Autobiography
Definition of autobiography, difference between autobiography and memoir, six types of autobiography, importance of autobiography, examples of autobiography in literature, example #1: the box: tales from the darkroom by gunter grass, example #2: the story of my life by helen keller, example #3: self portraits: fictions by frederic tuten, example #4: my prizes by thomas bernhard, example #5: the autobiography of benjamin franklin by benjamin franklin, synonyms of autobiography, related posts:, post navigation.
- Literary Terms
- Autobiography
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write Autobiography

I. What is Autobiography?
An autobiography is a self-written life story.
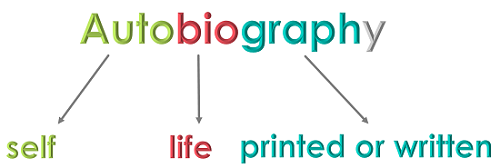
It is different from a biography , which is the life story of a person written by someone else. Some people may have their life story written by another person because they don’t believe they can write well, but they are still considered an author because they are providing the information. Reading autobiographies may be more interesting than biographies because you are reading the thoughts of the person instead of someone else’s interpretation.
II. Examples of Autobiography
One of the United States’ forefathers wrote prolifically (that means a lot!) about news, life, and common sense. His readings, quotes, and advice are still used today, and his face is on the $100 bill. Benjamin Franklin’s good advice is still used through his sayings, such as “We are all born ignorant, but one must work hard to remain stupid.” He’s also the one who penned the saying that’s seen all over many schools: “Tell me and I forget. Teach me and I remember. Involve me and I learn.” His autobiography is full of his adventures , philosophy about life, and his wisdom. His autobiography shows us how much he valued education through his anecdotes (stories) of his constant attempts to learn and improve himself. He also covers his many ideas on his inventions and his thoughts as he worked with others in helping the United States become free from England.
III. Types of Autobiography
There are many types of autobiographies. Authors must decide what purpose they have for writing about their lives, and then they can choose the format that would best tell their story. Most of these types all share common goals: helping themselves face an issue by writing it down, helping others overcome similar events, or simply telling their story.
a. Full autobiography (traditional):
This would be the complete life story, starting from birth through childhood, young adulthood, and up to the present time at which the book is being written. Authors might choose this if their whole lives were very different from others and could be considered interesting.
There are many types of memoirs – place, time, philosophic (their theory on life), occupational, etc. A memoir is a snapshot of a person’s life. It focuses on one specific part that stands out as a learning experience or worth sharing.
c. Psychological illness
People who have suffered mental illness of any kind find it therapeutic to write down their thoughts. Therapists are specialists who listen to people’s problems and help them feel better, but many people find writing down their story is also helpful.
d. Confession
Just as people share a psychological illness, people who have done something very wrong may find it helps to write down and share their story. Sharing the story may make one feel he or she is making amends (making things right), or perhaps hopes that others will learn and avoid the same mistake.
e. Spiritual
Spiritual and religious experiences are very personal . However, many people feel that it’s their duty and honor to share these stories. They may hope to pull others into their beliefs or simply improve others’ lives.
f. Overcoming adversity
Unfortunately, many people do not have happy, shining lives. Terrible events such as robberies, assaults, kidnappings, murders, horrific accidents, and life-threatening illnesses are common in some lives. Sharing the story can inspire others while also helping the person express deep emotions to heal.
IV. The Importance of Autobiography
Autobiographies are an important part of history. Being able to read the person’s own ideas and life stories is getting the first-person story versus the third-person (he-said/she-said) version. In journalism, reporters go to the source to get an accurate account of an event. The same is true when it comes to life stories. Reading the story from a second or third source will not be as reliable. The writer may be incorrectly explaining and describing the person’s life events.
Autobiographies are also important because they allow other people in similar circumstances realize that they are not alone. They can be inspiring for those who are facing problems in their lives. For the author, writing the autobiography allows them to heal as they express their feelings and opinions. Autobiographies are also an important part of history.
V. Examples of Autobiography in Literature
A popular autobiography that has lasted almost 100 years is that of Helen Keller. Her life story has been made into numerous movies and plays. Her teacher, Anne Sullivan, has also had her life story written and televised multiple times. Students today still read and learn about this young girl who went blind and deaf at 19 months of age, causing her to also lose her ability to learn to speak. Sullivan’s entrance into Helen’s life when the girl was seven was the turning point. She learned braille and soon became an activist for helping blind and deaf people across the nation. She died in 1968, but her autobiography is still helping others.
Even in the days before my teacher came, I used to feel along the square stiff boxwood hedges, and, guided by the sense of smell, would find the first violets and lilies. There, too, after a fit of temper, I went to find comfort and to hide my hot face in the cool leaves and grass. What joy it was to lose myself in that garden of flowers, to wander happily from spot to spot, until, coming suddenly upon a beautiful vine, I recognized it by its leaves and blossoms, and knew it was the vine which covered the tumble-down summer-house at the farther end of the garden! (Keller).
An autobiography that many middle and high school students read every year is “Night” by Elie Wiesel. His story is also a memoir, covering his teen years as he and his family went from the comfort of their own home to being forced into a Jewish ghetto with other families, before ending up in a Nazi prison camp. His book is not that long, but the details and description he uses brings to life the horrors of Hitler’s reign of terror in Germany during World War II. Students also read “The Diary of Anne Frank,” another type of autobiography that shows a young Jewish girl’s daily life while hiding from the Nazis to her eventual capture and death in a German camp. Both books are meant to remind us to not be indifferent to the world’s suffering and to not allow hate to take over.
“The people were saying, “The Red Army is advancing with giant strides…Hitler will not be able to harm us, even if he wants to…” Yes, we even doubted his resolve to exterminate us. Annihilate an entire people? Wipe out a population dispersed throughout so many nations? So many millions of people! By what means? In the middle of the twentieth century! And thus my elders concerned themselves with all manner of things—strategy, diplomacy, politics, and Zionism—but not with their own fate. Even Moishe the Beadle had fallen silent. He was weary of talking. He would drift through synagogue or through the streets, hunched over, eyes cast down, avoiding people’s gaze. In those days it was still possible to buy emigration certificates to Palestine. I had asked my father to sell everything, to liquidate everything, and to leave” (Wiesel 8).
VI. Examples of Autobiography in Pop Culture
One example of an autobiography that was a hit in the movie theaters is “American Sniper,” the story of Navy SEAL Chris Kyle. According to an article in the Dallas, Texas, magazine D, Kyle donated all the proceeds from the film to veterans and their families. He had a story to tell, and he used it to help others. His story is a memoir, focusing on a specific time period of his life when he was overseas in the military.
An autobiography by a young Olympian is “Grace, Gold and Glory: My Leap of Faith” by Gabrielle (Gabby) Douglas. She had a writer, Michelle Burford, help her in writing her autobiography. This is common for those who have a story to tell but may not have the words to express it well. Gabby was the darling of the 2012 Olympics, winning gold medals for the U.S. in gymnastics along with being the All-Around Gold Medal winner, the first African-American to do so. Many young athletes see her as an inspiration. Her story also became a television movie, “The Gabby Douglas Story.”
VII. Related Terms
The life story of one person written by another. The purpose may to be highlight an event or person in a way to help the public learn a lesson, feel inspired, or to realize that they are not alone in their circumstance. Biographies are also a way to share history. Historic and famous people may have their biographies written by many authors who research their lives years after they have died.

VIII. Conclusion
Autobiographies are a way for people to share stories that may educate, inform, persuade, or inspire others. Many people find writing their stories to be therapeutic, healing them beyond what any counseling might do or as a part of the counseling. Autobiographies are also a way to keep history alive by allowing people in the present learn about those who lived in the past. In the future, people can learn a lot about our present culture by reading autobiographies by people of today.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center

autobiography summary
Know about the emergence of autobiography with some notable examples.
autobiography , Biography of oneself narrated by oneself. Little autobiographical literature exists from antiquity and the Middle Ages; with a handful of exceptions, the form begins to appear only in the 15th century. Autobiographical works take many forms, from intimate writings made during life that are not necessarily intended for publication (including letters, diaries, journals, memoirs, and reminiscences) to the formal autobiography. Outstanding examples of the genre extend from St. Augustine ’s Confessions ( c. ad 400) to Vladimir Nabokov ’s Speak, Memory (1951).

All Subjects
study guides for every class
That actually explain what's on your next test, autobiography, from class:, american literature – 1860 to present.
An autobiography is a self-written account of one's life, reflecting personal experiences, thoughts, and feelings. This form of writing often serves to give readers insight into the author's identity and perspectives, making it a powerful tool for self-expression and historical documentation. In various contexts, autobiographies can shed light on broader societal issues and movements, allowing readers to connect individual narratives with collective experiences.
congrats on reading the definition of autobiography . now let's actually learn it.
5 Must Know Facts For Your Next Test
- Autobiographies often provide a unique perspective on historical events by offering personal viewpoints and experiences related to those events.
- Many influential civil rights figures have written autobiographies to share their struggles and triumphs, contributing significantly to the literature surrounding social justice.
- The genre has evolved over time, with modern autobiographies often incorporating elements of social critique and reflection on identity.
- Autobiographical writing can serve as a form of activism, allowing authors to raise awareness about injustices they have faced or witnessed.
- Some notable autobiographies have become pivotal in shaping public understanding of civil rights movements and the personal impact of systemic oppression.
Review Questions
- Autobiographies provide a personal lens through which readers can connect with the broader narratives of social movements. By detailing personal experiences within these movements, authors illustrate how systemic issues affect individuals on a human level. This storytelling can evoke empathy and understanding, allowing readers to grasp the complexities and emotional weight of societal struggles.
- Autobiographies serve as crucial primary sources for understanding civil rights movements by documenting firsthand accounts of events and personal struggles. They provide context and nuance that may be absent from traditional historical texts. Through their detailed reflections, authors capture the emotions, motivations, and challenges they faced, ensuring that future generations can learn from these powerful narratives and understand their significance in history.
- The genre of autobiography often reveals the intricate layers of identity that individuals navigate, particularly in the context of civil rights literature. Authors use their life stories to explore themes such as race, gender, class, and social justice. By articulating their personal journeys amidst systemic oppression, these writers challenge stereotypes and provide richer understandings of identity that intersect with larger cultural narratives. This reflective process not only contributes to personal growth but also fosters collective awareness about ongoing struggles for equality.
Related terms
A memoir is a specific type of autobiography that focuses on particular themes or events in the author's life rather than covering their entire life story.
narrative : A narrative is the structured account of a series of events or experiences, which can be fictional or nonfictional, often used in autobiographies to convey personal stories.
Identity refers to the qualities, beliefs, and characteristics that make up an individual, which autobiographies often explore through personal reflection and storytelling.
" Autobiography " also found in:
Subjects ( 20 ).
- 18th and 19th Century Literature
- AP European History
- African American Literature Before 1900
- African American Literature Since 1900
- American Architecture
- American Literature: Before 1800
- Archaeology of Ancient Egypt
- English and Language Arts Education
- History of Black Women in America
- Introduction to Comparative Literature
- Introduction to Modern Chinese Literature and Culture
- Literary Theory and Criticism
- Medieval Literature
- Middle English Literature
- Native American Literature
- Sacred Arts in China
- World Literature II
- Writing the Narrative Short
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
Ap® and sat® are trademarks registered by the college board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website..
Literature Glossary
Autobiography, don’t be an oxymoron. know your literary terms..
Over 200 literary terms, Shmooped to perfection.
Definition:
When you read an autobiography, you're reading the story of someone's life written in their own words: from the day they were born up until, well, whenever the autobiography is written. Unlike a memoir, which focuses on specific times or topics in a person's life, an autobiography is interested in the development of the writer over the course of his or her life (from birth to death). And unlike a biography , an autobiography comes straight from the author's mouth… or pen.
Benjamin Franklin's The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin is a classic example of the genre—heck, it's right there in the title.
Logging out…
Logging out....
You've been inactive for a while, logging you out in a few seconds...
W hy's T his F unny?

COMMENTS
Definition of Autobiography. Autobiography is one type of biography, which tells the life story of its author, meaning it is a written record of the author’s life. Rather than being written by somebody else, an autobiography comes through the person’s own pen, in his own words.
autobiography, the biography of oneself narrated by oneself. Autobiographical works can take many forms, from the intimate writings made during life that were not necessarily intended for publication (including letters, diaries , journals , memoirs , and reminiscences) to a formal book-length autobiography.
An autobiography is a self-written life story. It is different from a biography, which is the life story of a person written by someone else. Some people may have their life story written by another person because they don’t believe they can write well, but they are still considered an author because they are providing the information.
An autobiography, [a] sometimes informally called an autobio, is a self-written biography of one's own life. Definition. The word "autobiography" was first used deprecatingly by William Taylor in 1797 in the English periodical The Monthly Review, when he suggested the word as a hybrid, but condemned it as "pedantic".
An autobiography (awe-tow-bye-AWE-gruh-fee) is a self-written biography. The author writes about all or a portion of their own life to share their experience, frame it in a larger cultural or historical context, and/or inform and entertain the reader.
autobiography, Biography of oneself narrated by oneself. Little autobiographical literature exists from antiquity and the Middle Ages; with a handful of exceptions, the form begins to appear only in the 15th century.
An autobiography is a self-written account of the author's own life, offering personal insights and reflections on their experiences. This literary form not only documents events but also explores the author's thoughts, feelings, and motivations, often revealing how they perceive their identity within the larger cultural and historical context.
An autobiography is a self-written account of one's life, reflecting personal experiences, thoughts, and feelings. This form of writing often serves to give readers insight into the author's identity and perspectives, making it a powerful tool for self-expression and historical documentation.
An autobiography is the story of one person's life, written by that person. It is usually told in first-person point of view and covers the author's entire life.
Definition: When you read an autobiography, you're reading the story of someone's life written in their own words: from the day they were born up until, well, whenever the autobiography is written.