
Mar 23, 2019
880 likes | 1.7k Views
Vitamins. Brought to you by the Flintstones. C.5.1 Define the term vitamin. So, what exactly is a vitamin?. Here’s the technical definition: An organic molecule that is required in only trace amounts and can only be obtained through the diet since it cannot be synthesized.

Share Presentation
- water soluble
- fat soluble
- fat soluble vitamins
- rhodopsin light sensitive material

Presentation Transcript
Vitamins Brought to you by the Flintstones
C.5.1 Define the term vitamin.
So, what exactly is a vitamin? • Here’s the technical definition: An organic molecule that is required in only trace amounts and can only be obtained through the diet since it cannot be synthesized.
In other words… • Vitamins are “Vital amines” that we need to survive, but can’t make ourselves. • Most vitamins are coenzymes or are precursors to coenzymes, and many are antioxidants. • Your body can’t differentiate between synthetic and natural vitamins. • Fun Fact: 1g of B12 is enough for 500,000 people! Crazy right??
C.5.2 Deduce whether a vitamin is water or fat soluble from its structure.
Water Soluble Vitamins • There are nine total water soluble vitamins. and are found in aqueous environments inside cells, where most are needed as components of coenzymes. • Excess of these vitamins is excreted by urine, so it needs to be constantly replenished in small amounts. • These are carried by the blood-stream.
How do you recognize them? • Water soluble vitamins all have –OH, -COOH or other polar groups to make them water soluble. (more on this later…) • Example: Vitamin C and Vitamin B
Fun Fact • Ever wondered where the names B and C came from? They are the names of the test tubes where the vitamins were first recognized. Scientists later realized that test tube contained more than one type of vitamin, which resulted in vitamins B1, B6, B12 etc.
Fat Soluble Vitamins • These are stored in the body’s fat deposits and cell membranes. • Because they are not continuously excreted by the body, excess of fat soluble vitamins is more hazardous than water soluble since they can accumulate in body fats. • None has been identified as a coenzyme.
What do they look like? • The structures of fat soluble vitamins are more hydrocarbon-like and have less functional groups. • Nonpolar • Examples: Vitamins A, D, E & K
C.5.3 Describe the structures and major functions of retinol (vitamin A), calciferol (vitamin D) and ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
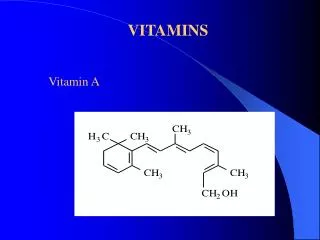
Retinol/Vitamin A • Fat Soluble • It has 3 active forms: retinol, retinal, and retinoic acid • It is produced by cleavage of (b) carotene (this is the molecule that gives carrots their orange color), so it is required for the synthesis of visual pigments • It is an antioxidant! How does it work? • Hint: Look at the functional groups at the end of each hydrocarbon chain...more to come!
What is Vitamin A used for? • It is essential for night vision (particularly rhodopsin), healthy eyes, normal development of epithelial tissues, formation of bone, reproduction and more! • Required for the production of rhodopsin (light-sensitive material in the rods of the retina). • Rhodopsin: a pigment of the retina that is responsible for both the formation of the photoreceptor cells and the first events in the perception of light.
Forms of Vitamin A http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/misc_topics/vitamina.gif
Vitamin A Deficiency • Deficiency can cause night blindness and xerophthalmia. • Xerophthalmia: is a medical condition in which the eye fails to produce tears; it may be caused due to a lack of vitamin A • Macular degeneration: a medical condition in which the light sensing cells in the macula (part of the retina) malfunction and, over time, cease to work (blindness).
Xerophthalmia http://www.milesresearch.com/eerf/images/xerophthalmia1.jpg http://www.milesresearch.com/eerf/images/bitot-step0.jpg
Calciferol/Vitamin D • Fat Soluble • It is related in structure to cholesterol. • It is synthesized when UV light from the sun strikes a cholesterol derivative in the skin. • In your kidney, vitamin D is converted to a hormone which regulates calcium absorption and bone formation.
Vitamin D Structure
Function and Deficiency of Vitamin D • Required for the uptake of calcium from food. Deficiency can cause weak bones (rickets). • Rickets: softening of the bones in children potentially leading to fractures and deformity; results from severe malnutrition and is predominant in developing countries • Osteomalacia is used to describe a similar condition occurring in adults. • Sufficient vitamin D levels can also be achieved through dietary supplementation. • Most dermatologists recommend vitamin D supplementation as an alternative to unprotected UV exposure due to the increased risk of skin cancer associated with sun exposure.
Rickets http://www.dinf.ne.jp/doc/english/global/david/dwe002/dwe002g/dwe00215g01.gif http://www.e-radiography.net/radpath/r/Rickets_wrist_healing.jpg
Ascorbic Acid/Vitamin C • Water Soluble • It is biologically active without any change in structure from the form it has in food. • It has been proven to be a valuable anti-oxidant (you will get to see this for yourself today!) • We are one of the few species that obtain it from our diet, most others synthesize it from glucose.
Structure of Vitamin C
Function of Vitamin C • Its most characteristic role is to function as a co-substrate in the formation of structural collagen • It makes up much of skin, ligaments, tendons, and also serves as matrix on which bone and teeth are formed.
What is Collagen? • Collagen is the main protein of connective tissue in animals and the most abundant protein in mammals, making up about 25% of the total protein content. • Fibrous structural protein • Bundles of collagen are called collagen fibers • Support most tissues • Gives cells structure inside and out • Main component of cartilage, ligaments, tendons, bone, teeth • Responsible for skin strength and elasticity
Collagen http://www.3dchem.com/imagesofmolecules/Collagen2.jpg
Deficiency of Vitamin C • Deficiency can cause scorbutus (scurvy). • Scurvy leads to the formation of liver spots on the skin, spongy gums, and bleeding from all mucous membranes.
Scurvy http://www.med.uc.edu/departme/cellbiol/Image7.gif http://www.faqs.org/nutrition/images/nwaz_02_img0214.jpg
Antioxidants and Preservatives • A substance that prevents oxidation by reacting w/ an oxidizing agent and gets oxidized itself. • Many foods get spoiled because they get oxidized, so they are protected by “phenolic” additives. • A naturally occurring phenolic antioxidant is vitamin E.
Antioxidants Continued… • Rancidity: it is when fats and oils develop an odor/flavor upon exposure to moist air, which is the result of the oxidation of the carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chains in the tri-glycerols. • So, antioxidants prevent rancidity in foods by preventing them from getting oxidized, by getting oxidized themselves. • Our principal dietary antioxidants are vitamins C, E, B, and selenium. These work by defusing the potentially harmful free radicals in the body
C.5.4 Describe the effects of food processing on the vitamin content of food.
Effects of Cooking on Vitamin Contents • Vitamins containing carbon-carbon double bonds and hydroxyl groups are easily oxidized and thus can be destroyed by prolonged cooking and high temperatures (which speeds up oxidation).
Vitamin C • Vitamin C is water soluble and readily oxidized. So boiling vegetables can deplete a lot of Vitamin C content. • Scurvy, from lack of vitamin C, was common in sailors because they spent long periods without fresh foods. • Solutions: • Keeping food refrigerated can slow the oxidation process. • Steaming foods instead of boiling
Vitamin C Oxidation http://online.redwoods.cc.ca.us/depts/science/chem/chem1A/Labs/VitaminC/VitaminC.gif
Other Vitamins • Vitamin D can be destroyed through oxidation by some bleaching agents used in manufacturing purified flour. • Vitamin A is not readily broken down by cooking.
Genetic Modification • Does not lower nutrition value/destroy vitamins • Increases food productivity • Food more resistant to disease/toxins • Better flavor texture, nutritional value and shelf life • May contaminate DNA or increase risk of a disease- long term effects are unknown
Genetically Modified Tomato
And Now for the Lab…
- More by User

Vitamins Helping you to: Create a Healthy Lifestyle! Click here to play an interactive game. Vitamins A vitamin is a compound that contributes to basic metabolic reactions in the body. True False Vitamins
1.71k views • 100 slides

VITAMINS. Vitamins may be regarded as organic compounds required in the diet in small amounts to perform specific biological functions for normal maintenance of optimum growth and health of the organism. There are about 15 vitamins, essential for humans.
2.48k views • 132 slides

Vitamins . Dr. Prabhakar Adake MD Asst. Professor Department of Pharmacology Yenepoya Medical College. Case scenario.
2.81k views • 74 slides

VITAMINS. Vijayalakshmi. INTRODUCTION. organic molecules with wide variety of capacities prominent function - cofactors for enzymatic reactions generally cannot be synthesized by mammalian cells Vitamins are usually supplied in the diet or in dietary supplements
794 views • 30 slides

Vitamins. UNIT V: Integration of Metabolism. I. Overview Vitamins are chemically unrelated organic compounds that cannot be synthesized in adequate quantities by humans and, therefore, must be supplied by the diet.
1.69k views • 102 slides

VITAMINS . By SG Bhuvan Kumar. VITAMINS - deficiency diseases History of vitamins : The story of vitamin dates back to 18 th century. Sailors of this period knew that eating of liver cures a disease called night blindness and Eating of lemons cures another disease called scurvy.
1.2k views • 23 slides
VITAMINS. Vitamin A. b - Carotene. Vitamin A and b - Carotene Determination. b - CAROTENE STANDARD ABSORBANCES AT 440 AND 620 nm . at 440 nm. A. and 620 nm. A at 440 nm . A. at 620 nm.
394 views • 17 slides

Vitamins. Chapter 7. Learning Objectives. Explain the roles vitamins play in growth and good health List and describe the general functions and food sources of fat-soluble vitamins and water-soluble vitamins
867 views • 44 slides

Vitamins. Compounds that help regulate many vital body processes. Should we take vitamins by pill?. Yes, as a supplement. Water Soluble Vitamins:. Body can get rid of them if you take too much . Vitamin C. Important roles in the body: Helps the body to heal & fight infection.
480 views • 16 slides

Vitamins. Types Of Vitamins -Vitamin A -Vitamin C -Vitamin D -Vitamin E -Vitamin B12 -Vitamin B6 -Niacin/Vitamin B3 Continued on next page. Vitamins Pg. 2. More V itamins : - Thiamin /Vitamin B1 -Riboflavin/Vitamin B2 - Folate /Folic Acid/Vitamin B9 Foods You can find Vitamins in:
1.81k views • 7 slides
Vitamins . Solubility Function Sources . Mrs. Harrop. Solubility. Vitamins are either water or fat soluble. Water soluble are those that dissolve in water. They are then transported through the body. Fat soluble are those that require a lipid.
418 views • 17 slides

Vitamins. Our body depends on them!. 1. Can our bodies produce vitamins?. NO! We have to get them through eating food that contains them! Nerve functions, muscles and skin require vitamins to function properly. What are the two types of vitamins?. Fat soluble Water soluble.
537 views • 17 slides

VITAMINS!. FUNCTION PERFORMED ON BODY.
232 views • 8 slides

Necessary for Growth Maintenance Reproduction. Vitamins. Two Types. Fat Soluble: A,D,E,K Excesses stored in body and can reach dangerous levels. Water Soluble: B & C Excess Excreted. VITAMIN A. Functions: Helps night vision Growth of teeth and bones
582 views • 36 slides

Vitamins. Introduction
421 views • 23 slides

VITAMINS: FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS
VITAMINS: FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS. DR Norhasmah Sulaiman Department of Resources Management and Consumer Studies Faculty Of Human Ecology UPM. Thanks….
330 views • 7 slides

Vitamins. Definition - Organic compound required in small amounts. A few words about each. Vitamin A Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12 Vitamin D Vitamin E Vitamin K. Vitamin A - Retinol . Retinol (vitamin A) .
489 views • 19 slides

Vitamins. Essential in small quantities for growth, maintenance and reproduction. Vitamins. Have the potential for toxicity when taken at extremely high doses over a long time. Vitamins. The government has determined recommended daily allowances (RDAs) for various vitamins and minerals.
601 views • 26 slides

Vitamins!!!
Vitamins!!!. What is a vitamin?. Vitamins are organic substances necessary for life Why do I need them? essential to the normal functioning of our bodies, and except for a few exceptions, cannot be made by our bodies. How do vitamins do it all????. Fat Soluble Vitamins
637 views • 10 slides

Vitamins. Lecture 6. Vitamins. Organic compound essential for health but only in trace amounts (ppm). Required for normal growth and maintenance of animal life. Function as catalyst Enzymes or coenzymes in metabolic processes. Vitamin Supplementation.
398 views • 10 slides

Vitamins. Definitions:. Vitamins are organic compounds required by the body in trace amounts to perform specific function, and can not be synthesized by humans, or can not be synthesized in adequate (sufficient) quantities to meet needs.
993 views • 46 slides

Vitamins!!!. HFN1O. What is a vitamin?. Vitamins are organic substances necessary for life Why do I need them? essential to the normal functioning of our bodies, and except for a few exceptions, cannot be made by our bodies. How do vitamins do it all????. Fat Soluble Vitamins
467 views • 10 slides
Chapter 8: Vitamins and Minerals
Define the Following Terms:
- 1. antioxidants—substances that protect body cells and the immune system from damage by harmful chemicals in air and foods.
- 2. electrolyte minerals—sodium, chloride, and potassium, which control and balance fluid flow in and out of cells.
- 3. fat-soluble vitamins—vitamins absorbed and transported by fat.
- 4. free-radicals—harmful by-product excreted when cells burn oxygen to produce energy.
- 5. hypertension—high-blood pressure linked to high salt intake.
- 6. iron-deficiency anemia—lack of enough iron in the body, resulting in fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
- 7. major minerals—macrominerals with special duties in the body; calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, chloride, and potassium.
- 8. osteomalacia—a disease caused by a lack of vitamin D in adults.
- 9. osteoporosis—condition caused by calcium deficiency; bones become porous, weak, fragile.
- 10. pica—Condition linked to iron deficiency; causes unusual appetite for ice, clay, and other nonfood items.
- 11. toxicity—excessive amount of substance that reacts as poison in the body.
- 12. trace minerals—minerals needed in only small amounts but serving vital body functions.
- 13. water-soluble vitamins—vitamins dissolve in water and pass easily into the bloodstream during digestion.
Answer the following questions:�
- 1. Why are vitamins and minerals called micronutrients?
- They are needed in smaller amounts than other nutrients.
2. Why are some vitamins considered to be antioxidants?
- They protect body cells and the immune system by either transforming harmful free radicals into less damaging compounds or repairing damaged cells.
3. Compare water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins.
- Water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water and are carried in the bloodstream; they are not stored, and excess amounts are eliminated with waste products. Fat-soluble vitamins are absorbed and transported by fat; excess amounts are stored by the body for later use.
4. What does vitamin C do for you?
- Helps maintain healthy capillaries, bones, skin, and teeth. Helps your body heal wounds and resist infections. Aids in the absorption of iron and works as an antioxidant. Plays a role in caring for collagen that gives structure to bones, cartilage, muscle, and blood vessels.
5. One family stored milk in small, clear containers. What do you think of this practice?
- Not good because light through the containers will destroy riboflavin in the milk.
6. What function in the body do riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, vitamin B5, and biotin have in common?
- They are all involved in using carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
7. Why is folate a very important vitamin?
- It helps the body use proteins, builds red blood cells, and forms genetic material. It prevents birth defects that damage the brain and spinal cord.
8. What can occur with vitamin A deficiency?
- Rough, scaly skin and infections in the respiratory tract and other areas of the body; causes night blindness and total blindness in many children in developing countries.
9. What is toxicity?�
- An excessive amount of a substance that is poisonous in the body.
� 10. What are two ways to get vitamin D?
- Through exposure to sunlight and in fortified milk.
11. Why do cooks need to pay particular attention to the ways that foods are prepared?
- Some cooking techniques can destroy certain vitamins.
12. Compare major and trace minerals.
- The amount of trace minerals the body needs is much smaller than the amount of major minerals needed.
13. Why do teens need to think about osteoporosis?
- Bone mass builds u p during childhood, the teen years, and young adulthood, so care taken to consume calcium during early life can prevent the disease from developing later.
14. Why are sodium, chloride, and potassium called electrolyte minerals?
- They form chemical particles called electrolytes, which attract fluids. Cells move electrolytes through cell walls as needed to balance fluids and keep cells from collapsing or bursting.
15. What can help reduce hypertension?
- Lowering intake of table salt.
16. What are some signs of iron-deficiency anemia?
- Being tired, weak, short of breath, pale, and cold.
17. One teen chewed on ice to the point that her friends noticed and commented on the frequency. What might be wrong?
- She might have pica, an unusual appetite for ice, clay, or other nonfood items, indicating an iron deficiency.
18. Why is fluoride needed in the diet?
- To prevent tooth decay and strengthen bones.
19. What do you think about the trend to fortify many food products with vitamins and minerals?
- Might help some people, but also has the potential to cause toxic excesses
How does your diet rate?
Balanced Diet = Good Health

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.1 – Introduction to Vitamins
Learning objectives.
- Define the term vitamin.
- Compare and contrast fat-and water-soluble vitamins and identify vitamins that fit in each category.
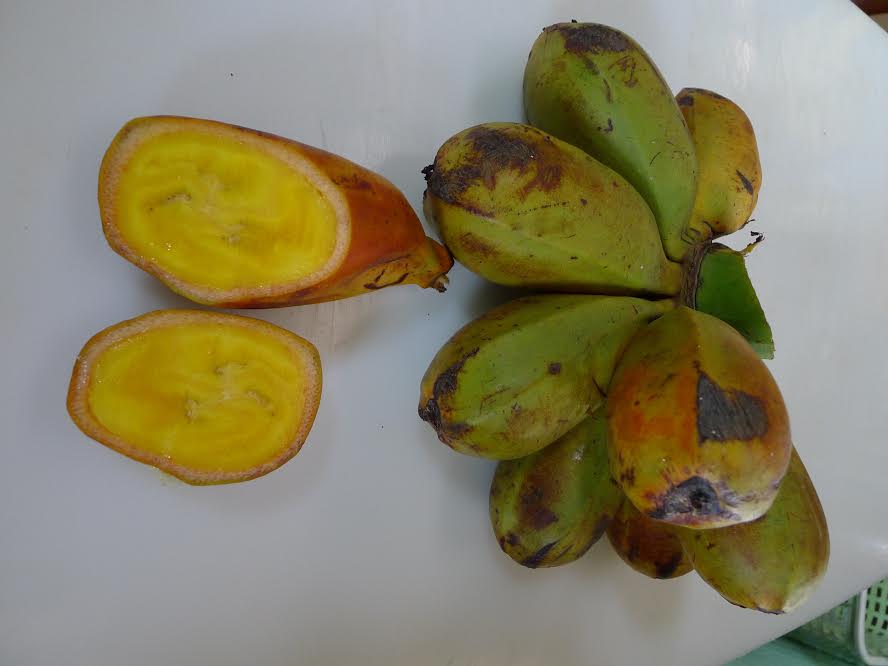

To combat this issue the Island Food Community of Pohnpei has been instrumental in promoting the citizens of Pohnpei to increase local karat banana consumption. The karat banana is rich in beta-carotene (a source of vitamin A) and increasing consumption among the locals will decrease the prevalence of vitamin A deficiencies in Pohnpei. For further information on this issue visit the Island Food Community of Pohnpei’s website and watch this video .
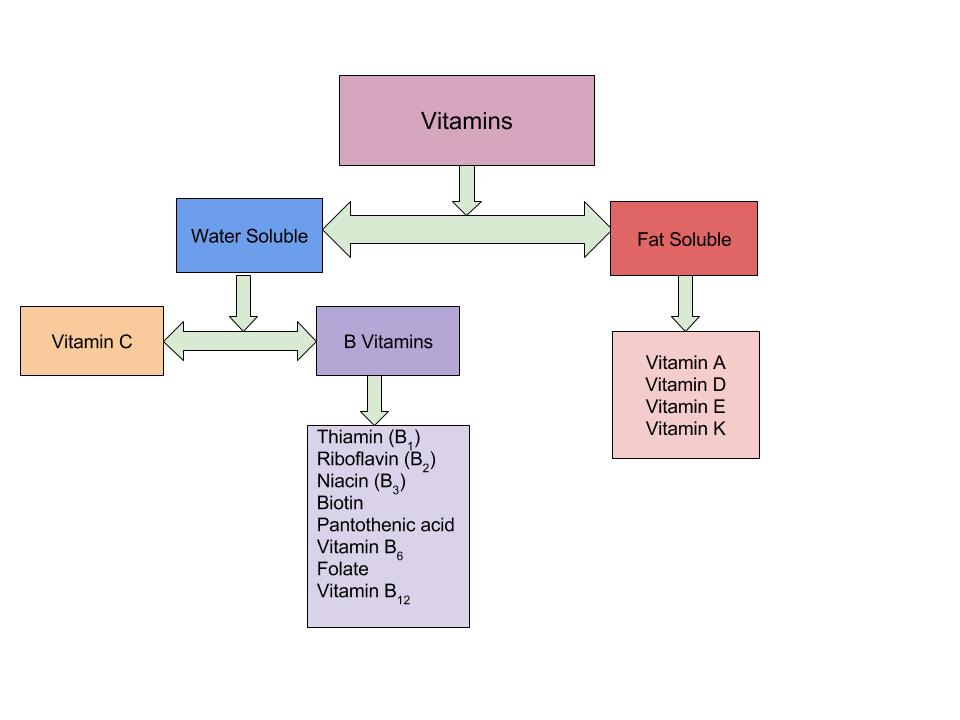
Vitamins are organic compounds that are traditionally assigned to two groups fat-soluble(hydrophobic) or water-soluble (hydrophilic). This classification determines where they act in the body. Water-soluble vitamins act in the cytosol of cells or in extracellular fluids such as blood; fat-soluble vitamins are largely responsible for protecting cell membranes from free radical damage. The body can synthesize some vitamins, but others must be obtained from the diet.
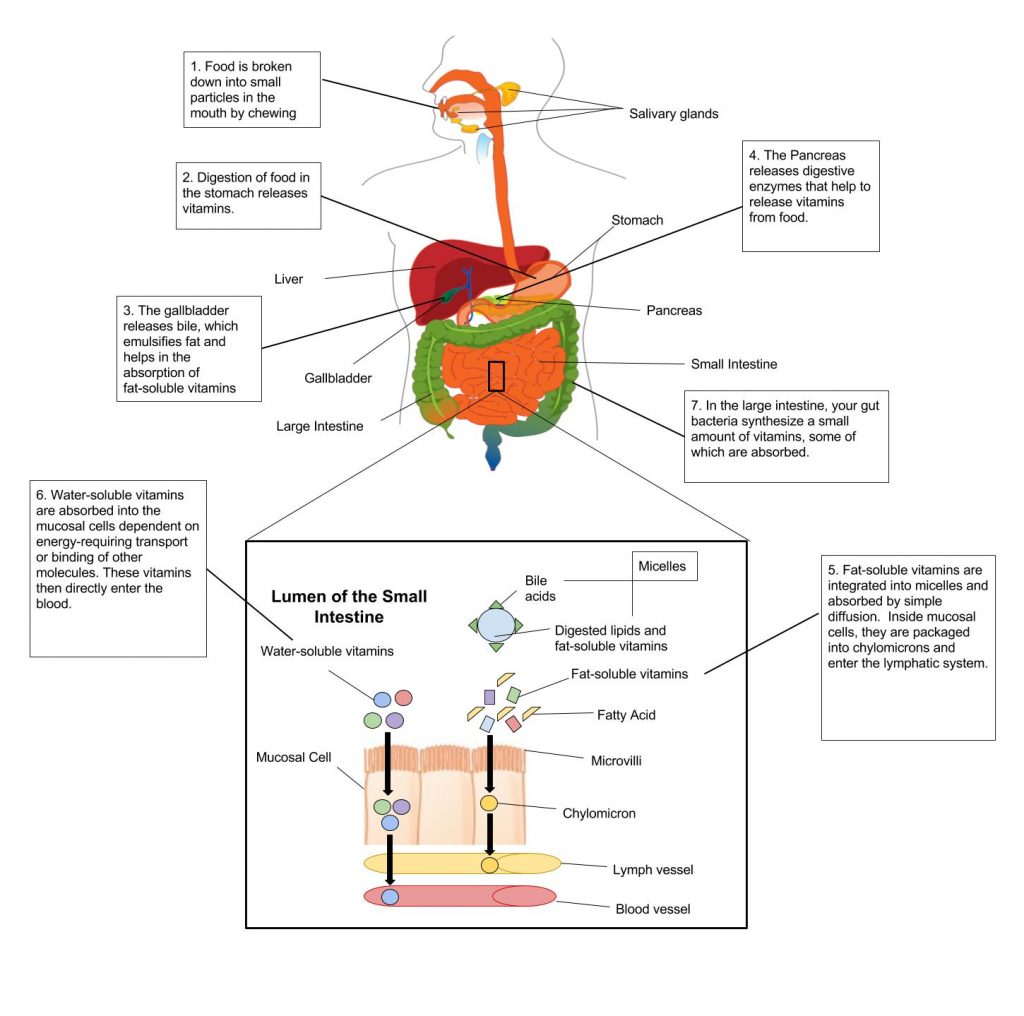
One major difference between fat-soluble vitamins and water-soluble vitamins is the way they are absorbed in the body. Vitamins are absorbed primarily in the small intestine and their bioavailability is dependent on the quality of the diet. Including a small amount of fat or oils in your meal enhances fat-soluble vitamin absorption. Once fat-soluble vitamins have been absorbed in the small intestine, they are packaged and incorporated into chylomicrons along with other fatty acids and transported in the lymphatic system to the liver. Water-soluble vitamins, on the other hand, are absorbed in the small intestine but are transported to the liver through blood vessels. (Figure 10.1.3 ).
1 Yamamura CM, Sullivan KM. Risk factors for vitamin A deficiency among preschool-aged children in Pohnpei, Federated States of Micronesia . J Trop Pediatr. 2004; 50(1),16-9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14984164. Accessed May 23, 2019.
key Takeaways
- Vitamins are organic compounds that are traditionally assigned to two groups fat-soluble(hydrophobic) or water-soluble (hydrophilic).
- Water-soluble vitamins act in the cytosol of cells or in extracellular fluids such as blood; fat-soluble vitamins are largely responsible for protecting cell membranes from free radical damage. The body can synthesize some vitamins, but others must be obtained from the diet.
- The fat-soluble vitamins include vitamins A, D, E, K. The water-soluble vitamins include the B vitamins and vitamin C.
Contributors
University of Hawai’i at Mānoa Food Science and Human Nutrition Program: Allison Calabrese, Cheryl Gibby, Billy Meinke, Marie Kainoa Fialkowski Revilla, and Alan Titchenal
Nutrition 100 Nutritional Applications for a Healthy Lifestyle Copyright © by Lynn Klees and Alison Borkowska is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Preferences

Vitamins - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

Vitamins Goals -To give students information about vitamins so they can eat healthy foods-For students to know which foods have a lot of vitamins – PowerPoint PPT presentation
- -To give students information about vitamins so they can eat healthy foods
- -For students to know which foods have a lot of vitamins
- By the end of the lesson students should be able to
- name the vitamins A, B, C, D
- talk about which vitamins are contained in different healthy foods
- answer the questions given at the end of the lesson accurately in their journals
- talk about which vitamins are in their own diet
- Pictures of food items, vegetables, fruits
- Text about vitamins
- Diagram about vitamins, where they are found, what they are useful for, how they are used and what happens when someone is deficient.
- Letter cards spelling out the word vitamins
- Activity II Wh questions? Two s-s ask questions? What is this? Is this a juice? What kind of vegetables do you know? What do you know about vitamin D?
- Students will answer Yes/ No questions.
- Presentations
- Deficiency -???????
- Smooth - ???????
- Fatigue - ?????????
- Nerve damage -??????? ???????????
- Sensitive skin - ?????? ????
- Osteoporosis ??????????
- Swollen gum - ??????? ?????
- Vitamin - ??????? ?????
- Reproduction - ???????????
- A smooth tongue
- Sensitive skin
- Poor growth
- Problem with reproduction
- Osteoporosis
- Loose teeth
- Swollen gums
- Students read the text, than in small group they will discuss about USEAGE, DEFICIENCIES, FOUND in, USED for. Make notes for your self.
- Write and read about their own diet breakfast, lunch and dinner then share with your pair.
- Write a Cinquaine poem Vitamins.
- Vitamins play a very important role in human health. Over dosage of some vitamins may be harmful, so people must take normal doses of vitamins.
- When the winter months come your food becomes rather poor of vitamins.
- Winter is the time for virus infections, colds and flu and your resistance is especially jow. Take vitamins A, D, C every day.
- They are often called winter vitamins.
- Line 1 noun
- Line 2 2 adjectives that describe the noun
- Line 3 3 verbs that describe the noun
- Line 4 One complete, related sentence
- Line 5 Noun-synonym of the noun in line 1.
- Useful, soluble
- Help, protect, keep
- It is impotant for heath
- Essay Healthy Foods.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.
- Biology Article
Vitamins And Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are both essential nutrients which are required in a daily diet. Altogether, there are 13 essential vitamins and many minerals which are required for the body to function properly and to maintain the optimal health. Both vitamins and minerals combine to perform hundreds of roles in the body.
Let us learn in detail about these vitamins and minerals below.
Also Read: Difference between Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins are organic compounds, found in natural foods which are required for normal growth and maintenance of the body. Both humans and animals require vitamins for their growth.
The word vitamin is a combination of Latin words “vita” and “amine” which means life and nitrogen respectively. Casimir Funk discovered a substance that helps in the growth and maintenance of the body and named it in 1884.
Vitamins act as a catalyst in the generation of energy by utilizing carbohydrates and fats properly. Humans cannot live without vitamins and the human body cannot produce it on its own (except vitamin D and Vitamin B3). So it should be taken in required quantities through other sources such as the food we take, vitamin capsules etc. Vitamins can be found in major foods like meat, leafy vegetables, fruits etc.
Vitamin deficiency may cause some diseases and overdose also causes diseases.
Types of Vitamins
Vitamins are of two types:
- Fat-soluble – which are dissolved in fat
- Water-soluble – which are dissolved in water
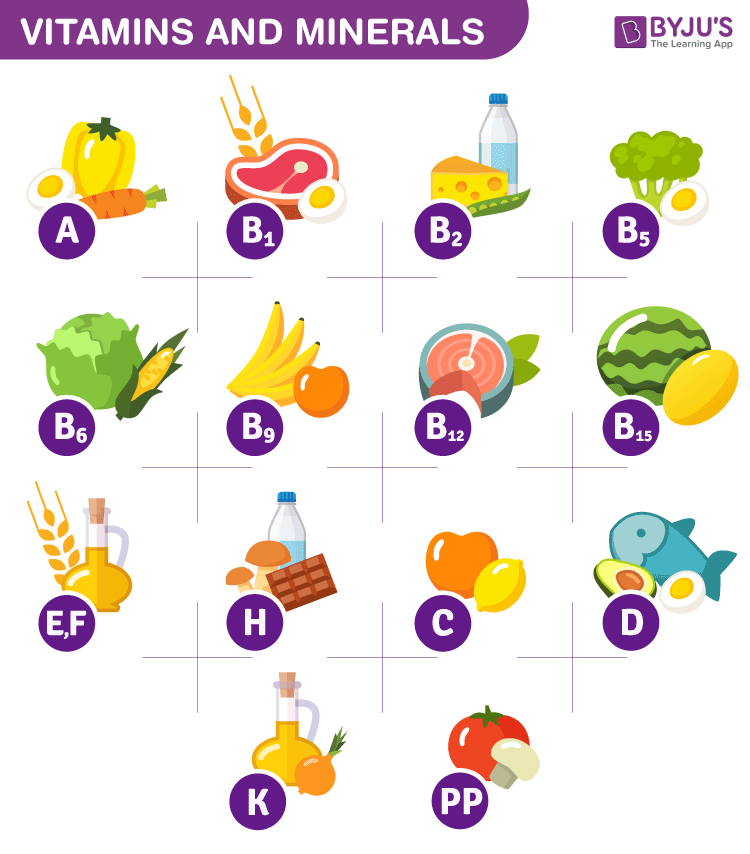
Here is a table that illustrates the type of vitamins, sources, and diseases due to vitamin deficiency.
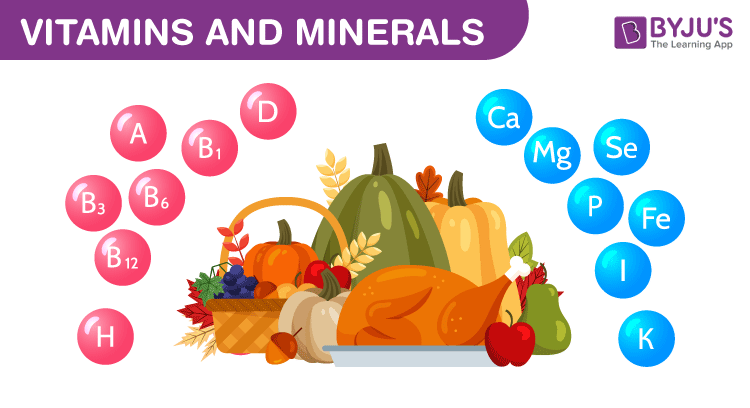
Minerals are also organic compounds found in nature, which helps in the growth of the human body. Minerals are essential for the human body to work properly. Deficiency of minerals leads to several disorders.
List of Minerals, their sources and functions
For more information about Vitamins, Minerals and sources of nutrition, visit BYJU’S.
- Vitamin B-12 Deficiency
- Vitamin A Deficiency
- Vitamin – B
- Nutrition In Human Beings

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
its super and thank you
right and must have experienced live chat with the experienced teacher of Byjus it was cool
liked it specially the live chat was better more info in it i feel lucky i love byjus thanks
So helpful teachers so interesting app I feel very lucky I LIKE BYJUS
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

11 templates

teacher appreciation

mother teresa
18 templates

memorial day
12 templates

summer vacation
25 templates


Nutrition Presentation templates
Do you know the different foods of the healthy eating pyramid on the ground level are bread, cereals and pasta, then vegetables, fruit, meat and finally, sweets. a healthy lifestyle is made of variety, just like this selection of templates. choose your favorite and prepare a presentation about healthy lifestyle choices.

Nutrition Newsletter
This minimalist newsletter is perfect to talk about nutrition with your team. Share announcements, activities and provide company insights. These slides contain a lot of colorful pictures of food, diagrams and many sections related to events or new employees.

Enteral Nutrition Case Report
Download the "Enteral Nutrition Case Report" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. A clinical case is more than just a set of symptoms and a diagnosis. It is a unique story of a patient, their experiences, and their journey towards healing. Each case is an opportunity for healthcare professionals to...

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
Sports Nutrition Infographics
The biggest factor that affects your sport performance is your nutrition. Food is the fuel that you give your body to do the amazing sports you want it to do! That’s why a good nutrition is the key! Learn all about micros, macros, nutrients and health with these visual infographics...

Food Science and Nutrition Conference
Organize your nutrition and food science conference with this delicious yet formal Google Slides and PowerPoint template, crafted to empower you in delivering a captivating setup that delves into the latest advancements in the field. With thoughtfully designed slides and a wide selection of fully editable visuals at your disposal,...

Plant-Based Lamb Business Plan
Download the "Plant-Based Lamb Business Plan" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Conveying your business plan accurately and effectively is the cornerstone of any successful venture. This template allows you to pinpoint essential elements of your operation while your audience will appreciate the clear and concise presentation, eliminating any potential...

Health Subject for Elementary - 3rd Grade: Nutrition
In order to prepare your students for possible future careers that they might be interested in, you can give a little sneak peek at earlier levels. For example, how about using this template to create a presentation for classes on nutrition? Health is an important issue, so to get the...

Nutritionist Day in Latin America
Do you know how to have the best eating habits? There have been so many studies about the best food and how to improve our intake. But how did it all start? Well, with nutritionists studying and making more and more discoveries! There has been one particular one: Dr. Pedro...

Nutrition and Diet Workshop
If you are a nutritionist, this template comes just right. Prepare a workshop on diet and nutrition with the resources we offer. Its background with food illustrations goes great with the theme. We include tables to divide meals by categories. This will make it easier for you to explain the...

Food and Nutrition Workshop
In English (and in Spanish too), there's a saying that goes "you are what you eat". That means that it's important to have a balanced diet so that your body has all types of nutrients and substances that it requires to function perfectly. If you're an expert nutritionist, give a...

Fructose Malabsorption Syndrome
Download the "Fructose Malabsorption Syndrome" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Taking care of yourself and of those around you is key! By learning about various illnesses and how they are spread, people can get a better understanding of them and make informed decisions about eating, exercise, and seeking medical...

Download the Food Wheel presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different graphic resources. You...

Health Subject for Elementary - 2nd Grade: Nutrition & Physical Activity
In order to grow up with lots of energy, you need to keep a healthy nutrition as a kid. You can use this new template to teach your students the benefits of physical activity and eating well. There's a bit of simplicity in the design of the layouts, and there...

Healthy Nutrition Coach Portfolio
Are you a healthy nutrition coach looking to showcase your expertise? We've got the perfect solution for you! This Google Slides & PowerPoint template is designed specifically for nutrition coaches, complete with eye-catching illustrations of colorful and healthy fruits and vegetables. Plus, if you're stuck on what to include in...

Carbs Importance on Balanced Diet
Download the Carbs Importance on Balanced Diet presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Healthcare goes beyond curing patients and combating illnesses. Raising awareness about diseases, informing people about prevention methods, discussing some good practices, or even talking about a balanced diet—there are many topics related to medicine that you could...

Nutrition and Healthy Eating Habits - Health - 10th Grade
Savor the flavors of knowledge with a very healthy and nutritious lesson for 10th grade. Engage students in an enriching diet of learning with cute hand-drawn illustrations. Delightfully designed with a happy vibe using a refreshing palette of fruit and veggie illustrations, it makes learning about nutrition fun and enjoyable....

Take care of your stomach - Social Media Strategy
Download the Take care of your stomach - Social Media Strategy presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. How do you use social media platforms to achieve your business goals? If you need a thorough and professional tool to plan and keep track of your social media strategy, this fully customizable...

Nutrition for People with Diabetes Workshop
Download the Nutrition for People with Diabetes Workshop presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. If you are planning your next workshop and looking for ways to make it memorable for your audience, don’t go anywhere. Because this creative template is just what you need! With its visually stunning design, you...

Healthy Lifestyle Products MK Plan
Nourishing your body with healthy food and products is the key to having a long life! But what are the best products? There’s so many to choose from, different brands, different types… in order to create the perfect marketing strategy that puts your products in the spotlight you must design...
- Page 1 of 7
Great presentations, faster
Slidesgo for Google Slides :
The easy way to wow

Register for free and start editing online

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Fat soluble vitamins: Fat soluble vitamins, Vitamin A, D, E and K and their their source, structure, properties, metabolism, physiological significance, deficiency disease and human requirements. Vitamin A-Carotene in plants-α-carotenes, β-carotenes and γ-carotenes, 3 forms of vitamin A-Retinol, Retinal, Retinoic acid.
Individual vitamins serve different functions. As a group vitamins assist in 5 things: Nutrient metabolism. . Ability to break up & use nutrients Energy Production & release. . Take energy from energy nutrients. . Vitamins have no calories therefore they give no energy Tissue Maintenance Normal Digestion. .
B Vitamins Thiamin (B1) Riboflavin (B2) Niacin Pantothenic Acid Biotin Vitamin B6 Folic Acid Vitamin B12 • Indispensable for metabolism. • B vitamins help the body to produce energy. • B complex vitamin are necessary for healthy skin, hair, eyes and liver, also help the nervous system function properly. 1.
Calciferol/Vitamin D • Fat Soluble • It is related in structure to cholesterol. • It is synthesized when UV light from the sun strikes a cholesterol derivative in the skin. • In your kidney, vitamin D is converted to a hormone which regulates calcium absorption and bone formation. Vitamin D Structure.
Define the Following Terms: 1. antioxidants—substances that protect body cells and the immune system from damage by harmful chemicals in air and foods. 2. electrolyte minerals—sodium, chloride, and potassium, which control and balance fluid flow in and out of cells. 3. fat-soluble vitamins—vitamins absorbed and transported by fat.
1. Food is broken down into small particles in the mouth by 2. Digestion o food in the stomach releases vitamins. 3. The gallbladder releases bile, which emulsifies fat and helps in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. 4. The Pancreas releases digestive enzymes that help to release vitamins from food. 5.
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) Functions. Helps maintain healthy capillaries, bones, skin, and teeth. Helps form collagen, which gives structure to bones, cartilage, muscles, and blood vessels. Helps your body heal wounds and resist infections. Aids in absorption of iron. Works as an antioxidant.
Free Google Slides theme, PowerPoint template, and Canva presentation template. Vitamin A can be found in foods such as eggs or carrots, vitamin B in red meat, fish, dairy…. Vitamin C in citrus and dairy, salmon or nuts contain calcium and beef or spinach are rich in iron. There are many vitamins and minerals to take into account to have a ...
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. Teaching nutrition concepts to middle schoolers can be not easy, as it can be hard for them to appreciate veggies when tasty snacks are at their disposal. But with the template for nutrition lessons for Middle School, your students will look forward to learning about their daily food intake!
When choosing a supplement, select one that meets 100‐300% of the RDA. A multivitamin should contain fat‐soluble vitamins A, D, E; water‐soluble vitamins B1, B2, B6, B12, niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin, folic acid , and Vitamin C. They will also usually have minerals such as zinc, magnesium, copper, and calcium in them.
1. Physiological increased need for vitamins, for example, during pregnancy, with heavy physical labor. 2. Long-term severe infectious diseases, as well as during the recovery period. 3. Disturbance of vitamin absorption in some diseases of the digestive tract, for example impaired absorption of fat-soluble vitamins is observed at
The known vitamins include A, C, D, E, and K, and the B. vitamins: thiamin (B 1), ribo avin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), pyridox-. ine (B 6), cyanocobalamin (B12), biotin, and folate ...
About This Presentation. Title: Vitamins. Description: Vitamins Goals -To give students information about vitamins so they can eat healthy foods-For students to know which foods have a lot of vitamins - PowerPoint PPT presentation. Number of Views: 188. Avg rating:3.0/5.0.
Simple Elegant Gray Gradient Cool Illustration Colorful Geometric Medical Health Minimalist Corporate Abstract Breakthrough Editor's Choice. Download this minimalistic template with colorful illustrations and fill it with your content to educate people on vitamins and minerals!
Vitamins are organic compounds, found in natural foods which are required for normal growth and maintenance of the body. Both humans and animals require vitamins for their growth. The word vitamin is a combination of Latin words "vita" and "amine" which means life and nitrogen respectively. Casimir Funk discovered a substance that helps ...
OPEN EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES - University of Medical Sciences, Ondo
14 likes • 30,528 views. V. VidhiBhutia. best chemistry project class 12. Science. 1 of 21. Download now. Download to read offline. Project chemistry on vitamins - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
We've got the perfect solution for you! This Google Slides & PowerPoint template is designed specifically for nutrition coaches, complete with eye-catching illustrations of colorful and healthy fruits and vegetables. Plus, if you're stuck on what to include in... Business. 16:9.
It plays an essential role in vision, cell growth and differentiation. Vitamin A is absorbed in the small intestine and transported to the liver where it is stored. A deficiency can impair vision and cause dry eyes and corneal ulceration or blindness in severe cases. The recommended daily intake is 400-1000 μg depending on age, sex and life stage.