- eSignatures
- Product updates
- Document templates

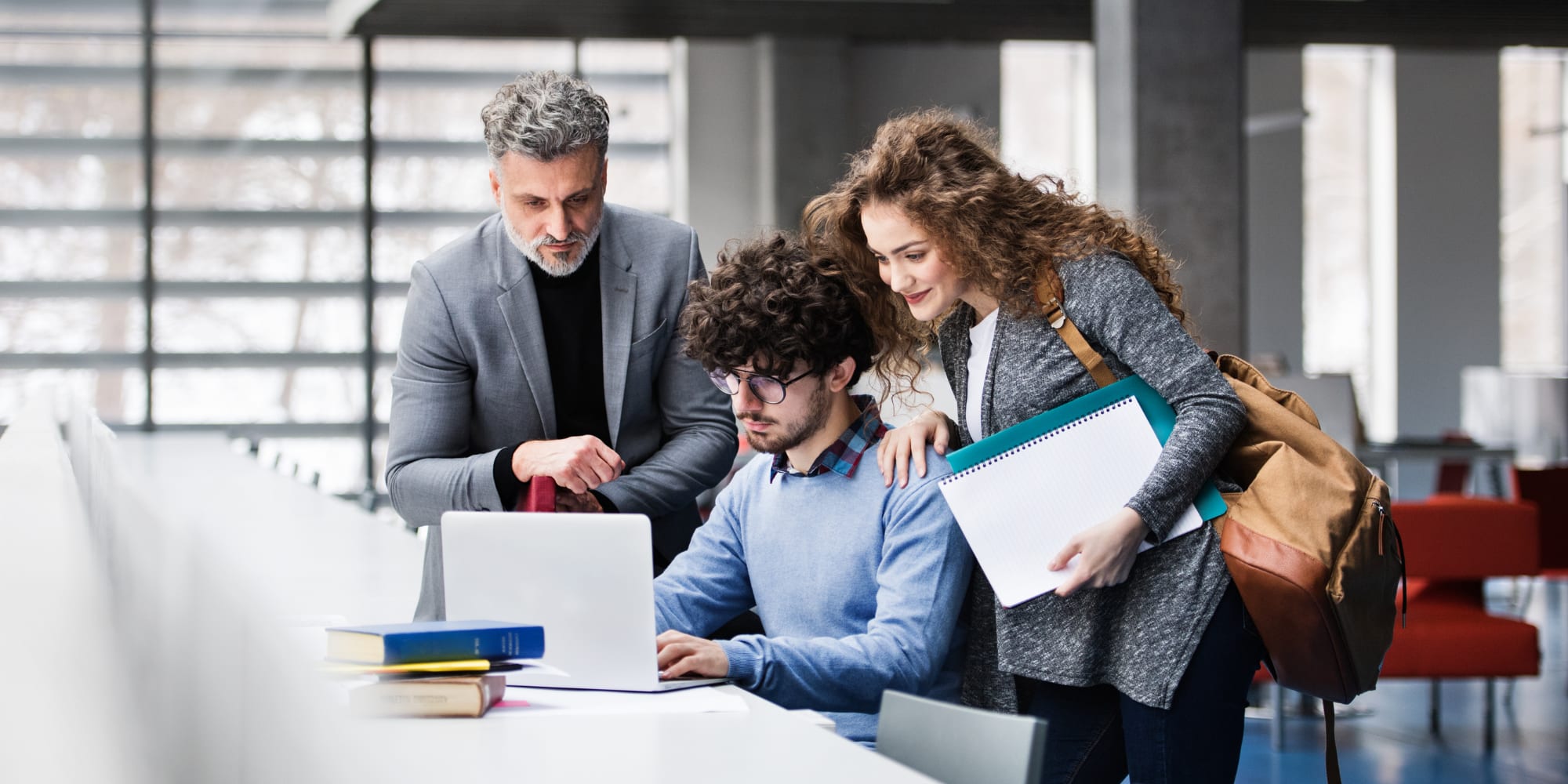
How to nail your PhD proposal and get accepted
Bethany Fagan Head of Content Marketing at PandaDoc
Reviewed by:
Olga Asheychik Senior Web Analytics Manager at PandaDoc
- Copy Link Link copied
A good PhD research proposal may be the deciding factor between acceptance and approval into your desired program or finding yourself back at the drawing board. Being accepted for a PhD placement is no easy task, and this is why your PhD proposal needs to truly stand out among a sea of submissions.
That’s why a PhD research proposal is important: It formally outlines the intended research, including methodology, timeline, feasibility, and many other factors that need to be taken into consideration.
Here is a closer look at the PhD proposal process and what it should look like.
→DOWNLOAD NOW: FREE PHD PROPOSAL TEMPLATE
Key takeaways
- A PhD proposal summarizes the research project you intend to conduct as part of your PhD program.
- These proposals are relatively short (1000-2000 words), and should include all basic information and project goals, including the methodologies/strategies you intend to use in order to accomplish them.
- Formats are varied. You may be able to create your own formats, but your college or university may have a required document structure that you should follow.
What is a PhD proposal?
In short, a PhD research proposal is a summary of the project you intend to undertake as part of your PhD program.
It should pose a specific question or idea, make a case for the research, and explain the predicted outcomes of that research.
However, while your PhD proposal may predict expected outcomes, it won’t fully answer your questions for the reader.
Your research into the topic will provide that answer.
Usually, a PhD proposal contains the following elements:
- A clear question that you intend to answer through copious amounts of study and research.
- Your plan to answer that question, including any methodologies, frameworks, and resources required to adequately find the answer.
- Why your question or project is significant to your specific field of study.
- How your proposal impacts, challenges, or improves the existing body of knowledge around a given topic.
- Why your work is important and why you should be the one to receive this opportunity.
In terms of length when writing a PhD proposal, there isn’t a universal answer.
Some institutions will require a short, concise proposal (1000 words), while others allow for a greater amount of flexibility in the length and format of the proposal.
Fortunately, most institutions will provide some guidelines regarding the format and length of your research proposal, so you should have a strong idea of your requirements before you begin.
Benefits of a strong PhD application
While the most obvious benefit of having a strong PhD application is being accepted to the PhD program , there are other reasons to build the strongest PhD application you can:
Better funding opportunities
Many PhD programs offer funding to students , which can be used to cover tuition fees and may provide a stipend for living expenses.
The stronger your PhD application, the better your chances of being offered funding opportunities that can alleviate financial burdens and allow you to focus on your research.
Enhanced academic credentials
A strong PhD application, particularly in hot-button areas of study, can lead to better career opportunities in academics or across a variety of industries.
Opportunities for networking and research
Research proposals that are very well grounded can provide footholds to networking opportunities and mentorships that would not be otherwise available.
However, creating an incredible proposal isn’t always easy.
In fact, it’s easy to get confused by the process since it requires a lot of procedural information.
Many institutions also place a heavy emphasis on using the correct proposal structure.
That doesn’t have to be the issue, though.
Often, pre-designed templates, like the PandaDoc research proposal templates or PhD proposal templates provided by the institution of your choice, can do most of the heavy lifting for you.

Research Proposal Template
Used 7990 times
4.1 rating (30 reviews)
Reviewed by Olga Asheychik
How to write a Phd proposal with a clear structure
We know that the prospect of writing a research proposal for PhD admission may appear the stuff of nightmares. Even more so if you are new to producing a piece such as this.
But, when you get down to the nitty gritty of what it is, it really isn’t so intimidating. When writing your PhD proposal you need to show that your PhD is worth it, achievable, and that you have the ability to do it at your chosen university.
With all of that in mind, let’s take a closer look at each section of a standard PhD research proposal and the overall structure.
1. Front matter
The first pages of your PhD proposal should outline the basic information about the project. That will include each of the following:
Project title
Typically placed on the first page, your title should be engaging enough to attract attention and clear enough that readers will understand what you’re trying to achieve.
Many proposals also include a secondary headline to further (concisely) clarify the main concept.
Contact information
Depending on the instructions provided by your institution, you may need to include your basic contact information with your proposal.
Some institutions may ask for blind submissions and ask that you omit identifying information, so check the program guidelines to be sure.
Research supervisor
If you already have a supervisor for the project, you’ll typically want to list that information.
Someone who is established in the field can add credibility to your proposal, particularly if your project requires extensive funding or has special considerations.
The guidelines from your PhD program should provide some guidance regarding any other auxiliary information that you should add to the front of your proposal.
Be sure to check all documentation to ensure that everything fits into the designated format.
2. Goals, summaries, and objectives
Once you’ve added the basic information to your document, you’ll need to get into the meat of your PhD proposal.
Depending on your institution, your research proposal may need to follow a rigid format or you may have the flexibility to add various sections and fully explain your concepts.
These sections will primarily be focused on providing high-level overviews surrounding your PhD proposal, including most of the following:
Overall aims, objectives, and goals
In these sections, you’ll need to state plainly what you aim to accomplish with your PhD research.
If awarded funding, what questions will your PHd proposal seek to answer? What theories will you test? What concepts will you explore in your research?
Briefly, how would you summarize your approach to this project?
Provide high-level summaries detailing how you mean to achieve your answers, what the predicted outcomes of your PhD research might be, and precisely what you intend to test or discover.
Significance
Why does your research matter? Unlike with many other forms of academic study (such as a master’s thesis ), doctorate-level research often pushes the bounds of specific fields or contributes to a given body of work in some unique way.
How will your proposed PhD research do those things?
Background details
Because PhD research is about pushing boundaries, adding background context regarding the current state of affairs in your given field can help readers better understand why you want to pursue this research and how you arrived at this specific point of interest.
While the information here may (or may not) be broken into multiple sections, the content here is largely designed to provide a high-level overview of your PhD proposal and entice readers to dig deeper into the methodologies and angles of approach in future sections.
Because so much of this section relies on the remainder of your document, it’s sometimes better to skip this portion of the PhD proposal until the later sections are complete and then circle back to it.
That way, you can provide concise summaries that refer to fully defined research methods that you’ve already explained in subsequent areas.
3. Methodologies and plans
Unlike a master’s thesis or a similar academic document, PhD research is designed to push the boundaries of its subject matter in some way.
The idea behind doctoral research is to expand the field with new insights and viewpoints that are the culmination of years of research and study, combined with a deep familiarity of the topic at hand.
The methodologies and work plans you provide will give advisors some insights into how you plan to conduct your research.
While there is no one right way to develop this section, you’ll need to include a few key details:
Research methods
Are there specific research methods you plan to use to conduct your PhD research?
Are you conducting experiments? Conducting qualitative research? Surveying specific individuals in a given environment?
Benefits and drawbacks of your approach
Regardless of your approach to your topic, there will be upsides and downsides to that methodology.
Explain what you feel are the primary benefits to your research method, where there are potential flaws, and how you plan to account for those shortfalls.
Choice of methodology
Why did you choose a given methodology?
What makes it the best method (or collection of methods) for your research and/or specific use case?
Outline of proposed work
What work is required for PhD research to be complete?
What steps will you need to take in order to capture the appropriate information? How will you complete those steps?
Schedule of work (including timelines/deadlines)
How long will it take you to complete each stage or step of your project?
If your PhDproject will take several years, you may need to provide specifics for more immediate timelines up front while future deadlines may be flexible or estimated.
There is some flexibility here.
It’s unlikely that your advisors will expect you to have the answer for every question regarding how you plan to approach your body of research.
When trying to push the boundaries of any given topic, it’s expected that some things may not go to plan.
However, you should do your best to make timelines and schedules of work that are consistent with your listed goals.
Remember : At the end of your work, you are expected to have a body of original research that is complete within the scope and limitations of the PhD proposal you set forth.
If your advisors feel that your subject matter is too broad, they may encourage you to narrow the scope to better fit into more standardized expectations.
4. Resources and citations
No PhD research proposal is complete without a full list of the resources required to carry out the project and references to help prove and validate the research.
Here’s a closer look at what you’ll need to submit in order to explain costs and prove the validity of your proposal:
Estimated costs and resources
Most doctoral programs offer some level of funding for these projects.
To take advantage of those funds, you’ll need to submit a budget of estimated costs so that assessors can better understand the financial requirements.
This might include equipment, expenses for fieldwork or travel, and more.
Citations and bibliographies
No matter your field of study, doctoral research is built on the data and observations provided by past contributors.
Because of this, you’ll need to provide citations and sources referenced in your PhD proposal documentation.
Particularly when it comes to finances and funding, it might be tempting to downplay the cost of the project.
However, it’s best to provide a realistic estimate in terms of costs so that you have enough of a budget to cover the PhD research.
Adjustments can be made at a later date, particularly as you conduct more research and dive further into the project.
Resources are often presented in the form of a table to make things easier to track and identify.
Using PhD proposal templates
Aside from any guidelines set forth by your institution, there are no particularly strict rules when it comes to the format of PhD proposals.
Your supervisor will be more than capable of guiding you through the process.
However, since everything is so structured and formal, you might want to use a PhD proposal template to help you get started.
Templates can help you stay on track and make sure your research proposal follows a certain logic.
A lot of proposal software solutions offer templates for different types of proposals, including PhD proposals.
But, should you use Phd proposal templates? Here are some pros and cons to help you make a decision.
- Expedites the proposal process.
- Helps you jumpstart the process with a flexible document structure.
- Often provides sections with pre-filled examples.
- Looks better than your average Word document.
- May be limiting if you adhere to it too much.
- Might not be perfectly suited to your specific field of research, requiring some customization.
In our PhD research proposal template , we give you just enough direction to help you follow through but we don’t limit your creativity to a point that you can’t express yourself and all the nuances of your research.
For almost all sections, you get a few useful PhD research proposal examples to point you in the right direction.
The template provides you with a typical PhD proposal structure that’s perfect for almost all disciplines.
It can come in quite handy when you have everything planned out in your head but you’re just having trouble putting it onto the page!
Writing a PhD proposal that convinces
Writing and completing a PhD proposal might be confusing at first.
You need to follow a certain logic and share all the required information without going too long or sharing too much about the project.
And, while your supervisor will certainly be there to guide you, the brunt of the work will still fall on your shoulders.
That’s why you need to stay informed, do your research, and don’t give up until you feel comfortable with what you’ve created.
If you want to get a head start, you might want to consider our research proposal template .
It will offer you a structure to follow when writing a PhD proposal and give you an idea on what to write in each section.
Start your 14 days trial with PandaDoc and check out all the tools you’ll have at your disposal!
Research proposals for PhD admission: tips and advice
One of the most important tips for any piece of writing is to know your audience. The staff reviewing your PhD proposal are going through a pile of them, so you need to make sure yours stands within a few seconds of opening it.
The way to do this is by demonstrating value and impact. Academic work is often written for a niche community of researchers in one field, so you need to demonstrate why your work would be valuable to people in that area.
The people reviewing your proposal will likely be in that field. So your proposal should be a little like a sales pitch: you need to write something engaging that identifies with the “customer”, speaks to a problem they’re having, and shows them a solution.
Taking some inspiration from the former University of Chicago professor Larry McEnerney , here are some ideas to keep in mind…
- It’s common for undergraduates and even seasoned academics to write in a specific format or style to demonstrate their understanding and signal that they’re part of the academic community. Instead, you want to write in such a way that actually engages the reader.
- Identify an uncharted or underexplored knowledge gap in your field, and show the reader you have what it takes to fill in that gap.
- Challenge the status quo. Set up an idea that people in your field take for granted — maybe a famous study you think is flawed — and outline how your project could knock it down.
- This is why it’s important to understand who your audience is. You have to write your proposal in such a way that it’s valuable for reviewers. But within your proposal, you should also clearly define which community of researchers your project is for, what problems they have, and how your project is going to solve those problems.
- Every community of researchers has their own implicit “codes” and “keywords” that signal understanding. These will be very different in each field and could be very subtle. But just by reading successful PhD research proposal examples in your field, you can get a sense of what those are and decide how you want to employ them in your own work.
- In this model authors start “at the bottom of the glass” with a very narrow introduction to the idea of the paper, then “fill the glass” with a broader and broader version of the same idea.
- Instead, follow a “problem-solution” framework. Introduce a problem that’s relevant to your intended reader, then offer a solution. Since “solutions” often raise their own new problems or questions, you can rinse and repeat this framework all the way through any section of your proposal.
But how can you apply that advice? If you’re following something like our research proposal template , here are some actionable ways to get started.
- Your title should be eye-catching , and signal value by speaking to either a gap in the field or challenging the status quo.
- Your abstract should speak to a problem in the field, one the reviewers will care about, and clearly outline how you’d like to solve it.
- When you list the objectives of your proposal , each one should repeat this problem-solution framework. You should concretely state what you want to achieve, and what you’re going to do to achieve it.
- While you survey your chosen field in the literature review, you should refer back to the knowledge gap or status quo that you intend to work on. This reinforces how important your proposed project is, and how valuable it would be to the community if your project was successful.
- While listing your research limitations , try to hint at new territory researchers might be able to explore off the back of your work. This illustrates that you’re proposing boundary-pushing work that will really advance knowledge of the field.
- While you’re outlining your funding requirements , be clear about why each line item is necessary and bring it back to the value of your proposed research. Every cent counts!
Frequently asked questions
How long should a phd proposal be.
There really isn’t a specific rule when it comes to the length of a PhD proposal. However, it’s generally accepted that it should be between 1,000 and 2,000 words.
It’s difficult to elaborate on such a serious project in less than 1,000 words but going over 2,000 is often overkill. You’ll lose people’s attention and water down your points.
What’s the difference between a dissertation proposal and a PhD proposal?
There seems to be some confusion over the terms “dissertation” and “PhD” and how you write proposals for each one. However, “dissertation” is just another name for your PhD research so the proposal for a dissertation would be the same since it’s quite literally the same thing.
Does a PhD proposal include budgeting?
Yes, as mentioned, you need to demonstrate the feasibility of your project within the given time frame and with the resources you need, including budgets. You don’t need to be exact, but you need to have accurate estimates for everything.
How is a PhD proposal evaluated?
This will change from one institution to another but these things will generally have a big impact on the reviewers:
- The contribution of the project to the field.
- Design and feasibility of the project.
- The validity of the methodology and objectives.
- The supervisor and their role in the field.
PandaDoc is not a law firm, or a substitute for an attorney or law firm. This page is not intended to and does not provide legal advice. Should you have legal questions on the validity of e-signatures or digital signatures and the enforceability thereof, please consult with an attorney or law firm. Use of PandaDocs’ services are governed by our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Originally published June 9, 2023, updated February 6, 2024
Related articles

Proposals 24 min

Sales 5 min

Document templates 13 min
Streamline your document workflow & close deals faster
Get personalized 1:1 demo with our product specialist.
- Tailored to your needs
- Answers all your questions
- No commitment to buy
- Fill out the form
- Book a time slot
- Attend a demo
By submitting this form, I agree that the Terms of Service and Privacy Notice will govern the use of services I receive and personal data I provide respectively.

How to Write a PhD Research Proposal
- Applying to a PhD
- A research proposal summarises your intended research.
- Your research proposal is used to confirm you understand the topic, and that the university has the expertise to support your study.
- The length of a research proposal varies. It is usually specified by either the programme requirements or the supervisor upon request. 1500 to 3500 words is common.
- The typical research proposal structure consists of: Title, Abstract, Background and Rationale, Research Aims and Objectives, Research Design and Methodology, Timetable, and a Bibliography.
What is a Research Proposal?
A research proposal is a supporting document that may be required when applying to a research degree. It summarises your intended research by outlining what your research questions are, why they’re important to your field and what knowledge gaps surround your topic. It also outlines your research in terms of your aims, methods and proposed timetable .
What Is It Used for and Why Is It Important?
A research proposal will be used to:
- Confirm whether you understand the topic and can communicate complex ideas.
- Confirm whether the university has adequate expertise to support you in your research topic.
- Apply for funding or research grants to external bodies.
How Long Should a PhD Research Proposal Be?
Some universities will specify a word count all students will need to adhere to. You will typically find these in the description of the PhD listing. If they haven’t stated a word count limit, you should contact the potential supervisor to clarify whether there are any requirements. If not, aim for 1500 to 3500 words (3 to 7 pages).
Your title should indicate clearly what your research question is. It needs to be simple and to the point; if the reader needs to read further into your proposal to understand your question, your working title isn’t clear enough.
Directly below your title, state the topic your research question relates to. Whether you include this information at the top of your proposal or insert a dedicated title page is your choice and will come down to personal preference.
2. Abstract
If your research proposal is over 2000 words, consider providing an abstract. Your abstract should summarise your question, why it’s important to your field and how you intend to answer it; in other words, explain your research context.
Only include crucial information in this section – 250 words should be sufficient to get across your main points.
3. Background & Rationale
First, specify which subject area your research problem falls in. This will help set the context of your study and will help the reader anticipate the direction of your proposed research.
Following this, include a literature review . A literature review summarises the existing knowledge which surrounds your research topic. This should include a discussion of the theories, models and bodies of text which directly relate to your research problem. As well as discussing the information available, discuss those which aren’t. In other words, identify what the current gaps in knowledge are and discuss how this will influence your research. Your aim here is to convince the potential supervisor and funding providers of why your intended research is worth investing time and money into.
Last, discuss the key debates and developments currently at the centre of your research area.
4. Research Aims & Objectives
Identify the aims and objectives of your research. The aims are the problems your project intends to solve; the objectives are the measurable steps and outcomes required to achieve the aim.
In outlining your aims and objectives, you will need to explain why your proposed research is worth exploring. Consider these aspects:
- Will your research solve a problem?
- Will your research address a current gap in knowledge?
- Will your research have any social or practical benefits?
If you fail to address the above questions, it’s unlikely they will accept your proposal – all PhD research projects must show originality and value to be considered.
5. Research Design and Methodology
The following structure is recommended when discussing your research design:
- Sample/Population – Discuss your sample size, target populations, specimen types etc.
- Methods – What research methods have you considered, how did you evaluate them and how did you decide on your chosen one?
- Data Collection – How are you going to collect and validate your data? Are there any limitations?
- Data Analysis – How are you going to interpret your results and obtain a meaningful conclusion from them?
- Ethical Considerations – Are there any potential implications associated with your research approach? This could either be to research participants or to your field as a whole on the outcome of your findings (i.e. if you’re researching a particularly controversial area). How are you going to monitor for these implications and what types of preventive steps will you need to put into place?
6. Timetable
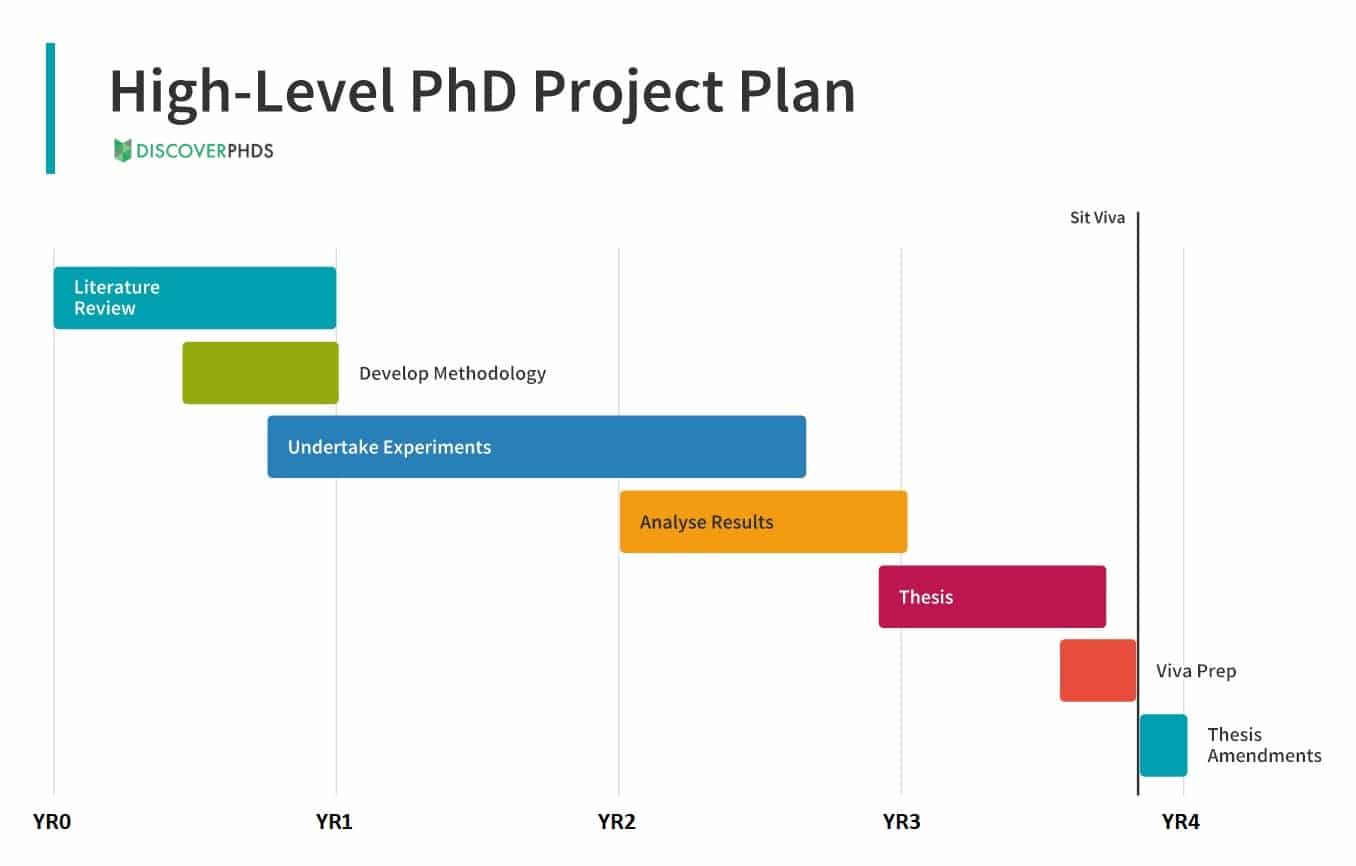
We’ve outlined the various stages of a PhD and the approximate duration of a PhD programme which you can refer to when designing your own research study.
7. Bibliography
Plagiarism is taken seriously across all academic levels, but even more so for doctorates. Therefore, ensure you reference the existing literature you have used in writing your PhD proposal. Besides this, try to adopt the same referencing style as the University you’re applying to uses. You can easily find this information in the PhD Thesis formatting guidelines published on the University’s website.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Questions & Answers
Here are answers to some of the most common questions we’re asked about the Research Proposal:
Can You Change a Research Proposal?
Yes, your PhD research proposal outlines the start of your project only. It’s well accepted that the direction of your research will develop with time, therefore, you can revise it at later dates.
Can the Potential Supervisor Review My Draft Proposal?
Whether the potential supervisor will review your draft will depend on the individual. However, it is highly advisable that you at least attempt to discuss your draft with them. Even if they can’t review it, they may provide you with useful information regarding their department’s expertise which could help shape your PhD proposal. For example, you may amend your methodology should you come to learn that their laboratory is better equipped for an alternative method.
How Should I Structure and Format My Proposal?
Ensure you follow the same order as the headings given above. This is the most logical structure and will be the order your proposed supervisor will expect.
Most universities don’t provide formatting requirements for research proposals on the basis that they are a supporting document only, however, we recommend that you follow the same format they require for their PhD thesis submissions. This will give your reader familiarity and their guidelines should be readily available on their website.
Last, try to have someone within the same academic field or discipline area to review your proposal. The key is to confirm that they understand the importance of your work and how you intend to execute it. If they don’t, it’s likely a sign you need to rewrite some of your sections to be more coherent.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
You're viewing this site as a domestic an international student
You're a domestic student if you are:
- a citizen of Australia or New Zealand,
- an Australian permanent resident, or
- a holder of an Australian permanent humanitarian visa.
You're an international student if you are:
- intending to study on a student visa,
- not a citizen of Australia or New Zealand,
- not an Australian permanent resident, or
- a temporary resident (visa status) of Australia.


How to write a good PhD proposal
Study tips Published 3 Mar, 2022 · 5-minute read
Want to make sure your research degree starts smoothly? We spoke with 2 PhD candidates about overcoming this initial hurdle. Here’s their advice for how to write a good PhD proposal.
Writing your research proposal is an integral part of commencing a PhD with many schools and institutes, so it can feel rather intimidating. After all, how you come up with your PhD proposal could be the difference between your supervisor getting on board or giving your project a miss.
Let’s explore how to make a PhD research proposal with UQ candidates Chelsea Janke and Sarah Kendall.
Look at PhD proposal examples

Look at other PhD proposals that have been successful. Ask current students if you can look at theirs.
Nobody’s asking you to reinvent the wheel when it comes to writing your PhD proposal – leave that for your actual thesis. For now, while you’re just working out how to write a PhD proposal, examples are a great starting point.
Chelsea knows this step is easier if you’ve got a friend who is already doing a PhD, but there are other ways to find a good example or template.
“Look at other PhD proposals that have been successful,” she says.
“Ask current students if you can look at theirs.”
“If you don’t know anyone doing their PhD, look online to get an idea of how they should be structured.”
What makes this tricky is that proposals can vary greatly by field and disciplinary norms, so you should check with your proposed supervisor to see if they have a specific format or list of criteria to follow. Part of writing a good PhD proposal is submitting it in a style that's familiar to the people who will read and (hopefully) become excited by it and want to bring you into their research area.
Here are some of the key factors to consider when structuring your proposal:
- meeting the expected word count (this can range from a 1-page maximum to a 3,000-word minimum depending on your supervisor and research area)
- making your bibliography as detailed as necessary
- outlining the research questions you’ll be trying to solve/answer
- discussing the impact your research could have on your field
- conducting preliminary analysis of existing research on the topic
- documenting details of the methods and data sources you’ll use in your research
- introducing your supervisor(s) and how their experience relates to your project.
Please note this isn't a universal list of things you need in your PhD research proposal. Depending on your supervisor's requirements, some of these items may be unnecessary or there may be other inclusions not listed here.
Ask your planned supervisor for advice
Alright, here’s the thing. If sending your research proposal is your first point of contact with your prospective supervisor, you’ve jumped the gun a little.
You should have at least one researcher partially on board with your project before delving too deep into your proposal. This ensures you’re not potentially spending time and effort on an idea that no one has any appetite for. Plus, it unlocks a helpful guide who can assist with your proposal.
PhD research isn’t like Shark Tank – you’re allowed to confer with academics and secure their support before you pitch your thesis to them. Discover how to choose the right PhD supervisor for you.
For a time-efficient strategy, Chelsea recommends you approach your potential supervisor(s) and find out if:
- they have time to supervise you
- they have any funds to help pay for your research (even with a stipend scholarship , your research activities may require extra money)
- their research interests align with yours (you’ll ideally discover a mutual ground where you both benefit from the project).
“The best way to approach would be to send an email briefly outlining who you are, your background, and what your research interests are,” says Chelsea.
“Once you’ve spoken to a potential supervisor, then you can start drafting a proposal and you can even ask for their input.”
Chelsea's approach here works well with some academics, but keep in mind that other supervisors will want to see a research proposal straight away. If you're not sure of your proposed supervisor's preferences, you may like to cover both bases with an introductory email that has a draft of your research proposal attached.
Sarah agrees that your prospective supervisor is your most valuable resource for understanding how to write a research proposal for a PhD application.
“My biggest tip for writing a research proposal is to ask your proposed supervisor for help,” says Sarah.
“Or if this isn’t possible, ask another academic who has had experience writing research proposals.”
“They’ll be able to tell you what to include or what you need to improve on.”
Find the 'why' and focus on it

One of the key aspects of your research proposal is emphasising why your project is important and should be funded.
Your PhD proposal should include your major question, your planned methods, the sources you’ll cite, and plenty of other nitty gritty details. But perhaps the most important element of your proposal is its purpose – the reason you want to do this research and why the results will be meaningful.
In Sarah’s opinion, highlighting the 'why' of your project is vital for your research proposal.
“From my perspective, one of the key aspects of your research proposal is emphasising why your project is important and should be funded,” she says.
“Not only does this impact whether your application is likely to be successful, but it could also impact your likelihood of getting a scholarship .”
Imagine you only had 60 seconds to explain your planned research to someone. Would you prefer they remember how your project could change the world, or the statistical models you’ll be using to do it? (Of course, you’ve got 2,000 words rather than 60 seconds, so do make sure to include those little details as well – just put the why stuff first.)
Proofread your proposal, then proof it again
As a PhD candidate, your attention to detail is going to be integral to your success. Start practising it now by making sure your research proposal is perfect.
Chelsea and Sarah both acknowledge that clarity and writing quality should never be overlooked in a PhD proposal. This starts with double-checking that the questions of your thesis are obvious and unambiguous, followed by revising the rest of your proposal.
“Make sure your research questions are really clear,” says Sarah.
“Ensure all the writing is clear and grammatically correct,” adds Chelsea.
“A supervisor is not going to be overly keen on a prospective student if their writing is poor.”
It might sound harsh, but it’s fair. So, proofread your proposal multiple times – including after you get it back from your supervisor with any feedback and notes. When you think you’ve got the final, FINAL draft saved, sleep on it and read it one more time the next morning.
Still feeling a little overwhelmed by your research proposal? Stay motivated with these reasons why a PhD is worth the effort .
Want to learn more from Chelsea and Sarah? Easy:
- Read about Chelsea’s award-winning PhD thesis on keeping crops healthy.
- Read Sarah’s series on becoming a law academic .
Share this Facebook X LinkedIn Email
Related stories

How to get a PhD
4-minute read

How to find a PhD supervisor
5-minute read

How long does a PhD take?
3-minute read

Tips for PhD students from Samantha and Glenn
7-minute read
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

- Current Students Hub

Doctoral handbook
You are here
- Dissertation Proposal
On this page:
Proposal Overview and Format
Proposal committee, proposal hearing or meeting.
- Printing Credit for Use in School of Education Labs
Students are urged to begin thinking about a dissertation topic early in their degree program. Concentrated work on a dissertation proposal normally begins after successful completion of the Second-Year Review, which often includes a “mini” proposal, an extended literature review, or a theoretical essay, plus advancement to doctoral candidacy. In defining a dissertation topic, the student collaborates with their faculty advisor or dissertation advisor (if one is selected) in the choice of a topic for the dissertation.
The dissertation proposal is a comprehensive statement on the extent and nature of the student’s dissertation research interests. Students submit a draft of the proposal to their dissertation advisor between the end of the seventh and middle of the ninth quarters. The student must provide a written copy of the proposal to the faculty committee no later than two weeks prior to the date of the proposal hearing. Committee members could require an earlier deadline (e.g., four weeks before the hearing).
The major components of the proposal are as follows, with some variations across Areas and disciplines:
- A detailed statement of the problem that is to be studied and the context within which it is to be seen. This should include a justification of the importance of the problem on both theoretical and educational grounds.
- A thorough review of the literature pertinent to the research problem. This review should provide proof that the relevant literature in the field has been thoroughly researched. Good research is cumulative; it builds on the thoughts, findings, and mistakes of others.
- its general explanatory interest
- the overall theoretical framework within which this interest is to be pursued
- the model or hypotheses to be tested or the research questions to be answered
- a discussion of the conceptual and operational properties of the variables
- an overview of strategies for collecting appropriate evidence (sampling, instrumentation, data collection, data reduction, data analysis)
- a discussion of how the evidence is to be interpreted (This aspect of the proposal will be somewhat different in fields such as history and philosophy of education.)
- If applicable, students should complete a request for approval of research with human subjects, using the Human Subjects Review Form ( http://humansubjects.stanford.edu/ ). Except for pilot work, the University requires the approval of the Administrative Panel on Human Subjects in Behavioral Science Research before any data can be collected from human subjects.
Registration (i.e., enrollment) is required for any quarter during which a degree requirement is completed, including the dissertation proposal. Refer to the Registration or Enrollment for Milestone Completion section for more details.
As students progress through the program, their interests may change. There is no commitment on the part of the student’s advisor to automatically serve as the dissertation chair. Based on the student’s interests and the dissertation topic, many students approach other GSE professors to serve as the dissertation advisor, if appropriate.
A dissertation proposal committee is comprised of three academic council faculty members, one of whom will serve as the major dissertation advisor. Whether or not the student’s general program advisor serves on the dissertation proposal committee and later the reading committee will depend on the relevance of that faculty member’s expertise to the topic of the dissertation, and their availability. There is no requirement that a program advisor serve, although very often they do. Members of the dissertation proposal committee may be drawn from other area committees within the GSE, from other departments in the University, or from emeriti faculty. At least one person serving on the proposal committee must be from the student’s area committee (CTE, DAPS, SHIPS). All three members must be on the Academic Council; if the student desires the expertise of a non-Academic Council member, it may be possible to petition. After the hearing, a memorandum listing the changes to be made will be written and submitted with the signed proposal cover sheet and a copy of the proposal itself to the Doctoral Programs Officer.
Review and approval of the dissertation proposal occurs normally during the third year. The proposal hearing seeks to review the quality and feasibility of the proposal. The Second-Year Review and the Proposal Hearing are separate milestones and may not occur as part of the same hearing or meeting.
The student and the dissertation advisor are responsible for scheduling a formal meeting or hearing to review the proposal; the student and proposal committee convene for this evaluative period. Normally, all must be present at the meeting either in person or via conference phone call.
At the end of this meeting, the dissertation proposal committee members should sign the Cover Sheet for Dissertation Proposal and indicate their approval or rejection of the proposal. This signed form should be submitted to the Doctoral Programs Officer. If the student is required to make revisions, an addendum is required with the written approval of each member of the committee stating that the proposal has been revised to their satisfaction.
After submitting the Proposal Hearing material to the Doctoral Programs Officer, the student should make arrangements with three faculty members to serve on their Dissertation Reading Committee. The Doctoral Dissertation Reading Committee form should be completed and given to the Doctoral Programs Officer to enter in the University student records system. Note: The proposal hearing committee and the reading committee do not have to be the same three faculty members. Normally, the proposal hearing precedes the designation of a Dissertation Reading Committee, and faculty on either committee may differ (except for the primary dissertation advisor). However, some students may advance to Terminal Graduate Registration (TGR) status before completing their dissertation proposal hearing if they have established a dissertation reading committee. In these cases, it is acceptable for the student to form a reading committee prior to the dissertation proposal hearing. The reading committee then serves as the proposal committee.
The proposal and reading committee forms and related instructions are on the GSE website, under current students>forms.
Printing Credit for Use in GSE Labs
Upon completion of their doctoral dissertation proposal, GSE students are eligible for a $300 printing credit redeemable in any of the GSE computer labs where students are normally charged for print jobs. Only one $300 credit per student will be issued, but it is usable throughout the remainder of her or his doctoral program until the balance is exhausted. The print credit can be used only at the printers in Cubberley basement and CERAS, and cannot be used toward copying.
After submitting the signed dissertation proposal cover sheet to the Doctoral Programs Officer indicating approval (see above), students can submit a HELP SU ticket online at helpsu.stanford.edu to request the credit. When submitting the help ticket, the following should be selected from the drop-down menus for HELP SU:
Request Category : Computer, Handhelds (PDAs), Printers, Servers Request Type : Printer Operating System : (whatever system is used by the student, e.g., Windows XP.)
The help ticket will be routed to the GSE's IT Group for processing; they will in turn notify the student via email when the credit is available.
- Printer-friendly version
Handbook Contents
- Timetable for the Doctoral Degree
- Degree Requirements
- Registration or Enrollment for Milestone Completion
- The Graduate Study Program
- Student Virtual and Teleconference Participation in Hearings
- First Year (3rd Quarter) Review
- Second Year (6th Quarter) Review
- Committee Composition for First- and Second-Year Reviews
- Advancement to Candidacy
- Academic Program Revision
- Dissertation Content
- Dissertation Reading Committee
- University Oral Examination
- Submitting the Dissertation
- Registration and Student Statuses
- Graduate Financial Support
- GSE Courses
- Curriculum Studies and Teacher Education (CTE)
- Developmental and Psychological Sciences (DAPS)
- Learning Sciences and Technology Design (LSTD)
- Race, Inequality, and Language in Education (RILE)
- Social Sciences, Humanities, and Interdisciplinary Policy Studies in Education (SHIPS)
- Contact Information
- Stanford University Honor Code
- Stanford University Fundamental Standard
- Doctoral Programs Degree Progress Checklist
- GSE Open Access Policies
PhD students, please contact

MA POLS and MA/PP students, please contact

EDS, ICE/IEPA, Individually Designed, LDT, MA/JD, MA/MBA students, please contact

Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
- Department of Sociological Studies
Writing a research proposal
Guidelines on preparing a thesis proposal to support your application.

These guidelines are intended to assist you in developing and writing a thesis proposal. Applications for admission to a research degree cannot be dealt with unless they contain a proposal.
Your proposal will help us to make sure that:
- The topic is viable
- That the department can provide appropriate supervision and other necessary support
- You have thought through your interest in and commitment to a piece of research
- You are a suitable candidate for admission
The process of producing a proposal is usually also essential if you need to apply for funding to pay your fees or support yourself whilst doing your research. Funding bodies will often need to be reassured that you are committed to a viable project at a suitable university.
The research proposal – an outline
Your proposal should be typed double-spaced, if possible, and be between 1,000 and 2,000 words. Your PhD proposal can be added under the 'Supporting Documents' section of the Postgraduate Applications Online System .
Your proposal should contain at least the following elements:
- A provisional title
- A key question, hypothesis or the broad topic for investigation
- An outline of the key aims of the research
- A brief outline of key literature in the area [what we already know]
- A description of the topic and an explanation of why further research in the area is important [the gap in the literature - what we need to know]
- Details of how the research will be carried out, including any special facilities / resources etc. which would be required and any necessary skills which you either have already or would need to acquire [the tools that will enable us to fill the gap you have identified]
- A plan and timetable of the work you will carry out
For more detailed information on each element of your research proposal, see our extended guidance document .
Three additional points:
- Try to be concise. Do not write too much – be as specific as you can but not wordy. It is a difficult balance to strike.
- Bear in mind that the proposal is a starting point. If you are registered to read for a PhD you will be able to work the proposal through with your supervisor in more detail in the early months.
- Take a look at the Department’s staff profiles, research centres, and research clusters. Can you identify possible supervisors and intellectual support networks within the Department?
Examples of Successful PhD Proposals
- PhD sample proposal 1
- PhD sample proposal 2
- PhD sample proposal 3
- PhD sample proposal 4
- PhD sample proposal 5
- PhD sample proposal 6
- PhD sample proposal 7
- PhD sample proposal 8
Related information
Applying for a PhD
Our Research Themes
Our Research Areas
Search for PhD opportunities at Sheffield and be part of our world-leading research.

How to Write a PhD Research Proposal

Starting on PhD research is a big step in a researcher’s academic journey, and submitting a research proposal is a significant part of it. Indeed, many PhD scholars seek guidance on how to write a PhD research proposal , which is the foundational document that outlines the scope, objectives, and methodology of their prospective doctoral study. This article takes a look at the essential elements of a PhD research proposal and discuss practical steps to help develop an effective and strong document.
What is a PhD Research Proposal ?
Think of a PhD research proposal as a blueprint for your research. It lays out the main questions you want to seek answers to in your study, and presents an overview of the field you are planning to dive into. The PhD research proposal is not just about summarizing what is already available in the public domain. It is a critical document that demonstrates the feasibility, significance, and originality of the proposed research, and therefore, plays a crucial role in influencing admission decisions and securing funding opportunities. It also explains how your research is different and new and underscores the unique angles, perspectives and originality of your area of study.[ 1]
Why is a PhD Research Proposal Needed?
Even though your research proposal focuses on what you plan to do in the future, supervisors and funders also want to see what you have already achieved academically. Their interest lies in how well you understand the existing research, including recent studies and discussions in your academic field.
Therefore, it is essential to showcase your awareness about gaps in current knowledge and how your research will develop new knowledge and perspectives. Presenting a clear and detailed picture of this background is critical.[ 2]
How to Structure Your PhD Research Proposal ?
Research proposals can vary based on the institution you wish to send the proposal to or your subject of study, but there is a broad structure that needs to be followed.[ 3][4][5] A good PhD research proposal structure should highlight what makes your idea unique, feasible, and significant.
Follow these proven tips to structure a PhD research proposal and make it stand out:
- Provisional Title: The title should not only describe the subject matter but also hint at your approach or main question.
- Key Question: The key question is crucial for defining the scope and purpose of the research, making sure everything stays clear and organized.
- Topic Description: This section serves to introduce readers to the topic being studied, outlines its key focus areas, and helps establish a clear context for the study.
- Existing Knowledge: Here, researchers are required to provide a brief outline of existing knowledge drawn from seminal works, recent research findings, and ongoing debates and highlight gaps in the literature, demonstrating their awareness of existing scholarship.
- Detailed Bibliography: A detailed bibliography not only reflects the thoroughness of the literature review but also provides credibility to the proposed study. It allows reviewers to assess the quality and relevance of sources and enables them to gauge the scholarly merit of the PhD proposal.
- Research Methodology: Details of a comprehensive plan outlining the methodology, procedures, and techniques that will be employed to address the research objectives are included here. Methodology includes information on any special facilities, resources, or equipment required for data collection, analysis, or experimentation.
- Research Plan: This section provides a structured outline of the tasks and activities to be undertaken, along with their respective deadlines or milestones. It includes key phases such as literature review, data collection, analysis, and writing up the findings.
How Long Should a PhD Research Proposal be?
A research proposal typically spans approximately 2,500 words, although there is flexibility in the length as there is no strict upper or lower limit. However, the length may vary depending on the requirements of the institution or funding agency.
Tips for Writing Your PhD Research Proposal
Now that you understand the structure of a PhD research proposal , here are some tips to help you craft a compelling document: [7]
- Start early: Begin drafting your research proposal well in advance to allow yourself ample time for revisions and refinement.
- Be specific: Provide clear and detailed explanations of your objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
- Seek feedback: Share your proposal with peers or advisors to receive constructive feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Write clearly and concisely: Use clear and concise language to convey your ideas effectively, avoiding unnecessary jargon or technical terms.
- Be ethical: Address any ethical considerations related to your research, such as participant consent or data privacy.
- Revise and proofread: Take time to revise, proofread and proofread again. Best to weed out any inconsistencies and errors for a favourable impression and to clearly communicate your ideas.
- Be passionate: Clearly convey your enthusiasm for the research topic and potential impact of your proposed study. Let your passion for your research topic shine through your proposal.
References:
- How to write a PhD research proposal – University of Liverpool
- How to write a successful research proposal – Prospects
- How to write a good PhD proposal – The University of Queensland
- Writing a research proposal – Sociological Studies – The University of Sheffield
- Writing a Good PhD Research Proposal – Researchgate
- Guidelines to Writing a Research Proposal – University of Oxford
- Top tips for writing your research proposal – University of Birmingham
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How to Write the First Draft of a Research Paper with Paperpal?
- Research Funding Basics: What Should a Grant Proposal Include?
- How to Write Your Research Paper in APA Format
How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
Best wordtune alternative: detailed review and comparison, you may also like, what are the types of literature reviews , abstract vs introduction: what is the difference , mla format: guidelines, template and examples , machine translation vs human translation: which is reliable..., how to cite in apa format (7th edition):..., dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write your research paper in apa....
- Postgraduate
Research degrees
- Examples of Research proposals
- Find a course
- Accessibility
Examples of research proposals
How to write your research proposal, with examples of good proposals.
Research proposals
Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use.
We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
In your proposal, please tell us if you have an interest in the work of a specific academic at York St John. You can get in touch with this academic to discuss your proposal. You can also speak to one of our Research Leads. There is a list of our Research Leads on the Apply page.
When you write your proposal you need to:
- Highlight how it is original or significant
- Explain how it will develop or challenge current knowledge of your subject
- Identify the importance of your research
- Show why you are the right person to do this research
- Research Proposal Example 1 (DOC, 49kB)
- Research Proposal Example 2 (DOC, 0.9MB)
- Research Proposal Example 3 (DOC, 55.5kB)
- Research Proposal Example 4 (DOC, 49.5kB)
Subject specific guidance
- Writing a Humanities PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- Writing a Creative Writing PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- About the University
- Our culture and values
- Academic schools
- Academic dates
- Press office
Our wider work
- Business support
- Work in the community
- Donate or support
Connect with us
York St John University
Lord Mayor’s Walk
01904 624 624
York St John London Campus
6th Floor Export Building
1 Clove Crescent
01904 876 944
- Policies and documents
- Module documents
- Programme specifications
- Quality gateway
- Admissions documents
- Access and Participation Plan
- Freedom of information
- Accessibility statement
- Modern slavery and human trafficking statement
© York St John University 2024
Colour Picker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Dui id ornare arcu odio.
Felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis ipsum. Et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Faucibus pulvinar elementum integer enim neque volutpat ac. Hac habitasse platea dictumst vestibulum rhoncus.
Nec ullamcorper sit amet risus nullam eget felis eget. Eget felis eget nunc lobortis mattis aliquam faucibus purus.
University of Bristol Law School
How to write a phd proposal.
We are delighted to consider applications for PhD research. We have a fantastic, diverse and energetic student body who are making the most of fabulous resources for postgraduate students. We welcome you to join us.
In order to help you with your application, the information below aims to give some guidance on how a typical research proposal might look.
Please be aware that if you are applying for ESRC funding then the proposal must be no longer than 1,300 words , and if you are applying for University of Bristol Postgraduate Research Scholarship then the proposal must be no longer than 1,000 words (incl. footnotes). There are no word limits for the research proposal for the PhD in Law application , all word limits apply to shortened proposals which will need to be input on separate funding application forms.
Your aim here is to showcase your ability to carry out postgraduate research. PhD research often travels and what you apply to study for may differ from your ultimate PhD. It is perfectly acceptable for research to move over time in response to findings or changes in preference/supervision.
Please note: we do not generally have the expertise to supervise PhD proposals that are exclusively in a jurisdiction outside UK, EU or international law. We have many expert supervisors in comparative, international and regional law but if your proposal is only to study the law in your home country, we may not be able to offer you supervision even if you meet the admission requirements.
Title. A short, indicative title is best.
Abstract. This is a succinct summary of your research proposal that will present a condensed outline, enabling the reader to get a very quick overview of your proposed project, lines of inquiry and possible outcomes. An abstract is often written last, after you have written the proposal and are able to summarise it effectively.
Rationale for the research project. This might include a description of the question/debate/phenomenon of interest, and the context(s) and situation in which you think the research will take place; an explanation of why the topic is of interest to you; and an outline of the reasons why the topic should be of interest to research and/ or practice (the 'so what?' question).
Issues and initial research question. What legal or governance question(s) do you intend to investigate? (This may be quite imprecise at the application stage); what might be some of the key literatures that might inform the issues (again, indicative at the application stage); and, as precisely as you can, what is the question you are trying to answer? A research proposal can and should make a positive and persuasive first impression and demonstrate your potential to become a good researcher. In particular, you need to demonstrate that you can think critically and analytically as well as communicate your ideas clearly.
Intended methodology. How do you think you might go about answering the question? At Bristol we supervise an incredibly wide range of PhDs, including doctrinal, theoretical, empirical, historical, comparative or policy-focused work. Even if your methods are, for example, doctrinal, please do make this clear and give some indication why you think this is the best methodology for your proposed study. If you have a key theorist in mind, do please outline this in your application, together with some understanding of any critiques that have been raised. If you are planning to do empirical work, do please give some indication of what your methods might be (quantitative (surveys, statistics etc); qualitative (interviews, ethnography etc)
Expected outcomes and impact. How do you think the research might add to existing knowledge; what might it enable organisations or interested parties to do differently? Increasingly in academia (and this is particularly so for ESRC-funded studentships) PhD students are being asked to consider how their research might contribute to both academic impact and/or economic and societal impact . This is well explained on the ESRC website if you would like to find out more.
Timetable. What is your initial estimation of the timetable of the dissertation? When will each of the key stages start and finish (refining proposal; literature review; developing research methods; fieldwork; analysis; writing the draft; final submission). There are likely to overlaps between the stages.
Why Bristol? Why –specifically - do you want to study for your PhD at Bristol? How would you fit into our research themes and research culture (please see the ’10 reasons to study for a PhD at Bristol’ section on the website for more information). You do not need to identify supervisors at the application stage.
Bibliography. Do make sure that you cite what you see as the key readings in the field. This does not have to be comprehensive but you are illustrating the range of sources you might use in your research.
Scholarships
A number of scholarships are available to study for a PhD at Bristol. You can see more information regarding scholarships on our fees and funding page. If you have any questions about which scholarship to apply for and how your research might fit in please contact the PGR Director, Yvette Russell [email protected] .
Tips on writing a successful application
How to Write a PhD Cover Letter (With an Example)
In this article, I’ll guide you through how to write a compelling PhD motivation letter, explain what it entails, and provide tips to help you stand out based on my experience.
- ⏳ 3-5 min read
- Applying to Study Abroad

Page Content
Pursuing a PhD is a significant step in your academic and professional career. It requires dedication, passion, and a strong commitment to research. One of the key documents that can set you apart from other candidates is a motivation letter for a PhD application.
What is a motivation letter for PhD?
A motivation letter for a PhD is preferably 1page document that you add to anapplication to a doctoral program or if you apply for a PhD position in a particular laboratory. Its main goal is to provide a narrative that connects your academic background, research interests, and career aspirations to the specific PhD program you are applying for. Unlike a CV, which lists your qualifications and experience, a motivation letter allows you to express why you are passionate about your field of study and how you align with the program’s goals.
In this letter, you need to demonstrate your knowledge of the subject, readiness for independent research, and how you fit within the department or laboratory. It's your chance to convince the admissions committee or a Principal Investigator (PI) that you are the ideal candidate for their program.
Why write a motivation letter for a PhD?
Writing a motivation letter is crucial for several reasons:
- It demonstrates your passion and commitment to the field. A well-writtenmotivation letter shows that you are deeply interested in the subject and have a clear vision for your research.
- It highlights your research interests and how they align with the program. Admissions committees or PIs look for candidates whose research goals and experience align with the expertise of their laboratory and the department’s focus areas.
Since many PhD positionsreceive hundreds of applications, a strong motivation letter can help you stand out by showing your unique perspective and enthusiasm for your chosen field.
How to write a motivation letter for PhD
Introduction: who you are and your academic background.
Start your letter with a brief introduction about yourself. Mention your name, current academic standing, and the degree you have obtained. Include any relevant details about your academic background, such as specific the name of you supervisor during the MCs program, research experience, significant academic achievements, or professional accomplishments that are directly related to your PhD field.
If you’re aiming to work with a particular PI, your chances of having your email read will be higher if you mention someone you’ve worked with before in the first line. In my experience, the best results came when I started a motivational letter by mentioning a mutual acquaintance.
Some PhD programs, particularly in Life Sciences, offer a salary. However, competition for scholarships that cover at least part of your salary is tough. If you’re fortunate enough to secure one, it’sa good idea to mention it in the first paragraph of your application to catch the attention of the PI.
Example: "I did my Master's thesis in the laboratory of Dr. Anderson at XYZ University, where I studied how mutations in gene Kled to development of orphan diseases in children. Working there, I obtained excellent skills in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology methods such as molecular cloning, PCR and western blotting. Throughout mystudies, I have been deeply engaged in research that explores the genetic basis of rare diseases and I would like to continue my research in your laboratory. I have obtained a scholarship from ABC for 4 years and would be happy to discuss my candidacy to do this project in your laboratory."
Research interests and future goals
This section should explain your research interests in detail. What topics are you passionate about, and why? How do these interests align with the specific PhD program you're applying to? Discuss your long-term career goals and how the PhD will help you achieve them.To increase your chances of being accepted, do the homework and read thoroughly about research a specific laboratory does, and how you can contribute.
Example: "My primary research interest lies in understanding the genetic factors that contribute to neurodegenerative diseases. I am particularly drawn to your program because of the innovative research being conducted by Dr. Smith’s lab on gene therapy approaches, which aligns perfectly with my goal of contributing to groundbreaking treatments for neurological disorders."
Previous research experience and skills
Highlight any relevant research experience, including any publications, conferences, or significant projects. This is where you demonstrate your preparedness for a PhD. Discuss specific skills you have acquired that will help you succeed in the program, such as data analysis, lab techniques, or academic writing.
Example: "During my Master's program, I conducted research on the role of epigenetics in cancer development, which was published in the Journal of Molecular Biology. I have also presented my findings at the International Conference on Genetic Research, which further refined my research and presentation skills."
Demonstrating your fit for the program
Discuss personal qualities or experiences that make you a good fit for the program. Explain how you can contribute to the department or laboratory through your unique perspective, skills, or collaborative approach.
It’sbeneficial if you can prepare a project proposal, PIs appreciate independent students the most.At the end, after defending your PhD thesis, you become a researcher who must demonstratethe ability to conduct independent research.
Example: "I am a proactive researcher with a collaborative spirit, thriving in teamwork. I am confident that my background in molecular genetics and my commitment to scientific inquiry will make me a valuable addition to your research team. I would like to discuss the idea of how protein A interacts with protein B in cell type X and how it leads to mutation in gene K".
PhD cover letter example
Here is an example of a good PhD motivation letter to give you a better idea of how to structure yours:
[Your Name] [Email Address] [Phone Number]
Dear Members of the Admissions Committee / Dear Dr. Trinity,
I am writing to express my interest in the PhD program in [Field] at [University Name]. As a recent graduate with a Master's degree in [Your Field] from [Your University], I am eager to continue my academic journey and contribute to groundbreaking research in [Specific Research Area]. My academic background in [Specific Field] and research experience in [Specific Research Focus] have equipped me with a solid foundation to excel in this program.
[Continue with your personal motivations, research interests, alignment with the program, relevant experiences, and conclusion.]
Thank you for considering my application. I am looking forward to the opportunity to discuss how my background, skills, and passion align with your program’s goals.
Sincerely, [Your Name]
Tips for writing an effective motivation letter
- Be specific and tailor your letter: Customize your letter for each program or PI who you write to. Avoid generic statements.
- Maintain a professional tone: Keep your language formal and respectful. Avoid casual or overly familiar language.
- Proofread and edit thoroughly: Check for grammar and spelling errors. Don’t forget to cut in paragraphs for the convenience of a reader.
- Seek feedback from mentors or peers.
Common pitfalls to avoid
- Being too general or vague: Make sure your letter is specific to the program or laboratory and highlights your unique qualifications.
- Excessive flattery: Stay genuine and avoid over-the-top praise for the program or faculty.
- Ignoring instructions or guidelines: Follow the application guidelines carefully to show that you can follow directions.
Writing a compelling motivation letter for a PhD program is a critical step in your application process. Start early, revise often, and seek feedback to refine your letter. A well-crafted motivation letter can make a significant difference in setting you apart from other candidates.

Natalia Akkuratova Author
Natalia holds a PhD in Medical Science from the Karolinska Institute in Sweden and has 13 years of academic experience, including teaching and student mentorship. After defending her PhD, she worked as a digital marketing specialist at Keystone Education Group.
Find a program in these categories
- Doctoral Degrees
Read related articles

How to Study Abroad Guide: What Can I Study Abroad?
July 2024 Master's Degree Bachelor's Degree Preparing to Study Abroad Associate's Degree PhD

Tips for Studying Abroad in the Netherlands
July 2024 Study Abroad in the Netherlands Study Abroad in Europe Applying to Study Abroad During Study Abroad Deciding Where to Study

What Americans Need to Know to Study Abroad
July 2024 Information for American Students Preparing to Study Abroad Applying to Study Abroad Study Abroad Financing

COMMENTS
Learn what a research proposal is, what it needs to include and how to structure it for your PhD application. Find out how to demonstrate the worth, feasibility and capability of your project and why you are the right person to do it.
Learn how to write a good research proposal for your PhD application with six steps and tips. This guide covers the key elements of a research proposal, such as title, objectives, literature, methods, timetable and references.
Research proposal length. The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor's or master's thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
Learn how to write a comprehensive research proposal for your PhD application with a template and examples. Find out what to include in each section, such as aims, literature review, methods, outcomes, budget and schedule.
Learn the key elements and structure of a PhD proposal, and see how to use templates and tips to create a strong application. Find out the benefits of a PhD proposal and how to get accepted into your desired program.
Learn how to write a research proposal with two successful examples, one for a Master's-level project and one for a PhD-level dissertation. Download a free proposal template and get tips and coaching from Grad Coach.
Learn the structure, purpose and tips for writing a PhD research proposal. A research proposal summarises your intended research by outlining your question, rationale, aims, methods, timetable and bibliography.
A PhD proposal is a focused document that introduces your PhD study idea and seeks to convince the reader that your idea is interesting, original and viable within the allocated study period and ...
Learn how to write a persuasive and well-planned research proposal for a dissertation or thesis with this straightforward guide and examples. Follow the 5 essential ingredients: topic, introduction, scope, literature review and design.
Learn how to present your research idea, question and outcomes with clarity and significance in a PhD or research master's application. Follow the guide to include the essential elements of a research proposal, such as aims, methodology, timeline and resources.
Here's their advice for how to write a good PhD proposal. Writing your research proposal is an integral part of commencing a PhD with many schools and institutes, so it can feel rather intimidating. After all, how you come up with your PhD proposal could be the difference between your supervisor getting on board or giving your project a miss.
Learn how to write and defend a dissertation proposal at Stanford Graduate School of Education. Find out the components, format, committee, hearing, and printing credit requirements for your dissertation research.
Learn how to choose a research topic, write a proposal and apply for a PhD in law at The University of Sheffield. Find out the research strengths, priorities and expectations of the School of Law.
Learn how to write a research proposal for a PhD or PhD Professional at the University of Lincoln. Find out the purpose, content and structure of a proposal, and get tips and guidance from academic staff.
Guidelines on preparing a thesis proposal for PhD applications in sociology. Includes elements of a proposal, examples of successful proposals and links to staff and research centres.
proposed PhD research extends or builds upon your Master's work. 1.9 Personal Statement ... Provide a realistic timeline for your research, outlining key milestones like proposal defence, data collection, analysis, and writing of thesis chapters. *Minimum of 6and maximum of 10 pages; prioritize the most important information, such as the ...
Starting on PhD research is a big step in a researcher's academic journey, and submitting a research proposal is a significant part of it. Indeed, many PhD scholars seek guidance on how to write a PhD research proposal, which is the foundational document that outlines the scope, objectives, and methodology of their prospective doctoral study.This article takes a look at the essential ...
Find out how to write your research proposal for a PhD application at York St John University. Download examples of good proposals in different subject areas and get subject specific guidance.
Please note: we do not generally have the expertise to supervise PhD proposals that are exclusively in a jurisdiction outside UK, EU or international law. We have many expert supervisors in comparative, international and regional law but if your proposal is only to study the law in your home country, we may not be able to offer you supervision ...
A sample of a research proposal for PhD students, including background, objective, scope, methodology, budget, deliverables and references. The proposal is based on a situational analysis of shared leadership in a self-managing team.
It'sbeneficial if you can prepare a project proposal, PIs appreciate independent students the most.At the end, after defending your PhD thesis, you become a researcher who must demonstratethe ability to conduct independent research. Example: "I am a proactive researcher with a collaborative spirit, thriving in teamwork. I am confident that my ...