Solutions for NCERT Geography Class 6 (The Earth Our Habitat) - FREE PDF Download. The NCERT Geography Class 6 Solutions offers clear and detailed answers to all the questions in the textbook. These solutions help students straightforwardly understand important geographical concepts. The Earth Our Habitat is a crucial part of this subject.
Class 6 Social Science Chapter 1 Extra Questions and Answers Locating Places on the Earth. NCERT Class 6 Social Science Chapter 1 Locating Places on the Earth Important Extra Questions and Answers. Locating Places on the Earth Class 6 Very Short Answer Questions. Question 1. What is an atlas? Answer: An atlas is a book or collection of maps ...
Class 6 Social Science Chapter 1 MCQ Locating Places on the Earth MCQ Questions for Class 6 Social Science SST Chapter 1 Locating Places on the Earth 1. Choose the correct option in the following questions: Question 1. Map showing the distribution of forests. (a) Political map (b) Physical map (c) Thematic map (d) Colourful […]