Research Methods
Chapter 2 introduction.
Maybe you have already gained some experience in doing research, for example in your bachelor studies, or as part of your work.
The challenge in conducting academic research at masters level, is that it is multi-faceted.
The types of activities are:
- Finding and reviewing literature on your research topic;
- Designing a research project that will answer your research questions;
- Collecting relevant data from one or more sources;
- Analyzing the data, statistically or otherwise, and
- Writing up and presenting your findings.
Some researchers are strong on some parts but weak on others.
We do not require perfection. But we do require high quality.
Going through all stages of the research project, with the guidance of your supervisor, is a learning process.
The journey is hard at times, but in the end your thesis is considered an academic publication, and we want you to be proud of what you have achieved!
Probably the biggest challenge is, where to begin?
- What will be your topic?
- And once you have selected a topic, what are the questions that you want to answer, and how?
In the first chapter of the book, you will find several views on the nature and scope of business research.
Since a study in business administration derives its relevance from its application to real-life situations, an MBA typically falls in the grey area between applied research and basic research.
The focus of applied research is on finding solutions to problems, and on improving (y)our understanding of existing theories of management.
Applied research that makes use of existing theories, often leads to amendments or refinements of these theories. That is, the applied research feeds back to basic research.
In the early stages of your research, you will feel like you are running around in circles.
You start with an idea for a research topic. Then, after reading literature on the topic, you will revise or refine your idea. And start reading again with a clearer focus ...
A thesis research/project typically consists of two main stages.
The first stage is the research proposal .
Once the research proposal has been approved, you can start with the data collection, analysis and write-up (including conclusions and recommendations).
Stage 1, the research proposal consists of he first three chapters of the commonly used five-chapter structure :
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- An introduction to the topic.
- The research questions that you want to answer (and/or hypotheses that you want to test).
- A note on why the research is of academic and/or professional relevance.
- Chapter 2: Literature
- A review of relevant literature on the topic.
- Chapter 3: Methodology
The methodology is at the core of your research. Here, you define how you are going to do the research. What data will be collected, and how?
Your data should allow you to answer your research questions. In the research proposal, you will also provide answers to the questions when and how much . Is it feasible to conduct the research within the given time-frame (say, 3-6 months for a typical master thesis)? And do you have the resources to collect and analyze the data?
In stage 2 you collect and analyze the data, and write the conclusions.
- Chapter 4: Data Analysis and Findings
- Chapter 5: Summary, Conclusions and Recommendations
This video gives a nice overview of the elements of writing a thesis.


Chapter 2. Research Design
Getting started.
When I teach undergraduates qualitative research methods, the final product of the course is a “research proposal” that incorporates all they have learned and enlists the knowledge they have learned about qualitative research methods in an original design that addresses a particular research question. I highly recommend you think about designing your own research study as you progress through this textbook. Even if you don’t have a study in mind yet, it can be a helpful exercise as you progress through the course. But how to start? How can one design a research study before they even know what research looks like? This chapter will serve as a brief overview of the research design process to orient you to what will be coming in later chapters. Think of it as a “skeleton” of what you will read in more detail in later chapters. Ideally, you will read this chapter both now (in sequence) and later during your reading of the remainder of the text. Do not worry if you have questions the first time you read this chapter. Many things will become clearer as the text advances and as you gain a deeper understanding of all the components of good qualitative research. This is just a preliminary map to get you on the right road.

Research Design Steps
Before you even get started, you will need to have a broad topic of interest in mind. [1] . In my experience, students can confuse this broad topic with the actual research question, so it is important to clearly distinguish the two. And the place to start is the broad topic. It might be, as was the case with me, working-class college students. But what about working-class college students? What’s it like to be one? Why are there so few compared to others? How do colleges assist (or fail to assist) them? What interested me was something I could barely articulate at first and went something like this: “Why was it so difficult and lonely to be me?” And by extension, “Did others share this experience?”
Once you have a general topic, reflect on why this is important to you. Sometimes we connect with a topic and we don’t really know why. Even if you are not willing to share the real underlying reason you are interested in a topic, it is important that you know the deeper reasons that motivate you. Otherwise, it is quite possible that at some point during the research, you will find yourself turned around facing the wrong direction. I have seen it happen many times. The reason is that the research question is not the same thing as the general topic of interest, and if you don’t know the reasons for your interest, you are likely to design a study answering a research question that is beside the point—to you, at least. And this means you will be much less motivated to carry your research to completion.
Researcher Note
Why do you employ qualitative research methods in your area of study? What are the advantages of qualitative research methods for studying mentorship?
Qualitative research methods are a huge opportunity to increase access, equity, inclusion, and social justice. Qualitative research allows us to engage and examine the uniquenesses/nuances within minoritized and dominant identities and our experiences with these identities. Qualitative research allows us to explore a specific topic, and through that exploration, we can link history to experiences and look for patterns or offer up a unique phenomenon. There’s such beauty in being able to tell a particular story, and qualitative research is a great mode for that! For our work, we examined the relationships we typically use the term mentorship for but didn’t feel that was quite the right word. Qualitative research allowed us to pick apart what we did and how we engaged in our relationships, which then allowed us to more accurately describe what was unique about our mentorship relationships, which we ultimately named liberationships ( McAloney and Long 2021) . Qualitative research gave us the means to explore, process, and name our experiences; what a powerful tool!
How do you come up with ideas for what to study (and how to study it)? Where did you get the idea for studying mentorship?
Coming up with ideas for research, for me, is kind of like Googling a question I have, not finding enough information, and then deciding to dig a little deeper to get the answer. The idea to study mentorship actually came up in conversation with my mentorship triad. We were talking in one of our meetings about our relationship—kind of meta, huh? We discussed how we felt that mentorship was not quite the right term for the relationships we had built. One of us asked what was different about our relationships and mentorship. This all happened when I was taking an ethnography course. During the next session of class, we were discussing auto- and duoethnography, and it hit me—let’s explore our version of mentorship, which we later went on to name liberationships ( McAloney and Long 2021 ). The idea and questions came out of being curious and wanting to find an answer. As I continue to research, I see opportunities in questions I have about my work or during conversations that, in our search for answers, end up exposing gaps in the literature. If I can’t find the answer already out there, I can study it.
—Kim McAloney, PhD, College Student Services Administration Ecampus coordinator and instructor
When you have a better idea of why you are interested in what it is that interests you, you may be surprised to learn that the obvious approaches to the topic are not the only ones. For example, let’s say you think you are interested in preserving coastal wildlife. And as a social scientist, you are interested in policies and practices that affect the long-term viability of coastal wildlife, especially around fishing communities. It would be natural then to consider designing a research study around fishing communities and how they manage their ecosystems. But when you really think about it, you realize that what interests you the most is how people whose livelihoods depend on a particular resource act in ways that deplete that resource. Or, even deeper, you contemplate the puzzle, “How do people justify actions that damage their surroundings?” Now, there are many ways to design a study that gets at that broader question, and not all of them are about fishing communities, although that is certainly one way to go. Maybe you could design an interview-based study that includes and compares loggers, fishers, and desert golfers (those who golf in arid lands that require a great deal of wasteful irrigation). Or design a case study around one particular example where resources were completely used up by a community. Without knowing what it is you are really interested in, what motivates your interest in a surface phenomenon, you are unlikely to come up with the appropriate research design.
These first stages of research design are often the most difficult, but have patience . Taking the time to consider why you are going to go through a lot of trouble to get answers will prevent a lot of wasted energy in the future.
There are distinct reasons for pursuing particular research questions, and it is helpful to distinguish between them. First, you may be personally motivated. This is probably the most important and the most often overlooked. What is it about the social world that sparks your curiosity? What bothers you? What answers do you need in order to keep living? For me, I knew I needed to get a handle on what higher education was for before I kept going at it. I needed to understand why I felt so different from my peers and whether this whole “higher education” thing was “for the likes of me” before I could complete my degree. That is the personal motivation question. Your personal motivation might also be political in nature, in that you want to change the world in a particular way. It’s all right to acknowledge this. In fact, it is better to acknowledge it than to hide it.
There are also academic and professional motivations for a particular study. If you are an absolute beginner, these may be difficult to find. We’ll talk more about this when we discuss reviewing the literature. Simply put, you are probably not the only person in the world to have thought about this question or issue and those related to it. So how does your interest area fit into what others have studied? Perhaps there is a good study out there of fishing communities, but no one has quite asked the “justification” question. You are motivated to address this to “fill the gap” in our collective knowledge. And maybe you are really not at all sure of what interests you, but you do know that [insert your topic] interests a lot of people, so you would like to work in this area too. You want to be involved in the academic conversation. That is a professional motivation and a very important one to articulate.
Practical and strategic motivations are a third kind. Perhaps you want to encourage people to take better care of the natural resources around them. If this is also part of your motivation, you will want to design your research project in a way that might have an impact on how people behave in the future. There are many ways to do this, one of which is using qualitative research methods rather than quantitative research methods, as the findings of qualitative research are often easier to communicate to a broader audience than the results of quantitative research. You might even be able to engage the community you are studying in the collecting and analyzing of data, something taboo in quantitative research but actively embraced and encouraged by qualitative researchers. But there are other practical reasons, such as getting “done” with your research in a certain amount of time or having access (or no access) to certain information. There is nothing wrong with considering constraints and opportunities when designing your study. Or maybe one of the practical or strategic goals is about learning competence in this area so that you can demonstrate the ability to conduct interviews and focus groups with future employers. Keeping that in mind will help shape your study and prevent you from getting sidetracked using a technique that you are less invested in learning about.
STOP HERE for a moment
I recommend you write a paragraph (at least) explaining your aims and goals. Include a sentence about each of the following: personal/political goals, practical or professional/academic goals, and practical/strategic goals. Think through how all of the goals are related and can be achieved by this particular research study . If they can’t, have a rethink. Perhaps this is not the best way to go about it.
You will also want to be clear about the purpose of your study. “Wait, didn’t we just do this?” you might ask. No! Your goals are not the same as the purpose of the study, although they are related. You can think about purpose lying on a continuum from “ theory ” to “action” (figure 2.1). Sometimes you are doing research to discover new knowledge about the world, while other times you are doing a study because you want to measure an impact or make a difference in the world.
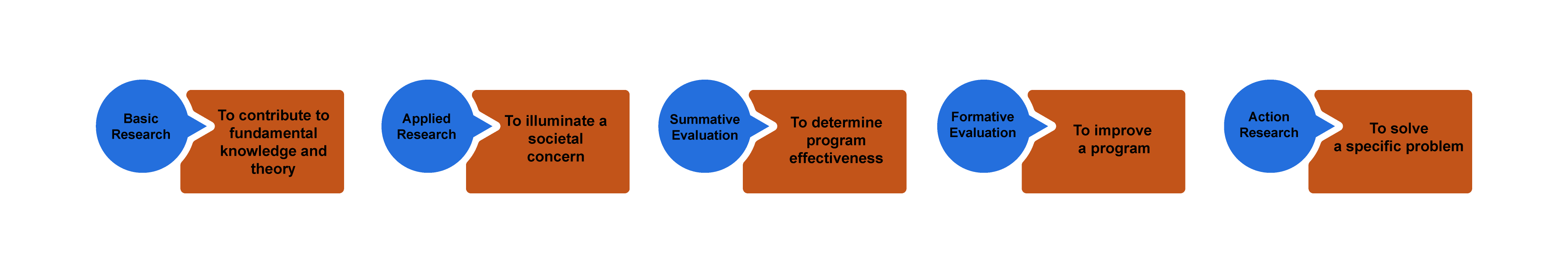
Basic research involves research that is done for the sake of “pure” knowledge—that is, knowledge that, at least at this moment in time, may not have any apparent use or application. Often, and this is very important, knowledge of this kind is later found to be extremely helpful in solving problems. So one way of thinking about basic research is that it is knowledge for which no use is yet known but will probably one day prove to be extremely useful. If you are doing basic research, you do not need to argue its usefulness, as the whole point is that we just don’t know yet what this might be.
Researchers engaged in basic research want to understand how the world operates. They are interested in investigating a phenomenon to get at the nature of reality with regard to that phenomenon. The basic researcher’s purpose is to understand and explain ( Patton 2002:215 ).
Basic research is interested in generating and testing hypotheses about how the world works. Grounded Theory is one approach to qualitative research methods that exemplifies basic research (see chapter 4). Most academic journal articles publish basic research findings. If you are working in academia (e.g., writing your dissertation), the default expectation is that you are conducting basic research.
Applied research in the social sciences is research that addresses human and social problems. Unlike basic research, the researcher has expectations that the research will help contribute to resolving a problem, if only by identifying its contours, history, or context. From my experience, most students have this as their baseline assumption about research. Why do a study if not to make things better? But this is a common mistake. Students and their committee members are often working with default assumptions here—the former thinking about applied research as their purpose, the latter thinking about basic research: “The purpose of applied research is to contribute knowledge that will help people to understand the nature of a problem in order to intervene, thereby allowing human beings to more effectively control their environment. While in basic research the source of questions is the tradition within a scholarly discipline, in applied research the source of questions is in the problems and concerns experienced by people and by policymakers” ( Patton 2002:217 ).
Applied research is less geared toward theory in two ways. First, its questions do not derive from previous literature. For this reason, applied research studies have much more limited literature reviews than those found in basic research (although they make up for this by having much more “background” about the problem). Second, it does not generate theory in the same way as basic research does. The findings of an applied research project may not be generalizable beyond the boundaries of this particular problem or context. The findings are more limited. They are useful now but may be less useful later. This is why basic research remains the default “gold standard” of academic research.
Evaluation research is research that is designed to evaluate or test the effectiveness of specific solutions and programs addressing specific social problems. We already know the problems, and someone has already come up with solutions. There might be a program, say, for first-generation college students on your campus. Does this program work? Are first-generation students who participate in the program more likely to graduate than those who do not? These are the types of questions addressed by evaluation research. There are two types of research within this broader frame; however, one more action-oriented than the next. In summative evaluation , an overall judgment about the effectiveness of a program or policy is made. Should we continue our first-gen program? Is it a good model for other campuses? Because the purpose of such summative evaluation is to measure success and to determine whether this success is scalable (capable of being generalized beyond the specific case), quantitative data is more often used than qualitative data. In our example, we might have “outcomes” data for thousands of students, and we might run various tests to determine if the better outcomes of those in the program are statistically significant so that we can generalize the findings and recommend similar programs elsewhere. Qualitative data in the form of focus groups or interviews can then be used for illustrative purposes, providing more depth to the quantitative analyses. In contrast, formative evaluation attempts to improve a program or policy (to help “form” or shape its effectiveness). Formative evaluations rely more heavily on qualitative data—case studies, interviews, focus groups. The findings are meant not to generalize beyond the particular but to improve this program. If you are a student seeking to improve your qualitative research skills and you do not care about generating basic research, formative evaluation studies might be an attractive option for you to pursue, as there are always local programs that need evaluation and suggestions for improvement. Again, be very clear about your purpose when talking through your research proposal with your committee.
Action research takes a further step beyond evaluation, even formative evaluation, to being part of the solution itself. This is about as far from basic research as one could get and definitely falls beyond the scope of “science,” as conventionally defined. The distinction between action and research is blurry, the research methods are often in constant flux, and the only “findings” are specific to the problem or case at hand and often are findings about the process of intervention itself. Rather than evaluate a program as a whole, action research often seeks to change and improve some particular aspect that may not be working—maybe there is not enough diversity in an organization or maybe women’s voices are muted during meetings and the organization wonders why and would like to change this. In a further step, participatory action research , those women would become part of the research team, attempting to amplify their voices in the organization through participation in the action research. As action research employs methods that involve people in the process, focus groups are quite common.
If you are working on a thesis or dissertation, chances are your committee will expect you to be contributing to fundamental knowledge and theory ( basic research ). If your interests lie more toward the action end of the continuum, however, it is helpful to talk to your committee about this before you get started. Knowing your purpose in advance will help avoid misunderstandings during the later stages of the research process!
The Research Question
Once you have written your paragraph and clarified your purpose and truly know that this study is the best study for you to be doing right now , you are ready to write and refine your actual research question. Know that research questions are often moving targets in qualitative research, that they can be refined up to the very end of data collection and analysis. But you do have to have a working research question at all stages. This is your “anchor” when you get lost in the data. What are you addressing? What are you looking at and why? Your research question guides you through the thicket. It is common to have a whole host of questions about a phenomenon or case, both at the outset and throughout the study, but you should be able to pare it down to no more than two or three sentences when asked. These sentences should both clarify the intent of the research and explain why this is an important question to answer. More on refining your research question can be found in chapter 4.
Chances are, you will have already done some prior reading before coming up with your interest and your questions, but you may not have conducted a systematic literature review. This is the next crucial stage to be completed before venturing further. You don’t want to start collecting data and then realize that someone has already beaten you to the punch. A review of the literature that is already out there will let you know (1) if others have already done the study you are envisioning; (2) if others have done similar studies, which can help you out; and (3) what ideas or concepts are out there that can help you frame your study and make sense of your findings. More on literature reviews can be found in chapter 9.
In addition to reviewing the literature for similar studies to what you are proposing, it can be extremely helpful to find a study that inspires you. This may have absolutely nothing to do with the topic you are interested in but is written so beautifully or organized so interestingly or otherwise speaks to you in such a way that you want to post it somewhere to remind you of what you want to be doing. You might not understand this in the early stages—why would you find a study that has nothing to do with the one you are doing helpful? But trust me, when you are deep into analysis and writing, having an inspirational model in view can help you push through. If you are motivated to do something that might change the world, you probably have read something somewhere that inspired you. Go back to that original inspiration and read it carefully and see how they managed to convey the passion that you so appreciate.
At this stage, you are still just getting started. There are a lot of things to do before setting forth to collect data! You’ll want to consider and choose a research tradition and a set of data-collection techniques that both help you answer your research question and match all your aims and goals. For example, if you really want to help migrant workers speak for themselves, you might draw on feminist theory and participatory action research models. Chapters 3 and 4 will provide you with more information on epistemologies and approaches.
Next, you have to clarify your “units of analysis.” What is the level at which you are focusing your study? Often, the unit in qualitative research methods is individual people, or “human subjects.” But your units of analysis could just as well be organizations (colleges, hospitals) or programs or even whole nations. Think about what it is you want to be saying at the end of your study—are the insights you are hoping to make about people or about organizations or about something else entirely? A unit of analysis can even be a historical period! Every unit of analysis will call for a different kind of data collection and analysis and will produce different kinds of “findings” at the conclusion of your study. [2]
Regardless of what unit of analysis you select, you will probably have to consider the “human subjects” involved in your research. [3] Who are they? What interactions will you have with them—that is, what kind of data will you be collecting? Before answering these questions, define your population of interest and your research setting. Use your research question to help guide you.
Let’s use an example from a real study. In Geographies of Campus Inequality , Benson and Lee ( 2020 ) list three related research questions: “(1) What are the different ways that first-generation students organize their social, extracurricular, and academic activities at selective and highly selective colleges? (2) how do first-generation students sort themselves and get sorted into these different types of campus lives; and (3) how do these different patterns of campus engagement prepare first-generation students for their post-college lives?” (3).
Note that we are jumping into this a bit late, after Benson and Lee have described previous studies (the literature review) and what is known about first-generation college students and what is not known. They want to know about differences within this group, and they are interested in ones attending certain kinds of colleges because those colleges will be sites where academic and extracurricular pressures compete. That is the context for their three related research questions. What is the population of interest here? First-generation college students . What is the research setting? Selective and highly selective colleges . But a host of questions remain. Which students in the real world, which colleges? What about gender, race, and other identity markers? Will the students be asked questions? Are the students still in college, or will they be asked about what college was like for them? Will they be observed? Will they be shadowed? Will they be surveyed? Will they be asked to keep diaries of their time in college? How many students? How many colleges? For how long will they be observed?
Recommendation
Take a moment and write down suggestions for Benson and Lee before continuing on to what they actually did.
Have you written down your own suggestions? Good. Now let’s compare those with what they actually did. Benson and Lee drew on two sources of data: in-depth interviews with sixty-four first-generation students and survey data from a preexisting national survey of students at twenty-eight selective colleges. Let’s ignore the survey for our purposes here and focus on those interviews. The interviews were conducted between 2014 and 2016 at a single selective college, “Hilltop” (a pseudonym ). They employed a “purposive” sampling strategy to ensure an equal number of male-identifying and female-identifying students as well as equal numbers of White, Black, and Latinx students. Each student was interviewed once. Hilltop is a selective liberal arts college in the northeast that enrolls about three thousand students.
How did your suggestions match up to those actually used by the researchers in this study? It is possible your suggestions were too ambitious? Beginning qualitative researchers can often make that mistake. You want a research design that is both effective (it matches your question and goals) and doable. You will never be able to collect data from your entire population of interest (unless your research question is really so narrow to be relevant to very few people!), so you will need to come up with a good sample. Define the criteria for this sample, as Benson and Lee did when deciding to interview an equal number of students by gender and race categories. Define the criteria for your sample setting too. Hilltop is typical for selective colleges. That was a research choice made by Benson and Lee. For more on sampling and sampling choices, see chapter 5.
Benson and Lee chose to employ interviews. If you also would like to include interviews, you have to think about what will be asked in them. Most interview-based research involves an interview guide, a set of questions or question areas that will be asked of each participant. The research question helps you create a relevant interview guide. You want to ask questions whose answers will provide insight into your research question. Again, your research question is the anchor you will continually come back to as you plan for and conduct your study. It may be that once you begin interviewing, you find that people are telling you something totally unexpected, and this makes you rethink your research question. That is fine. Then you have a new anchor. But you always have an anchor. More on interviewing can be found in chapter 11.
Let’s imagine Benson and Lee also observed college students as they went about doing the things college students do, both in the classroom and in the clubs and social activities in which they participate. They would have needed a plan for this. Would they sit in on classes? Which ones and how many? Would they attend club meetings and sports events? Which ones and how many? Would they participate themselves? How would they record their observations? More on observation techniques can be found in both chapters 13 and 14.
At this point, the design is almost complete. You know why you are doing this study, you have a clear research question to guide you, you have identified your population of interest and research setting, and you have a reasonable sample of each. You also have put together a plan for data collection, which might include drafting an interview guide or making plans for observations. And so you know exactly what you will be doing for the next several months (or years!). To put the project into action, there are a few more things necessary before actually going into the field.
First, you will need to make sure you have any necessary supplies, including recording technology. These days, many researchers use their phones to record interviews. Second, you will need to draft a few documents for your participants. These include informed consent forms and recruiting materials, such as posters or email texts, that explain what this study is in clear language. Third, you will draft a research protocol to submit to your institutional review board (IRB) ; this research protocol will include the interview guide (if you are using one), the consent form template, and all examples of recruiting material. Depending on your institution and the details of your study design, it may take weeks or even, in some unfortunate cases, months before you secure IRB approval. Make sure you plan on this time in your project timeline. While you wait, you can continue to review the literature and possibly begin drafting a section on the literature review for your eventual presentation/publication. More on IRB procedures can be found in chapter 8 and more general ethical considerations in chapter 7.
Once you have approval, you can begin!
Research Design Checklist
Before data collection begins, do the following:
- Write a paragraph explaining your aims and goals (personal/political, practical/strategic, professional/academic).
- Define your research question; write two to three sentences that clarify the intent of the research and why this is an important question to answer.
- Review the literature for similar studies that address your research question or similar research questions; think laterally about some literature that might be helpful or illuminating but is not exactly about the same topic.
- Find a written study that inspires you—it may or may not be on the research question you have chosen.
- Consider and choose a research tradition and set of data-collection techniques that (1) help answer your research question and (2) match your aims and goals.
- Define your population of interest and your research setting.
- Define the criteria for your sample (How many? Why these? How will you find them, gain access, and acquire consent?).
- If you are conducting interviews, draft an interview guide.
- If you are making observations, create a plan for observations (sites, times, recording, access).
- Acquire any necessary technology (recording devices/software).
- Draft consent forms that clearly identify the research focus and selection process.
- Create recruiting materials (posters, email, texts).
- Apply for IRB approval (proposal plus consent form plus recruiting materials).
- Block out time for collecting data.
- At the end of the chapter, you will find a " Research Design Checklist " that summarizes the main recommendations made here ↵
- For example, if your focus is society and culture , you might collect data through observation or a case study. If your focus is individual lived experience , you are probably going to be interviewing some people. And if your focus is language and communication , you will probably be analyzing text (written or visual). ( Marshall and Rossman 2016:16 ). ↵
- You may not have any "live" human subjects. There are qualitative research methods that do not require interactions with live human beings - see chapter 16 , "Archival and Historical Sources." But for the most part, you are probably reading this textbook because you are interested in doing research with people. The rest of the chapter will assume this is the case. ↵
One of the primary methodological traditions of inquiry in qualitative research, ethnography is the study of a group or group culture, largely through observational fieldwork supplemented by interviews. It is a form of fieldwork that may include participant-observation data collection. See chapter 14 for a discussion of deep ethnography.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and research design that focuses on an individual case (e.g., setting, institution, or sometimes an individual) in order to explore its complexity, history, and interactive parts. As an approach, it is particularly useful for obtaining a deep appreciation of an issue, event, or phenomenon of interest in its particular context.
The controlling force in research; can be understood as lying on a continuum from basic research (knowledge production) to action research (effecting change).
In its most basic sense, a theory is a story we tell about how the world works that can be tested with empirical evidence. In qualitative research, we use the term in a variety of ways, many of which are different from how they are used by quantitative researchers. Although some qualitative research can be described as “testing theory,” it is more common to “build theory” from the data using inductive reasoning , as done in Grounded Theory . There are so-called “grand theories” that seek to integrate a whole series of findings and stories into an overarching paradigm about how the world works, and much smaller theories or concepts about particular processes and relationships. Theory can even be used to explain particular methodological perspectives or approaches, as in Institutional Ethnography , which is both a way of doing research and a theory about how the world works.
Research that is interested in generating and testing hypotheses about how the world works.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and approach to analyzing qualitative data in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction. This approach was pioneered by the sociologists Glaser and Strauss (1967). The elements of theory generated from comparative analysis of data are, first, conceptual categories and their properties and, second, hypotheses or generalized relations among the categories and their properties – “The constant comparing of many groups draws the [researcher’s] attention to their many similarities and differences. Considering these leads [the researcher] to generate abstract categories and their properties, which, since they emerge from the data, will clearly be important to a theory explaining the kind of behavior under observation.” (36).
An approach to research that is “multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives." ( Denzin and Lincoln 2005:2 ). Contrast with quantitative research .
Research that contributes knowledge that will help people to understand the nature of a problem in order to intervene, thereby allowing human beings to more effectively control their environment.
Research that is designed to evaluate or test the effectiveness of specific solutions and programs addressing specific social problems. There are two kinds: summative and formative .
Research in which an overall judgment about the effectiveness of a program or policy is made, often for the purpose of generalizing to other cases or programs. Generally uses qualitative research as a supplement to primary quantitative data analyses. Contrast formative evaluation research .
Research designed to improve a program or policy (to help “form” or shape its effectiveness); relies heavily on qualitative research methods. Contrast summative evaluation research
Research carried out at a particular organizational or community site with the intention of affecting change; often involves research subjects as participants of the study. See also participatory action research .
Research in which both researchers and participants work together to understand a problematic situation and change it for the better.
The level of the focus of analysis (e.g., individual people, organizations, programs, neighborhoods).
The large group of interest to the researcher. Although it will likely be impossible to design a study that incorporates or reaches all members of the population of interest, this should be clearly defined at the outset of a study so that a reasonable sample of the population can be taken. For example, if one is studying working-class college students, the sample may include twenty such students attending a particular college, while the population is “working-class college students.” In quantitative research, clearly defining the general population of interest is a necessary step in generalizing results from a sample. In qualitative research, defining the population is conceptually important for clarity.
A fictional name assigned to give anonymity to a person, group, or place. Pseudonyms are important ways of protecting the identity of research participants while still providing a “human element” in the presentation of qualitative data. There are ethical considerations to be made in selecting pseudonyms; some researchers allow research participants to choose their own.
A requirement for research involving human participants; the documentation of informed consent. In some cases, oral consent or assent may be sufficient, but the default standard is a single-page easy-to-understand form that both the researcher and the participant sign and date. Under federal guidelines, all researchers "shall seek such consent only under circumstances that provide the prospective subject or the representative sufficient opportunity to consider whether or not to participate and that minimize the possibility of coercion or undue influence. The information that is given to the subject or the representative shall be in language understandable to the subject or the representative. No informed consent, whether oral or written, may include any exculpatory language through which the subject or the representative is made to waive or appear to waive any of the subject's rights or releases or appears to release the investigator, the sponsor, the institution, or its agents from liability for negligence" (21 CFR 50.20). Your IRB office will be able to provide a template for use in your study .
An administrative body established to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects recruited to participate in research activities conducted under the auspices of the institution with which it is affiliated. The IRB is charged with the responsibility of reviewing all research involving human participants. The IRB is concerned with protecting the welfare, rights, and privacy of human subjects. The IRB has the authority to approve, disapprove, monitor, and require modifications in all research activities that fall within its jurisdiction as specified by both the federal regulations and institutional policy.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Welcome to Chapter 2
How to Critically Analyze Sources
Learning about synthesis analysis, chapter 2 webinars.
- Student Experience Feedback Buttons
- Library Guide: Research Process This link opens in a new window
- ASC Guide: Outlining and Annotating This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Organizing Research & Citations This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: RefWorks This link opens in a new window
- Library Guide: Copyright Information This link opens in a new window
- Library Research Consultations This link opens in a new window
Jump to DSE Guide
Need help ask us.

- Research Process An introduction to the research process.
- Determining Information Needs A Review Scholarly Journals and Other Information Sources.
- Evaluating Information Sources This page explains how to evaluate the sources of information you locate in your searches.
- Video: Doctoral Level Critique in the Literature Review This video provides doctoral candidates an overview of the importance of doctoral-level critique in the Literature Review in Chapter 2 of their dissertation.
What D oes Synthesis and Analysis Mean?
Synthesis: the combination of ideas to

- show commonalities or patterns
Analysis: a detailed examination
- of elements, ideas, or the structure of something
- can be a basis for discussion or interpretation
Synthesis and Analysis: combine and examine ideas to
- show how commonalities, patterns, and elements fit together
- form a unified point for a theory, discussion, or interpretation
- develop an informed evaluation of the idea by presenting several different viewpoints and/or ideas
- Article Spreadsheet Example (Article Organization Matrix) Use this spreadsheet to help you organize your articles as you research your topic.
Was this resource helpful?
- Next: Library Guide: Research Process >>
- Last Updated: Apr 19, 2023 11:59 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1007176

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 2: Getting Started in Research
2.1 Basic Concepts 2.2 Generating Good Research Questions 2.3 Reviewing the Research Literature
Research Methods in Psychology Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Here is the abstract of a 2014 article in the journal Psychological Science.
Taking notes on laptops rather than in longhand is increasingly common. Many researchers have suggested that laptop note taking is less effective than longhand note taking for learning. Prior studies have primarily focused on students’ capacity for multitasking and distraction when using laptops. The present research suggests that even when laptops are used solely to take notes, they may still be impairing learning because their use results in shallower processing. In three studies, we found that students who took notes on laptops performed worse on conceptual questions than students who took notes longhand. We show that whereas taking more notes can be beneficial, laptop note takers’ tendency to transcribe lectures verbatim rather than processing information and reframing it in their own words is detrimental to learning. (Mueler & Oppenheimer, 2014, p. 1159) [1]
In this abstract, the researcher has identified a research question—about the effect of taking notes on a laptop on learning—and identified why it is worthy of investigation—because the practice is ubiquitous and may be harmful to learning. In this chapter, we give you a broad overview of the various stages of the research process. These include finding a topic of investigation, reviewing the literature, refining your research question and generating a hypothesis, designing and conducting a study, analyzing the data, coming to conclusions, and reporting the results.
- Mueller, P. A., & Oppenheimer, D. M. (2014). The pen is mightier than the keyboard: Advantages of longhand over laptop note taking. Psychological Science, 25 (6), 1159-1168. ↵

Share This Book
- Increase Font Size

- Request new password
- Create a new account
Research Methods in Early Childhood: An Introductory Guide
Student resources, chapter 2: the research proposal.
Get to know the resources that are available to you.
- Before you write your research proposal you should investigate what resources are ‘out there’ to help you.
- Ask your research tutor or supervisor if there are examples of research proposals from previous students that you can look at.
- The study skills section of your institutions website may have examples.
- Look at YouTube presentations on the topic. (A note of caution here: some presentations will be more relevant than others. Quantitative research proposals are different from qualitative proposals, although the basic structure will be similar. Don’t be put off if the video you are interested in is directed at masters or PhD students, again the principles will be the same.)
Case study: Betty is studying for a degree in Early Childhood Studies. She has a placement for 2 days a week in a day care setting with children aged 3–4. She wants to investigate parents’ views on how much screen time children should be exposed to, and whether or not this is an area of conflict between them and their children. She decides to conduct a qualitative study, using a questionnaire containing open questions to all parents using the setting, together with in-depth informal interviews with four parents.
- Outline a research proposal for this study (no need to conduct a literature review).
- Who are the ‘gatekeepers’ that will need to give permission for the study to go ahead?
Sage research methods content
Abdulai, R.T. and Owusu-Ansah, A. (2014) ‘Essential ingredients of a good research proposal for undergraduate and postgraduate students in the social sciences’, SAGE Open , 4(3): 1–11 . http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2158244014548178
This article is a comprehensive guide to writing research proposals. It is recommended that you read Chapters 1 and 2 in the textbook before you read this article as the article looks at both research proposals and research design. You will discover that terminology is not fixed. Different authors will use different terms to describe the same thing. For example, in this article the research question is called the research objective. Your institution may expect you to use specific terminology, but as long as you define your terms and use them consistently, these differences are of no account.
Wharewera-Mika, J., Cooper, E., Kool, B., Pereira, S. and Kelly, P. (2015) ‘Caregivers’ voices: the experiences of caregivers of children who sustained serious accidental and non-accidental head injury in early childhood’, Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry , 21(2): 268–86. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1359104515589636
This article looks at parents’ experiences of caring for children who received a head injury before the age of 5. It is a New Zealand study. Imagine you were the researchers at the beginning of the research process. They were required to present a research proposal to one of New Zealand Health and Disability Ethics Committees. Outline what their proposal might look like (minus the literature review).
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Quick Guide to Chapter Two

Related Papers
• Learning outcomes • The nature of a literature review • Identifying the main subject and themes • Reviewing previous research • Emphasizing leading research studies • Exploring trends in the literature • Summarizing key ideas in a subject area • Summary A literature review is usually regarded as being an essential part of student projects, research studies and dissertations. This chapter examines the reasons for the importance of the literature review, and the things which it tries to achieve. It also explores the main strategies which you can use to write a good literature review.
Rebekka Tunombili
tecnico emergencias
Learning how to effectively write a literature review is a critical tool for success for an academic, and perhaps even professional career. Being able to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic not only demonstrates having a good grasp on available information for a topic, but it also assists in the learning process. Although literature reviews are important for one's academic career, they are often misunderstood and underdeveloped. This article is intended to provide both undergraduate and graduate students in the criminal justice field specifically, and social sciences more generally, skills and perspectives on how to develop and/or strengthen their skills in writing a literature review. Included in this discussion are foci on the structure , process, and art of writing a literature review. What is a Literature Review? In essence, a literature review is a comprehensive overview of prior research regarding a specific topic. The overview both shows the reader what is known about a topic, and what is not yet known, thereby setting up the rationale or need for a new investigation, which is what the actual study to which the literature review is attached seeks to do. Stated a bit differently (Creswell 1994, pp. 20, 21) explains: The literature in a research study accomplishes several purposes: (a) It shares with the reader the results of other studies that are closely related to the study being reported (Fraenkel & Wallen, 1990. (b) It relates a study to the larger, ongoing dialog in the literature about a topic, filling in gaps and extending prior studies (Marshall & Rossman, 1989). (c) It provides a framework for establishing the importance of the study. As an overview, a well done literature review includes all of the main themes and subthemes found within the general topic chosen for the study. These themes and subthemes are usually interwoven with the methods or findings of the prior research. Also, a literature review sets the stage for and JOURNAL
Gazala Hasan
A literature review is a critical part of any research project, serving as a foundation for the entire study. It showcases your ability to research, synthesize, and evaluate information, which not only demonstrates your expertise on a given topic but also aids in building a strong argument for your research. This guide will elaborate on what a literature review is, its purpose, how to organize and synthesize information, and the different parts of a literature review.
KANNANAYAKAL RAJAN
Review of literature is an integral part of any research. However, the scope and purpose of review of literature vary with the context. The most common contexts in which review of literature is demanded are - - (1) A course assignment, (2) A short review for a research article, (3) A review for research proposal, (4) A stand alone review article and (5) A chapter-length review for thesis/dissertation. There are seven important steps in the task of review of literature. They are - - (1) How to search for studies? (2) How to select studies? (3) How to analyze studies? (4) Which scheme is appropriate for analysis? (5) How to compose/organize review of literature? (6) Scheme of presentation of review and (7) Conclusion.
yakubu nawati
Bob mweetwa
research proposal as a problem to investigate, it usually has to be fairly narrow and focused, and because of this it can be difficult to appreciate how one's research subject is connected to other related areas. Therefore, the overall purpose of a literature review is to demonstrate this, and to help the reader to understand how your study fits into a broader context. This paper seeks to examine this topic of literature review, its significance and role in research proposal and report. It will start by explaining in detail what literature is; by citation of different scholars and its constituent components, such as the theoretical framework. Thereafter, it will look at the importance of literature review and its role in research proposals and reports. Finally, a conclusion will be written based on this topic. A Literature Review is a critical review of existing knowledge on areas such as theories, critiques, methodologies, research findings, assessment and evaluations on a particular topic. A literature review involves a critical evaluation identifying similarities and differences between existing literatures and the work being undertaken. It reviews what have already been done in the context of a topic. Therefore, on the basis of the existing knowledge, people can build up innovative idea and concept for further research purpose (Cooper, 1998). In doing empirical literature review is reading reports of other relevant studies conducted by different researchers. In doing so, a researcher gets knowledge and experiences that were established by other researchers when conducting their studies. While Conceptual framework is a set of coherent ideas or concepts organised in a manner that makes them easy to communicate to others. It represents less formal structure and used for specific concepts and propositions derived from empirical observation and intuition (ibid). According Aveyard, H. (2010) Theoretical framework is a theoretical perspective. It can be simply a theory, but can also be more general a basic approach to understanding something. Typically, a theoretical framework consists of concepts, together with their definitions, and existing framework must demonstrate an understanding of theories, and existing framework demonstrate an understanding of theories and concepts that are relevant to the topic of your research proposal and that will relate it to the broader fields of knowledge in the class you are taking.
selorm kuffour
A literature review must be coherent, systematic and clear. The review of literature must stick to answering the research question and also there must be a justification of every argument using extracts and illustrations. It is essential that all sources used in the literature review are properly recorded and referenced appropriately to avoid the incidence of plagiarism. Finally the work must be proof-read. It is also worth noting that literature review is not producing a list of items. Also it is essential that the contents of the literature to be reviewed are well read and also spelling mistakes or wrong dates of publication are avoided.
Andrew Johnson
This chapter describes the process of writing a literature review and what the product should look like
HUMANUS DISCOURSE
Humanus Discourse
The importance of literature review in academic writing of different categories, levels, and purposes cannot be overemphasized. The literature review establishes both the relevance and justifies why new research is relevant. It is through a literature review that a gap would be established, and which the new research would fix. Once the literature review sits properly in the research work, the objectives/research questions naturally fall into their proper perspective. Invariably, other chapters of the research work would be impacted as well. In most instances, scanning through literature also provides you with the need and justification for your research and may also well leave a hint for further research. Literature review in most instances exposes a researcher to the right methodology to use. The literature review is the nucleus of a research work that might when gotten right spotlights a work and can as well derail a research work when done wrongly. This paper seeks to unveil the practical guides to writing a literature review, from purpose, and components to tips. It follows through the exposition of secondary literature. It exposes the challenges in writing a literature review and at the same time recommended tips that when followed will impact the writing of the literature review.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Amanda Bolderston
Vikash Mishra
Ignacio Illan Conde
Gavin Mount
Christopher N Lawrence
Auxiliadora Padilha
Velvet Raven
International Journal of P R O F E S S I O N A L Business Review
Global Journal of Artificial Intelligence
Oluwatobi Balogun
Journal of Asian Development
Erni Murniarti
Frances Slack
Research Methodology Assignment
Alfi Rahman
Nirmal Kumar Raut
Sarah Quinton
Seda Khadimally
Cut Oktaviani
Journal of Practical Studies in Education
Meriel Louise Anne Villamil
Mike Lambert
Coaching: An International Journal of Theory, Research and Practice
Mark N K Saunders , Céline Rojon
Sadruddin Qutoshi
Tatam Chiway , Abdullah Ramdhani , Muhammad Ali Ramdhani
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Advertise with us
- Friday, August 23, 2024
Most Widely Read Newspaper
PunchNG Menu:
- Special Features
- Sex & Relationship
ID) . '?utm_source=news-flash&utm_medium=web"> Download Punch Lite App
Project Chapter Two: Literature Review and Steps to Writing Empirical Review

Kindly share this story:
- Conceptual review
- Theoretical review,
- Empirical review or review of empirical works of literature/studies, and lastly
- Conclusion or Summary of the literature reviewed.
- Decide on a topic
- Highlight the studies/literature that you will review in the empirical review
- Analyze the works of literature separately.
- Summarize the literature in table or concept map format.
- Synthesize the literature and then proceed to write your empirical review.
All rights reserved. This material, and other digital content on this website, may not be reproduced, published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or in part without prior express written permission from PUNCH.
Contact: [email protected]
Stay informed and ahead of the curve! Follow The Punch Newspaper on WhatsApp for real-time updates, breaking news, and exclusive content. Don't miss a headline – join now!
VERIFIED NEWS: As a Nigerian, you can earn US Dollars with REGULAR domains, buy for as low as $24, resell for up to $1000. Earn $15,000 monthly. Click here to start.

Latest News
A'ibom youths storm nnpc premises in rivers over kinsman's death, mpox: ncdc records 40 confirmed cases, supreme court upholds imo gov, uzodimma’s re-election victory, fidelity bank faults ndpc data breach allegation, student loan: no response from s'east institutions yet - nelfund.

Meet Justice Kekere-Ekun, Nigeria's second female CJN
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, conse adipiscing elit.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2 Chapter 2 (Introducing Research)
Joining a Conversation
Typically, when students are taught about citing sources, it is in the context of the need to avoid plagiarism. While that is a valuable and worthwhile goal in its own right, it shifts the focus past one of the original motives for source citation. The goal of referencing sources was originally to situate thoughts in a conversation and to provide support for ideas. If I learned about ethics from Kant, then I cite Kant so that people would know whose understanding shaped my thinking. More than that, if they liked what I had to say, they could read more from Kant to explore those ideas. Of course, if they disliked what I had to say, I could also refer them to Kant’s arguments and use them to back up my own thinking.
For example, you should not take my word for it that oranges contain Vitamin C. I could not cut up an orange and extract the Vitamin C, and I’m only vaguely aware of its chemical formula. However, you don’t have to. The FDA and the CDC both support this idea, and they can provide the documentation. For that matter, I can also find formal articles that provide more information. One of the purposes of a college education is to introduce students to the larger body of knowledge that exists. For example, a student studying marketing is in no small part trying to gain access to the information that others have learned—over time—about what makes for effective marketing techniques. Chemistry students are not required to derive the periodic table on their own once every four years.
In short, college classes (and college essays) are often about joining a broader conversation on a subject. Learning, in general, is about opening one’s mind to the idea that the person doing the learning is not the beginning nor the end of all knowledge.
Remember that most college-level assignments often exist so that a teacher can evaluate a student’s knowledge. This means that displaying more of that knowledge and explaining more of the reasoning that goes into a claim typically does more to fulfill the goals of an assignment. The difference between an essay and a multiple choice test is that an essay typically gives students more room to demonstrate a thought process in action. It is a way of having students “show their work,” and so essays that jump to the end without that work are setting themselves up for failure.
Learning, Not Listing
Aristotle once claimed “It is the mark of an educated mind to be able to entertain a thought without accepting it.” Many students are familiar with the idea of search . The internet makes it tremendously easy to search for information—and misinformation. It takes a few seconds to find millions of results on almost any topic. However, that is not research. Where, after all, is the re in all of that? The Cambridge Dictionary offers the following definition:
Research (verb): to study a subject in detail, especially in order to discover new information or reach a new understanding.
Nothing about that implies a casual effort to type a couple of words into search engine and assuming that a result on the first screen is probably good enough. Nor does that imply that a weighted or biased search question, like “why is animal testing bad” will get worthwhile results. Instead, research requires that the researcher searches, learns a little, and then searches again . Additionally, the level of detail matters. Research often involves knowing enough to understand the deeper levels of the subject.
For example, if someone is researching the efficacy of animal testing, they might encounter a claim that mice share a certain percentage of their DNA with human beings. Even this is problematic, because measuring DNA by percentage isn’t as simple as it sounds. However, estimates range from 85% to 97.5%, with the latter number being the one that refers to the active or “working” DNA. Unfortunately, the casual reader still knows nothing of value about using mice for human research. Why? Because the casual reader doesn’t know if the testing being done involves the 97.5% or the 2.5%, or even if the test is one where it can be separated.
To put it bluntly, Abraham Lincoln once had a trip to the theater that started 97.5% the same as his other trips to the theater.
In order for casual readers to make sense of this single factoid, they need to know more about DNA and about the nature of the tests being performed on the animals. They probably need to understand biology at least a little. They certainly need to understand math at a high enough level to understand basic statistics. All of this, of course, assumes that the student has also decided that the source itself is worthy of trust. In other words, an activist website found through a search engine that proclaims “mice are almost identical to humans” or “mice lack 300 million base pairs that humans have”. Neither source is lying. Just neither source helps the reader understand what is being talked about (if the sources themselves even understand).
Before a student can write a decent paper, the student needs to have decent information. Finding that information requires research, not search. Often, student writers (and other rhetors) mistakenly begin with a presupposed position that they then try to force into the confines of their rhetoric. Argumentation requires an investigation into an issue before any claim is proffered for discussion. The ‘thesis statement’ comes last; in many ways it is the product of extensive investigation and learning. A student should be equally open to and skeptical of all sources.
Skepticism in Research
Skepticism is not doubting everyone who disagrees with you. True skepticism is doubting all claims equally and requiring every claim to be held to the same burden of proof (not just the claims we disagree with). By far, the biggest misconception novice writers struggle with is the idea that it is okay to use a low-quality source (like a blog, or a news article, or an activist organization) because they got “just facts” from that source.
The assumption seems to be that all presentations of fact are equally presented, or that sources don’t lie. However, even leaving aside that many times people do lie in their own interests, which facts are presented and how they are presented changes immensely. There’s no such thing as “just facts.” The presentation of facts matters, as does how they are gathered. Source evaluation is a fundamental aspect of advanced academic writing.
“Lies” of Omission and Inclusion: One of the simplest ways to misrepresent information is simply to exclude material that could weaken the stance that is favored by the author. This tactic is frequently called stacking the deck , and it is obviously dishonest. However, there is a related problem known as observational bias , wherein the author might not have a single negative intention whatsoever. Instead, xe simply only pays attention to the evidence that supports xir cause, because it’s what’s relevant to xir.
- Arguments in favor of nuclear energy as a “clean” fuel source frequently leave out the problem of what to do with the spent fuel rods (i.e. radioactive waste). Similarly, arguments against nuclear energy frequently count only dramatic failures of older plants and not the safe operation of numerous modern plants; another version is to highlight the health risks of nuclear energy without providing the context of health risks caused by equivalent fuel sources (e.g. coal or natural gas).
- Those who rely on personal observation in support of the idea that Zoomers are lazy might count only the times they see younger people playing games or relaxing, ignoring the number of times they see people that same age working jobs or—more accurately—the times they don’t see people that age because they are too busy helping around the house or doing homework.
A source that simply lists ideas without providing evidence or justifying how the evidence supports its conclusions is likely not a source that meets the rigor needed for an academic argument. While later chapters will go into the subject in greater detail, these guidelines suggest that in general, news media are not ideal sources. Neither are activist webpages, nor are blogs or government outlets. As later chapters will explore, all of these “sources” are not in fact sources of information. Inevitably, these documents to not create information, they simply report it. Instead, finding the original studies (performed by experts, typically controlled for bias, and reviewed by other experts before being published) is a much better alternative.
Examining Sources Using the Toulmin Model
On most issues, contradictory evidence exists and the researcher must review the options in a way that establishes one piece of evidence as more verifiable, or as otherwise preferable, to the other. In essence, researchers must be able to compare arguments to one another.
Stephen Toulmin introduced a model of analyzing arguments that broke arguments down into three essential components and three additional factors. His model provides a widely-used and accessible means of both studying and drafting arguments.
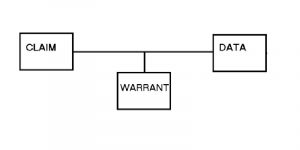
The Toulmin model can be complicated with three other components, as well: backing, rebuttals, and qualifiers. Backing represents support of the data (e.g. ‘the thermostat has always been reliable in the past’ or ‘these studies have been replicated dozens of times with many different populations’). Rebuttals, on the other hand, admit limits to the argument (e.g. ‘unless the thermostat is broken’ or ‘if you care about your long-term health’). Finally, qualifiers indicate how certain someone is about the argument (e.g. ‘it is definitely too cold in here’ is different than ‘it might be too cold in here’; likewise, ‘you might want to stop smoking’ is a lot less forceful than ‘you absolutely should stop smoking’).
At a minimum, an argument (either one made by the student or by a source being evaluated) should have all three of the primary components, even if they are incorporated together. However, most developed arguments (even short answers on tests or simple blog posts) should have all six elements in place. If they are missing, it is up to the reader to go looking for what is missing and to try to figure out why it might have been left out.
Here is an example of an underdeveloped argument that is simply phrased like an absolute claim of fact. It is a poor argument, in that it offers none of the rationale behind what it says—it just insists that it is correct:
“Other countries hate the United States for a reason.”
What other countries? What reason? Is it just one reason, or is it one reason per country?
By contrast, here is an argument that has at least some minimal development:
“In the eyes of many (Qualifier), the United States has earned the hatred of other countries (Claim). The U.S. involvement in Iranian politics alone has earned the country criticism (Data). By helping to overthrow a democratically elected leader in favor of a monarch in 1953, the U.S. acted in a manner that seemed hypocritical and self-interested (Backing). While many countries do act in favor of their own interests (Rebuttal), the U.S. publicly championing democracy while covertly acting against it serves to justify criticism of the country (Warrant).”
Is there room to disagree with this argument? Yes. However, this argument provides its rationale, it offers at least some sort of evidence for its claims, and it provides a place to begin engagement. A researcher who wishes to know more about this argument can go looking into the history of U.S.-Iran relations, for example.
When reviewing a source, or making their own arguments, researchers should consider the following questions. Is there evidence that can be verified and examined by others (in the same spirit as the scientific method)? More specifically:
- What is the claim?
- What data backs up this claim?
- What assumptions do I have to make to consider this evidence to be adequate support?
The various pieces of data which support claims in the Toulmin model are often called into question. Studies are refuted, statistics countered with rival numbers, and their applicability to the claim in question is often murky. Evidence—whether offered as matters of fact or as subjective considerations—does not exist in a vacuum. Data are themselves claims. If the supporting data are accepted as true, the argument has a generally accepted conclusion. Such pieces of ‘evidence’ are contentions .
Although Toulmin distinguishes between qualifiers and rebuttal conditions, such a distinction is difficult to maintain in practice. The important consideration—the one acknowledged by both terms—is that unconditional or absolute claims are difficult to support. Specific fields have their own ways of hedging their bets. Science has its error bar (Sagan) and the terminology of probability. Statistics and polling have a margin of error. Ethnography has its confrontation of personal bias. When a rhetor expresses the limitations of a given claim, when the unconditional becomes conditional, claims become more than categorical propositions or thesis statements. They become arguments.
Example 1: Here is a minimalistic overview of one claim on the topic of traffic cameras.
- Claim = Traffic cameras increase minor accidents
- Evidence = David Kidwell and Alex Richards of The Chicago Tribune performed a study that was later cited by ABC News.
- Assumptions = This study was conducted honestly and reasonably represents the reality of accidents around these cameras (i.e. I can trust the agenda and the methods of the Chicago Tribune staff).
Example 2 : And here is a second claim on the same subject.
- Claim = The types of accidents by traffic cameras tend to be less severe
- Evidence = The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety examined national trends and compared medical reports, police reports, and various bills, posting the results on their website.
- Assumptions = If the IIHS has a bias, it would be toward fewer accidents, or at least less severe accidents (because this means they have to pay less money out).
As an Essay Fragment : According to some, traffic cameras actually increase accidents. A study conducted by the Chicago Tribune found that rear-end collisions increased when traffic cameras were installed, meaning that they make things worse, not better (Kidwell and Richards). However, the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety points out that while there are sometimes increases in minor collisions, the number of crashes resulting in injuries actually decreases.
- “According to…not better (Kidwell and Richards).” This uses a parenthetical source citation to provide a “link” to the evidence and to invite readers to examine both the data and the warrants.
- “However, the…decreases.” This uses a signal statement to introduce the source of the evidence first, often because the source has so much credibility the author is hoping to impress the reader.
Note that this is not a particularly powerful fragment–it is simply the minimum level of rigor that a student should offer (or look for) in an academic essay or in an academic source.
Academic arguments typically make concessions. These concessions help define the scope of the argument and the range of the inquiry. In Section 1, I mentioned a relatively straightforward value claim: “Plan X is bad.” Argumentation engages such value claims and defines their scope and limits. Who is plan X bad for? By what standards? Why then is anyone in favor of plan X? A more practical approach could be “If you favor Y, then Plan X is bad.” This is a concession, of sorts—Plan X is only bad if you favor Y. The argument admits that if you do not, then Plan X might not be all that bad, after all.
Such a concession, worded in such a way, has added merit. It functions as what Aristotle would have called an artistic proof, although maybe not an enthymeme. It establishes a bond between the rhetor and the audience through the shared favoring of Y; it nurtures consubtantiality—the basis of what Burke calls identification. Clearly, concessions can be made in a way that both prevents some counterarguments from applying and still furthers a rhetorical point.
Such phrasing is practical, and only truly cynical interrogators would consider it sinister. An inversion of this approach is possible. “Unless you favor Y, Plan X is bad.” So long as Y is sufficiently negative in the minds of the audience, the rhetor loses no actual impact here. Here, connecting Y to X might require substantiation on the part of the rhetor, because the concession has become, itself, a justification of why X is bad (it is related to or involves Y). The additional rhetorical power—gained through positive and negative associations—often compensates for such additional effort.
Research, Evidence, and Written Arguments Copyright © by jsunderb. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
Published on September 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on March 27, 2023.

The introduction to a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your topic and get the reader interested
- Provide background or summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Detail your specific research problem and problem statement
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The introduction looks slightly different depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or constructs an argument by engaging with a variety of sources.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: introduce your topic, step 2: describe the background, step 3: establish your research problem, step 4: specify your objective(s), step 5: map out your paper, research paper introduction examples, frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The first job of the introduction is to tell the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening hook.
The hook is a striking opening sentence that clearly conveys the relevance of your topic. Think of an interesting fact or statistic, a strong statement, a question, or a brief anecdote that will get the reader wondering about your topic.
For example, the following could be an effective hook for an argumentative paper about the environmental impact of cattle farming:
A more empirical paper investigating the relationship of Instagram use with body image issues in adolescent girls might use the following hook:
Don’t feel that your hook necessarily has to be deeply impressive or creative. Clarity and relevance are still more important than catchiness. The key thing is to guide the reader into your topic and situate your ideas.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
This part of the introduction differs depending on what approach your paper is taking.
In a more argumentative paper, you’ll explore some general background here. In a more empirical paper, this is the place to review previous research and establish how yours fits in.
Argumentative paper: Background information
After you’ve caught your reader’s attention, specify a bit more, providing context and narrowing down your topic.
Provide only the most relevant background information. The introduction isn’t the place to get too in-depth; if more background is essential to your paper, it can appear in the body .
Empirical paper: Describing previous research
For a paper describing original research, you’ll instead provide an overview of the most relevant research that has already been conducted. This is a sort of miniature literature review —a sketch of the current state of research into your topic, boiled down to a few sentences.
This should be informed by genuine engagement with the literature. Your search can be less extensive than in a full literature review, but a clear sense of the relevant research is crucial to inform your own work.
Begin by establishing the kinds of research that have been done, and end with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to respond to.
The next step is to clarify how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses.

Argumentative paper: Emphasize importance
In an argumentative research paper, you can simply state the problem you intend to discuss, and what is original or important about your argument.
Empirical paper: Relate to the literature
In an empirical research paper, try to lead into the problem on the basis of your discussion of the literature. Think in terms of these questions:
- What research gap is your work intended to fill?
- What limitations in previous work does it address?
- What contribution to knowledge does it make?
You can make the connection between your problem and the existing research using phrases like the following.
| Although has been studied in detail, insufficient attention has been paid to . | You will address a previously overlooked aspect of your topic. |
| The implications of study deserve to be explored further. | You will build on something suggested by a previous study, exploring it in greater depth. |
| It is generally assumed that . However, this paper suggests that … | You will depart from the consensus on your topic, establishing a new position. |
Now you’ll get into the specifics of what you intend to find out or express in your research paper.
The way you frame your research objectives varies. An argumentative paper presents a thesis statement, while an empirical paper generally poses a research question (sometimes with a hypothesis as to the answer).
Argumentative paper: Thesis statement
The thesis statement expresses the position that the rest of the paper will present evidence and arguments for. It can be presented in one or two sentences, and should state your position clearly and directly, without providing specific arguments for it at this point.
Empirical paper: Research question and hypothesis
The research question is the question you want to answer in an empirical research paper.
Present your research question clearly and directly, with a minimum of discussion at this point. The rest of the paper will be taken up with discussing and investigating this question; here you just need to express it.
A research question can be framed either directly or indirectly.
- This study set out to answer the following question: What effects does daily use of Instagram have on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls?
- We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls.
If your research involved testing hypotheses , these should be stated along with your research question. They are usually presented in the past tense, since the hypothesis will already have been tested by the time you are writing up your paper.
For example, the following hypothesis might respond to the research question above:
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
The final part of the introduction is often dedicated to a brief overview of the rest of the paper.
In a paper structured using the standard scientific “introduction, methods, results, discussion” format, this isn’t always necessary. But if your paper is structured in a less predictable way, it’s important to describe the shape of it for the reader.
If included, the overview should be concise, direct, and written in the present tense.
- This paper will first discuss several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then will go on to …
- This paper first discusses several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then goes on to …
Full examples of research paper introductions are shown in the tabs below: one for an argumentative paper, the other for an empirical paper.
- Argumentative paper
- Empirical paper
Are cows responsible for climate change? A recent study (RIVM, 2019) shows that cattle farmers account for two thirds of agricultural nitrogen emissions in the Netherlands. These emissions result from nitrogen in manure, which can degrade into ammonia and enter the atmosphere. The study’s calculations show that agriculture is the main source of nitrogen pollution, accounting for 46% of the country’s total emissions. By comparison, road traffic and households are responsible for 6.1% each, the industrial sector for 1%. While efforts are being made to mitigate these emissions, policymakers are reluctant to reckon with the scale of the problem. The approach presented here is a radical one, but commensurate with the issue. This paper argues that the Dutch government must stimulate and subsidize livestock farmers, especially cattle farmers, to transition to sustainable vegetable farming. It first establishes the inadequacy of current mitigation measures, then discusses the various advantages of the results proposed, and finally addresses potential objections to the plan on economic grounds.
The rise of social media has been accompanied by a sharp increase in the prevalence of body image issues among women and girls. This correlation has received significant academic attention: Various empirical studies have been conducted into Facebook usage among adolescent girls (Tiggermann & Slater, 2013; Meier & Gray, 2014). These studies have consistently found that the visual and interactive aspects of the platform have the greatest influence on body image issues. Despite this, highly visual social media (HVSM) such as Instagram have yet to be robustly researched. This paper sets out to address this research gap. We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls. It was hypothesized that daily Instagram use would be associated with an increase in body image concerns and a decrease in self-esteem ratings.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, March 27). Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved August 23, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-introduction/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, writing a research paper conclusion | step-by-step guide, research paper format | apa, mla, & chicago templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Research Fundamentals
- First Online: 14 January 2018
Cite this chapter

- Edzard Ernst 3 &
- Kevin Smith 4
895 Accesses
1 Citations
Research is the gathering of data, information and facts for the advancement or completion of knowledge. By adding to the store of human knowledge, scientific research has great intrinsic value. Research also has substantial practical value, in the guise of beneficial technologies flowing from such knowledge.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Although frequently referred to in the singular, the ‘placebo effect’ in fact comprises several distinct components.
For example, suppose an ancestral human eats a toadstool and a few hours later is violently sick. If this experience makes her to believe that the toadstool caused the vomiting, it will aid her survival by helping her avoid a possible source of poisoning in the future. This pattern-recognition mechanism ought to be error-prone in the direction of making false assumptions about causality: if the toadstool is not actually toxic (and the sickness actually resulted from some other unseen cause), the resultant false knowledge carries some cost (in terms of the erroneous avoidance of a potential food source), but this is unlikely to greatly threaten survival. By contrast, if the cause-effect link fails to be made in the case of a genuinely toxic toadstool, the cost is likely be much higher: if more toadstools are eaten, the effects could be lethal. Thus, the genetic sequences underlying the error-prone cause-and-effect heuristic are transmitted to the following generations through natural selection. It is clear that such pressures have influenced the evolution of the human brain such that we have a strong inbuilt tendency to make error-prone assumptions about causality.
For example, see Nuzzo ( 2014 ), and Schwalbe ( 2016 ).
There is ongoing academic debate on the extent to which the medical literature is corrupted with false findings. For example, a recent survey of major (mainstream) medical journals claimed that the false positive rate is 14%—a high rate but one that is less than the claim of ‘most’ published findings being false (Jager and Leek 2014 ). However, Ioannidis and other academics have repudiated this claim of 14%, pointing to various flaws in the paper in terms of sampling, calculations, and conclusions, and pointing out that it uses only a very small portion of select papers in top journals (Ioannidis 2014 ; Benjamini and Hechtlinger 2014 ).
In the context of observational studies (as opposed to clinical trials), the equivalent term is false discovery rate , in the context of the problem of multiple comparisons.
There is debate amongst statisticians as to whether p < 0.05 or p = 0.05 is the better interpretation. The former is used by many papers on medical statistics, however it is arguably less realistic than the latter, which tends to generate higher false positive risk values. An in-depth exposition of this subtle but important distinction is beyond the scope of this book; see Colquhoun ( 2017 ) for more detailed discussion.
It is ethically questionable to conduct such small-scale RCT s, because they are inherently underpowered and thus prone to generating misleading results. Moreover, because effect size and sample size are interrelated, small samples can lead to overestimations of effect sizes. However, in some specific cases the determination of effect size can be aided by data from such trials.
This will only be true if the power calculation has been valid.
This is optimistic because, as discussed elsewhere in this book, the alleged specific effects of acupuncture are supposedly due to completely implausible physiological features and mechanisms, including Qi (‘vital energy’) flowing through meridians (body channels), none of which have been discovered by science and all of which are implausible.
Various ways exist to calculate false positive risk; the values that result vary according to methodology, but all valid approaches yield risks that are substantially greater than the 5% assumed by the common but disastrously wrong assumption that p = 0.05 equates with a 5% false positive risk. For example, in simplified terms, we can compute the expected false positive risk for p < 0.05 by: [a] multiplying the sample size by the prior probability, then multiplying the proportion of the sample with a real effect by the power value, to establish the number of true responders; then [b] multiplying the proportion of the sample who are expected to have showed no effect with the threshold p -value (0.05) to establish the expected number of false positives; and finally [c] expressing as a percentage the number of false positives from the overall number of positive results. For the example given above, this computes to 86%. Note that for p = 0.05, using the methodology used by Colquhoun ( 2017 ), the false positive risk computes to be even higher, at 97%.
An alternative way of expressing this is to say that if you observe p = 0.05 then, in order to achieve a false positive risk of 5%, you would need a prior probability of 87%—clearly preposterously high (Colquhoun 2017 ).
The numbering is ours, and the wording of #2 had been adapted slightly, to remove reference to ‘business or policy decisions’.
This example is chosen to illustrate an inherently absurd modality, recognisable as such to all reasonable people. Sadly however, proponents of such ‘intercessory therapeutic prayer’ exist; indeed, some of them have even conducted ‘clinical trials’ into this form of CAM (Roberts et al. 2009 ). We shall consider one such real-life case later in the next chapter.
An online statistics tool was used to calculate this sample size (ClinCalc LLC 2017 ).
This was calculated using a z-test; other suitable tests exist, but all of these will approximate to this value.
There is an interesting ethical side question here: should subjects who cannot feasibly be affected in any way whatsoever by a remote experiment (such as intercessory prayer) be required to give consent?
The statistical analysis of such combined data is referred to as ‘meta-analysis’, and some systematic review publications are titled as meta-analyses.
For example, a search of the academic publications database Web of Science (which includes all the major CAM journals) covering 2007–2017 using various relevant search terms ( p -value , reproducibility crisis, p-hacking) led to merely one CAM paper dealing with the issue of problematic statistical interpretation of clinical data (Benbassat 2016 ).
Beecher H (1955) The powerful placebo. J Am Med Assoc (JAMA) 159(17):1602–1606
Article Google Scholar
Benbassat J (2016) Inferences from unexpected findings of scientific research: common misconceptions. Eur J Integr Med 8(3):188–190. doi: 10.1016/j.eujim.2015.12.010
Benjamin DJ, Berger J, Johannesson M et al (2017) Redefine statistical significance. PysArXiv preprints. https://osf.io/preprints/psyarxiv/mky9j/ . Accessed 14 Aug 2017
Benjamini Y, Hechtlinger Y (2014) Discussion: an estimate of the science-wise false discovery rate and applications to top medical journals by Jager and Leek. Biostatistics 15(1):13–16. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxt032
ClinCalc LLC (2017) Sample size calculator. ClinCalc.com. http://clincalc.com/stats/samplesize.aspx . Accessed 11 Feb 2017
Colquhoun D (2014) An investigation of the false discovery rate and the misinterpretation of p-values. Roy Soc Open Sci 1(3):140216. doi: 10.1098/rsos.140216
Colquhoun D (2017) The reproducibility of research and the misinterpretation of P values. Roy Soc Open Sci. http://www.biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/08/07/144337.full.pdf . Accessed 12 Aug 2017
Ernst E (2006) Prevalence surveys: to be taken with a pinch of salt. Complement Ther Clin Pract 12(4):272–275. doi:S1744-3881(06)00042-9 [pii]
Google Scholar
Ernst E (2013a) More dismal chiropractic research. Edzard Ernst | MD, PhD, FMedSci, FSB, FRCP, FRCPEd. http://edzardernst.com/2013/02/more-dismal-research-of-chiropractic/ . Accessed 15 Jan 2017
Ernst E (2013b) What can be more irresponsible than implying that homeopathy cures cancer? Edzard Ernst | MD, PhD, FMedSci, FSB, FRCP, FRCPEd. http://edzardernst.com/2013/09/what-can-be-more-irresponsible-than-implying-that-homeopathy-cures-cancer/ . Accessed 15 Jan 2017
Ernst E (2016a) Acupuncture: the current state of the scientific literature. Edzard Ernst|MD, PhD, FMedSci, FSB, FRCP, FRCPEd. http://edzardernst.com/2016/03/acupuncture-the-current-state-of-the-scientific-literature/ . Accessed 15 Jan 2017
Ernst E (2016b) The current state of research into homeopathy. Edzard Ernst | MD, PhD, FMedSci, FSB, FRCP, FRCPEd. http://edzardernst.com/2016/08/the-current-state-of-research-into-homeopathy/ . Accessed 15 Jan 2017
Ernst E (2016c) Data fabrication in China is an ‘open secret’. Edzard Ernst | MD, PhD, FMedSci, FSB, FRCP, FRCPEd. http://edzardernst.com/2016/10/data-fabrication-in-china-is-an-open-secret/ . Accessed 15 Jan 2017
Ernst E, Pittler M (1997) Alternative therapy bias. Nature 385(6616):480. doi: 10.1038/385480c0
Hrobjartsson A, Gotzsche PC (2010) Placebo interventions for all clinical conditions. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev (1):CD003974. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003974.pub3
Ioannidis J (2005) Why most published research findings are false. Plos Medicine 2(8):696–701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020124
Ioannidis J (2014) Discussion: why “an estimate of the science-wise false discovery rate and application to the top medical literature” is false. Biostatistics 15(1):28–36. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxt036
Jager LR, Leek JT (2014) An estimate of the science-wise false discovery rate and application to the top medical literature. Biostatistics 15(1):1–12. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxt007
McGorry R, Webster B, Snook S et al (2000) The relation between pain intensity, disability, and the episodic nature of chronic and recurrent low back pain. Spine 25(7):834–840. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200004010-00012
Medawar PB (1967) The art of the soluble. Methuen, London
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Plos Med 6(7):e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Nuzzo R (2014) Statistical errors. Nature 506(7487):150–152
Pandolfi M, Carreras G (2014) The faulty statistics of complementary alternative medicine (CAM). Eur J Intern Med 25(7):607–609. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2014.05.014
Roberts L, Ahmed I, Hall S et al (2009) Intercessory prayer for the alleviation of ill health. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2):CD000368. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000368.pub3
Schwalbe M (2016) Statistical challenges in assessing and fostering the reproducibility of scientific results. National Academy of Sciences, USA
Book Google Scholar
Tang JL, Zhan SY, Ernst E (1999) Review of randomised controlled trials of traditional Chinese medicine. BMJ 319(7203):160–161
Vickers A, Goyal N, Harland R et al (1998) Do certain countries produce only positive results? A systematic review of controlled trials. Control Clin Trials 19(2):159–166. doi: 10.1016/S0197-2456(97)00150-5 [pii]
Wasserstein RL, Amer Statistical Assoc (2016) ASA statement on statistical significance and P-values. Am Stat 70(2):131–133
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Exeter, Exeter, UK
Edzard Ernst
School of Science, Engineering and Technology, Abertay University, Dundee, UK
Kevin Smith
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Edzard Ernst or Kevin Smith .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this chapter
Ernst, E., Smith, K. (2018). Research Fundamentals. In: More Harm than Good?. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-69941-7_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-69941-7_2
Published : 14 January 2018
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-69940-0
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-69941-7
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
- January 2019

- Alagappa University
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Johndelle A Potutan

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 2: Citing Sources
By the end of this chapter, you should be able to:
- Demonstrate ability to cite sources in APA Style Format. (LO4)
- Examine strategies for maintaining academic integrity. (LO5)
Test Yourself
Complete this pre-test to see what you know already about citations. Then, review the following content to identify more strategies for maintaining academic integrity.
Citations Continued
Citations are formatted in specific ways, depending on the style being used. For this textbook, we are only going to use APA Style. But MLA is another popular option (and there are many more!). In-text citation for APA Style should at minimum include the author(s) and year of publication. It is recommended to include a page range, so the reader can more easily refer to it, but it is not required. Here’s some examples of in-text citation:
Citations can be summaries, paraphrases, or direct quotations. Summaries are when you provide a brief overview of what the source material provided. Paraphrases are when you restate the ideas from the source using your own words and style. And direct quotes are exactly that: direct quotes. Can you look at the examples above and determine which kind of in-text citation it is?
Regardless of citation style (e.g. APA, MLA, etc.), there should be a hanging indent. The hanging indent leaves the beginning of the citation at the far left of the document and then each line after the the first is indented. To do this in Microsoft Word follow these steps:
- Highlight the citation information
- From the Home Tab, select the bottom-right hand arrow in the paragraph menu (Keyboard short cut for highlighted text: Control + t)
- Or, if you prefer to use a drop-down menu, highlight text and go to “Home” then “Paragraph”.
- Select the “Indents and Spacing” tab. Under “Special” select the drop down menu and change to “Hanging”.
- Select “Okay” to save these settings.
References for Remixed Content:
American Psychological Association (2022). Style and grammar guidelines. APA Style. https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines
PALNI (2022, June 3). Understanding plagiarism and citing sources. PALNI Information Literacy Modules. https://libguides.palni.edu/instruction_resources/ILModule11
Purdue Online Writing Lab (2022). General format. Purdue OWL. https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/general_format.html
Research and Information Literacy with Library Resources by Andrea Bearman and Jill Noyes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

The New Classroom Instruction That Works: The Best Research-Based Strategies for Increasing Student Achievement
$26.36 member price join now.
The book that inspired millions of educators to refine their approach to teaching returns for an all-new third edition. Built on a more rigorous research base and updated to emphasize student diversity, equity, and inclusion, The New Classroom Instruction That Works offers a streamlined focus on the 14 instructional strategies proven to promote deep, meaningful, and lasting learning:
Table of contents
Introduction: Professionalizing Education
Chapter 1. Helping Students Become Interested in Learning
Chapter 2. Helping Students Commit to Learning
Chapter 3. Helping Students Focus on New Learning
Chapter 4. Helping Students Make Sense of Learning
About the authors

Bryan Goodwin is the president and CEO of McREL International, a Denver-based nonprofit education research and development organization. Goodwin, a former teacher and journalist, has been at McREL for more than 20 years, serving previously as chief operating officer and director of communications and marketing. Goodwin writes a monthly research column for Educational Leadership and presents research findings and insights to audiences across the United States and in Canada, the Middle East, and Australia.

Kristin Rouleau serves as the executive director of learning services and innovation at McREL International, where she guides a team of consultants who help schools, districts, and state education agencies and ministries of education across the United States, Canada, Micronesia, Australia, the Middle East, and China translate research into solutions that transform teaching, leading, and learning.
A licensed school administrator with more than 25 years of classroom and school leadership experience, she coauthored Learning That Sticks: A Brain-Based Model for K–12 Instructional Design and Delivery, Curiosity Works: A Guidebook for Moving Your School from Improvement to Innovation and Unstuck: How Curiosity, Peer Coaching , and Teaming Can Change Your School .
Book details
Product no., 978-1-4166-3161-3, release date, member book, topics in this book, related books.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Chapter 2 Introduction. Chapter 2. Introduction. Maybe you have already gained some experience in doing research, for example in your bachelor studies, or as part of your work. The challenge in conducting academic research at masters level, is that it is multi-faceted. The types of activities are: Writing up and presenting your findings.
CHAPTER 2: Literature Review. This chapter will explore the literature that is relevant to understanding the development of, and interpreting the results of this convergent study. The first two parts of this review of the literature will describe two types of research: research on teaching and research on teachers' conceptions.
Preparing to WriteChapter 2: The Literature ReviewA literature review is a section of your thesis or dissertation in. hich you discuss previous research on your subject. Following your Chapter 1, your literature review begins as you try to answer your larger research question: Wh.
parts: the Introduction (Chapter 1), the Review of Related Literature and/or Research (Chapter 2), and the Methodology (Chapter 3). The completed dissertation begins with the same three chapters and concludes with two additional chapters that report research findings (Chapter 4) and conclusions, discussion, and recommendations (Chapter 5).
Chapter 2. Research Design Getting Started. When I teach undergraduates qualitative research methods, the final product of the course is a "research proposal" that incorporates all they have learned and enlists the knowledge they have learned about qualitative research methods in an original design that addresses a particular research question.
In a mixed methods study, the researcher uses either a qualitative or a quantitative approach to the literature, depending on the type of strategy being used. In a sequential approach, the literature is presented in each phase in a way consistent with the method being used. For example, if the study begins with a quantitative phase, then the ...
res thata research topic can and should be researched. Even though the literature review is the second chapter of the dissertation, students begin this process first since an extensive review of the literatur. is necessary for developing a proposed research topi. ps are taken, a dissertati.
Chapter 2 covers the literature review. It provides a detailed analysis of the theory/conceptual framework used in the study. In addition, chapter 2 offers a thorough synthesis of the available, current, scholarly literature on all aspects of the topic, including all points of view.
Contents. Publisher Information. Chapter 1: The Science of Psychology. 1.1 Understanding Science. 1.2 Scientific Research in Psychology. ... Chapter 2: Getting Started in Research 2.1 Basic Concepts 2.2 Generating Good Research Questions 2.3 Reviewing the Research Literature.
In this chapter, we give you a broad overview of the various stages of the research process. These include finding a topic of investigation, reviewing the literature, refining your research question and generating a hypothesis, designing and conducting a study, analyzing the data, coming to conclusions, and reporting the results. Mueller, P. A ...
2. Describe the research circle. 3. Identify the four major goals of social research. 4. Write a checklist of the W's. 5. Understand the reasons for both reporting and interpreting numbers. 6. State the importance of specifying the direction and magnitude of a pattern. In this chapter, I lay the groundwork for the rest of the book by defining and
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Chapter 2: The research proposal. Activity 1. Get to know the resources that are available to you. Before you write your research proposal you should investigate what resources are 'out there' to help you. Ask your research tutor or supervisor if there are examples of research proposals from previous students that you can look at.
Review of literature is an integral part of any research. However, the scope and purpose of review of literature vary with the context. The most common contexts in which review of literature is demanded are - - (1) A course assignment, (2) A short review for a research article, (3) A review for research proposal, (4) A stand alone review article and (5) A chapter-length review for thesis ...
Steps to Writing an Empirical Review. Decide on a topic. Just like in every research work, deciding on a befitting research topic is always among the first things to do. When the empirical review ...
Chapter 2 (Introducing Research) Joining a Conversation. Typically, when students are taught about citing sources, it is in the context of the need to avoid plagiarism. While that is a valuable and worthwhile goal in its own right, it shifts the focus past one of the original motives for source citation. The goal of referencing sources was ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Section2 discusses the compositional and morphological features of layers, which can be investigated using various analytical and mineralogical techniques. Section3 outlines the various substrates (marble, limestone, wall and easel paintings, mortars, written materials, and glass) described in the literature.
Male workforce participation has been on a continuously downward trend as well, since the 1960s decreasing from 84% participation in 1960 to 71% in 2008 with projections. showing a continuing decrease (U.S. Census Bureau, 2008). Men 25-54 years of age have a. workforce participation rate of 89.3% (U.S. Census, 2008).
2.1 Introduction. This chapter provides an overview of previous research on knowledge sharing and intranets. It introduces the framework for the case study that comprises the main focus of the research described in this thesis. It is important to set the context of the literature review work by first providing:
Chapter 2 Research Fundamentals Research is the gathering of data, information and facts for the advancement or completion of knowledge. By adding to the store of human knowledge, scientific research has great intrinsic value. Research also has substantial practical value, in the guise of beneficial technologies flowing from such knowledge.
INTRODUCTION. A review of literature is a classification and evaluation of what accredited scholars and. researchers have written on a topic, organized according to a guiding concept such as a ...
To do this in Microsoft Word follow these steps: Highlight the citation information. From the Home Tab, select the bottom-right hand arrow in the paragraph menu (Keyboard short cut for highlighted text: Control + t) Or, if you prefer to use a drop-down menu, highlight text and go to "Home" then "Paragraph". Select the "Indents and ...
ICC Digital Codes is the largest provider of model codes, custom codes and standards used worldwide to construct safe, sustainable, affordable and resilient structures.
ICC Digital Codes is the largest provider of model codes, custom codes and standards used worldwide to construct safe, sustainable, affordable and resilient structures.
The book that inspired millions of educators to refine their approach to teaching returns for an all-new third edition. Built on a more rigorous research base and updated to emphasize student diversity, equity, and inclusion, The New Classroom Instruction That Works offers a streamlined focus on the 14 instructional strategies proven to promote deep, meaningful, and lasting learning:
ICC Digital Codes is the largest provider of model codes, custom codes and standards used worldwide to construct safe, sustainable, affordable and resilient structures.